Indigenous Management of Tapia Woodlands [ប្រទេសម៉ាដាហ្គាស្កា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Unknown User
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1359 - ប្រទេសម៉ាដាហ្គាស្កា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Kull Christian
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University
ប្រទេសអូស្ត្រាលី
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
School of Geography and Environmental Science, Monash University - ប្រទេសអូស្ត្រាលី1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
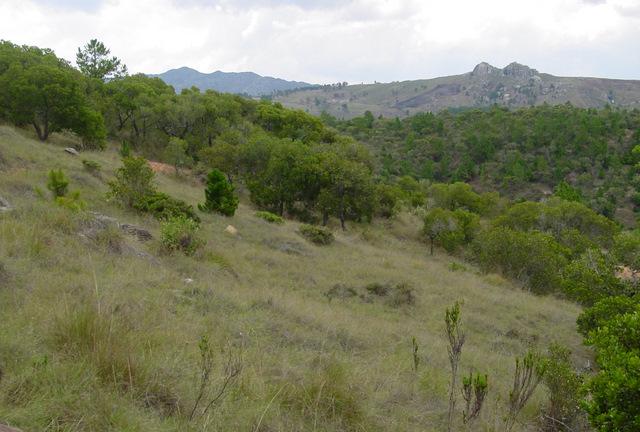
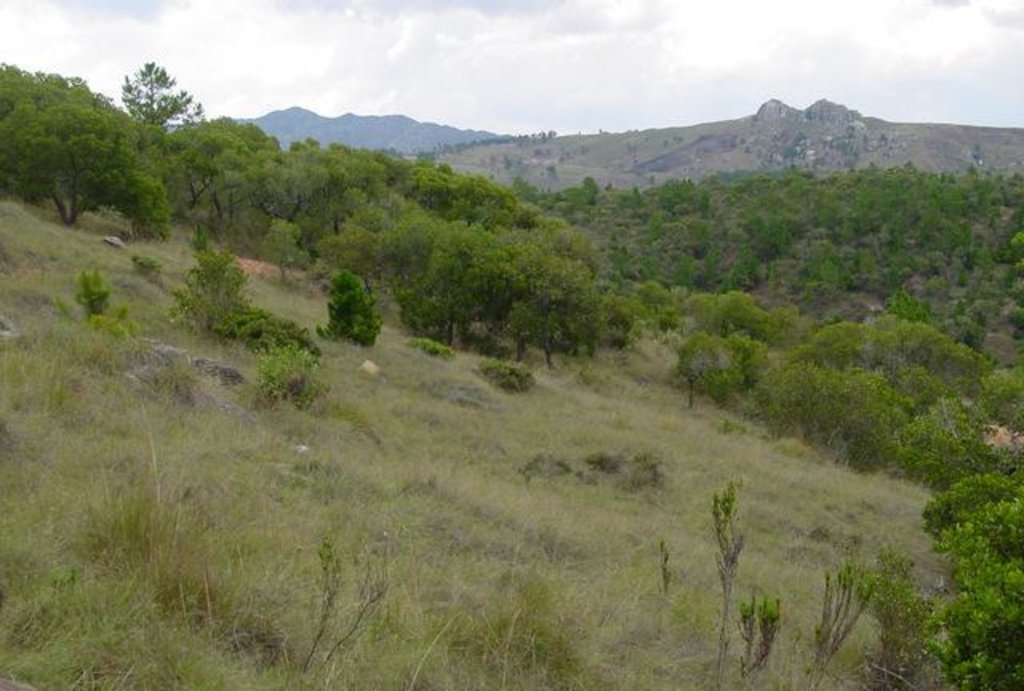
For centuries, the population of the highlands of central and south-western Madagascar has sustainably managed and conserved the local tapia woodlands.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
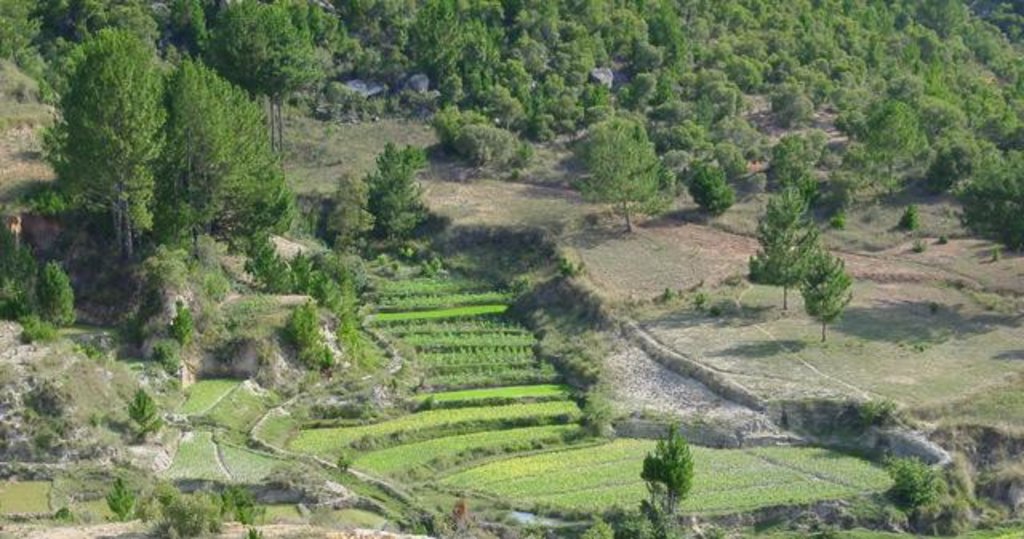
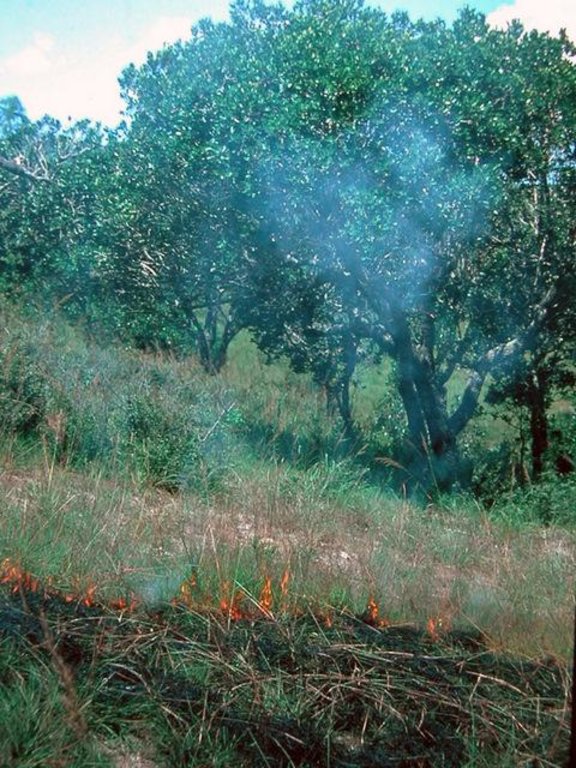
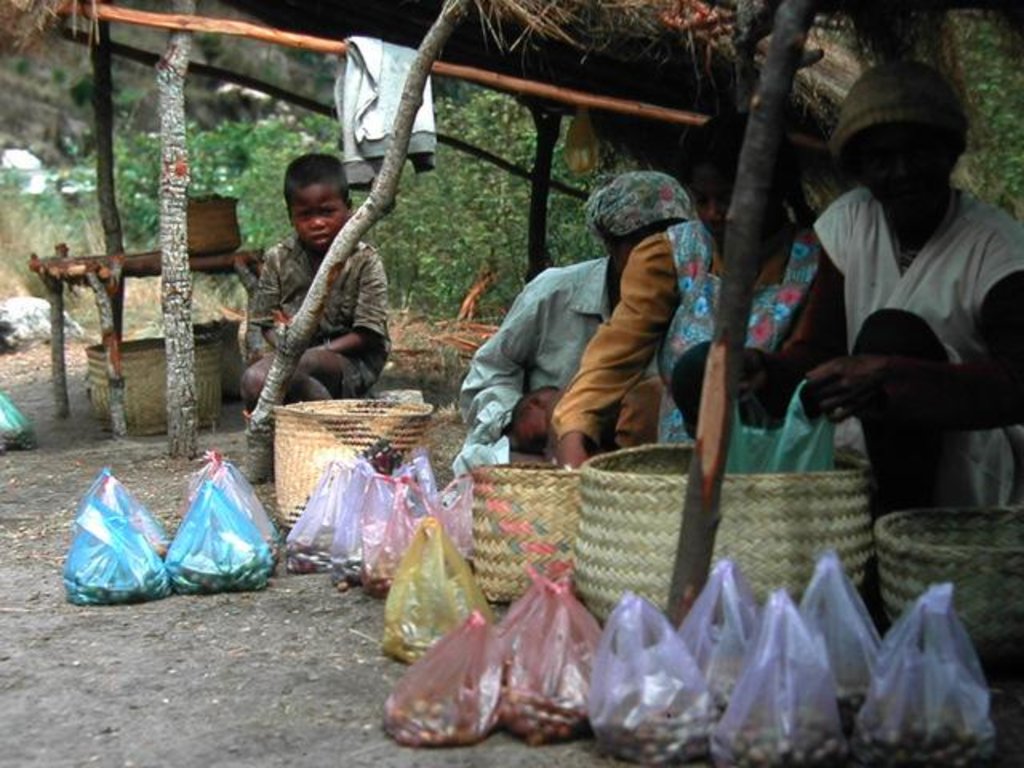
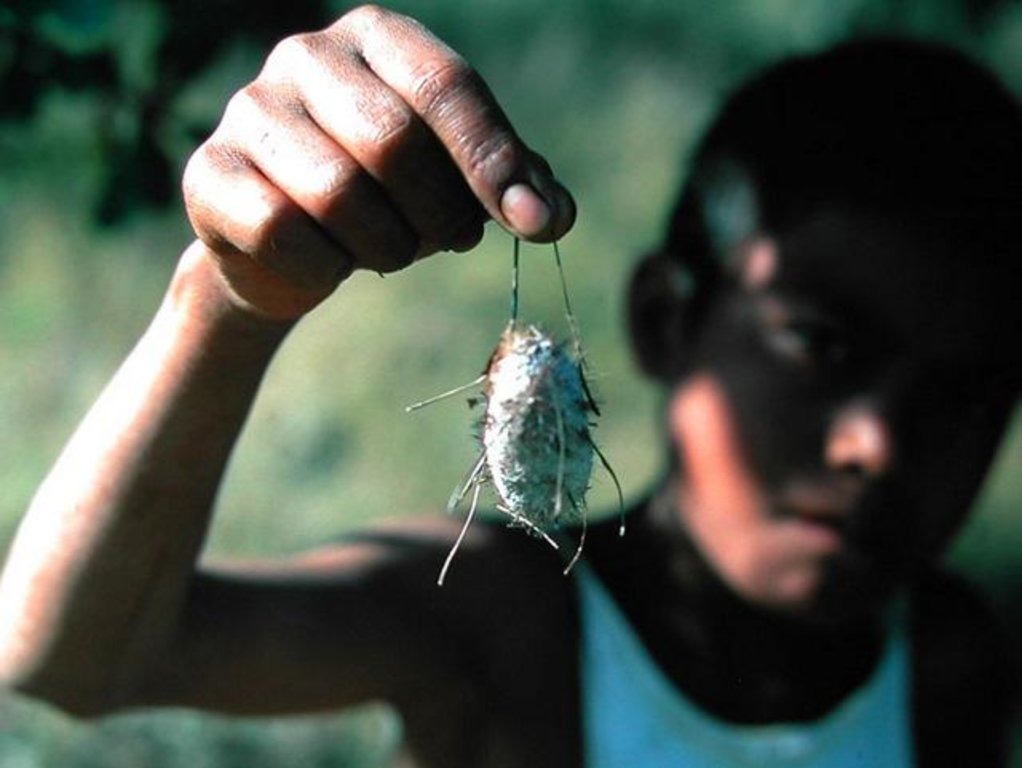
These woodlands play an important economic role as a source of non-timber forest products (NTFP) such as wild silk, fruit, mushrooms, edible insects, and herbal medicines. Tapia trees (Uapaca bojeri) comprise up to 90% of all trees in these woodlands, bear an edible fruit, and their leaves nourish an endemic silkworm (landibe). Landibe silk is used to produce ritual burial shrouds throughout the highlands. Trading silk products and tapia fruits is a crucial source of cash income for the local communities. The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting. Burning favours the dominance of pyrophytic (fire-tolerant) tapia trees and protects silkworms from parasites. Selective cutting of non-tapia species and pruning of dead branches also favours tapia dominance and perhaps growth. Other common species include the endemic Sarcolaena eriophora and the invasive Pinus patula/khasya. The Tapia woodland is clearly an anthropogenically shaped forest. However, the creation and maintenance of the woodlands should be seen as positive transformation rather than a form of degradation.
Local and state-imposed regulations protect the woodlands from overexploitation. The Forest Service has placed restrictions on forest cutting and burning while allowing for traditional use rights. The collection of forest products is regulated through a type of common-property regime. For example, fuelwood collection is limited to dead trees or fallen branches. It is forbidden to break off large branches to access cocoons. Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសម៉ាដាហ្គាស្កា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Col des Tapia
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Antsirabe and Ambositra
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានសាយភាយពាសពេញតំបន់ណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់ទំហំផ្ទៃដីអនុវត្តន៍ (គិតជា គ.ម2):
2600,0
មតិយោបល់:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2600 km2.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- ច្រើនជាង 50 ឆ្នាំមុន (ប្រពៃណី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- ដីព្រៃឈើ និងដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ

ដីសម្រាប់ចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
- Sustainable forest management
ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ / ដីព្រៃ៖ បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទនៃការគ្រប់គ្រង:
- កាប់តែមួយចំនួន
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ឈើហ៊ុប
- អុស
- ផ្លែឈើ និងគ្រាប់ធញ្ញជាតិ
- ផលិតផលព្រៃផ្សេងៗ
- វាលស្មៅ
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduction of vegetation cover; Quantity biomass decline
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Other type of forest: sustainable forest management
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងព្រៃធម្មជាតិ និងព្រៃពាក់កណ្តាលធម្មជាតិ
- ការចិញ្ចឹមឃ្មុំ, វារីវប្បកម្ម, ការចិញ្ចឹមបសុបក្សី, ទន្សាយ, ដង្កូវនាង ។ល។
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: (traditional practice)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (children often harvest fruit; silk cocoon harvest is easy)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The tapia woodlands are maintained by the local villagers through burning and selective cutting
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | N |
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective cutting of non-tapia species, especially invasive pines | |
| 2. | Pruning of dead branches | |
| 3. | Controlled burning mainly through understory fires after the rainy season | Jan-May |
| 4. | Collection of non-wood forest products such as fruits, medicinal plants, mushrooms, berries, insects, and hunting of mammals etc | Sept.-Dec |
| 5. | Collection of landibe silkworm twice a year. The cocoons are cooked, spun and woven into silk fabric | Nov-Dec and May-June |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 20,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 20,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Traditional method; no establishment phase and costs.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The estimation of costs is difficult - fruit are gathered over a two month period by school children going out for an hour in the early morning each day; the silkworms are collected by individuals (usually experienced collectors) on free days. In some areas, projects exist that run silkworm nurseries, establish firebreaks in the woodlands, grow and plant tapia seedlings, and finance the purchase of silk looms. These projects obviously require much larger budgets.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
7 months of dry season
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Slopes on average: hilly (16-30%), steep (31-60%), very steep (>60%)
Altitudinal zones: 500-2000 m a.s.l.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil texture is coarse/light (sandy) (silica-rich soils compared to the main lateritic soils of highland Madagascar)
Soil fertility is low ( mostly nutrient-poor or rocky soils )
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Population density: 20-40 persons/ km2 in the central highlands and 10-20 in the western highlands
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Woodlands are officially state-owned, but in practice managed by neighbouring communities (either unofficially, or increasingly through community-based management contracts
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Stable supply of fuelwood
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Through selling silk-fabrics and other NTFP
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Production of NTFP as important dietary supplements
Provision of medicinal plants
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Thorugh the forest products
ឱកាសវប្បធម៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Sacred forest
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Endemic biodiversity
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
មតិយោបល់:
Silk and fruit harvests vary from season to season but drivers are poorly understood (could include precipitation and temperature)
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
មតិយោបល់:
The larger rainy season silk harvest provides crucial cash income during the meagre months before the rice harvest. In 1998 the price of 200 cocoons was between US$ 0.10-0.15. For a basket of Tapia fruits villagers earned between 0.02-0.06 US$/ kg. During
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on adoption trend: see Annex 3
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Thanks to these protective regulations, forest boundaries are mostly stable, and woodland density has increased in several cases |
| La vente des produits en soie et des fruits de Tapia est une source de revenus capitale pour les communautés locales |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Partly individual indiscriminate cutting and/or strong use of fires leads to overuse of the forest resources | needs clear regulations, guidelines and observation of the rules by the local authorities as well as awareness raising about the multiple benefits of the forests. As long as the communities continue to be interested in the forests and its products, they will protect it from destructive cutting. |
| Invasion of exotic tree species such as pine and eucalyptus from private and village woodlots | the forest service has rightly been encouraging communities to cut these trees from the tapia forests without the need for complicated permits. |
| Insecure land use rights | in 1996 a new legislation opened the way to officially decentralize management of state-owned renewable natural resources to adjacent communities, which would aid woodland protection by increasing stakeholder involvement. |
| In some areas, silkworm populations have been very low for decades | recent projects seek to establish silk nurseries and reintroduce the worm |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Kull CA (2002): The ‘Degraded’ Tapia Woodlands of Highland Madagascar: Rural Economy, Fire Ecology, and Forest Conservation. Journal of Cultural Geography Spring/ Summer 2002.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល