Intensive agroforestry system [ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Mathias Gurtner
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Deborah Niggli
Silvoagricultura (spanish)
technologies_1023 - ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/07/2004
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Desarrollo Rural Integral Comunitario [ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី]
En un proceso participativo y comunitario y a través de la capacitación, la asistencia técnica y la suministración de insumos importantes se fomenta el establecimiento de un sistema agrosilicultural en la comunidad indÃgena.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Mathias Gurtner
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
A protective and productive high-input agroforestry system comprising multi-purpose ditches with bunds, live barriers of grass, contour ridging,
annual crops and fruit trees.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
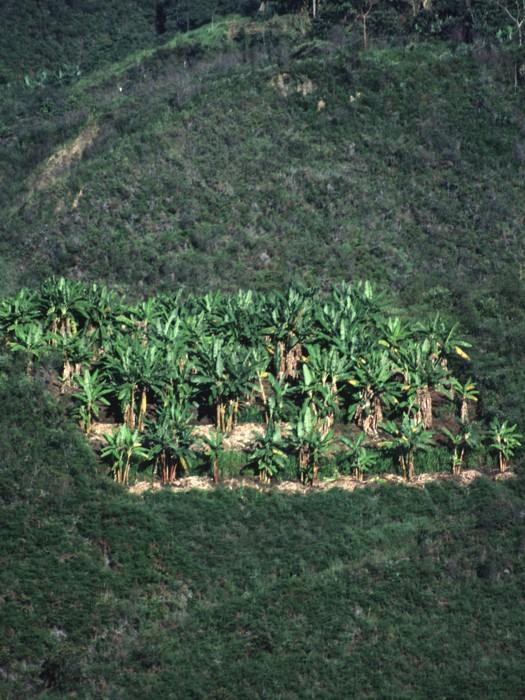
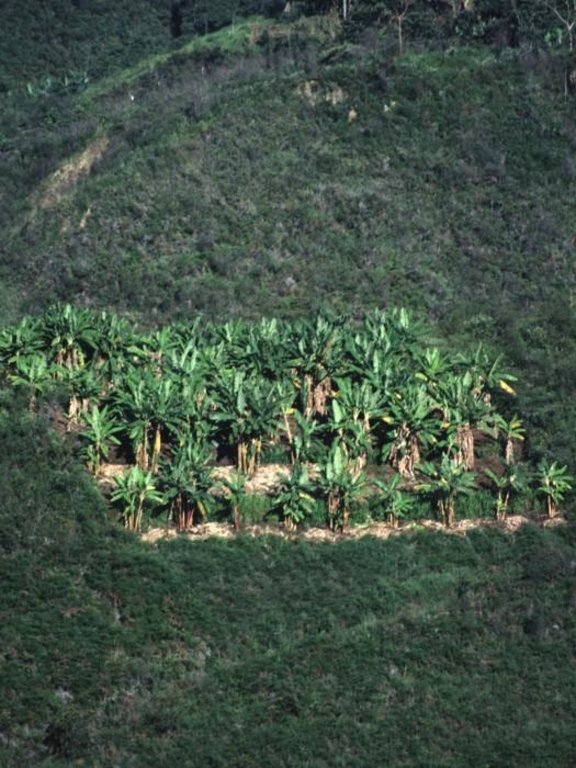
The intensive agroforestry system (silvoagricultura) combines traditional and newly developed practices adapted to the area’s conditions. The idea is to concentrate cropping on a limited area, a plot of 0.4 ha per household, in a highly integrated, intensive and diversified continuous land use system, thereby integrating soil and water conservation - specifically avoiding traditional slash and burn practices.
Each ‘agroforestry plot’ comprises four to five 50 cm wide and 40 m long multipurpose ditches that are excavated along the contour, 6 to 12 m apart, depending on the slope. The ditches retain runoff water which infiltrates the soil, thus reducing erosion and improving soil moisture. They also act as compost ditches for all types of organic residues on the farm. Residues, enriched with manure (from chickens and guinea pigs) are tipped into the ditches, and within 8 to12 months this decomposes into a fertile medium for the cultivation of vegetables and other crops.
The main purpose is to increase and diversify production, and at the same time to protect natural resources and regenerate degraded areas.
Grass strips are planted on the earth bund on the upper side of the ditch for stabilisation of the structure, retention of runoff and capture of eroded sediment. The grass is cut several times a year to feed guinea pigs, which in turn recycle this into manure. On the lower side of the contour ditches, fruit trees and bananas are planted. Rows of multipurpose trees (mainly indigenous species) are planted around each agroforestry plot as a windbreak and for economic reasons: yielding fruit and timber. Between the structures, annual (and semi-perennial) crops are grown on hand-dug micro-terraces/ridges, again sited along the contour. Some farmers intercrop with legumes. Supportive technologies are protection of wells,
afforestation and, where possible, irrigation to enhance production. Production is based on principles of organic farming.High initial inputs of external manure are subsidised by the project (CISEC; see associated approach). The remainder of each farmer’s land is left to natural regeneration, reforested, or where needed, used for conventional cropping
The system is implemented on degraded and often steep slopes in subhumid areas where intensive rainfall and dry periods alternate. The land is officially owned communally (an ‘Indigenous Reserve’), but land use rights are individual. The region has a high population density: people are basically of indigenous origin and live in very poor conditions.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Cauca
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Santander de Quilichao
Map
×2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ចម្រុះ (ដំណាំ/ វាលស្មៅ/ ដើមឈើ)គិតទាំងកសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - soil degradation/reduced soil fertility
- inappropriate soil management: monoculture, slash and burn, no or short fallow periods
- intensive rainfall on steep, unprotected slopes
- drought and wind erosion in dry season
- lack of economic resources
- high population density
Constraints of degraded land (before SWC)
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 240, Longest growing period from month to month: october untill may
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.2 m2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
- V2: ស្មៅនិងរុក្ខជាតិៗដែលដុះមានអាយុមិនលើសពី 2ឆ្នាំ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S2: ភ្លឺ ច្រាំង
- S3: កម្ពស់ភ្លឺ ប្រឡាយ ផ្លូវទឹក
- S4: កម្រិតភ្លឺ រណ្តៅ
មតិយោបល់:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (inadequate management of land with steep slopes), overgrazing (prior degradation by landowner's livestock), industrial activities and mining (degradation of gold mining and other products), education, access to knowledge and support services, inter-generational subdivision of land (traditional custom)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (primary forest alomst disappeared), poverty / wealth (lack of capital, poverty and further agricultural employers)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
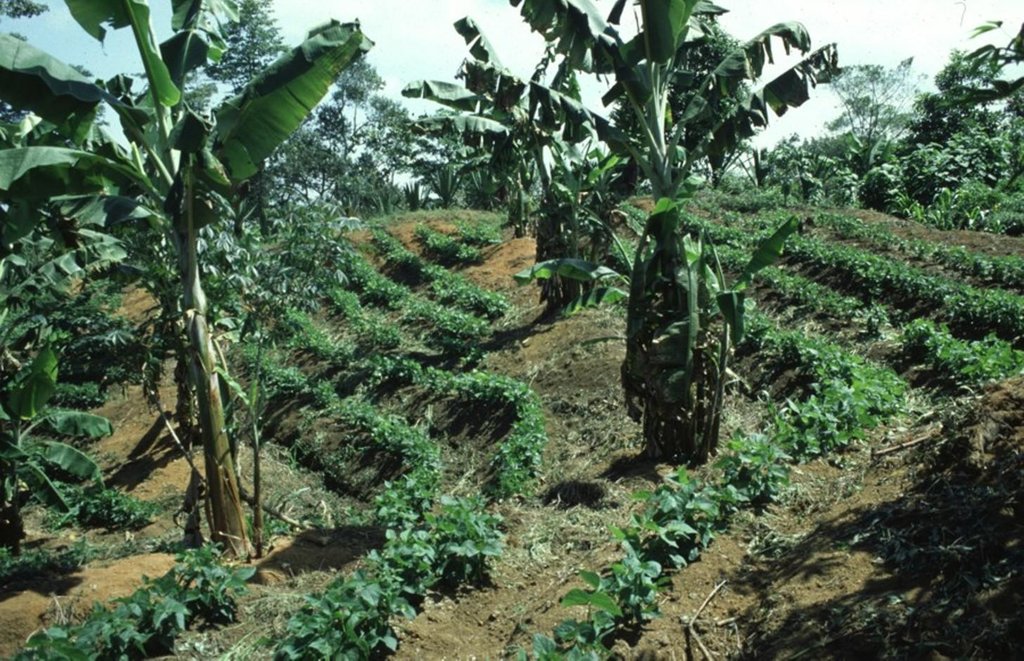
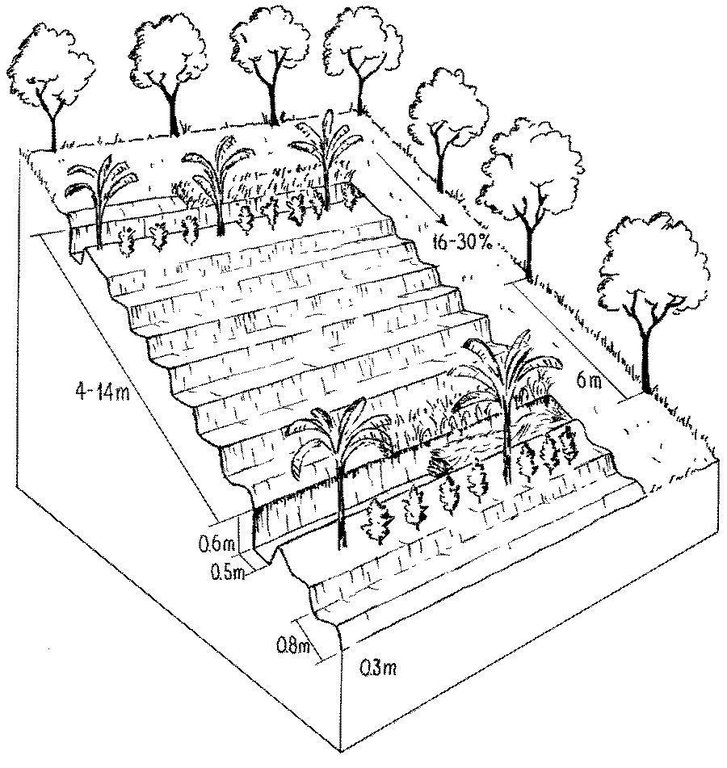
Detailed overview of the complex and intensive high-input, high output agroforestry system, usually limited to an area of 64 x 64 metres.
The agroforestry plots are bordered by trees of various species. Note the multipurpose ditches that serve as compost pits (lower ditch, right). Associated bunds are covered by grass (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed
Vegetative measure: bananas
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 16-30%
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. Clear land (only slashing, no burning). | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Beginning of rainy season (April) |
| 2. | 2. Determine contours with A-frame, spacing between structures dependson slope (4 m between ditches on steepest slopes, 14 m on gentle slopes). | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Beginning of rainy season (April) |
| 3. | 3. Dig ditches, build bunds above, and dig holes for tree seedlings. | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Beginning of rainy season (April) |
| 4. | 4. Establish micro-terraces/ridges (earth enriched with manure and residues:all structures along the contour). | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | During the dry season (June to September) |
| 5. | 6. Plant grass strips on the bund (for stabilisation of structure). | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | During the dry season (June to September) |
| 6. | 7. Plant fruit/banana trees and legumes below the bunds. | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | During the dry season (June to September) |
| 7. | 8. Plant fruit and timber trees along the boundaries of the agroforestry | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | During the dry season (June to September) |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | ha | 1,0 | 220,0 | 220,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 15,0 | 15,0 | 5,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 450,0 | 450,0 | 5,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 600,0 | 600,0 | 5,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 1285,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 5. Fill ditches with organic residues, adding earth mixed with manure. | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | During the dry season (June to September) / initial establishment |
| 2. | 4. Fill ditches with organic material, residues (after harvest), manure, etcand let it decompose. | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | |
| 3. | 6. Dig out compost and spread | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | (beginning of growing season (September) / |
| 4. | 7. Apply additional fertilizer/manure | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | / 3 times/year |
| 5. | 1. Cut grass ( grass used to feed guinea pigs). | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | /4–6 times/year |
| 6. | 2. Control weeds | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | /3 times/year |
| 7. | 5. Plant vegetables on fertile composted earth in ditches | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | /dry season, optional |
| 8. | 8. Plant various crops: contour cropping, intercropping, integrate greenmanures (legumes). | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | |
| 9. | 3. Rebuild/repair structures | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | dry season |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 145,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: machete, shovel, pickaxes, A-frame, planting stick (chuzo)
As an exception in this case study costs are calculated per plot and not per ha, since establishment is strictly limited
to an area of 0.4 ha per household. The remaining area is not treated but left for natural regeneration of vegetation or
conventional farming (if needed). Labour costs vary according to slope: a typical/average situation is given in the tables above (no further details available). Note that for comparison purposes with other technologies on a per hectare basis these costs would equate to US$ 3,135 for establishment and US$ 355 for maintenance.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Off-farm income specification: most farmers depend economically entirely on their own crop production
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ភាពខុសគ្នាផ្នែកសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
បន្ទុកការងារ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
friction between participants and non-participants
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ជាតិអាស៊ីត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
high content of organic matter
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
use of water for irrigation
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
260 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. There is a slight growing spontaneous adoption by land users living outside the approach area.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Rehabilitation of soil fertility over short term |
| Increased and permanent production |
| Increased food security and balanced diet |
| Adapted to very heterogeneous climatic and topographic conditions. |
| Protective-productive system: compromise between land capability class (forest) and cultivation needs |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Rigid design of the technology and fixed guidelines for implementation activities (pre-conditions for incentive support by project) | Give more flexibility to the farmers for individual modifications. |
| High demand for manual labour |
Emphasis on group work, implement in dry season (when labour force is available at the household level). |
| High external inputs at the beginning (makes the technology very expensive) |
Manure is needed to restore soil fertility in the short-term, land users pay the inputs in form of labour in the CISEC; revolving funds and composting ensure manure supplies on the long term. |
| Decreased pH (soil acidity) |
Compensate by ecological improvements such as application of lime and ashes. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
CISEC . Establecimiento de Lotes de Silvoagricultura. 1998.
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Gurtner M . Bodendegradierung und Bodenkonservierung inden Anden Kolumbiens – Eine Nachhaltigkeitsstudie im Rahmen des WOCAT-Programms, unpublished MSc Thesis, Science Faculty, University of Berne,Centre for Development and Environment. 1999.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Desarrollo Rural Integral Comunitario [ប្រទេសកូឡុំប៊ី]
En un proceso participativo y comunitario y a través de la capacitación, la asistencia técnica y la suministración de insumos importantes se fomenta el establecimiento de un sistema agrosilicultural en la comunidad indÃgena.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Mathias Gurtner
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល