Minimum Tillage [ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Peter Liebelt
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
Минимальная обработка
technologies_1315 - ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Sustainable land management in the Russian steppes (KULUNDA / GLUES)1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
23/06/2016
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរនៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM

Vocational Training [ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី]
Regular in-service training of land use specialists and farm managers in the fields of sustainable land use management, and monitoring in the agrarian sector.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Peter Liebelt

Field days [ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី]
Field days are events for regional stakeholders, mainly farmers in the study area, to discuss their demands regarding scientific help, and to be informed about the activities and results of new methods and technologies for conservation agriculture.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Peter Liebelt
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
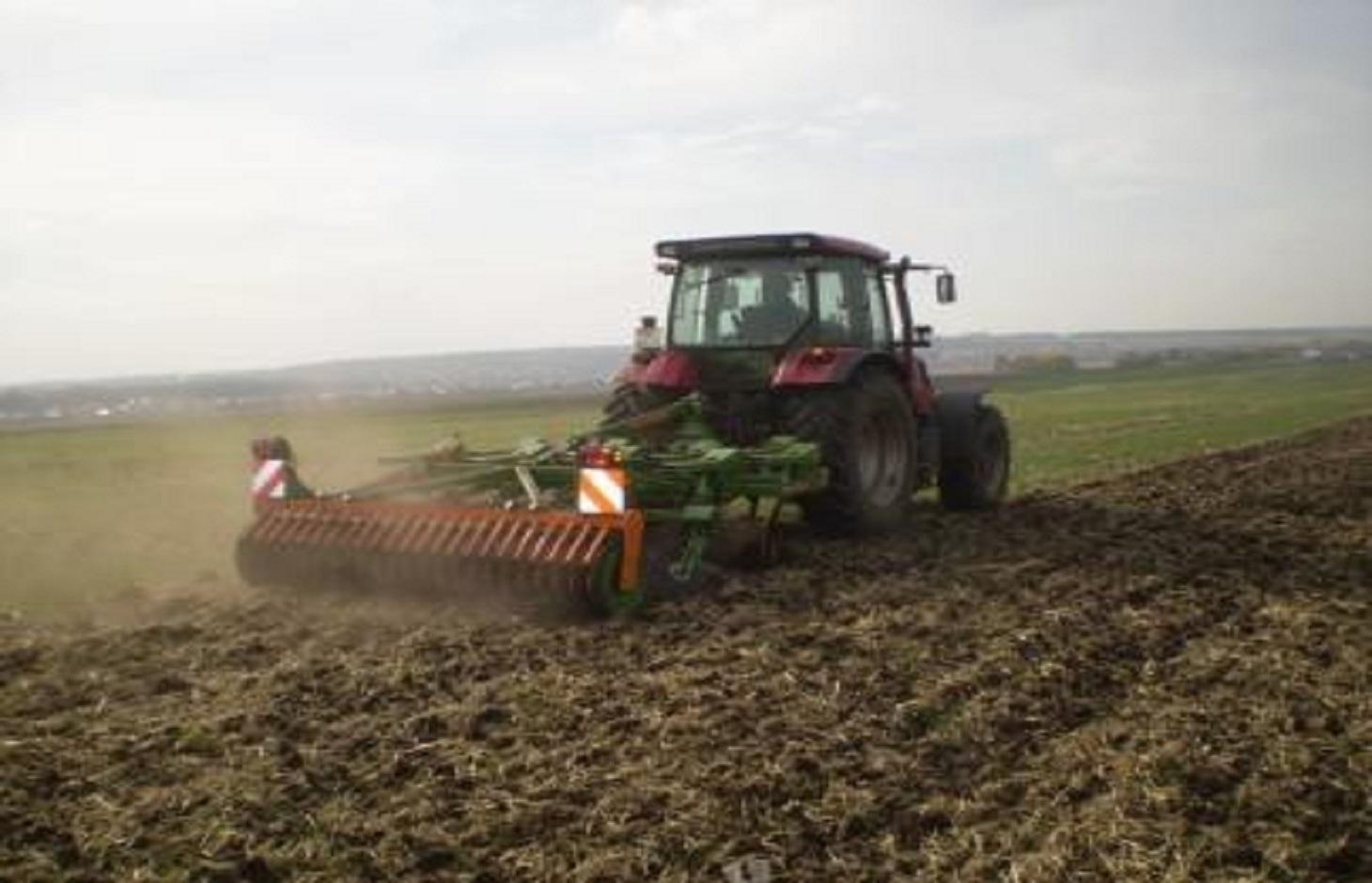
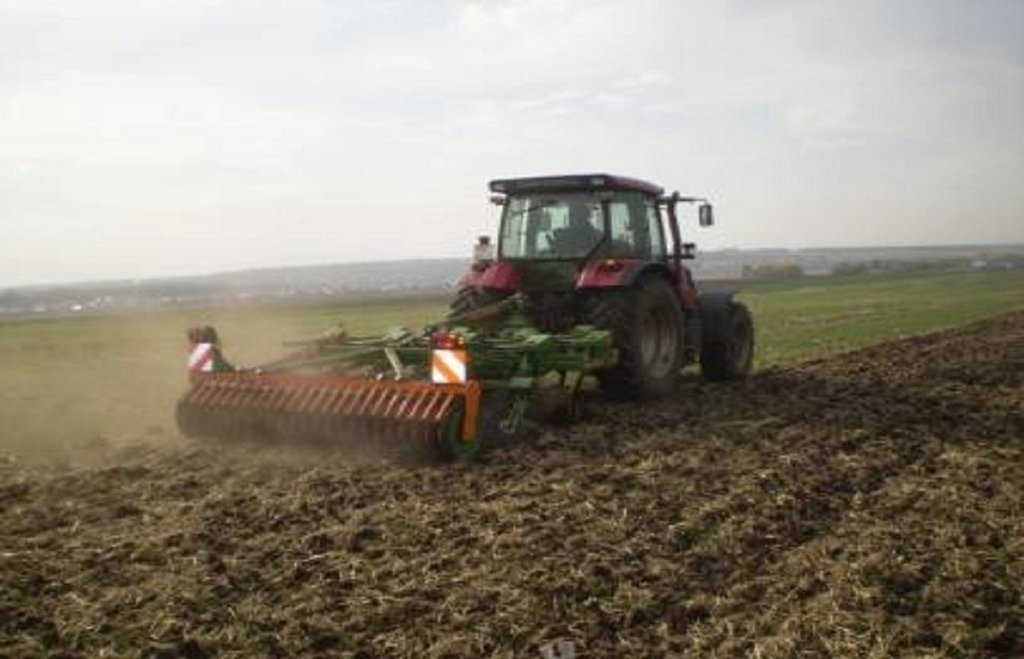
Minimum tillage is a one-pass operation combined with sowing, using a classic Russian seeder modified for seedbed preparation and soil mixing. It can include shallow stubble cultivation after harvesting.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Minimum tillage is a key element of the "adapted Soviet cropping system", which aims at more sustainable land use but based on predominantly local technologies. For successful implementation of minimum tillage, adaption of the whole cropping system is required, including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. Stubble cultivation in autumn is best performed with the "Catros" compact disc harrow for a quick, shallow operation. Seedbed preparation is carried out using a classic Russian seeder modified with wing shares for shallow seedbed preparation including soil mixing. In general, the performance of this drill is very close to that of a cultivator.
Minimizing tillage, saves time and fuel, and also helps to reduce evaporation, as well as protecting the soil against erosion. Shallow tillage with disc harrows after harvest ensures better stubble mixing and stimulates the germination of weed seeds. The adapted seeder, SZS 2.1, works with wing shares that open the soil and place the seed. Thus traditional deep tillage operations for the preparation of the seedbed can are omitted: that helps to reduce costs. With respect to crop protection, the first and most important element is to implement a full crop rotation. To control late germinating weeds and seeds of the previous crop, a disc harrow is used for shallow cultivation – this can be supplemented by the application of a non-selective herbicide if there is germination - to avoid the risk of flowering before the hard frost sets in. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under minimized soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system.
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that minimizing tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The adapted Soviet system is more profitable, due to higher gross margins.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
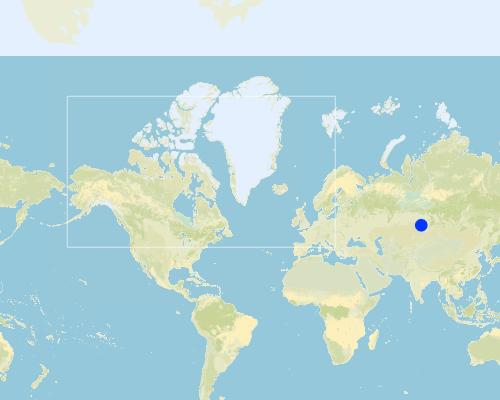
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
មតិយោបល់:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Already during the Soviet land use periode temporal,especially after the Virgin land campagne (1954-'63)efforts were made to minimize soil tillage intensity to obtain from conventional ploughing system. An important scientific thinker for this innovative farming systems was T. C. Malcev. But at this time the new approaches for minimized tillage systems were not seriously implemented in Russia. Only in the last decade a significant trend towards minimum soil tillage can be recodnized in the Russian agriculture
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils and loss of topsoil depth has led to a decrease in soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation, and the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation, is a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land users who were involved in the studies and implemented the new farming practices have a similar opinion. But there are still a lot of farmers that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from conventional/ traditional soil management.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- កាត់បន្ថយការរំខានដល់ដី
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ សូមកំណត់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍:
- 0.1-1 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 m2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to the test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha ; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha and 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha all managed by Minimum Tillage. This questionnaire is related to the test site in Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ
- Ed: អតិផរណា និង ការទម្លាក់
- Eo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាព

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional (intensive) soil tillage by phloughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow (without any vegetation cover)), wind storms / dust storms (Strong wind and storm (local name: Sukhovey) from the south-western central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (The linkages between research, education, extension services and end users need to strengthened, for better knowledge creation and transfer. Need for more efficient and qualified advisory service), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
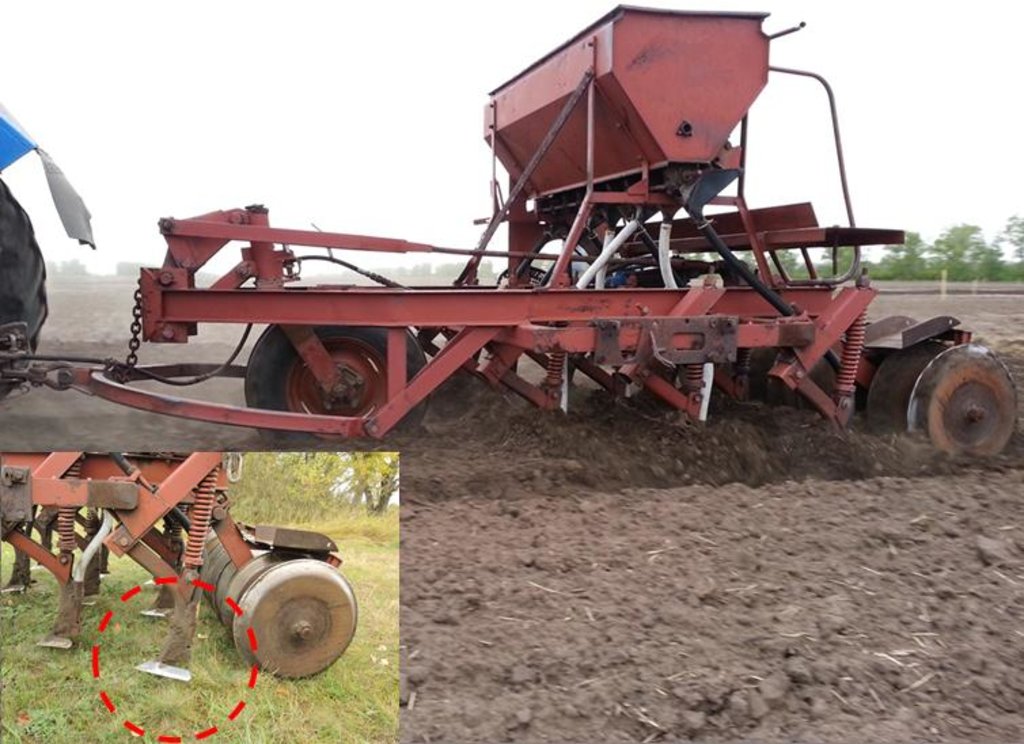
Soviet Seeder SZS 2.1 with wing shares for shallow soil mixing and seed bed preparation.
Location: Poluyamki. Altai Krai
Date: 20.05.2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Mulching
Material/ species: stubble cultivation with disc harrow or harrow weeder
Quantity/ density: 1/year
Green manure
Material/ species: pea
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: fertilization with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: (100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-raps
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stubble cultivation | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | september |
| 2. | Seeding | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | late april/early may |
| 3. | Seeding (extension) | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | |
| 4. | Pest management | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | period of vegetation |
| 5. | Pest management (extension) | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | |
| 6. | Harvest | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | september |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,34 | 4,34 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 37,4 | 37,4 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | fuel | ha | 1,0 | 47,34 | 47,34 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 25,3 | 25,3 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 30,83 | 30,83 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | pesticides | ha | 1,0 | 9,42 | 9,42 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 154,63 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The costs refers to 1ha land of the test field in Poluyamki.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The highest cost factors of minimum tillage are equipment, fuel, fertilizer and seeds. Compared to the conventional deep ploughing often without fertilizer application, fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
- មានខ្លាំង
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- មានបុគ្គលិក (ក្រុមហ៊ុន, រដ្ឋ)
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the agricultural sector are not so attractive for woman.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតធំ
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
mainly for initial investments and herbicides in the first years
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
but increase of costs for herbicides and fertilizer; decrease for fuel and labor
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Increase use of herbicide applications
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
particular necessary in the first years after the imlementation of the minimum tillage system
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region.
ការកាត់បន្ថយជម្លោះ
contribution to human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Technology makes a contribution to the long-term productivity of the soil – the most important factors in the rural areas of the Kulunda region. Furthermore, it leads to an increase in efficiency and to an improvement of the economic situation of farms, which might lead to a decrease in out-migration of the youth.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
រំហួត
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
ល្បឿនខ្យល់
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
Increased use of herbicide application
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Especially in the first years after the implementation of the minimum tillage system.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
there is a higher content of soil moisture under minimum tillage than under traditional ploughing especially in dry weather periods / drought periods.
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | មិនល្អ |
មតិយោបល់:
The increase of air temperature and wind lead to an increase of the evapotransporation rate and consequently, as well as rainfall decrease and droughts, to a decrease of soil water content that is one of the most important limiting factor in crop production. The minimization of soil tillage intensity helps to reduce the evapotranspiration rate and thus leads to a higher soil water content. The stubble slow down the wind, that protect the soil against erosion and reduce the evapotranspiration rate.
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms/ sites where minimum tillage was tested were already interested in conservation technologies and were able to invest in new machinery, which is not representative of the whole Kulunda region. There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers.
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. An advantage of the tested Adapted Soviet System in contrast to the Modern Soviet System is the less need for new machinery through the use of old Soviet machinery.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through the mulch layer |
| Protection of soil organisms thus ensuring natural soil forming processes |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations. |
| A great advantage of the tested ‘minimum tillage’ in contrast to ‘no till‘ is that the former needs no new machinery because of the use and adaptation of old Soviet machinery. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Need for comprehensive system knowledge and risk of significant crop losses in case of incorrect implementation | Knowledge transfer, Capacity building and extension services, State support (subsidies for new technologies) |
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| Challenging straw management that leads to higher risk of fungal infestation and poorer field crop emergence | Good straw management: effective straw chopping and spreading as well as stubble cultivation for an optimal straw/ soil ratio. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Vocational Training [ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី]
Regular in-service training of land use specialists and farm managers in the fields of sustainable land use management, and monitoring in the agrarian sector.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Peter Liebelt

Field days [ប្រទេសរុស្ស៊ី]
Field days are events for regional stakeholders, mainly farmers in the study area, to discuss their demands regarding scientific help, and to be informed about the activities and results of new methods and technologies for conservation agriculture.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Peter Liebelt
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល