Organic Agriculture (DOK Experiment) [ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Moritz Laub
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Jochen Mayer, Hans-Martin Krause
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Biologischer Landbau/ Biologische Landwirtschaft
technologies_7138 - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Research institut for organic agriculture (FiBL) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Forschungsanstalt Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon ART (Forschungsanstalt Agroscope Reckenholz-Tänikon ART) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីសឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ETH-Zürich (ETH-Zürich) - ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
Organic agriculture is a system of crop cultivation that uses biological methods of pest control and organic fertilizer as substitutes for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. It targets sustainability, enhancement of soil fertility, and biological diversity by aiming to close nutrient cycles while generally prohibiting synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, and growth hormones.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Organic agriculture is a globally applied technology practiced on agricultural land. It is carried out in 188 countries, with over 96 million hectares of agricultural land managed organically by at least 4.5 million farmers.
The main elements of this technology include the use of biological methods of pest control and organic fertilizer application, which replace chemical fertilizers and pesticides. It generally prohibits synthetic pesticides, antibiotics, synthetic fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, and growth hormones. The purpose of organic agriculture is to achieve sustainability in farming, enhancing soil fertility, increasing biological diversity and reducing the reliance on external inputs to agriculture, relying on nutrient recycling by applying manure and on biological nitrogen fixation from legumes. It also aims to provide a healthier and more environmentally friendly alternative to conventional farming practices. To establish and maintain organic agriculture, major activities include the application of organic fertilizers, crop rotation, and the use of pest-resistant plant varieties. Regular soil testing and monitoring of pest populations are also necessary. Certification of a farm as being officially organic is needed if the products are to be sold at a price premium.
Organic agriculture can improve soil health, reduce pollution of the surrounding environment, and contribute to biodiversity in the fields. Moreover, it can offer healthier food options and potentially higher income for farmers due to the premium prices of organic products. Land users appreciate organic agriculture for its environmental benefits and potential for higher income. However, some dislike the increased labour and time required, the 10-30% of reduction in yields, compared to conventional agriculture, as well as the need for a transition period before farms can be certified as organic and products sold at a premium price.
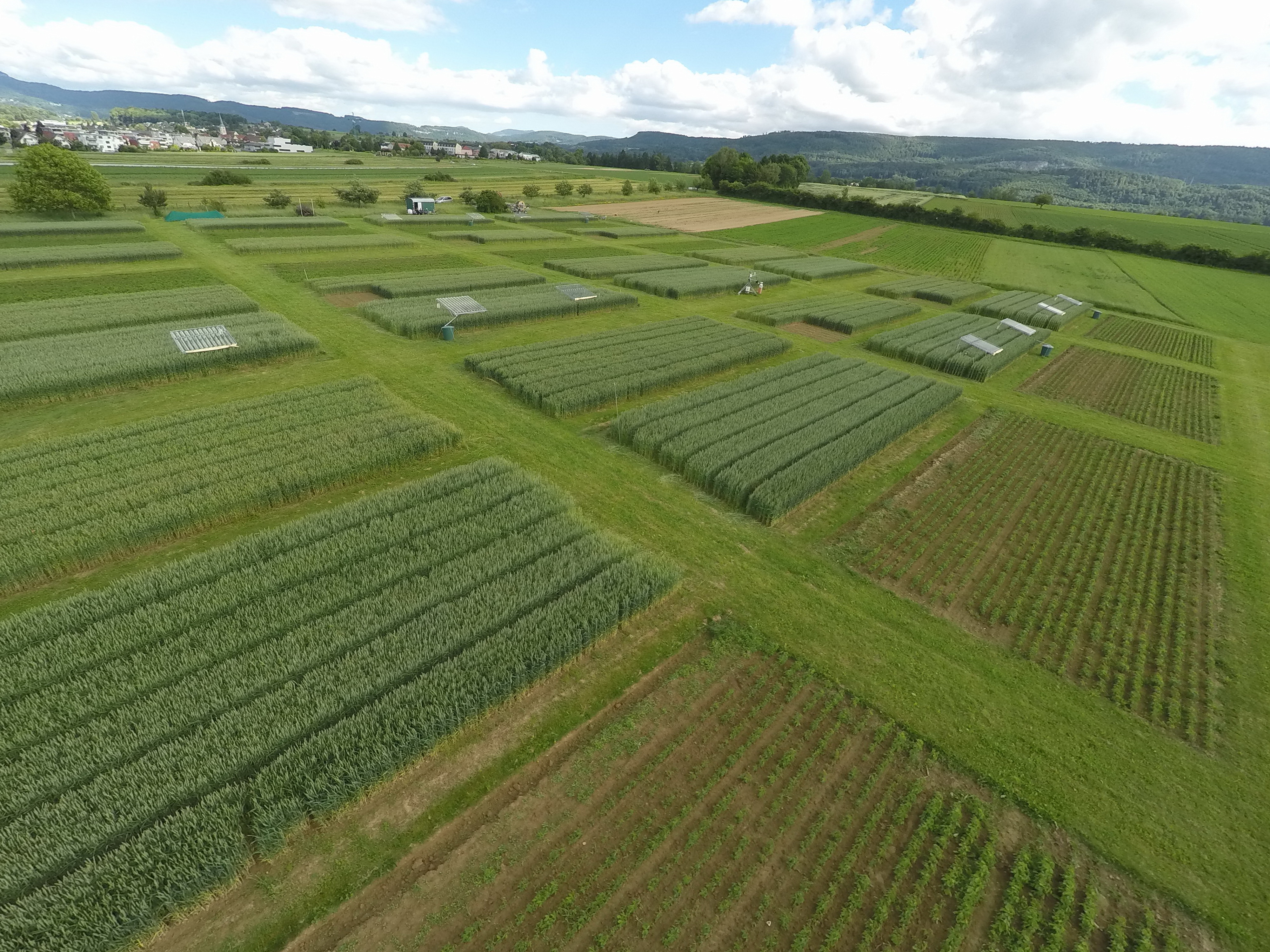
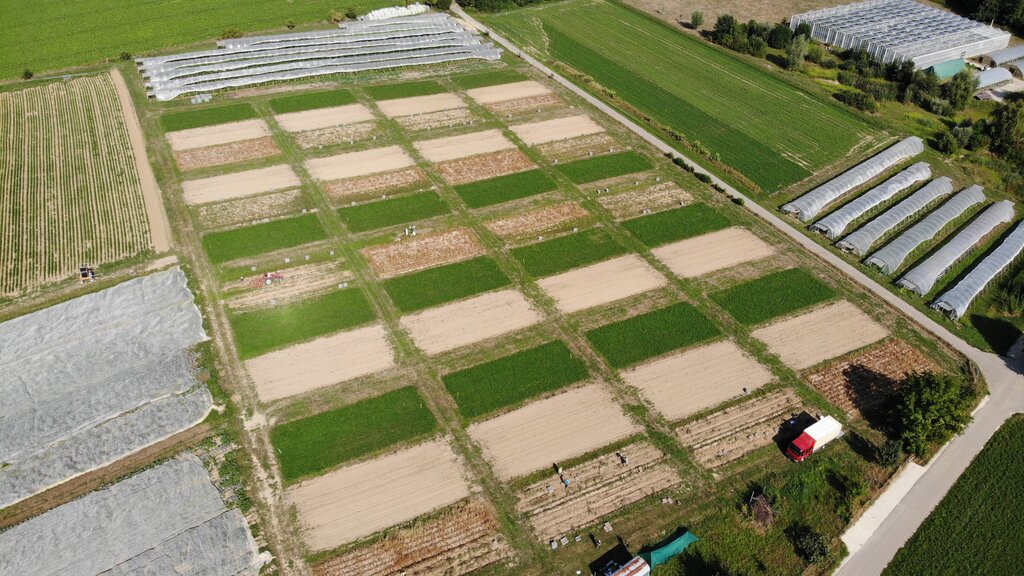
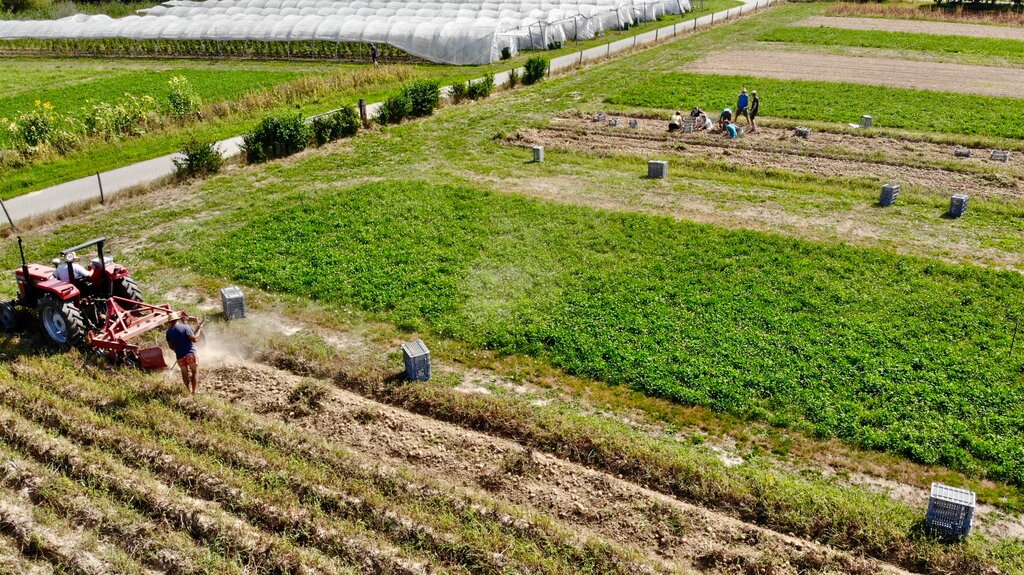
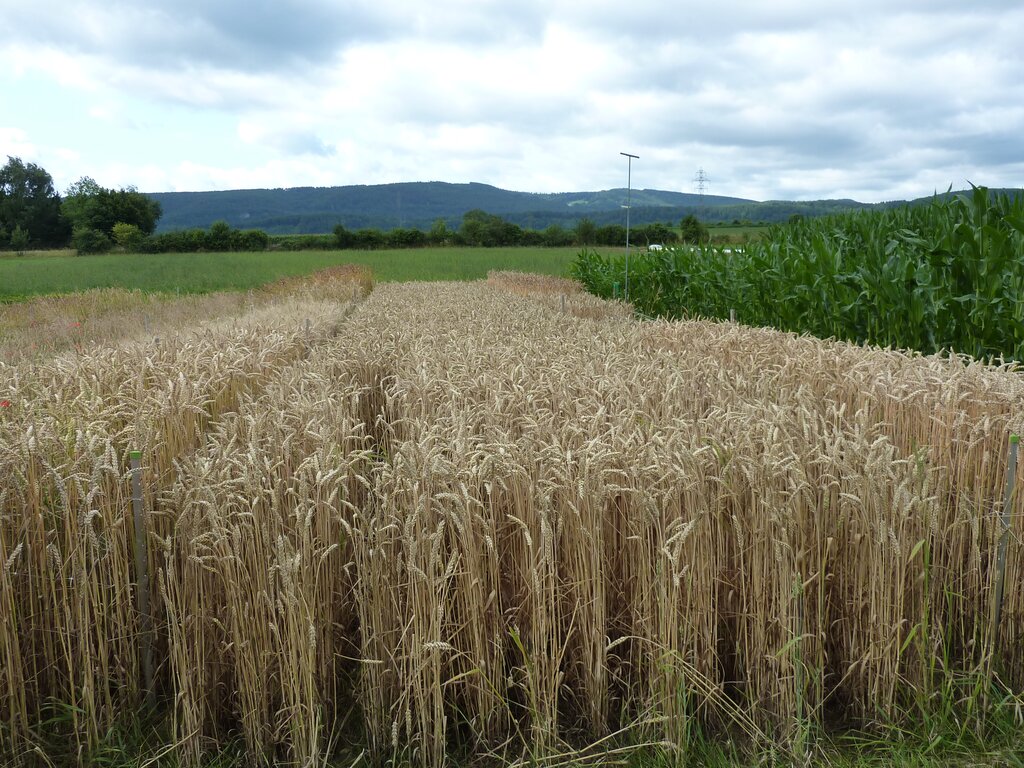
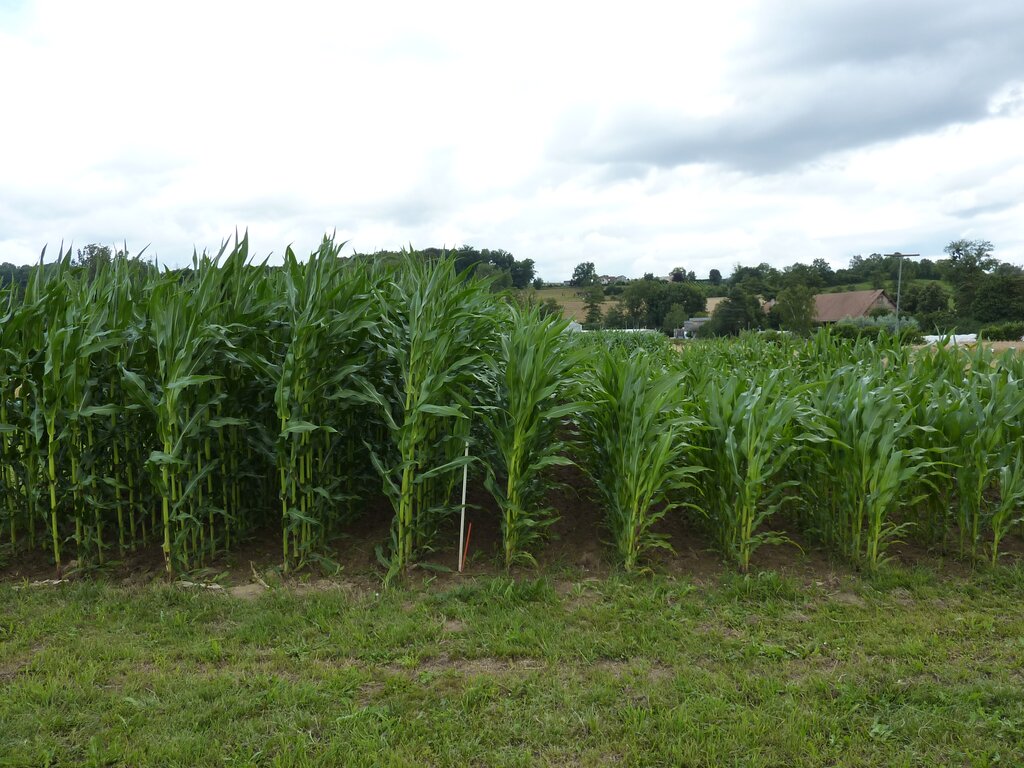
The DOK experiment presented here is representative of organic practices in the context of temperate regions (specifically, Switzerland and surrounding countries). It is jointly managed by the Research Institute of Organic Agriculture (FiBL), and by the Swiss Confederation's centre of excellence for agricultural research (Agroscope). The name "DOK Experiment" is derived from its main purpose, to compare three cultivation systems: Biodynamic (D), organic (O) and conventional (K) agriculture. These differ in terms of how they are fertilized (D: liquid manure, manure compost, biodynamic preparations; O: liquid manure, rotted manure; K: two variants, one with liquid manure, fresh or rotted manure, mineral fertilizer (CONFYM variant) and one with only mineral fertilizer (CONMIN variant)), as well as by plant protection (D and O: organic; K: chemical-synthetic). In addition to two fertilization levels of the three cultivation systems (half fertilization and standard practice fertilization), two controls are carried out, an unfertilized (N) and a purely mineral-fertilized variant (M). The experiment is spatially replicated four times. The results presented here refer to the conventional (K) and the organic (O) treatments at the standard practice fertilization level.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់សម្គាល់ទូទៅនៃរូបថត/រូភាព:
All photos are from the DOK experiment in Therwil.
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
DOK-Versuch: Biologische und konventionelle Landwirtschaft im Langzeitvergleich
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gDCLHxU0ijg
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
16/07/2014
ទីតាំង:
Therwil
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
Der DOK-Versuch - Eine Internationale Forschungsplattform (Juni 2015)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QYBS4Qj7T14
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
16/06/2015
ទីតាំង:
Therwil
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសស្វ៊ីស
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Basel
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Therwil
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
1978
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- ពេលកំពុងពិសោធន៍
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
This is a research site, investigating the benefits of organic agriculture.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្សប្រព័ន្ធអេកូឡូស៊ី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សង្គម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវសាលី (សិសិររដូវរងារ)
- ដំណាំចំណីសត្វ - ចន្ទល់ភ្នំ
- ពពួកសណ្តែក - សណ្តែកសៀង
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងបារាំង
ប្រព័ន្ធដាំដុះដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ:
ដំណាំស្រូវសាលី ឬប្រហែលវិលជុំជាមួយស្រូវ/ស្មៅ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
The typical crop rotation over the last three cycles was: silage maize, soybean, winter wheat, potato, winter wheat, and two years of grass-clover (Knapp et al. 2023).
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ប្រព័ន្ធដំណាំបង្វិល (ការដាំដំណាំវិលជុំ ការទុកដីចោលដើម្បីបង្កើនជីជាតិ កសិកម្មពនេចរ)
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- បញ្ចូលការគ្រប់គ្រងសត្វល្អិត និងជំងឺតាមបែបចម្រុះ (រួមទាំង កសិកម្មសរីរាង្គ)
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី
- A5: ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រាប់ពូជ បង្កើនប្រភេទពូជ
- A6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់
A6: បញ្ជាក់ពីការគ្រប់គ្រងកាកសំណល់:
A 6.4: រក្សាទុក
មតិយោបល់:
Comment to A5: It is aimed to use pest-resistant crop varieties, because chemical pesticides are not allowed in organic agriculture.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bs: សមាសភាពដែលមានគុណភាពនិងប្រភេទសត្វ/ការថយចុះនូវជីវចម្រុះ
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
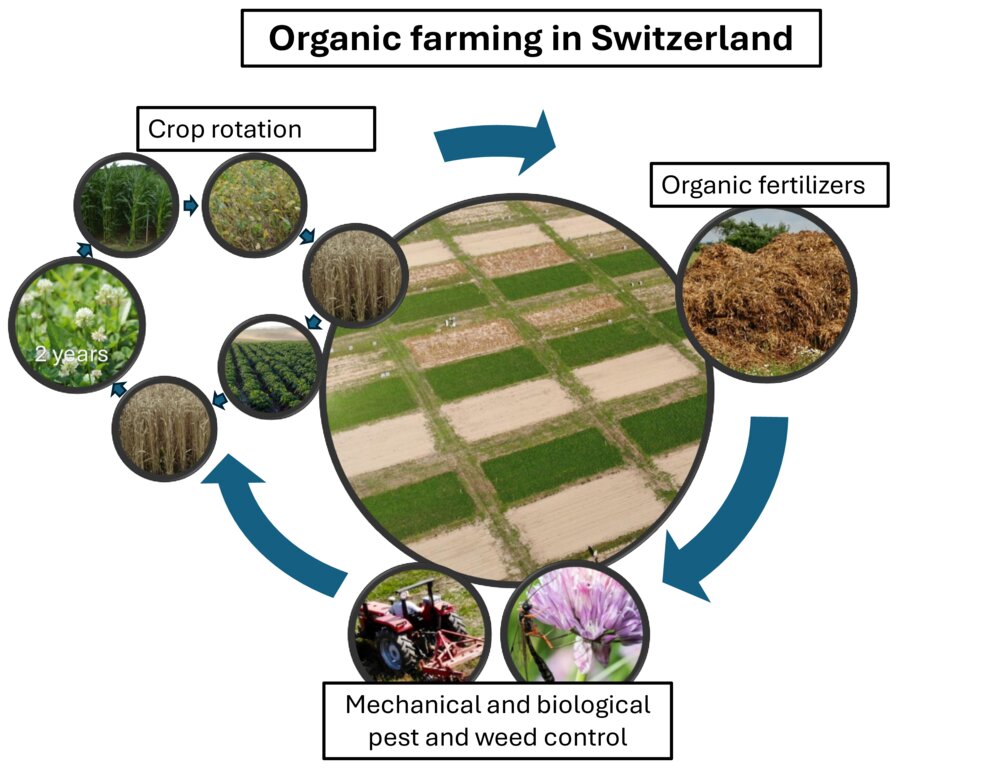
A summary of the principles of organic farming in Switzerland
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Moritz Laub
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
26/06/2024
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
ha
បើសិនប្រើឯកតាតាមតំបន់ សូមបញ្ជាក់តម្លៃបម្លែងវាទៅជាហិកតា (ឧ. 1 ហិកតា = 2.47 អា)៖ 1 ហិកតា =:
1 ha
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
CHF
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
0,91
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
160-240
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Courses on the principles of organic farming | Before transition |
| 2. | Transitioning period (already practicing but not yet certified) | 2 years |
| 3. | Certification | Start of year 3 |
មតិយោបល់:
Detailed information on the transition process and requirements can be found here:
https://www.fibl.org/de/shop/1001-umstellung
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់:
Courses are needed when transitioning to organic agriculture. They usually take around a week and the cost of courses depends locally.
Further, there are costs for certification, which are usually 400 CHF.
The main costs of transitioning is lost yields in the years during transition, when there is no price premium, yet. Subsidies depend on the Swiss Canton.
Some detailed information on the cost associated with transition can be found here:
https://www.bioaktuell.ch/grundlagen/umstellung/allgemein/kosten-und-beitraege
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application of manure | At least yearly |
| 2. | Application of slurry | Usually twice a year |
| 3. | Soil preparation by harrow or cultivator | Yearly |
| 4. | Weed supression by tine weeder | At least yearly |
| 5. | Biological pesticide application (e.g., Novodor) | When needed, mostly in potato |
| 6. | Planting of cover crop | After wheat |
| 7. | Mulching cover crop | Before planting soy/maize |
មតិយោបល់:
The measures here reflect the activities that are in addition to conventional management needs. Their exact sequence depends on selected crop rotation. In the DOK experiment is was silage maize, soybean, winter wheat, potato, winter wheat, and two years of grass-clover.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour requirements compared to conventional agriculture | % | 113,0 |
មតិយោបល់:
Because this is a research trial, the detailed costs are neither available nor would they be representative of typical organic farms. Therefore, it is best to rely on the estimated costs from an international study. Based on this study there are 13% higher labour costs in organic farming, but the higher labor cost in organic systems is offset by lower costs of purchased inputs. The total production cost is not different to conventional farming. When the actual organic premiums are considered, gross returns, benefit/cost ratios, and net present values are significantly higher for organic crops compared to conventional crops (21%, 24%, and 35%, respectively).
The study is available here:
https://www.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423674112
A good way to estimate the costs of organic vs conventional production is the KTBL Performance Cost calulator. It can be specified to farm and machinery size, soil type and has an option for organic agriculture to see the differences. (only in German language):
https://daten.ktbl.de/dslkrpflanze/postHv.html
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Reduced yield without price premium during transition period.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
840,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Typical temperate climate. Rainfall is mostly evenly distributed throughout the year with slightly higher values in May, June, July and August.
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកក្រោមដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
Area refers to typical users (not the DOK Experiment)
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
- ឯកជន
- irrigation not common
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
ទេ
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
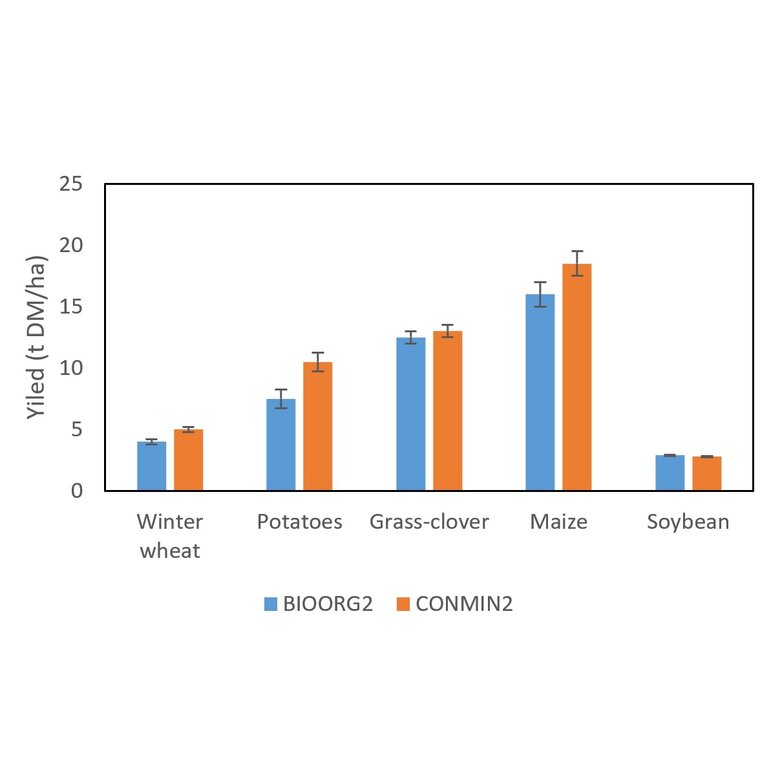
Mean wheat yield of 5 t DM/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Mean wheat yield of 4 t DM/ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Other mean yields of organic treatment (BIOORG2 with 1.4 livestock units):
Potatoes: 7.5 t DM/ha
Soybean: 2.8 t DM/ha
Other mean yields of conventional treatment with only mineral fertilizer(CONMIN2):
Potatoes: 10 t DM/ha
Soybean: 2.8 t DM/ha
ផលិតកម្មចំណីសត្វ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
Grass-clover: 13 t DM/ha
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Grass-clover: 12.5 t DM/ha
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Other mean yields of organic treatment (BIOORG2 with 1.4 livestock units):
Maize silage: 17 t DM/ha
Other mean yields of conventional treatment with only mineral fertilizer(CONMIN2):
Maize silage: 19 t DM/ha
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Refers to overall organic agriculture in Switzerland (not DOK experiment)
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Refers to overall organic agriculture in Switzerland (not DOK experiment)
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Refers to overall organic agriculture in Switzerland (not DOK experiment)
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Refers to overall organic agriculture in Switzerland (not DOK experiment)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គដី/ការបូនក្រោមដី
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
About 1.3% SOC in the mineral fertilizer treatment in 2020
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
About 1.6% SOC in the organic agriculture treatment in 2020
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Organic treatment refers to BIOORG2 with 1.4 livestock units. Conventional treatment to the one with only mineral fertilizer (CONMIN2).
ជាតិអាស៊ីត
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
pH of 6.3 in the mineral fertilizer treatment in 2020
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
pH of 6.5 in the organic agriculture treatment in 2020
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Organic treatment refers to BIOORG2 with 1.4 livestock units. Conventional treatment to the one with only mineral fertilizer (CONMIN2).
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
All presented results are from published studies about the DOK experiment.
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកក្រោមដី/ ការបំពុលទឹកទន្លេ
Greenhouse gas emissions per land area
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Based on a recent modeling study, emissions were between 0.5 to 1 t CO2 equivalent less per ha and year in organic compared to conventional agriculture in Switzerland (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2020.102822).
Greenhouse gas emissions per calorie
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
In contrast to emissions per land area, it has been found that due to the lower yields there is little difference in terms of emissions per unit of food produced (https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa6cd5).
វាយតម្លៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
There are ongoing debates on whether organic agriculture really leads to lower emissions than conventional agriculture, and the conclusion largely depends on the unit of reference (amount of food vs. per ha).
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | ថយចុះ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មធ្យម |
មតិយោបល់:
Preliminary results from rain-emission shelters indicates similar resilience of the organic agriculture treatment as the conventional ones to drought.
However, organic agriculture in general is expected to better cope with climate change than conventional agriculture (https://www.fibl.org/fileadmin/documents/shop/1500-climate-change.pdf)
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
The main establishment costs is that in the first years of establishment, farmers have to apply all organic principles and thus have lower yields. However, certification as organic produce, which receive price premiums, is only possible 1-3 years after establishment, depending on the farm type. Thus, there is a period in which the lower yields are not yet compensated by a price premium. Once the system is certified and a price premium received, gross returns, benefit/cost ratios, and net present values are significantly higher for organic crops compared to conventional crops (https://www.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423674112)
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 11-50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
About 16% of all farms in Switzerland are currently organic. (BAFU; https://www.bfs.admin.ch/news/de/2024-0392)
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 51-90%
មតិយោបល់:
Switzerland has specific subsidies for those that practice organic farming but also many subsidies that all farmers receive. It is thus not 100% clear how many farmers were mainly incentivized by the additional subsidies. However, most become organic farmers out of conviction that it is the better and more sustainable farming system.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Higher income due to price premiums |
| Less dependance on external inputs |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| Better nutrient cycling and soil fertility. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Lower yields compared to conventional agriculture. | Price premium. Eating less meat, which consumes most of the agricultural produce. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
6
- ការចងក្រងពីរបាកការណ៍ និងឯកសារផ្សេងៗទៀតដែលមាន
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
27/02/2019
មតិយោបល់:
Date of most recent soil sampling
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Knapp, S., Gunst, L., Mäder, P., Ghiasi, S., Mayer, J., 2023. Organic cropping systems maintain yields but have lower yield levels and yield stability than conventional systems – Results from the DOK trial in Switzerland. Field Crops Research 302, 109072.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
For free: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2023.109072
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Krause, H.-M., Stehle, B., Mayer, J., Mayer, M., Steffens, M., Mäder, P., Fliessbach, A., 2022. Biological soil quality and soil organic carbon change in biodynamic, organic, and conventional farming systems after 42 years. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 42, 117.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
For free: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-022-00843-y
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Mayer, M., Krause, H.-M., Fliessbach, A., Mäder, P., Steffens, M., 2022. Fertilizer quality and labile soil organic matter fractions are vital for organic carbon sequestration in temperate arable soils within a long-term trial in Switzerland. Geoderma 426, 116080.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
For free: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.116080
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Crowder, D.W., Reganold, J.P., 2015. Financial competitiveness of organic agriculture on a global scale. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112, 7611–7616.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
For free: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1423674112
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
FIBL Webpage DOK trials
វេបសាយ:
https://www.fibl.org/en/themes/projectdatabase/projectitem/project/404
7.4 មតិយោបល់ទូទៅ
Costs are the most difficult to estimate from agricultural experiments (not real field conditions)
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល