Gully rehabilitation [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Qobiljon Shokirov
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1541 - ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Boev Jahonbek
Tajik Soil Institute
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថានឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - ប្រទេសកៀហ្ស៊ីស៊ីស្ថាន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Gulniso Nekushoeva
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
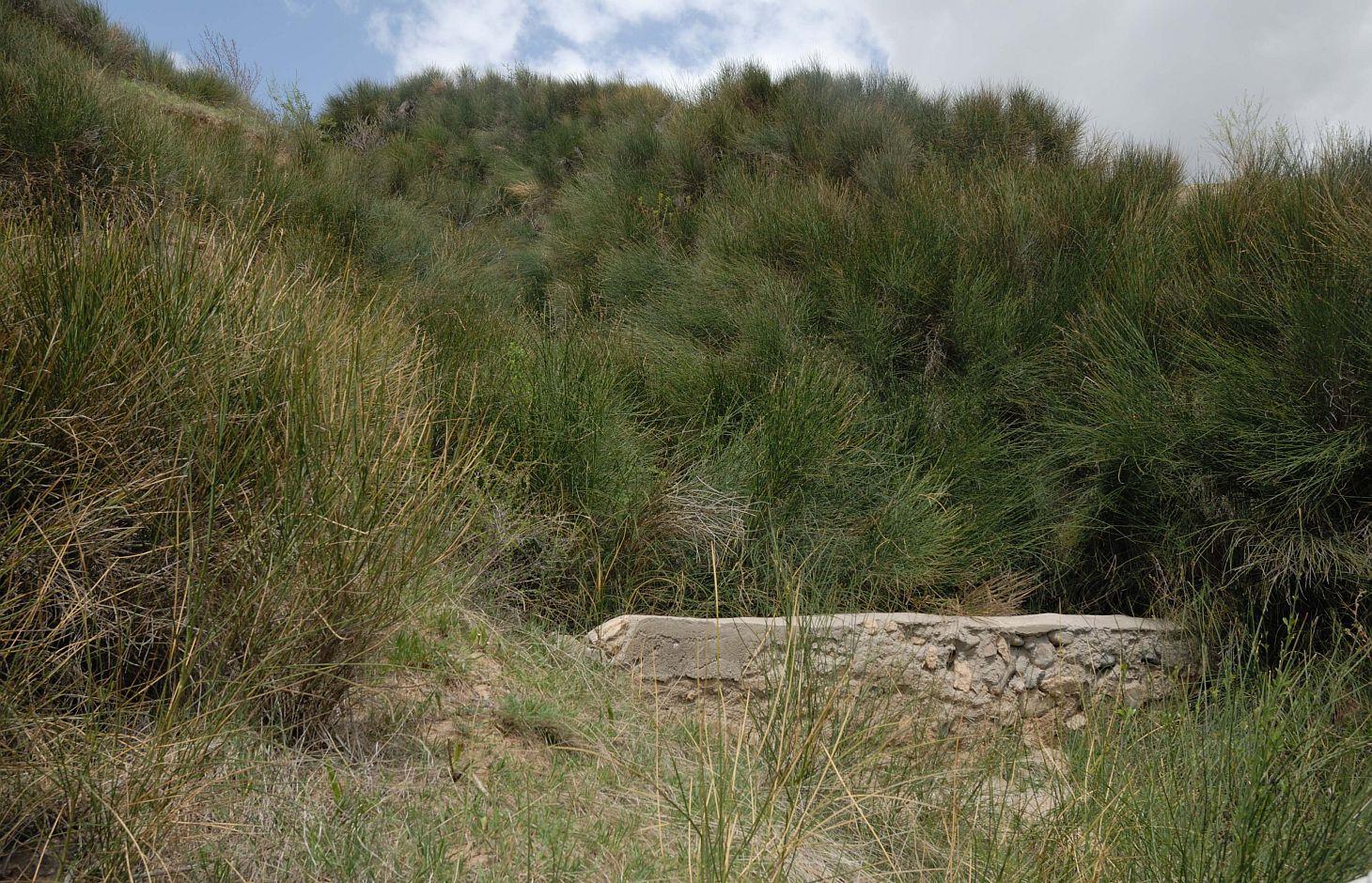
Gullies are stabilized through the establishment of a gabion and the plantation of spanish drok (Spartium junceum L).
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The research station of the Soil Science Institute tested the stabilisation of large gullies created by water erosion through the plantation of Spanish drok (Spartium junceum L). The plantation of Spanish drok was introduced in 1972 for the first time in the research field station. Spanish drok is a perennial plant and has the ability of spreading fast through its roots and also via seeds. Most of the gullies are covered with Spanish drok by now. In total 150,000 seedlings were planted at the research station.
Purpose of the Technology: Water erosion is highly threatening croplands by washing away the fertile topsoil. Severe gullies have formed on the hilly slopes. The research station of the soil institute therefore selected a number of gullies to test different techniques of rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In a first step a survey of gullies in the vicinity of the research station was conducted in order to determine an appropriate place for testing the stabilization. Spanish drok was planted and spread very fast through vegetative underground reproduction until the whole gully was covered. A gabion made out of stone and concrete was constructed at the foot of the gully. It contains a pipe to allow for outflow of excess water. Maintenance of the technology is less cost efficient and doesn't involve much cost associated activities.
Natural / human environment: The positive results of the implementation of this technology are very important as there is a great need for spreading it to other areas suffering from the same problems in Tajikistan. Spanish drok is generally not available in Tajikistan. Nowadays, the research station is providing seedlings for sale to interested farmers with a cost of roughly $ 0.40 per seedling.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
RRS
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Javanon, Karsang
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
through the Karsang field research station
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
- spanish drop
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period from month to month: April through November
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): loss of arable land, development of gullies, water erosion
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- វិធានការអនុវត្តកាត់ទទឹងទីជម្រាល
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wg: ការកកើតឡើងនូវកំទេចកំទីដីស្រទាប់ក្រោម
- Wo: ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពកន្លែងឆ្ងាយ
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It usually rains in March-April with duration of 20-45 minutes)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Wind storms in winter), droughts (Hot summer months without rain)
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
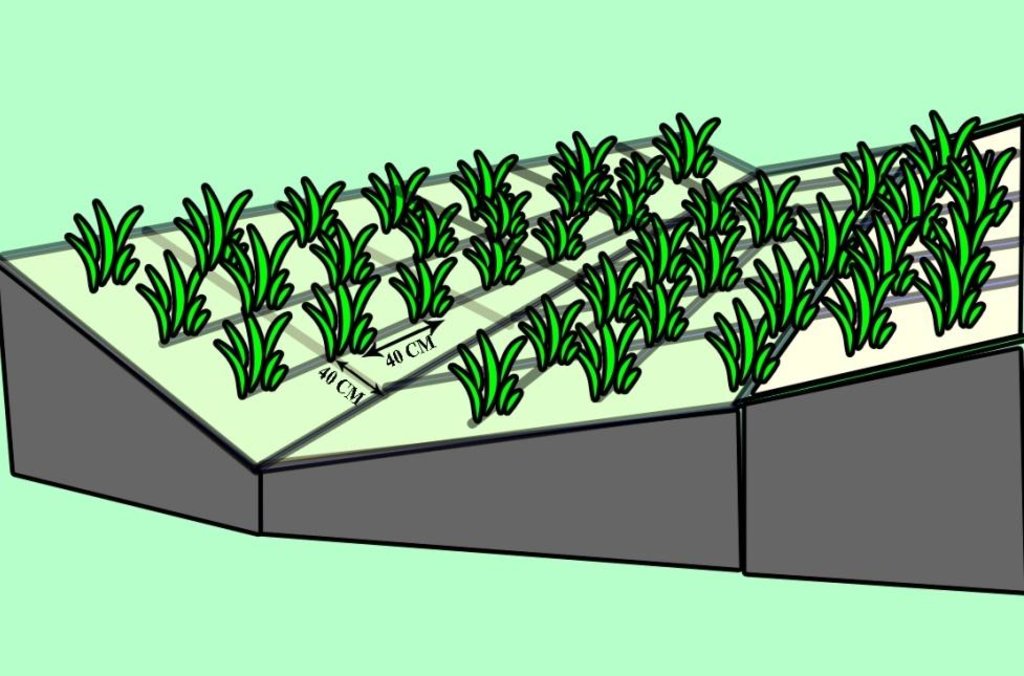
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
Scheme of how the Spanish Drok was planted on a eroded slopes of Karsang Research Field Station.
Location: Karsang Research Field Station. Javonon, Karsang
Date: 16-07-2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 5000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: Spanish drop.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3.5
Construction material (stone): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
Construction material (concrete): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Q. Shokirov
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Somoni
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
4,5
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
7.00
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of area | early spring |
| 2. | Planting of spanish drop | early march |
| 3. | Construction of gabion |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Selection of area | Persons/day | 30,0 | 30,0 | 900,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Planting of spanish drop | Persons/day | 36,0 | 30,0 | 1080,0 | |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction of gabion | Gabion | 1,0 | 700,0 | 700,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Stones | Gabion | 1,0 | 800,0 | 800,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 3480,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 773,33 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
Tajik Soil Institue
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | As the plant spreads through root propagation, the dispersal has to be limited by removing some of the plants every year |
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
buying seeds, tools, additional labor cost needs to be filled out more.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីផត
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- សម្រាប់ហូបក្នុងគ្រួសារ (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង)
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
90% of the land users are poor.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
មតិយោបល់:
Research station belongs to the State, but land is leased to the local farmers for use.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Spanish drok is used as firewood, increased availability
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Prevents gullies from spreading and destroying production area
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No need to take care of eroded land every year
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Farmers are aware of erosion problems and benefits of Spanish drok
Livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Many farmers have now understanding of mitigating soil erosion by water with the use of Spanish Drok.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
រំហួត
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
Buffering/សមត្ថភាពចម្រោះ
ខូចខាតដល់ស្រែអ្នកជិតខាង
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
ប៉ះពាល់តិចតួចបំផុត
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Full establishment of the Spanish drok takes about 10 years, however, through the establishment of the gabion some immediate benefits occur
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
NA
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology was implemented through the research station using their employees.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Earlier Spanish drok was not yet known among the farmers as it is an exotic species. A handful of farmers have been interested and adopted the technology in their plots. According to farmers from the station more people are interested applying such technologies as a protection for soil erosion and establishment of gabions.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Affordable technology for land restoration and degraded plots. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Effectively puts a halt to water erosion. |
| The bushes provide valuable firewood for the local land users. |
| A special microclimate is created through the establishment of the plants with humidity being preserved all year long and birds and bees seem to use it as a preferred habitat. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The planting material is generally not available in Tajikistan, only now the research station is selling it to interested farmers, however, availability is still very localised. | Farmer to farmer spreading of planting material in addition to providing planting material to the different tree nurseries in the country. |
| Spanish drok is very easily inflammable in the dry summermonths due to essential oils which can pose a potential risk. | Good care has to be taken during the dry period and maybe some warning signs put up to tell people not to drop their cigarette stumps. |
| For the coverage of a whole gully with spanish drok about 10 years are needed as it happens through natural root propagation. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [ប្រទេសតាហ្ស៊ីគីស្ថាន]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Gulniso Nekushoeva
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល