Intercropping of grass and corn to increase soil organic matter [ប្រទេសហូឡង់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Jason Stuka
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
Gras onderzaai bij mais (NL)
technologies_1248 - ប្រទេសហូឡង់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
Droevendaalsesteeg 4, 6708 PB Wageningen
ប្រទេសហូឡង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Leever Henk
HOEDuurzaam
ប្រទេសហូឡង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
Dorshorst 1a 7217 PH Harfsen
ប្រទេសហូឡង់
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Provincie Gelderland - ប្រទេសហូឡង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Hoe Duurzaam - ប្រទេសហូឡង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Ministerie van Economische Zaken - ប្រទេសហូឡង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - ប្រទេសហូឡង់ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - ប្រទេសហូឡង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
20/03/2015
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Regional process, social innovation [ប្រទេសហូឡង់]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Simone Verzandvoort
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Grass intercropping on corn fields
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
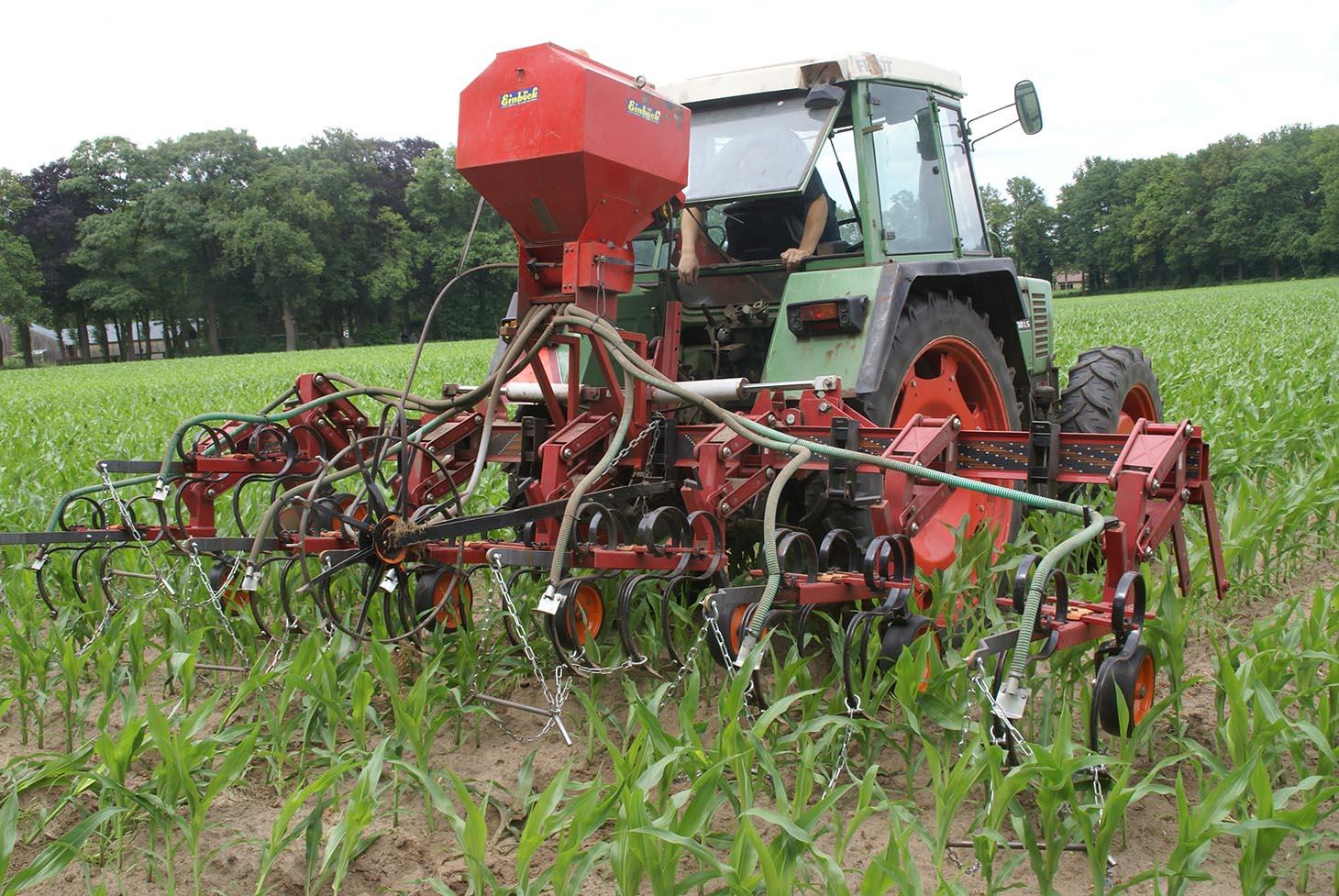
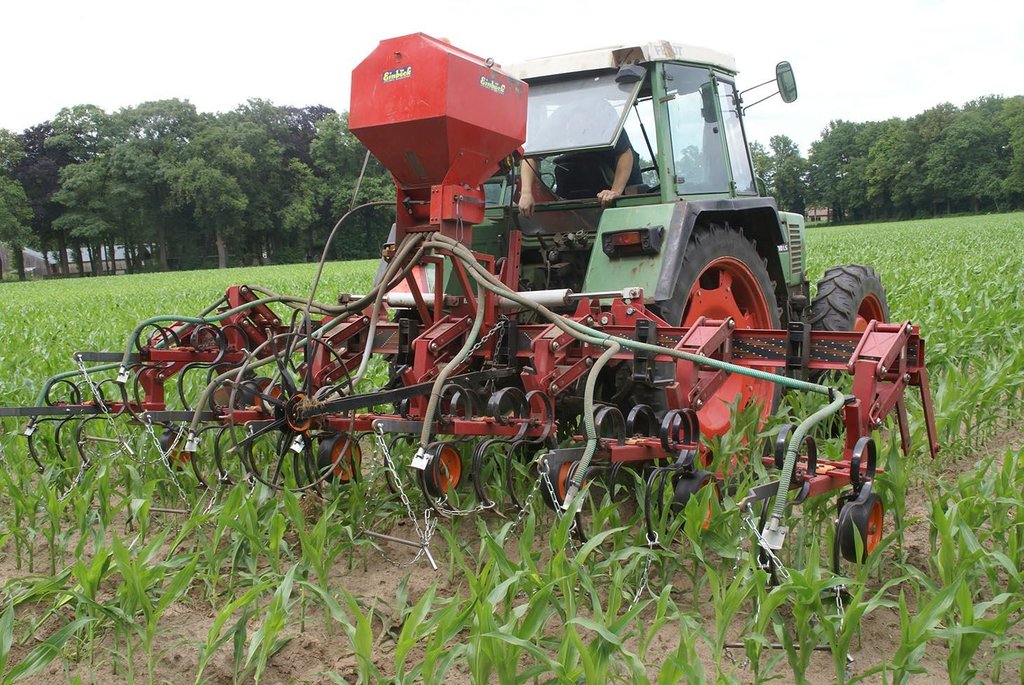
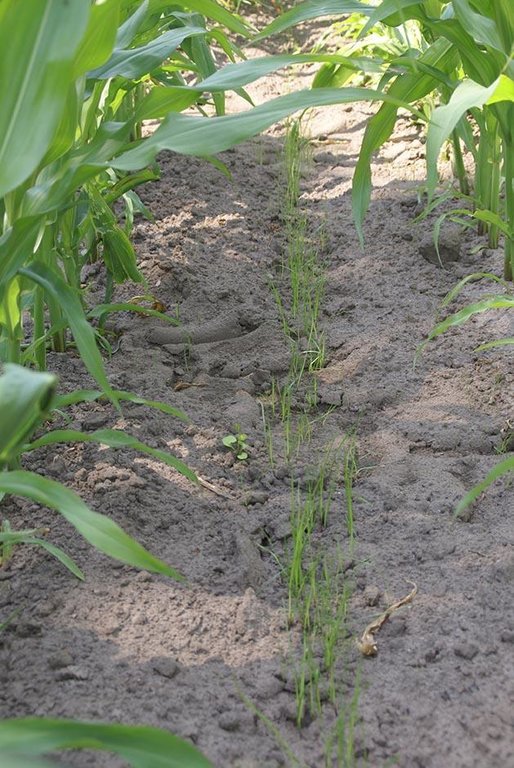
Italian rye grass is sown when the corn has grown to knee height, and has not yet developed a closed cover. The grass is plowed into the soil several months after the harvest of the corn crop.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to enable a good growth of the catch crop (the grass) and to increase root biomass production after the corn is harvested. This will contribute to the organic mater content of the soil, and reduce the leaching of nitrogen and potassium. After underplowing of the grass, the nitrogen and potassium will be released to the soil and become available for the next crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: When corn is well established (between 30-60 cm height), grass is seeded between rows. A special seeder is required. Tractor must have tires that fit between corn rows. Grass germinates, but growth is reduced as corn matures and creates shade. When corn is harvested, grass continues to grow as a winter catch-crop. Some years, grass is sprayed with fertiliser to increase mineralisation. Grass is cultivated into the soil in early spring.
Natural / human environment: Multi-functional rural area with land use for agriculture, recreation, residence and nature. Dairy agriculture in small farms for Dutch standards combined with arable cropping. High livestock density.
Undulating landscape with cover sands and clayey and loamy sediments. Podzols and cambisols developed in sandy substrate. The area also has patches of anthroposols, soils enriched in Medieval times with manure and organic residues. Phosphate and nitrogen levels in these soils are in general high.
Mean monthly temperature varies between 2 and 17°C. The long-term mean annual precipitation is between 800 and 825 mm, with the lowest amounts in spring, and the highest in autumn. The long-term average annual precipitation deficit is between 200 and 240 mm.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសហូឡង់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Gelderland
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
មតិយោបល់:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Left: 52.098865, 6.563182
Right: 52.095031, 6.634282
Top: 52.111764, 6.589390
Bottom: 52.081761, 6.620607
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The land users's initiative was through the application for the project Healthy Sand by a group of farmers. During the Gezond Zand Project the group organised themselves in the Foundation HOEDuurzaam. The project ran from 2012-2014 and is followed by the new project BodemRijk.
The external initiative was from the drinking water company Vitens and the Province of Gelderland in the same period.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Major cash crop: potatoes
Major food crop: Maize, cereals
Other: Grass
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main soil threat in the Olden-Eibergen Case Study area is the gradual decline of soil organic matter stocks. On average, agricultural fields have lost up till 5.4% of organic matter in the last 10 years according to farmers. This threatens the agricultural potential of the soil as well as its water holding capacity, and its potential to buffer leaching of nutrients and pesticides. In the long term, agricultural productivity will fall, costs of agricultural inputs such as manure, fertilizers, pesticides and irrigation will increase and the additional costs for cleaning drinking water withdrawn from ground water will rise.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience declining crop production, problems with too dry and too wet soils, and decreasing organic matter content in soil due to long-term monocultures of maize, the use of pig manure and legislation forcing farmers to process or export manure from their farms.
Grazingland comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
Type of grazing system comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 250Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- Intercropping
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 m2.
94 ha over 32 fields. 20 farmers applied this technology.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, green manure, rotations / fallows
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Hq: ការថយចុះគុណភាពទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (ploughing for renewal of grassland or rotation to arable cropping), governance / institutional (Stricter manure legislation since January 2014 deriving from the EU Nitrates Directive has forced farmers to process part of the manure from their farms on-farm, or to export it from their farms.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (long-term monoculture of maize and intensive cropping of seed potatoes)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
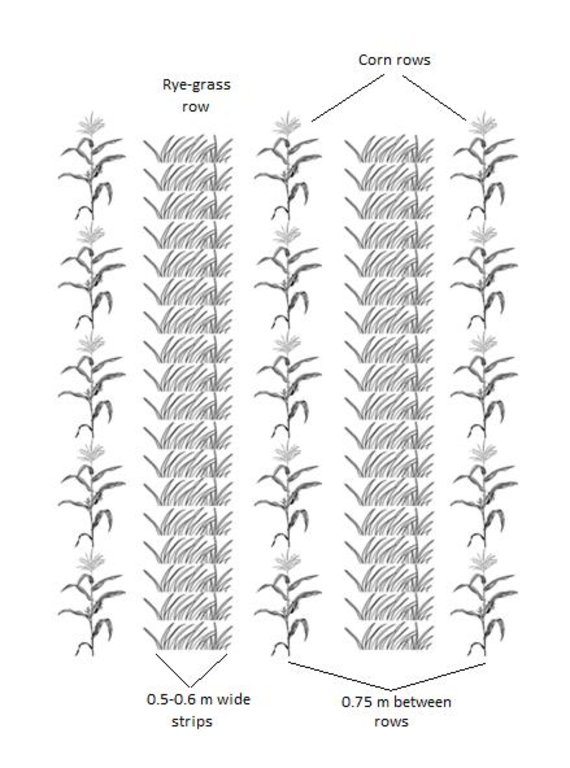
After the corn crop is growing, a tractor with a seeder sows Italian Rye-grass seeds between the rows of corn. The grass seeds are sown in strips parallel to the corn rows. The corn rows are 0.75 metres apart. The grass strips are usually between 0.50 and 0.60 metres wide, but this is according to the farmer's preference. this means that a spacing of between 0.075 and 0.125 metres remains bare on each side of the grass strip, between the grass and the corn.
Location: Haarlo - Oude Eibergen. Gelderland
Date: April 8 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Technical knowledge required for agricultural contractor: high (technical skills are required from an agricultural contractor with a special machine to sow the grass in the already standing maize crop.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Green manure
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Rotations / fallows
Remarks: The Italian rye grass is worked into the soil ca 5 months after the harvest of the maize.
Aligned: -linear
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): not applicable
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.75-1.25
Grass species: Italian rye grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): not applic%
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Euro
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,94
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
255.70
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a seeder | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Seeder | Machine | 1,0 | 5327,05 | 5327,05 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 5327,05 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
Life span of the seeder: 6 years
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | After corn is established |
| 2. | Fertilizer | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Every other year |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| សម្ភារៈ | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 117,2 | 117,2 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 42,62 | 42,62 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Fertilizer Hired(machine+fert) | ha | 1,0 | 9,06 | 9,06 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 168,88 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: Specific tractor to perform grass undersowing (seeder), tractor, sprayer/applicator
To seed the Rye-grass strips between the corn rows. Done a few months after the corn is seeded.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
New equipment (Seeder) - The seeding and fertilizer applications are hired from a company. The company purchases the new equipment to seed between the corn rows.
The greatest determinate factor to the land users are then the cost of hired machine hours.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
182 days of precipitation annually
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Flat and gentle (Only incidental)
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil depth on average: Deep (A and B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area) Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm) and very deep (Deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture is coarse/light (Most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (Soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area)) or very high (in Fimic Anthrosols originated due to application of farmyard manure since medieval times (12% of the area))
Topsoil organic matter is medium-high (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water table (H > 40-80 cm; L>120 cm) in the sandy soils on thick substrate of cover sands (in 65% of the area)) and medium (shallow groundwater tables in the Umbric Gleysols (35% of the area))
Soil water storage capacity is very high (in the Fimic Anthrosols with high SOM in the topsoil) and medium (in the other soils, varying with the soil organic matter content)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
< 5 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table is <5m (in all soil types the highest level of the groundwater table during the year is <140 cm below the soil surface. The lowest level can be lower than 120 cm)
Availability of surface water is medium (from small rivers (De Berkel) and creeks)
Water quality (untreated) is poor drinking water (treatement required - levels of the pesticides Bentazon, and MCPP in the groundwater have incidentally exceeded the norms for drinking water production between 1985 and 2009.)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងទៀតលើជីវចម្រុះ:
Soil biodiversity is high in the Fimic Anthrosols.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality, craft work. No B&B activities or educational services.
Market orientation: Mixed (Maize is completely used to feed cows (max 20% of the area is allowed under maize); other arable crops are sold to the market. Dairy production is commercial.)
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
15-50 ha 6 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
50-100 15 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
- ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់:
All agriculture land is owned or rented by individual farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. Leased land is less well managed, resulting in lower organic matter contents. Investments in SLM would lead to a higher renting fee, or the land owner taking the land back in exploitation.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected increase of maize production: to 6-7 tonnes/ha. Not proven yet.
Possible competition between crop and grass. Not shown yet.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Only for farmers with fields at higher elevations and drier soils.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Saves seeding winter crop in autumn.
Added planning, but work is hired.
Undersowing of grass in the standing maize crops requires specific skills.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Created farmer's foundation.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts of farming practices and organic matter in soils.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farmers collaborating with water company.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
គុណភាពទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet. Little to no slope.
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet. Claimed by some farmers already.
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Possibly. Not proven.
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
No modifications to the technology in response to climate change.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
មតិយោបល់:
Farmers are subsidized for seeding rye-grass between corn rows. If not subsidized, they are unlikely to invest. Few farmers have seen short-term benefits. Their willingness to invest is based on their understanding of the long-term benefits, brought about by the Approach developed in the Project Gezond Zand (and in RECARE).
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
20
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
|
increases maize crop yield in the long term How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
| increases available soil moisture |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Uncertainty of the success or positive effect of the measure. | |
| Uncertainty of negative effects to the crop. | |
| Uncertainty of competition between grass and crop for nutrients and moisture. | |
| Concerns about cost and labour | |
| Uncertainty of hindrance from legislation. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| technology requires hiring of skilled labour and machinery, which is not viable without subsidy in the short term | provide subsidy in the first 3-5 years of implementation |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort2014
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Freeannemieke.smit@wur.nl
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden EibergenBy Willem Rienks and Henk Leever2014
វេបសាយ:
Freehttp://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdf
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The NetherlandsArjan Reijneveld2013
វេបសាយ:
Wageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Regional process, social innovation [ប្រទេសហូឡង់]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Simone Verzandvoort
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល