Pipe Irrigation [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Sabita Aryal
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យ Fabian Ottiger
Pipe Sinchai
technologies_1599 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Karki Nimisha
+977 11-661399
Kathmandu University
Dhulikhel 45200
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Niraula Archana
+977 11-661399
Kathmandu University
Dhulikhel 45200
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Anish Adhikari
+977 11-661399
Kathmandu University
Dhulikhel 45200
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Kathmandu University (KU) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
02/12/2012
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Pipeline Irrigation [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
The process and measures taken to draw water from nearby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Sabita Aryal
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Waterways and pipelines to draw water from closeby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
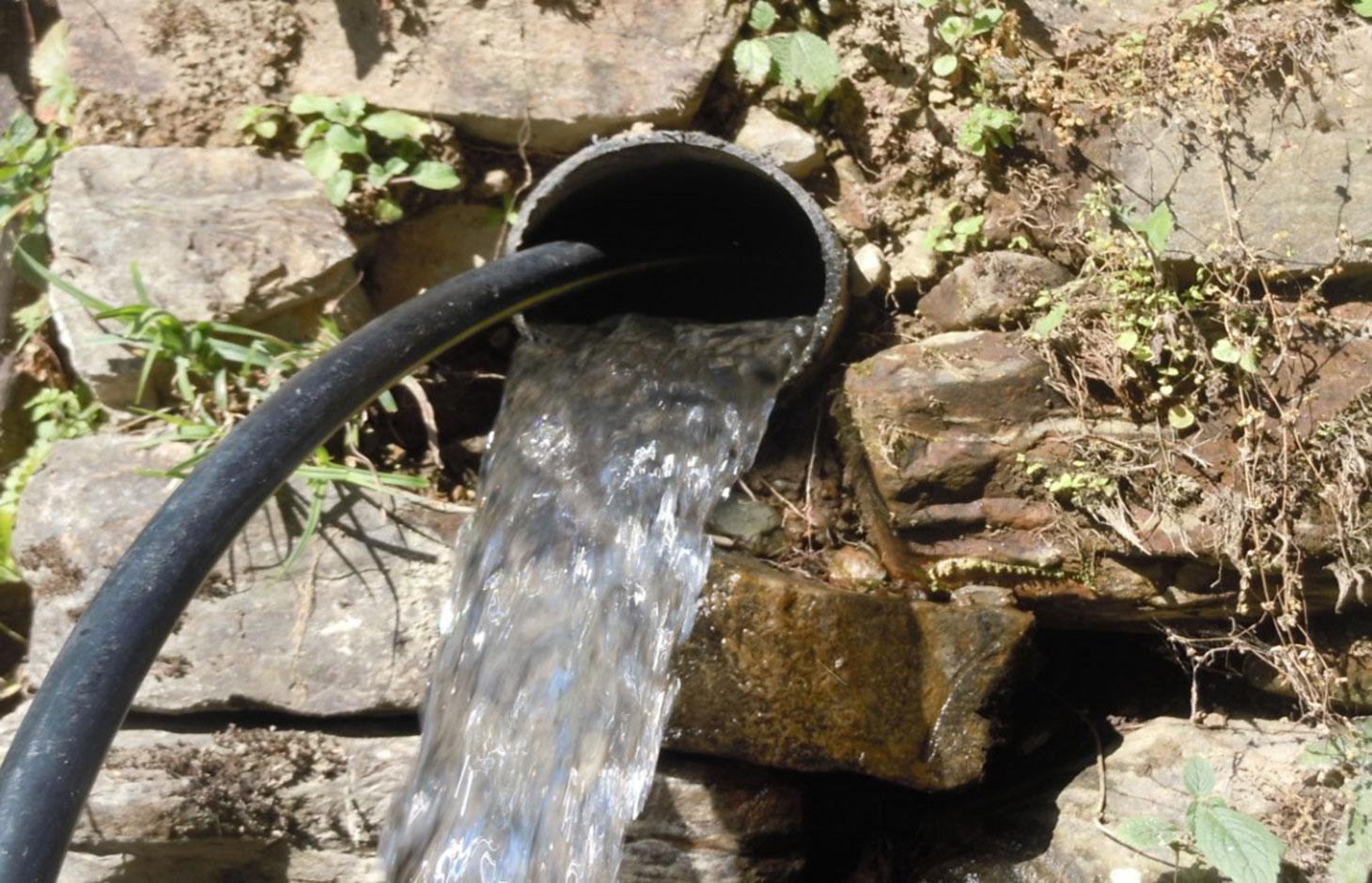
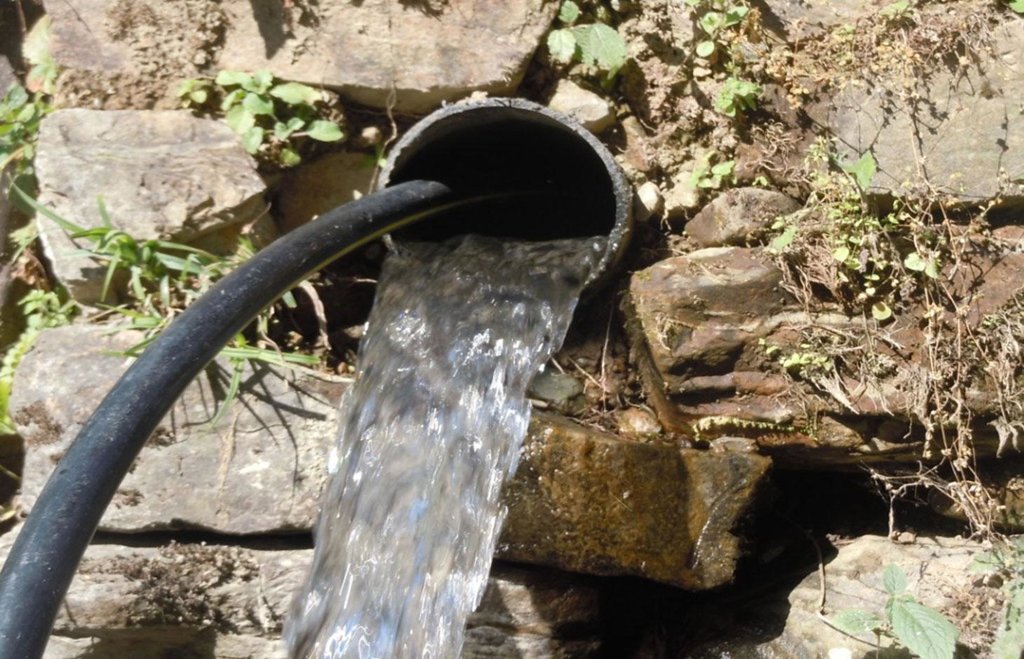
The technology involves the construction of diversion and waterways from the rivers to draw ample water sufficient for distribution to the different houses of the V.D.C .
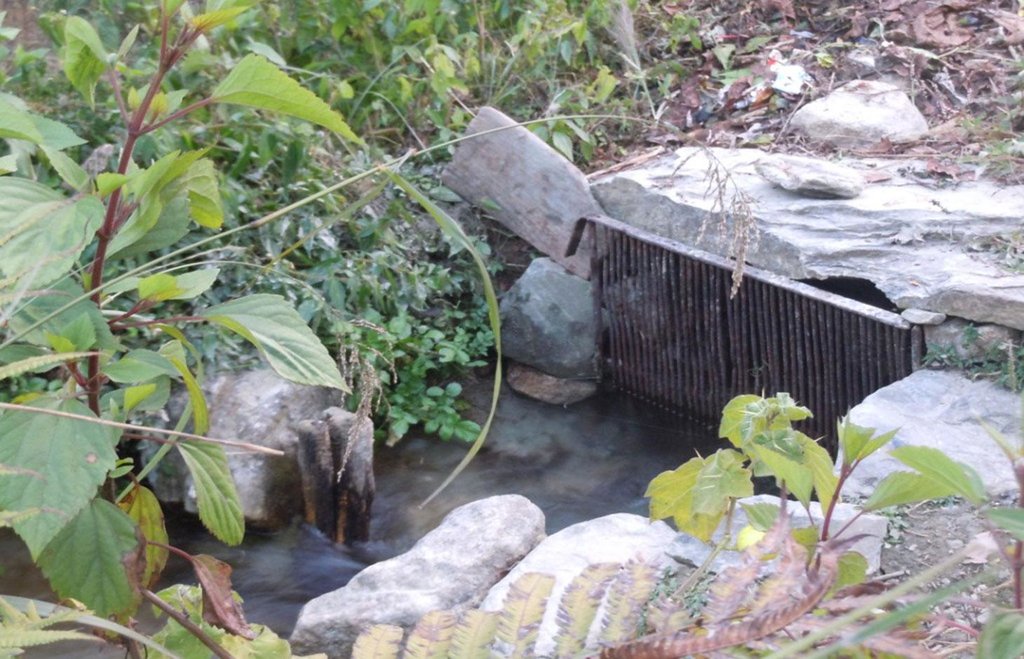
Water is drawn from two rivers via three routes, one route from 'Polsing' river and the two other from 'Ghatte river' .
In the upper areas, open digging is done up to 700 meters from the source and waterways are created.
However, in lower areas due to more stones, creation of waterways was not possible, hence pipelines had to be created over 425 meters.
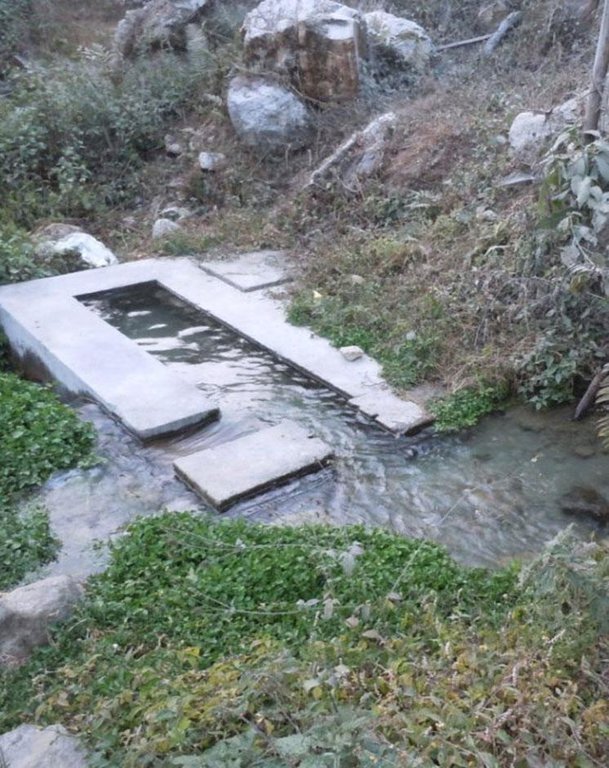
The pipeline opens in each house into a small reservoir for use in irrigation and household.
Purpose of the Technology: Mainly for conservation of land and soil along with provision of water to agricultural land.
Before the implementation of this technology, land was semi arid with few perennial crops.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Initially established and then managed by the combined effort of the users. All activities done voluntarily using easily available tools of daily usage by members of the households who benefit and make use of the technology. The only costs made were for the purpose of making pipelines which was borne half by the government and half by the land-users themselves.
No maintenance activities have been carried out so far, yet monthly collection of Rs 20 is done from each house which is stored for future use.
Natural / human environment: Chyamrangbesi VDC is a valley with subtropical type of climate. Precipitation level ranges from 750mm to 1500mm for about four months during the monsoons. The winters are dry however and hence the growing period is from 79 to 179 days, making the area semi-arid depending on the agro-climate division. Since the area falls on hill slopes with 8.16% steep so the technology is applied with convex manner.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Chyamrangbesi
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kavre
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Initial work started in 2004, improvements in the technology each year
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)

ផ្លូវទឹក ផ្ទៃទឹក ដីសើម
- ខ្សែទឹក ផ្លូវទឹក
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land semi-arid and dry, hence only few selected crops could be grown due to lack of sufficient water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Land could not be utilised properly due to lack of sufficient water for crops, dry condition.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 3
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 150, Longest growing period from month to month: Karthik (October) - Chaitra (April) Second longest growing period in days: 120, Second longest growing period from month to month: Asadh(June) - Ashwin (September)
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព (រួមទាំងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ)
- ការបែងចែកទឹក និងប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 28.97 km2.
Same technology covers entire area with water source
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S3: កម្ពស់ភ្លឺ ប្រឡាយ ផ្លូវទឹក
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (Construction of roads, not properly engineered, difficult to travel by and highly risky.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (In the 3 months of monsoon), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Roads construction and its use by large vehicles frequently)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
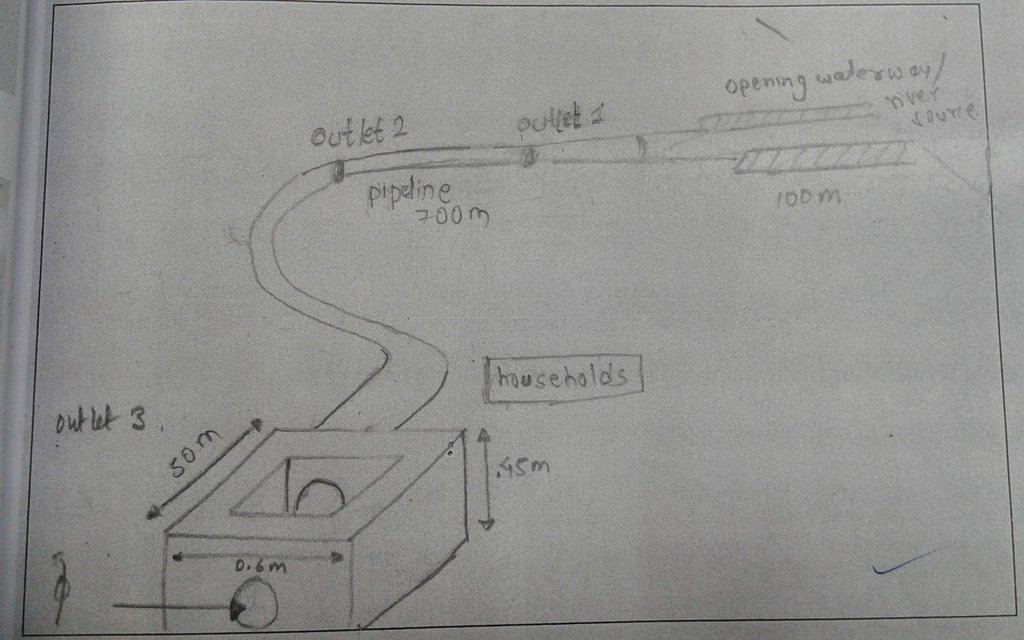
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
The drawing shows the path followed by the pipe irrigation, the various feautres
Location: Chamryangbesi VDC
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Designed by engineers
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Constructed by land users)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Waterway
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 700
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.45
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Construction material (earth): soil excavated and used to make bunds of the water ways
Construction material (concrete): used to make small reservoirs in houses
Construction material (other): pipes : to transfer water from the source to houses
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
rupees
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
98,47
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut into land from the source in suitable directions to bring water to their houses | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Dry season |
| 2. | Fitting of pipes | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | dry season |
| 3. | Construct small openings/reservoirs | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | dry season |
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Farmers cut into land from the source in suitable directions to bring water to their houses | mandays | 45,0 | |||
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Fitting of pipes | mandays | 15,0 | |||
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construct small openings/reservoirs | mandays | 15,0 | |||
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Pipe + cement | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 |
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Area to be covered by the pipeline and distance from the source are the most determinate factors.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Monsoon rains, dry winter
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីប៉ោង
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil depth on average: Varies from shallow to deep
Soil texture: Soil texture varies from place to place
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1, varies according to water availability) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Use of manure necessary for maintaining productivity
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (No groundwater found)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
ផ្ទៃខាងលើ
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
លើស
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, Groundwater use not much evident) and <5m (ranked 2)
Availability of surface water: Excess (ranked 1, Floods occurs in case of heavy seasonal rainfall; supply of water is good and sufficient) and good (ranked 2)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water (perennial surface water distributed through pipelines)
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មាន
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 5%
40% of the land users are rich.
60% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ការបង្កើតថាមពល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Water Mill ('Pani Ghatta')
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
ទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បានសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
គុណភាពទឹកសម្រាប់ការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
ស្ថាប័នជាតិ
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក
ការប្រមូលស្តុកទុកទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
រំហួត
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
ភាពប្រៃ
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃសត្វ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
ហានិភ័យនៃភ្លើងឆេះព្រៃ
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មិនស្គាល់ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនស្គាល់ |
មតិយោបល់:
In cases of excess water availability, pipelines have been made to divert water to mills , that uses water to rotate blades and grind crops.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Every year the irrigation line is being increased to encompass more houses of the VDC
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Water is equally available to all the households, with minor level decrease in the dry season. |
| The crop, fodder production has increased |
| Reduced top soil loss due to erosion |
| Maintenance requirement minimum |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| More houses could be Incorporated in the technology | Involvement of more local inhabitants so more households could benefit from the technology |
| Lack of Monitoring by Experts | Monitoring of SLM Experts could help improve the existing system to make it more sustainable and efficient. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Pipeline Irrigation [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
The process and measures taken to draw water from nearby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Sabita Aryal
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល