Artificial Reef [Philippines]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Alexandra Gavilano
Gango
technologies_3116 - Philippines
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
Sustainable Livelihood Officer (SLO):
exploitant des terres:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Danajon Communities WATCH ( DCW)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Philippine Partnership for the Development of Human Resoruces in Rural Areasy (PhilDHRRA) - Philippines1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
Artificial Reef is installed at the bottom of the sea and anchored in all corners, thus, any weather and climate condition can not directly affect the situation of the technology as an alternative marine habitat.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)

Social Enterprise (SE) [Philippines]
Social Enterprise (SE) aimed to provide social protection among its members and generate additional family income. Above all, this approach will encourage the conservation, preservation and protection of the resources available in the community.
- Compilateur : Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Artificial Reef is a fish aggregating device that is considered as a sustainable alternative in the islands of Bohol. This technology can withstand the effects of gale warning, typhoons and extreme heat.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
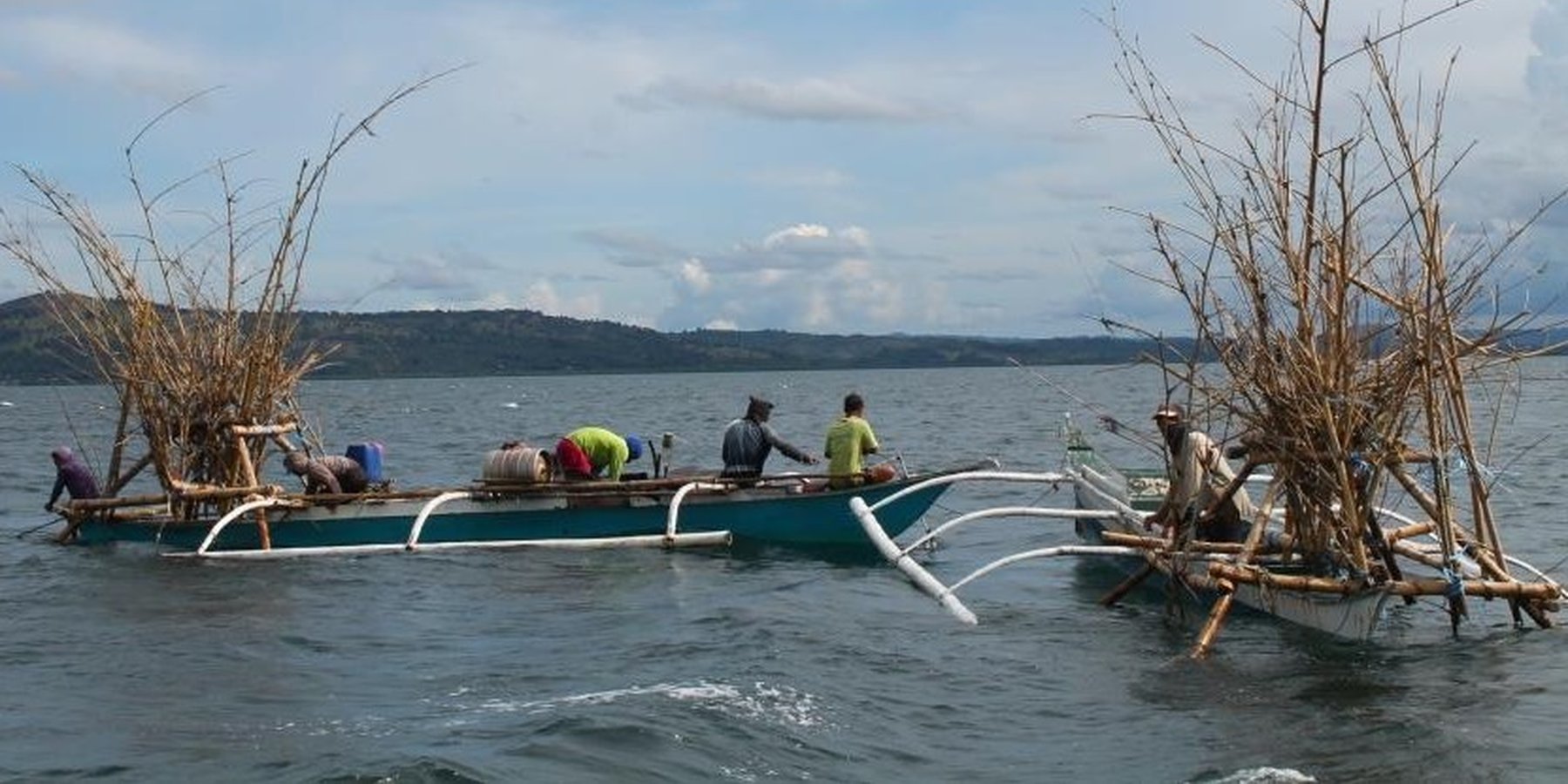
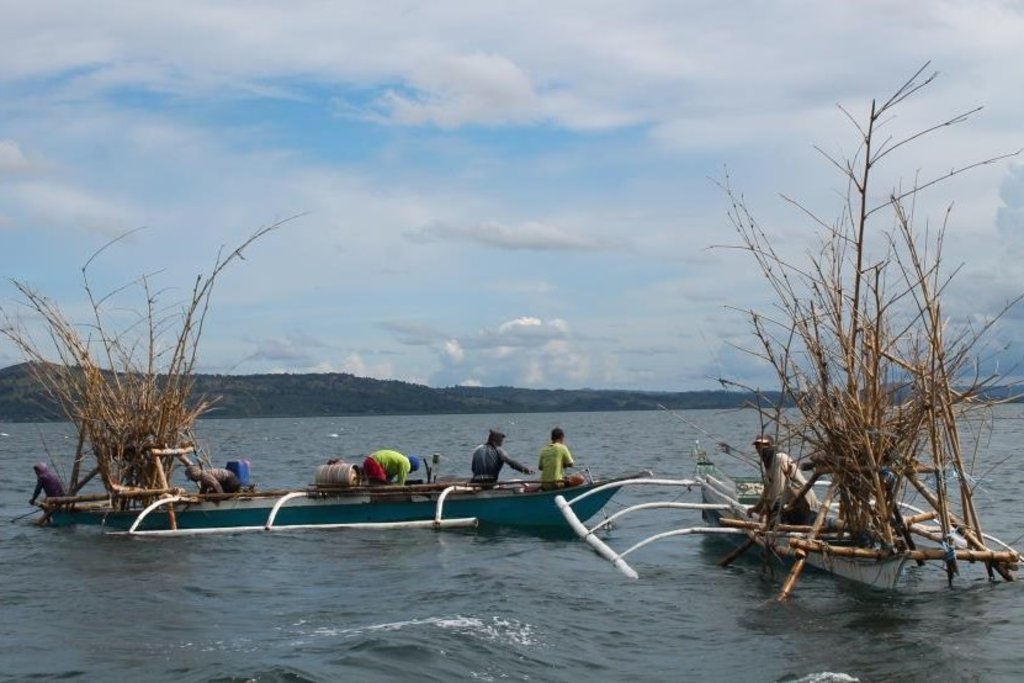
Description:
The fishers of Bohol have been using Artificial Reef over a long period of time. This is a fish aggregating device but at the same time, used for brown lip culture. Aside from the above mentioned functions of Artificial Reef, the Island of Bilangbilangan East in Bien Unido, Bohol installed this technology around the buffer zone of the marine sanctuary because the floater will serve as indicator of the marine protected area.
Artificial Reef Technology is a project of Bilangbilangan East Fishers Association (BEFA) from Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Bien Unido, Bohol; Calituban Fisherfolks Association (CFO) from Brgy. Calituban, Talibon, Bohol and Nasingin Fisherfolks and Mangrove Planters Association (NasFiMPA) from Brgy. Nasingin, Getafe. This technology is owned and managed by the People's Organization found in these three island barangays namely BEFA, CFO and NasFiMPA.
Artificial Reef if is primarily made of bamboo with a life span of 3 to 5 years. For stability, it is anchored in the four corners using a cemented container tied to every end of its corners. For markings, floaters are placed in the sea surface but Nasingin and Calituban fishers preferred not to use floaters for the security of their installed artificial reefs, rather, they used terrestrial points to identify the location.
This technology was installed within the municipal waters (15 kilometers from the shoreline) to help minimize fishing cost and avoid the hazards of sudden change in weather condition. The PO are now vigilant because they already installed Artificial Reefs before but were destroyed by the dynamite fishers. This encouraged the PO members to practice safe and legal forms of fishing in order to sustain their project. Above all, artificial reef will enhance fish spawning and provide alternative shelter to fishes during hot season.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
Remarques générales concernant les photos:
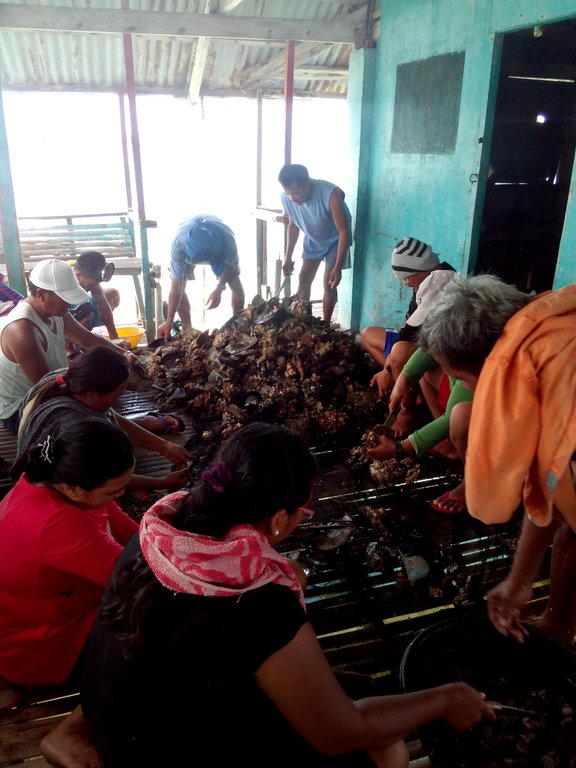
Brown lips will naturally grow in the artificial reef. After 3 months of installation, fishers can already harvest fish while the first harvest of brown lip can be done a year after the installation.
2.4 Vidéos de la Technologie
Commentaire, brève description:
Monitoring of the Artificial Reef in Bilangbilangan Island, Bien Unido, Bohol after 3 months of installation.
A Social Enterprise Project of Danajon Communities WATCH (DCW) Project. Implemented by PhilDHRRA, LPFI and A2D Project. In Partnership with Caritas Switzerland and JTIF.
Date:
01/06/2016
Lieu:
Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Bien Unido, Bohol
Nom du vidéaste:
Bilangbilangan East Fisherfolks Association (BEFA)
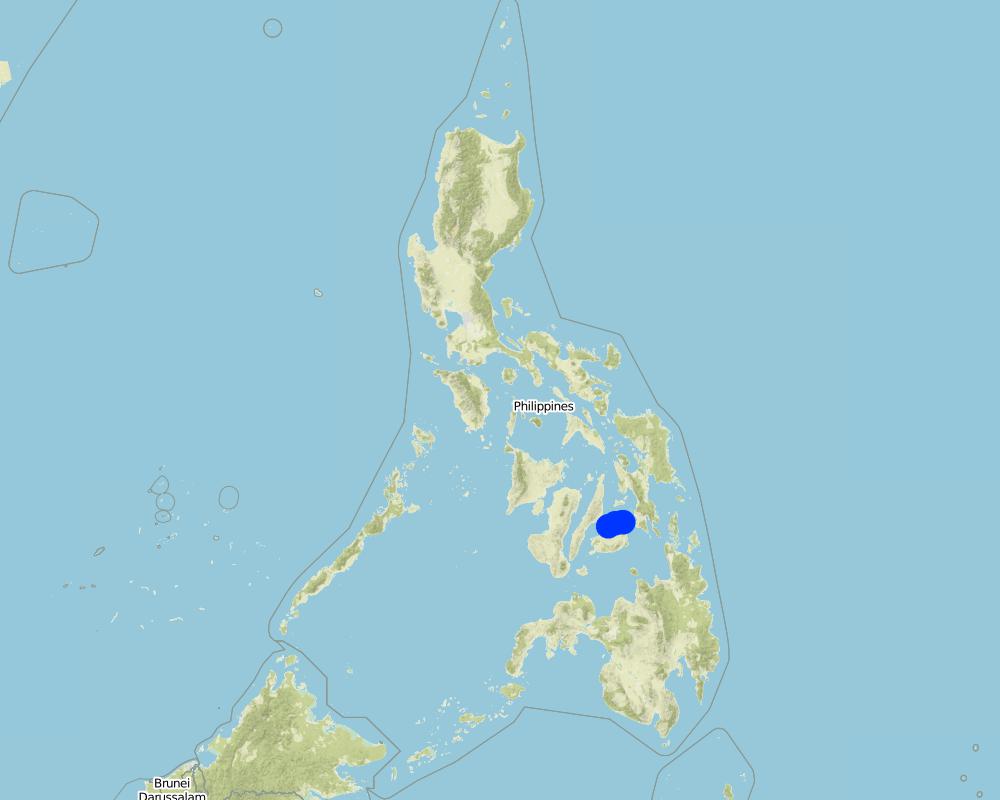
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Philippines
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Bohol
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Municipality of Bien Unido; Brgy. Calituban, Municipality of Talibon; Brgy. Nasingin, Municipality of Getafe
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- appliquée en des points spécifiques ou concentrée sur une petite surface
Commentaires:
The team decided to get the coordinates of the 2 ends and middle part of the Artificial Reef installed due to the weather and current of the tide. Also, these technologies were installed in a linear position.
Each Artificial Reef was installed 10 meters apart from each other.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2017
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The 3 areas have tried this kind of method even before DCW Project. However, it was not sustained mainly because of illegal fishing and illegal entry of fishers from the neighboring municipalities and barangays.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact social positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Voies d'eau, plans d'eau, zones humides
- sea
Principaux produits/ services:
Brown lip culture and fish aggregating device, fish
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)

Autre
Précisez:
Before the installation of Artificial Reefs, the fishers are obliged to go beyond the municipal waters which increased their production cost and risk to sudden change of weather. The Artificial Reef was installed within the municipal waters (15 kilometers from the shore line), fishers will lessen their production cost particularly their fuel consumption. This technology also increased fish spawning and marine conservation.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
autre (par ex., post-inondation):
- not applicable
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- amélioration des variétés végétales, des races animales
- gestion des eaux de surface (sources, rivières, lacs, mers)
- réduction des risques de catastrophe fondée sur les écosystèmes
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

structures physiques
- S9: Abris pour plantes et animaux
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- non applicable
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
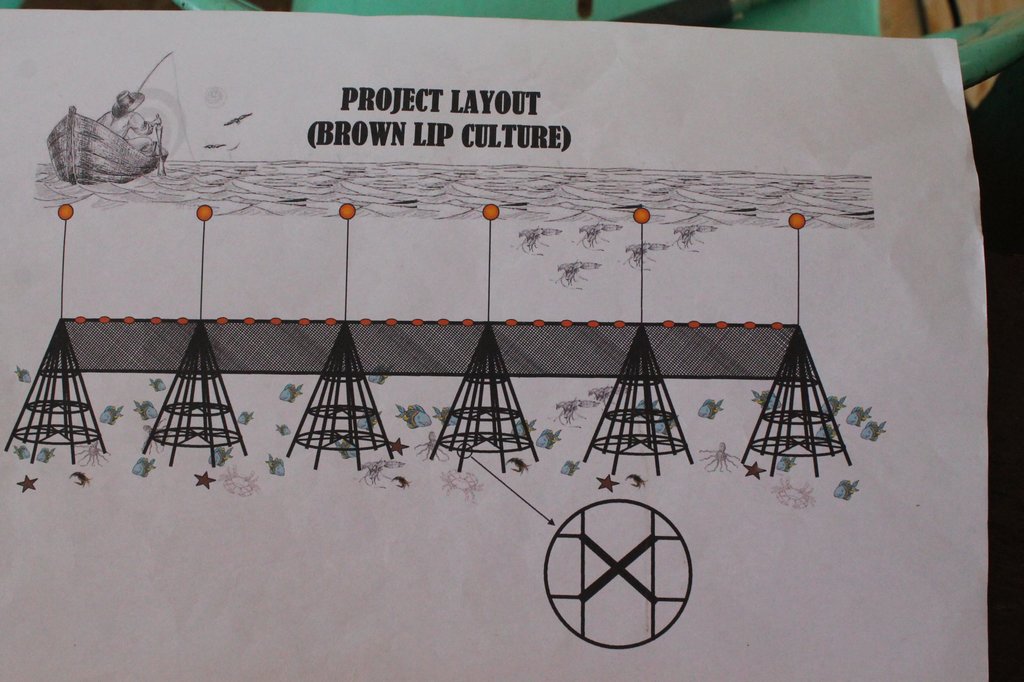
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Materials: bamboo pole, spiny bamboo, nylon #10 and coral stone as sinker
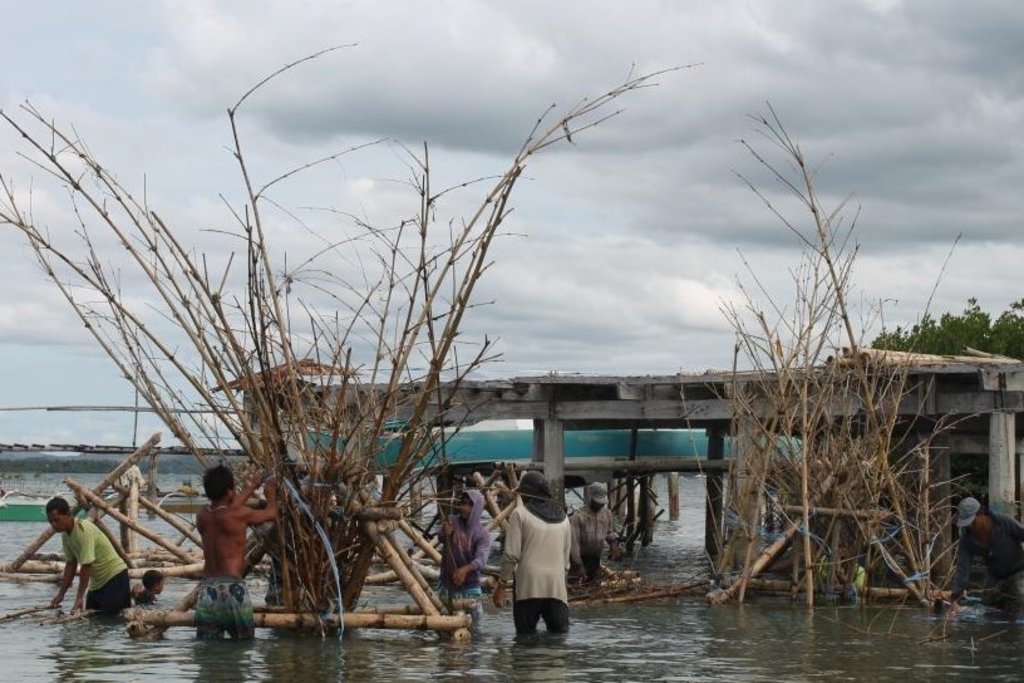
For this project with seed capital worth Php 30,000, 10 Artificial Reefs are targeted to be installed in a linear position.
Artificial Reef is pyramid in shape with the following dimensions:
Height: 12 - 15 feet
Base: 6.6 feet
Installation process:
Interval: 10 meters
Depth: 12 - 15 meters
Auteur:
Calituban Fisherfolks Organization
Date:
09/05/2015
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par entité de la Technologie
Précisez l'unité:
Php 3,200 per unit inclusive of installation; Php 32,000 for the 10 Artificial Reefs installed
Précisez les dimensions de l'unité de terrain (le cas échéant):
Length of spread: 90 meters
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Philippine Peso
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
51,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
Php 250.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | canvass of bamboo poles and spiny bamboo | before construction |
| 2. | purchase of construction materials | before construction |
| 3. | construction of artificial reefs | every 3-5 years |
| 4. | site selection | |
| 5. | installation of artificial reefs | |
| 6. | monitoring | 3 months after installation; monthly basis afterwards per artificial reef |
| 7. | harvest | 3 months after installation; monthly basis afterwards per artificial reef |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipements | motorboat rental | piece | 2,0 | 300,0 | 600,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Bamboo Pole | piece | 10,0 | 120,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Spiny Bamboo | piece | 4,0 | 50,0 | 200,0 | |
| Matériaux de construction | Nylon #10 | kilo | 10,0 | 120,0 | 1200,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3200,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 62,75 | |||||
Commentaires:
No labor cost because the organization agreed that they will do it voluntarily.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Monitoring | 3 months after installation, monthly basis after that |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | monitoring | persons-day | 2,0 | 250,0 | 500,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 500,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 9,8 | |||||
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Supply of bamboo poles and spiny bamboo since they have to find it from the interior part of the mainland.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
9999,00
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
as of 2016 data
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
https://weather-and-climate.com
Zone agro-climatique
- humide
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- non pertinent
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
The technology must be installed along the path.
5.3 Sols
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Not Applicable
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Not Applicable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Diversité des habitats:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- exploitation mixte (de subsistance/ commerciale)
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- pauvre
Individus ou groupes:
- groupe/ communauté
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- femmes
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
- personnes âgées
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- groupe
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- communautaire (organisé)
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- accès libre (non organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
Solid Waste Management:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production animale
diversité des produits
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
By installing artificial reefs the fishers are not obliged to go further.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
decrease in fuel consumption
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The fishers can catch fish even if there is gale warning.
risk exposure to sudden change of weather conditions
Impacts écologiques
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des cyclones, pluies torrentielles
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology will not be affected directly or indirectly by the effects of gale warning and typhoon.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
Not Applicable
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | très bien | |
| précipitations saisonnières | saison des pluies/ humide | décroît | très bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête tropicale | très bien |
| orage local | très bien |
| tempête de vent locale | très bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | très bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| élévation du niveau de la mer | très bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- > 50%
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
It's an organizational project with 80 - 120 members each organization.
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 11-50%
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Instead of using bamboo poles, one organization decided to cement the poles because it is very difficult to find bamboo in the mainland. Also, bamboo will only last for 2-3 years.
Another organization planned to use plastic straps instead of spiny bamboo so that it will be easier and convenient for them to harvest. Another reason is the availability of brown lip spawn that will stream either at the bottom of the sea, in the middle or along the sea water level. The PO strategize to use plastic straps because they will just hang it above the artificial reef to have better harvest on brown lip.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| According to the management team, the advantage is having alternative site for fishing even if there is gale warning. |
| It will minimize expenses because of lesser fuel consumption. |
| Having an Artificial Reef (AR) project encouraged the members, including their wives to protect the artificial reef site from illegal fishers especially dynamite fishing and trawling. As a result, the people became aware of the effects of illegal fishing and the destruction it will bring to their marine ecosystem. |
| The longer the Artificial Reef (AR) stayed undisturbed, the greater the income. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Artificial reef enhanced fish spawning, food chain and improved marine ecosystem. |
| Catalyst of behavioral change among the members of the People's Organization namely BEFA, CFO and NasFiMPA. |
| The organization work together for the preservation, protection and conservation of the project site. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Monitoring assignment of the members. | Be strict with the Sustainable Enterprise (SE) Management policy. |
| The harvest cost is very expensive because it needs diving gears and large fishing nets. | Collaborate with Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR) for harvest paraphernalia. |
| The organization has no police power to arrest the intruders and illegal fishers that will take advantage. |
Close coordination with the municipal fish wardens (Bantay Dagat). The organization will establish security measures to protect their Artificial Reefs (AR) installed. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The duty bearers should implement Philippine Fisheries Code of 1998 (Republic Act No. 8550). | Capacitate the People's Organization to lobby and and implement the law. |
| The local government unit lacks support mechanism for resource-based technologies promoting environment friendly and disaster resilient enterprise. | Partnership among the local government units, people's organization and non-government organizations. |
| Limited exposure to market, business ideas and linkaging. | Conduct Value Chain Analysis (VCA) training, financial coaching, Occupational Safety and Health Standards (OSHS) and on-site mentoring. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- visites de terrain, enquêtes sur le terrain
monthly monitoring visits to project sites
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
2 respondent per area
- interviews/ entretiens avec les spécialistes/ experts de GDT
Sustainable Livelihood Officer
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
05/04/2017
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Social Enterprise (SE) [Philippines]
Social Enterprise (SE) aimed to provide social protection among its members and generate additional family income. Above all, this approach will encourage the conservation, preservation and protection of the resources available in the community.
- Compilateur : Keeshia Lynn Marie Austria
Modules
Aucun module trouvé