Crop Residue Management [ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ GERBA LETA
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Tabitha Nekesa, Ahmadou Gaye, Siagbé Golli
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Sally Bunning
Hafte Midhani
technologies_6644 - ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
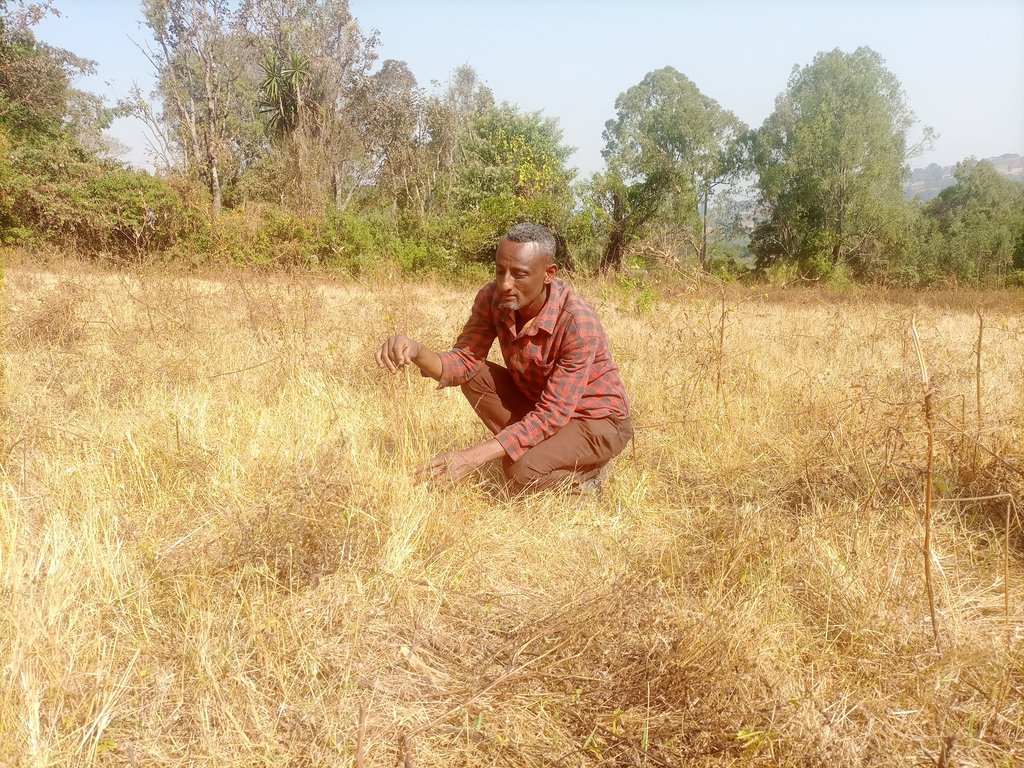
Woyessa Habtamu
Farmer
ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - ប្រទេសកេនយ៉ា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
1.5 ការយោងទៅលើកម្រងបញ្ជីសំណួរ (មួយ ឬច្រើន) នៃវិធីសាស្ត្រផ្សព្វផ្សាយ SLM (ដែលបានចងក្រងដោយទស្សនៈពិភពលោកស្តីពីវិធីសាស្ត្រ និងបច្ចេកទេសងអភិរក្ស WOCAT)

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ GERBA LETA
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
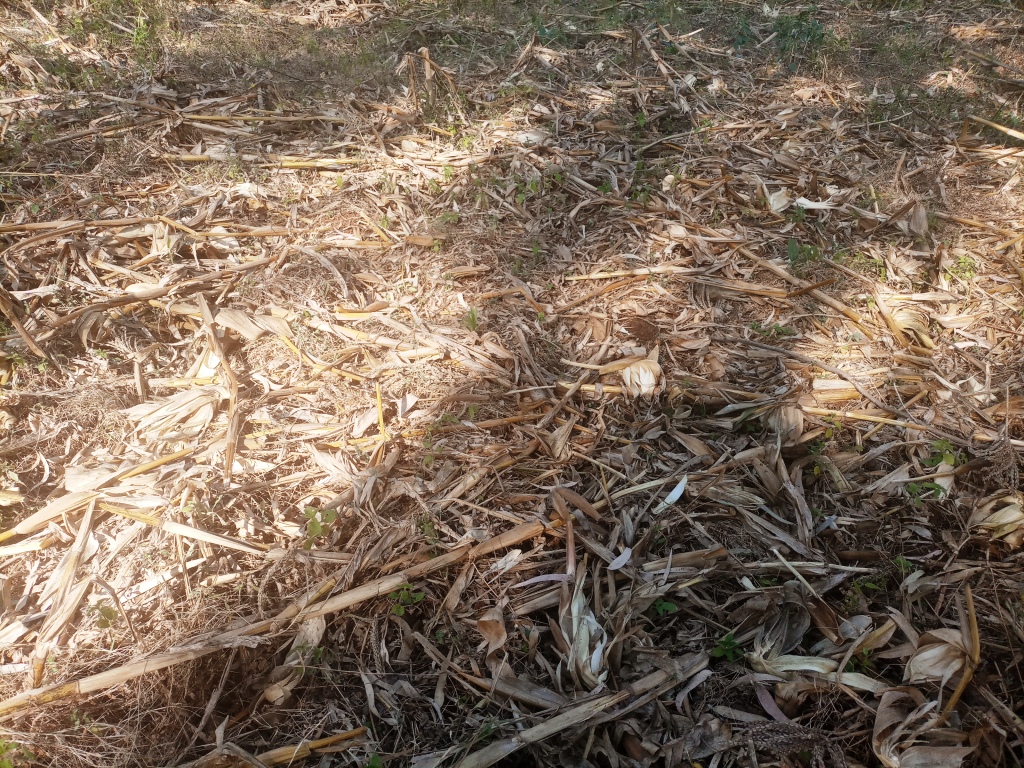
Crop residue management involves leaving stover and other trash from cereal crops (including tef, wheat and maize), as well as haulms of legumes, in the field. Crop residues keep the soil covered, retain organic matter and moisture in the soil, and help to ensure better production.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Crop residue management involves leaving stover and other trash from cereal crops (including tef, wheat and maize), as well as haulms of legumes, in the field. Crop residue (CR) management is integral to soil health: it yields multiple benefits such as mitigating the risks of soil loss to water erosion, reducing the decomposition of organic matter and storing extra carbon. It also increases the fertility status of degraded soils and helps to improve soil structure and moisture properties. Degraded soils are at risk of tillage, water, and wind erosion. Soils degrade quickly when not covered and when no effort is made to increase organic matter levels or improve soil structure. Crop residue management plays an important role in arresting soil degradation and improving soil properties, and eventually increasing crop production. Therefore, it has positive economic and ecological functions. The aim of applying this technology is to improve soil fertility, reduce soil acidity and demands for synthetic fertilizers. Overall, crop residue management allows land users to sustainably use their land over a long period without losing its productive potential. In this part of Ethiopia, land users used to leave maize and millet stover in the fields but this is challenged by the prevalence of free (open access) grazing. Thus, controlling grazing is one prerequisite to ensuring adoption of the technology. Monocropping also reduces biomass production. Land users appreciate the extra grain yields from crop residue-rich farms. CR management also retains moisture and enables early tillage operations. In summary, the application of appropriate CR management provides multiple benefits. It mitigates the risks of erosion, reduces excessive mining of CR, reduces the rate of decomposition of organic matter, increases the fertility status of degraded soils, and increases crop production and sustainable productivity.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
The photo portrays one of the many crop residue management practices applied on different crops.
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
Videos of this technology is not documented.
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Oromia
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- 0.1-1 គម2
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2015
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ជាផ្នែកនៃប្រព័ន្ធប្រពៃណី (> 50 ឆ្នាំ)
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+) of the GIZ.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី (និទាឃរដូវ)
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោតសាលី
- cereals - Tef
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងជីជាតិដីតាមបែបចម្រុះ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A3: ការរក្សាស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ
- A6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់
- A7: ផ្សេងៗ
A3: ប្រព័ន្ធភ្ជួររាស់ខុសៗគ្នា:
A 3.3: Full tillage (< 30% soil cover)
A6: បញ្ជាក់ពីការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់:
A 6.4: រក្សាទុក

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
មតិយោបល់:
With tillage, the crop residue is incorporated well into the soil system. It improves soil structure by contributing organic matter with the benefits of facilitating infiltration and reducing surface runoff.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)
- Ca: អាស៊ីតកម្ម

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pc: ការហាប់ណែន
- Ps: ការស្រុតចុះនូវសារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៃដី ការពន្លិចដី

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
មតិយោបល់:
It ensures the sustainable productivity potential of the soil.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
4 sanga
បើសិនប្រើឯកតាតាមតំបន់ សូមបញ្ជាក់តម្លៃបម្លែងវាទៅជាហិកតា (ឧ. 1 ហិកតា = 2.47 អា)៖ 1 ហិកតា =:
1ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
ETB
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
53,12
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mowing the crop by leaving some proportion on the ground. | Harvesting |
| 2. | Keep of livestock grazing | Dry season |
| 3. | Plow over the crop residue early on. | Late in the dry season. |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
The technology needs changing the mindset of the land users than the money/finance for the establishment and maintenance of it. Uniform distribution of rainfall is essential to plan the plowing time to incorporate the residue well into the soil.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Keep the farm with crop residue intact from livestock | During off-season. |
មតិយោបល់:
Prohibiting the use of a proportion of crop residue for fuel, construction, and livestock feed is enough to put in place the technology.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
ប្រសិនបើមិនអាចបំបែកតម្លៃដើមក្នុងតារាងខាងក្រោមទេ សូមផ្តល់នូវតម្លៃប៉ាន់ស្មានសរុបក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសនោះ:
2500,0
មតិយោបល់:
Allocated some money just to keep off the interference of livestock to the farmland during the off-season. The cost can be covered by land users themselves but need awareness creation on SLM using crop residue as one of the best practices.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Change of the cost is related to the inflation and economic instability.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
1947,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
The area received summer maximum rainfall.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Bedele
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
The uniform distribution of rainfall is helpful to incorporate the residue in time.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Since the farming at stallholder level is manual using traction power, the introduction of this technology is not obstructed by the topography as long as the land is under farming.
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- ប្រើកម្លាំងសត្វ
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
The land users engage in livestock business as off-farm income.
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- អាស្រ័យផលសេរី (មិនមានការកំណត់)
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
The land is inherited from the predecessors, though there was a land reallocation program in the past.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
មតិយោបល់:
Land users are benefited from various financial institutions to access credit and other services. Various credit institutions and revolving funds were mentioned my the land users.
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពដំណាំ
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The purpose is to use less of crop residue for soil amendment than as fodder.
គុណភាពចំណីសត្វ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The purpose is to reduces
ផលិតកម្មសត្វ
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
As it improves soil structure, moisture retention capacity, etc., the practice reduces risks of crop failure.
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃផលិតផល
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
គុណភាពទឹកបរិភោគ
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
ស្ថានភាពសុខភាព
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The health condition is convergent with considerable harvest and food security.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
បរិមាណទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
ប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី/ ដង្ហើមទឹក
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The health condition is convergent with considerable harvest and food security.
រំហួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The ground cover by crop residues inevitably contributes to the reduction of evaporation.
ដី
សំណើមដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ការកើនឡើងដី
ដីប្រេះ
ដីហាប់
វដ្តនៃសារធាតុចិញ្ចឹម/ការទទួលបាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improves on a gradual basis.
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
ជាតិអាស៊ីត
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ប្រភេទសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជំរក
ការគ្រប់គ្រងកត្តាចង្រៃ/ ជំងឺ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Crop residue may host some insects but obstruct the movement of others.
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃគ្រោះរាំងស្ងួត
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Increasing the moisture retention capacity of the soil improves crops' resilience to droughts and other adversity.
ការបំភាយនៃកាបូន និងឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Accumulation of crop residue increases carbon storage via the reduction of emissions.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
No facts are available to support the allegation. Besides, it needs long-term observation and documentation.
លំហូរទឹកដែលអាចប្រើប្រាស់បាននៅរដូវប្រាំង
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Impact of greenhouse gases reduced with accumulation of crop residues.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវប្រាំង | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | មិនស្គាល់ |
| ការមានបញ្ហាសត្វល្អិត/ដង្កូវ | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| អូសបន្លាយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អណាស់ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Actually, the technology demands only labor costs for the protection of the farmland from grazing the leftover and to avoid illegal burning of crop residues.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
មតិយោបល់:
Land users adopted the practice and plow over the crop residue when the first shower of rainfall intercepted.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| It improves soil fertility on gradual basis. |
| It assists to reduce soil acidity. |
| Increases production and productivity. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Absorbs and retain soil moisture for the crop to rely on for growth and grain filling as a coping mechanism to the unpredictable distribution of rainfall. |
| It reduces soil temperature and smother the weeds. |
| Sequesters carbon, a beneficial for climate change/variability. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Create tillage inconvenience as mechanization is less common among smallholders. | Using the excessive residue as trash line support the purpose of soil and water conservation. |
| Free grazing system and multiple uses of crop residue challenges retention of crop residue. | Institutionalizing controlled grazing system is of paramount important. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Less fodder available for the livestock and other multiple uses of crop residues. | Limit the amount of crop residue to be retained on the farm to 15 to 30 percent of the total non-grain biomass produced in the farm. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
2
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
1
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
06/02/2023
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Renard, C. 1997. Crop Residues in Sustainable Mixed Crop/Livestock Farming Systems. CAB International, Walingford. ISBN 0 851991777
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://core.ac.uk › download ›
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
IIRR and ACT. 2005. Conservation Agriculture. A manual for farmers and extension workers in Africa. International Institute of Rural Agriculture, Nairobi; African Conservation Tillage Network, Harare.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
http://www.act-africa.org ›
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Best management practices: residue management
វេបសាយ:
http://omaf.gov.on.ca/english/environment/bmp/AF179.pdf
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
Similar to any other technologies. some questions in the questionnaire are not relevant to this particular technology. Meaning, the technology doesn't address every issue stated therein.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់

Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) [ប្រទេសអេត្យូពី]
The Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM) approach has been adopted under the Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+). It was introduced as a quick-win solution to increase both crop and biomass production through the incremental promotion of varied but complementary technology packages.
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ GERBA LETA
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល