Gully plugging using check dams [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Nicole Guedel
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ David Streiff
Galchhi niyantran - Nepali
technologies_1493 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
01/11/2004
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Local initiatives for rehabilitating degraded communal grazing land [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
Supporting local initiatives and building local capacity for the rehabilitation of degraded communal land in the middle mountains of Nepal.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Madhav Dhakal
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
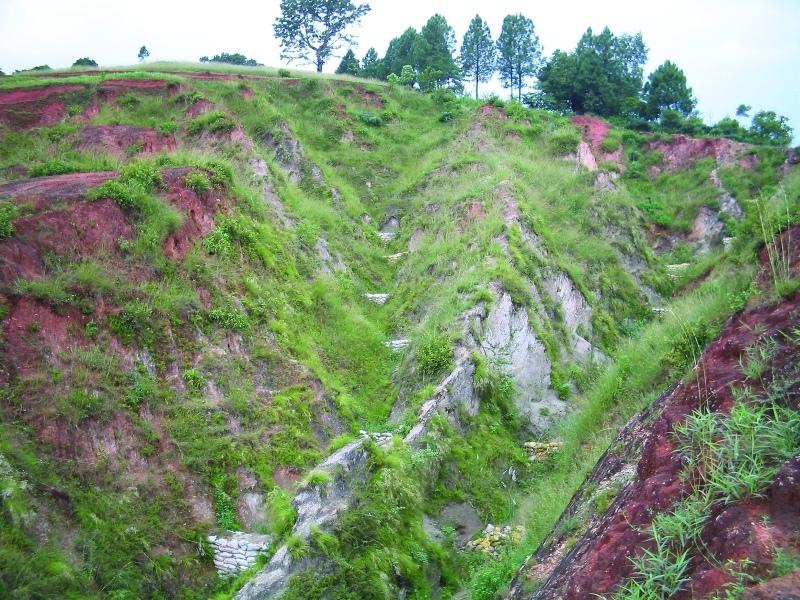
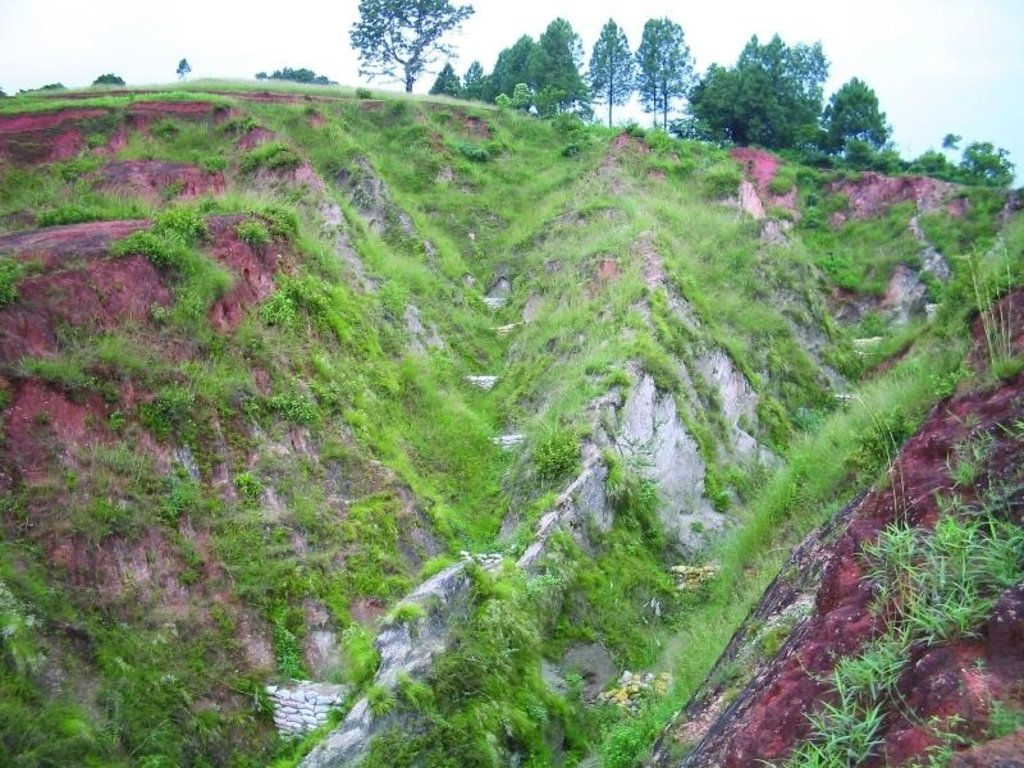
Small dam structures constructed across erosion gullies
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Check dams are small low structures built across a gully or a channel to prevent them from deepening further. These small dams reduce the speed of water flow and minimise the erosive power of runoff. They also promote the deposition of eroded materials to further stabilise the gullies.
Two gullies adjacent to a degraded area of communal grazing land were controlled by constructing check dams and with vegetative measures including planting bamboo. The main purpose was to control the further development of the gullies, which were affecting the adjacent grazing land and blocking a downstream irrigation channel. The site is community land used by the 40 households (240 people) of Dhotra village in the intensively used Jhikhu Khola watershed. Irrigated cropland lies downstream from the site, whilst the site itself is bordered by grazing land, degraded sal-dominated forest, and rainfed forward-sloping terraces.
The check dams were made of old cement bags filed with soil and were 1m high with 0.5m deep foundations. The check dams were spaced so that a line joining the top of two adjacent dams had about a 3% slope gradient. Twenty-four check dams were built in the two gullies using a total of 2400 filled cement bags. Forty clumps of bamboo were planted between the dams for stabilisation.
All that is needed to maintain this technology is to inspect the condition of the check dams occasionally, especially before and after the monsoon. Displaced bags should be replaced and the water courses cleared of branches and big stones. Further planting should be carried out if needed.
The case study area has a distinct dry season from November to May and a wet monsoon period from June to October. Annual rainfall is around 1200 mm. The site has red soils that are highly weathered and, if not properly managed, are very susceptible to erosion.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kavre Palanchok/ Dhotra village, Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
The basic idea of this technology has its origin in traditional methods. However, villagers approached the People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) for advice. PARDYP assisted, based on experiences made before with rehabilitation/gully plugging experiments under similar conditions. Mainly developed according to theoretical and site specific knowledge.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- reduce land loss
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ដីវាលស្មៅធំៗ:
- បែងចែកវាលស្មៅជាប្លុក
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem is the small per capita landholding size for cropping. These holdings are mostly rainfed, have a low soil fertility status and acidity problems, and are susceptible to erosion. Intense rainfall at the beginning of the rainy season causes considerable soil loss (rill and gully erosion).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Overgrazing leading to lack of vegetation and gully building.
Ranching: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 3
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.006 km2.
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (insufficient forage supply from the private land.), education, access to knowledge and support services (identification of appropriate SWC technologies and appropriate collaborators)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (for daily household needs ( litter , firewood, timber), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (excessive rainfall during pre-monsoon and monsoon), poverty / wealth (to buy planting materials and for logistics), labour availability (for community level social work)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
Schematic drawing of two gullies
with 24 check dams and bamboo
planted below the check dams for
stabilisation
Location: Dhotra. Khabre
Date: 22.6.06
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 40
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4 m
Trees/ shrubs species: Bamboo
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 25.00%
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 4 m
Construction material (earth): soil resulting from digging activities from the adjacent grassland was used to fill cement bags for
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 25%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Nepali Rupee
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
73,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
2.00
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantating of bamboo plants (clumps) below the check dams | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 2. | Placing filled cement bags across gullies to form checkdams | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 3. | Filling cement bag with soil | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 4. | Digging trenches for dam foundations | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Building dams and planting bamboo | Persons/day | 18,0 | 2,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Cement bags | ha | 1,0 | 73,0 | 73,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Lunch, tea for farmers | ha | 1,0 | 16,0 | 16,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Transportation | ha | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 139,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintaining gullies: repair or replace damaged check dams, plant | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 2. | Ensuring good drainage for bamboo | សារពើរុក្ខជាតិ | before onset of monsoon (June) |
| 3. | Maintaining gullies: repair or replace damaged check dams,plant more grassesor trees if needed | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | before onset of monsoon (June)/once a year |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, shovel, Spade, shovel
All costs and amounts were roughly estimated by the technicians and authors in 2004.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Altitudinal zone: 900 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Also very steep
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- ម៉ត់/ ធ្ងន់ (ឥដ្ឋ)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow at some places parent rockmaterial is exposed but variable.
Soil texture: Red soils with high clay content
Soil fertility was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities.
Topsoil organic matter before implementation of rehabilitation activities.
Soil drainage / infiltration was poor before implementation of rehabilitation activities.
Soil water storage capacity was very low before implementation of rehabilitation activities.
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Water quality: More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
95% of the land users are average wealthy.
3% of the land users are poor.
2% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
Only limitied grazing area for whole village.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
At the beginning a few people opposed the activities.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
ដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
into irrigation canal
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
Due to the high establishment costs, the short term benefit for the community only matches the costs. However, in the long-term the environmental benefit of rehabilitated land is high, and economic
benefit is positive.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- ច្រើនជាង 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
40 households in an area of 0.006 sq km
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
40 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: No initiative could be seen in the area.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
Reduced soil erosion, rill erosion, and top soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required |
|
The technology is easy to maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
It's a low cost technology , easy to apply, little knowledge needed. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of the structure and grasses is required |
|
The effect of the technology can be seen easily. How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Nakarmi, G. (2000) Soil Erosion Dynamics in the Middle Mountains of Nepal, a report submitted to PARDYP, ICIMOD, Kathmandu
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Schreier, H.; Brown, S.; Shah, P. B.; Shrestha, B.; Merz, J. (2002) Jhikhu Khola Watershed – Nepal, CD ROM. Vancouver: Institute for Resources and Environment, University of British Columbia.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Shrestha, B. (2004) Progress Report PARDYP- Nepal. Paper presented at the PARDYP Access Mid Year Meeting, 19-22 July 2004, ICIMOD, Kathmandu
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Local initiatives for rehabilitating degraded communal grazing land [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
Supporting local initiatives and building local capacity for the rehabilitation of degraded communal land in the middle mountains of Nepal.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Madhav Dhakal
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល