Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China [ប្រទេសចិន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Christian Rumbaur
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
膜下滴灌 (Chinese)
technologies_1305 - ប្រទេសចិន
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 4 ខែ មេសា ឆ្នាំ 2018 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 13 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2019 (public)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Müller Joachim
University of Hohenheim
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Zia-Kahn Shamaila
University of Hohenheim
ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Universität Hohenheim - ប្រទេសអាល្លឺម៉ង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
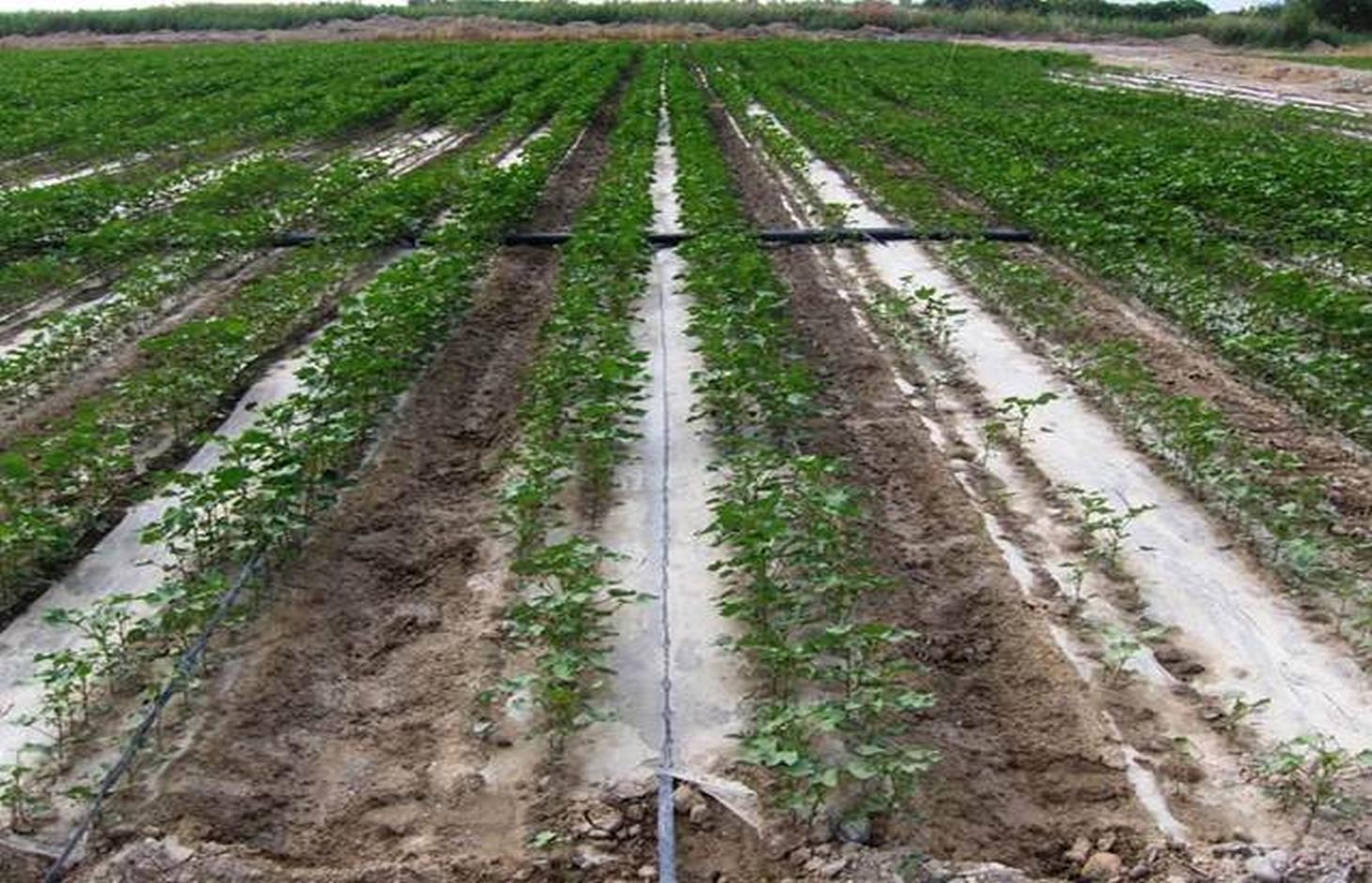
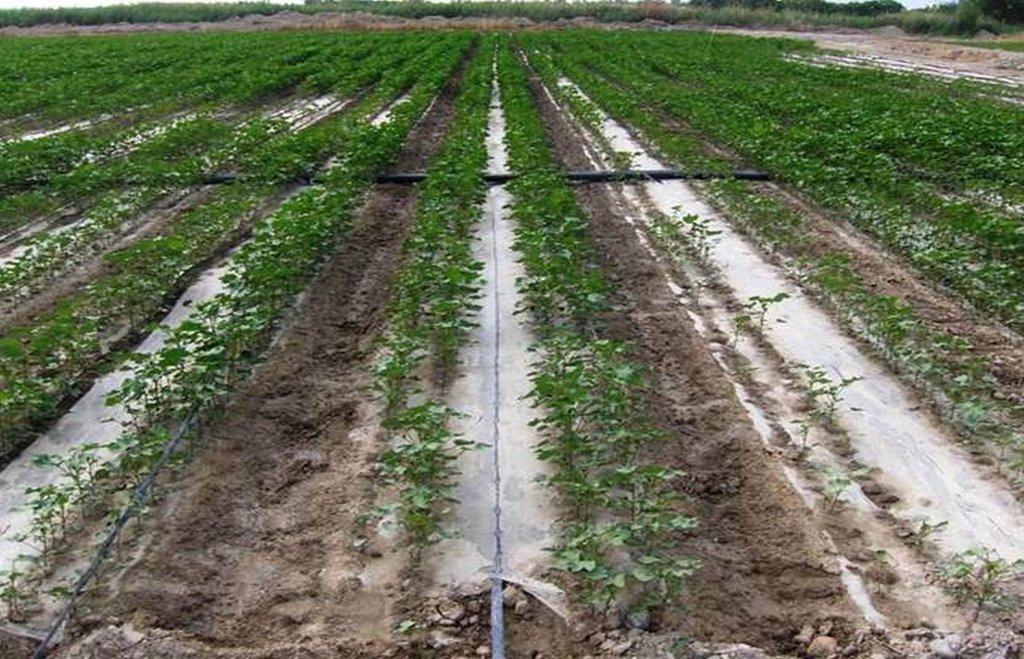
Drip irrigation under plastic mulch, associated with drainage, to reduce water demand and improve cotton yields in Xinjiang Province, China.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
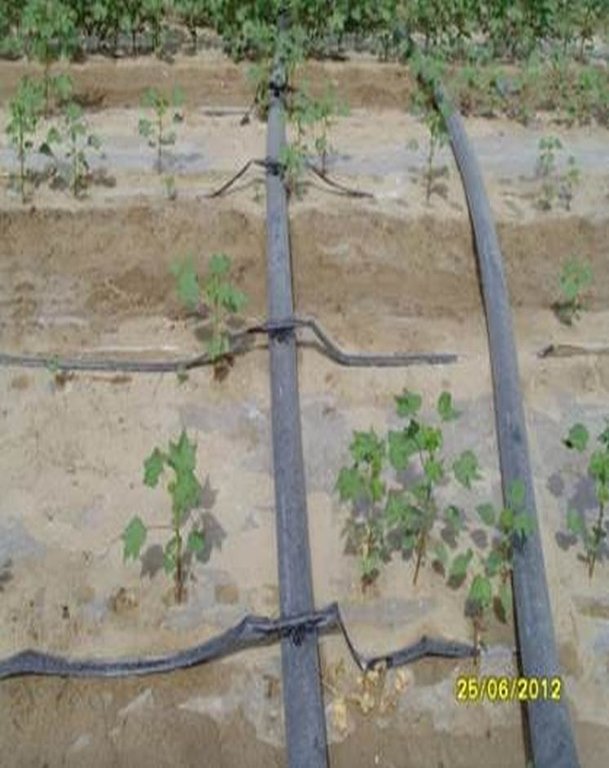
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសចិន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
China / Xinjiang Province
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Tarim River Basin
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- > 10,000 គម2
មតិយោបល់:
It might be used also in other provinces. But this not known to the author.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- 10-50 ឆ្នាំ
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
It is not clear how the technology was invented.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ដំណាំសរសៃ - កម្បាស ឬសំឡី
- wheat
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែឈើផ្សេងៗ
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
មតិយោបល់:
major cash crop: cotton
major food crop: wheat
other: fruit trees
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water use conflicts between agriculture and natural vegetation, soil salinization, desertification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization and water shortage.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: water availability, evaporation
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រពទាំងស្រុង
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- ការបែងចែកទឹក និងប្រព័ន្ធបង្ហូរ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A1: ដំណាំ/គម្របដី

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M2: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរការគ្រប់គ្រង/ កម្រិតអាំងតង់ស៊ីតេ
- M4: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរចម្បងៗក្នុងការកំណត់ ពេលអនុវត្តសកម្មភាព
- M6: ការគ្រប់គ្រងសំណល់ (កែឆ្នៃទ្បើងវិញ ប្រើប្រាស់ឡើងវិញ ឬបន្ថយការប្រើប្រាស់)
មតិយោបល់:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cs: សារធាតុប្រៃ/អាល់កាឡាំង

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pw: ទឹកនៅដក់ជាប់

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pw: waterlogging
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage - Increase of groundwater - salinization of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (cotton monoculture), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation to gain new arable land), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), wind storms / dust storms (Dust storms, blow out of top soil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (Doubling of population during the last thirty years.), land tenure (Land belongs to the state), poverty / wealth (Family farmers are poorer than city dwellers), education, access to knowledge and support services (Poorer farmers have less access to extension services.)
Secondary causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining (There is oil production in the region, but it was not studied), discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (use of surface and ground water for large scale irrigation), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests))
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
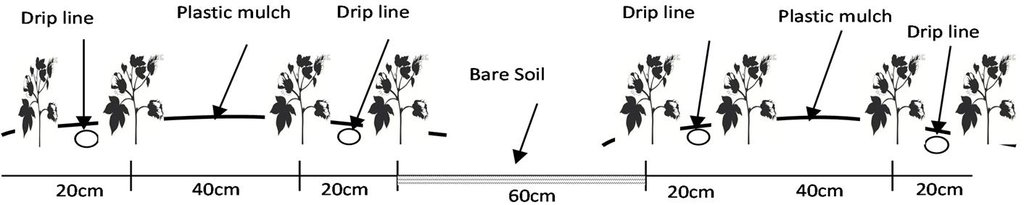
There are double rows of cotton 20 cm apart, with a drip line between. 40 cm then separates each double row. Two double rows are covered by one length of plastic mulch. There is a small strip of bare soil between each length of plastic mulch. Mulch covers around 80% of the soil surface.
Location: Korla City. Xinjiang Province / China
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For the easy and fast installation a tractor is needed)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), increase of water use efficiency
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: transparent plastic (Polyethylene), thickness: 0.08 mm
Quantity/ density: 7100 m/ha
Remarks: 1.4 m width in lines with spacing of 20 cm between lines
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Change from flood irrigation to drip irrigation
Major change in timing of activities: Plastic mulch enables early sowing of cotton
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Shamaila Zia-Khan
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
1
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor | |
| 2. | Drip line installation, plastic mulch and seeding tool | At sowing |
| 3. | Making holes for the (cotton) plants in the plastic mulch.Maintaining hoses | After emerging |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Drip line installation | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Tractor | Piece | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | seeds | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Plastic mulch | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | 50,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Black dripe lines | Set | 1,0 | 380,0 | 380,0 | 50,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 5510,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 5510,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.33 month(s)
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing and leveling of field. | Before sowing |
| 2. | Irrigation | |
| 3. | Removal of the drip lines and the plastic mulch |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Collecting mulch | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 98,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Irrigation and flooding water | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 13,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 13,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with installation tool for the drip irrigation under plastic mulch, other tools: hoe
The costs for the machine, the plastic hoses and the plastic mulch are calculated above are for 1 ha and were calculated on the basis of 2013 (subsequently costs have risen). Water price: 0.019 CNY/m3. Farmers need 3000 m3 per ha.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
90 mm per year. Jan, Feb, Apr and May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5 mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- ស្ងួត
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Altitudinal zone: altitudes of 800 to 1300 meters
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- គ្រើម/ មានពន្លឺ (ខ្សាច់)
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium high
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Ground water table: also < 5 m and the installation of drip irrigation under plastic mulch should be installed with a drainage system. If the groundwater table is too high salinisation of the soil will be the result
Availability of surface water: For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch mostly surface water is used. It is diverted by channels to the agricultural fields. There must be a good water availability at the fields.
Water quality (untreated): For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch the water quality must be quite high, otherwise the small holes of the drip lines will be blocked soon.
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម/ ទីផ្សារ
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មាន
- មានខ្លាំង
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the earth works in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land (income from large fields of cash crops).
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have not implemented the drip irrigation under plastic mulch also generate off-farm income.
Manual labour: harvesting
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
មតិយោបល់:
5-15 ha: state farms
< 0.5 ha: family farmers
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- រដ្ឋ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- កិច្ចសន្យាជួល
មតិយោបល់:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
15% of more cotton yield
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
តម្រូវការទឹកសម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ការចំណាយលើធាតុចូលកសិកម្ម
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថានភាពក្រុមដែលមានបញ្ហាក្នុងសង្គម និងសេដ្ឋកិច្ច
Livelihoods and human well-being
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
រំហួត
ដី
គម្របដី
ការបាត់បង់ដី
ភាពប្រៃ
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ីផ្សេងៗ
salinization below root zone
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
ខ្យល់នាំយកនូវធូរលី
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | មិនល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | មិនល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
No number on households
មតិយោបល់:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The government gives subsidies to the farmers who are installing the drip irrigation under plastic mulch.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government want to spread the technology in the whole region by giving subsidies to the farmers.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
helps to save water thus saves costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is subsidies by the government. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
It helps to save water during the vegetation period and thus helps to reduce the conflicts between the upstream and downstream farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology (drip + mulch) needs to be supplemented by installing a drainage system in the fields otherwise there will be a build-up of salinity and farmers will abandon land and move on. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Salinization of the soils is increasing The consequence is that the fields are flooded after harvest in November/December to leach out the salt. The water used for drip irrigation plus the water to flush the salts to lower soil layers add up to almost the same amount as if farmers were using the original flood irrigation technology. | drainage system in the fields required. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Zia-Khan,S., Spreer, W., et al. Effect of dust deposition on stomatal conductance and leaf temperature of cotton in Northwest China.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
Water 2015, 7, 116-131; doi: 10.3390/w7010116. www.mdpi.com/journal/water open access.
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល