Rooftop rainwater harvesting system [ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Madhav Dhakal
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ –
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Akase paani sankalan pranali - Nepali
technologies_1497 - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
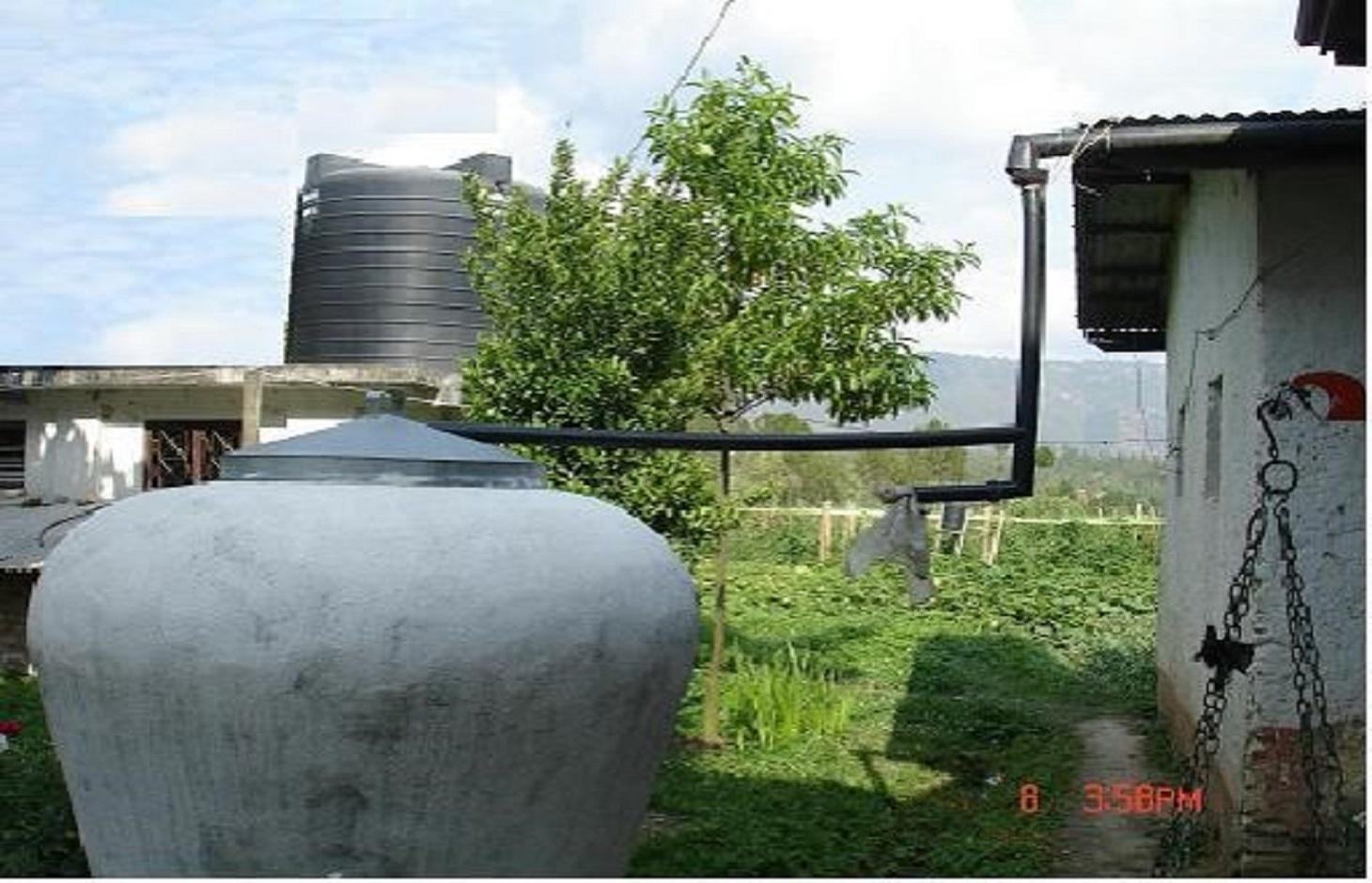
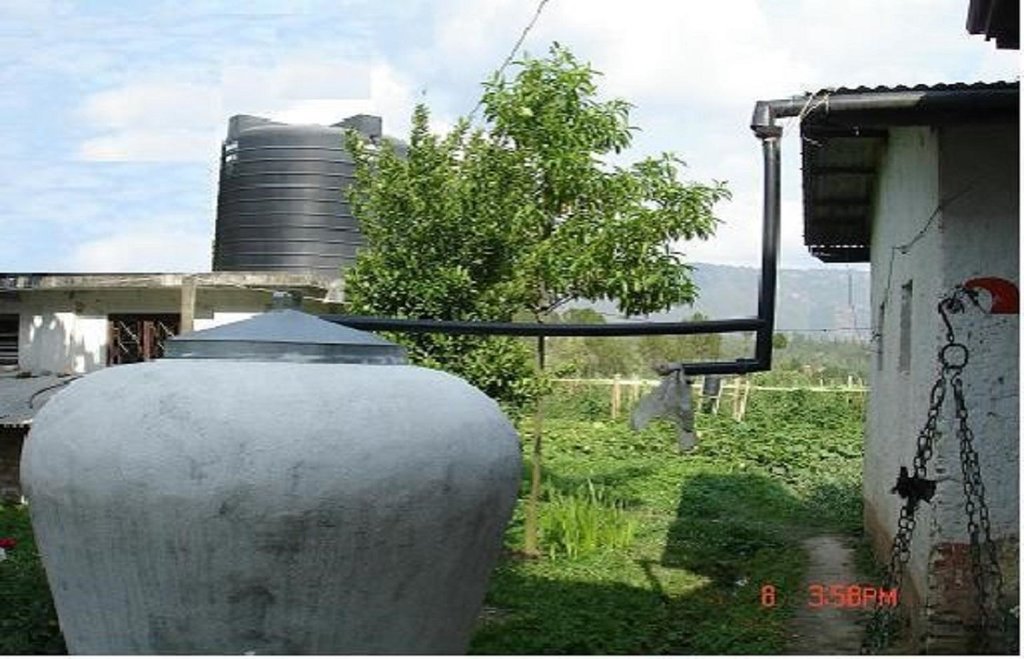
A water harvesting system in which rain falling on a roof is led through connecting pipes into a ferro-cement water collecting jar.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Many households in Nepal’s midhills suffer from water shortages during the pronounced dry season. The technology described here - harvesting roofwater during times of heavy rainfall for later use - is a promising way of improving people’s access to water for household use, especially for households with no or only limited access to spring or stream water. The technology has yet to be extensively adopted in Nepal’s midhills.
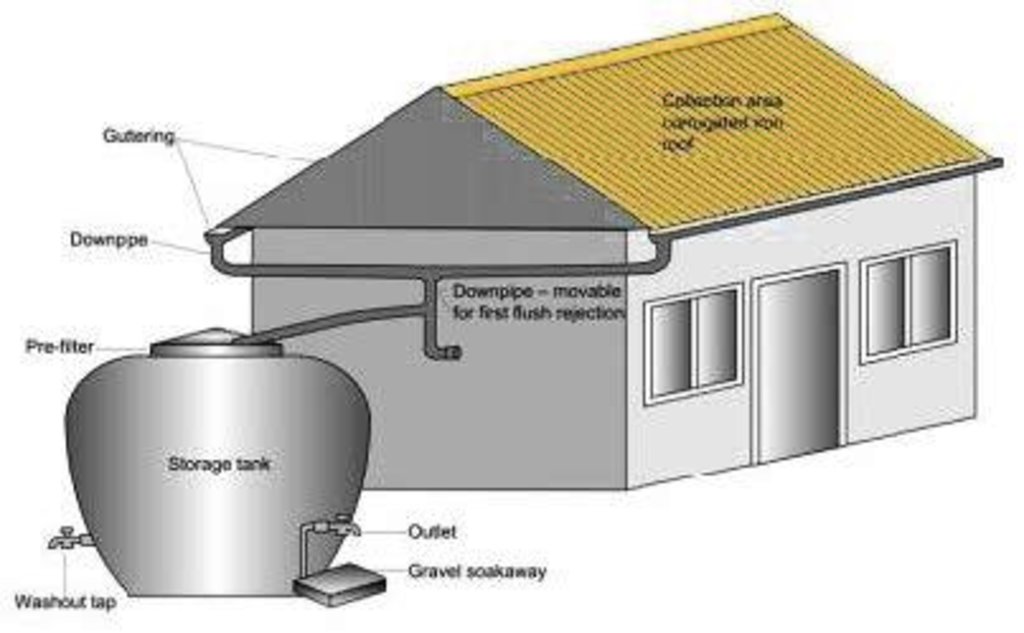
Purpose of the Technology: The technology was introduced in the Jhikhu Khola watershed to demonstrate an alternative source of water for domestic use (mainly drinking water). This technology is appropriate for scattered rural households in mountaineous areas. The harvesting system consists of a catchment roof, conveyance pipes, and a storage jar. The pipes include a gutter system made from longitudinally split polythene pipe which has a flushing system that allows the system to be periodically flushed clean.
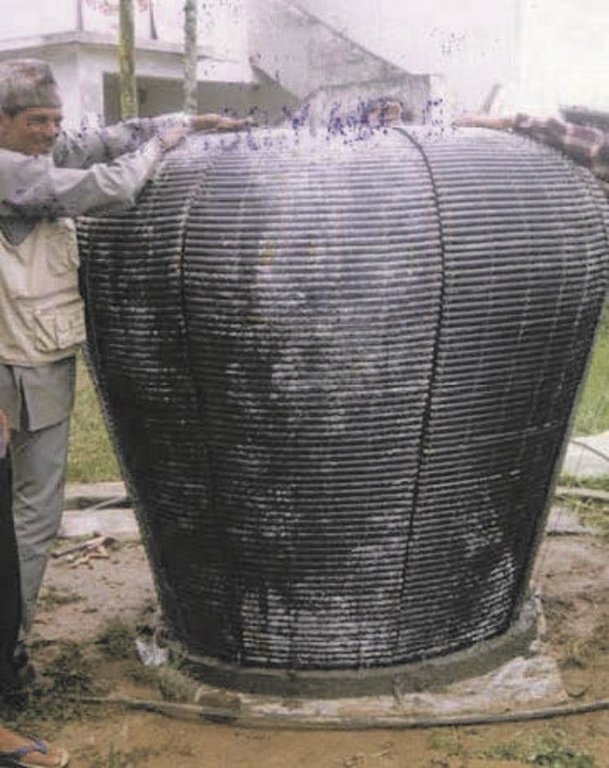
The collected water enters a 500 or 2000 litre capacity ferro-cement jar made using a mould (see photo). A preconstructed mould made from iron rods and polythene pipes is installed on a concrete base plate. Metal wires are extended from the base plate over the main mould to the top. Chicken mesh is then wrapped over the mould and tied securely with thin wire. A cement coating is applied over the metal structure. The jar is finished with three coatings of cement and the opening is covered with a fine nylon mesh to filter out undesired coarse matter. A tin lid is placed over the top.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A tap is fixed about 20 cm above the ground. This height allows for water to be collected in the typical 15 litre local water vessels (gagri) and avoids collection of too much water in bigger vessels as well as minimising the dead storage of water (Nakarmi et al. 2003). Trained masons can easily install the entire system. Provided all the materials and the mould are available, the entire system can be put together in about a week. The main maintenance task is to keep the roof clean, especially after long dry periods. This is done using the gutter pipe flushing system in which the first dirty water from the roof is diverted away from the jar.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសនេប៉ាល់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Kharelthok, Sathighar, Panchkhal, Hokse and Patalekhet VDCs of the Jhikhu Khola watershed
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kavrepalanchowk district
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
មតិយោបល់:
Roof rainwater harvesting jars were demonstrated mostly in the villages located at the watershed divides, hilltops, and elevated terraces where communities face chronic water shortage particularly during the dry period.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ឆ្នាំ សូមបញ្ជាក់កាលបរិច្ឆេទដែលប្រហាក់ប្រហែល:
- តិចជាង 10ឆ្នាំមុន (ថ្មី)
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Water harvesting is an ancient practice, the system used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed came from Thailand, so the technology is often called 'Thai jar". In Nepal, the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Support Programme (RWSSSP), which is jointly funded by the Government of Finland and His Majesties Government of Nepal, introduced it in the water deficit districts of western Nepal (Arghakhanchi, Gulmi, Kapilvastu, Nawalparasi, Palpa, Parbat, and Rupandehi).
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- Access to water
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

លំនៅដ្ឋាន ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
- ដីលំនៅស្ថាន អគារ
កំណត់សម្គាល់:
courtyard
មតិយោបល់:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Inadequate water supply during the late winter and pre-monsoon months and sediment contamination during the wet season. The discharge from traditional water sources like dug-out ponds, springs, seepage ‘holes’, shallow wells and streamlets becomes limited soon after the end of the monsoon.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Many settlements are located on ridge tops and most water sources are located below making it difficult to provide water to households through networks of pipes. Women and girls often face hardship in carrying the water uphill, especially during the monsoon when trails are slippery.
Constraints of settlement / urban
Number of growing seasons per year: 3
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការស្តុកទុកទឹក
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pw: ទឹកនៅដក់ជាប់
មតិយោបល់:
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
A water harvesting system with roof catchment, connecting pipes and storage tank.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Structural measure: Dam/ pan/ pond
Material: Concrete
Structural measure: Jar
Structural measure: Gutter
Structural measure: pipes
Construction material (other): Cement
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
A.K. Thaku
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងឯកតាបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ឯកតា:
Rooftop rainwater harvesting system
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
2.10
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct the concrete base plate with the help of base moluld | 1st day of a week |
| 2. | Curing work | 2nd to 7th days of a week |
| 3. | Final checking and metal cap putting over the top of the jar | 7th day of a week |
| 4. | First coat of cement | 2nd day of a week |
| 5. | Gutter and pipe fitting; including flush pipe | 4th day of a week |
| 6. | Inner coat of cement | 6th day of a week |
| 7. | Main mould installation with the help of metal wires, wrapping of chicken mesh | 2nd day of a week |
| 8. | Removal of mould | 6th day of a week |
| 9. | Second coat of cement | 3rd day of a week |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Construction of rooftop rainwater harvesting system | Persons/unit | 19,5 | 2,1 | 40,95 | 25,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Cement | unit | 1,0 | 23,6 | 23,6 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Sand and aggregate | unit | 1,0 | 1,4 | 1,4 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Chicken wire mesh | unit | 1,0 | 20,9 | 20,9 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Metal jar cover | unit | 1,0 | 5,5 | 5,5 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Plastic sheet/mosquito screen | unit | 1,0 | 1,5 | 1,5 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Polyethylene, pipes, reducer | unit | 1,0 | 23,7 | 23,7 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Nail, clamps, pipe elbow etc. | unit | 1,0 | 3,6 | 3,6 | |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Brass tap. socket, seal tap | unit | 1,0 | 3,5 | 3,5 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Paint | unit | 1,0 | 2,1 | 2,1 | |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 126,75 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 126,75 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.25 month(s)
Materials: cement (kg) 23.6 materials sand,aggregate (m3) 1.4 100 materials chicken wire mesh (m) 17.5 materials Iron wire (kg) 3.3 materials metal jar cover (no) 5.5 materials mosquito screen (m) 0.5 materials plastic sheet (m) 1 materials binding wire (kg) 0.1 materials snowcem paint (kg) 1.4 materials enamail paint (litre) 0.7 materials 90 mm HDP pipe (m) 10.3 materials 63 mm HDP pipe (m) 6.2 materials 40 mm HDP pipe (m) 6.8 materials reducer (no) 0.4 materials plain and roofing nails (kg) 0.2 materials metal clamp (no) 1.4 materials elbow, tee,end cap (no) 2.1 materials brass tap with latches (no) 2.1 materials 0 .5*10 inch GI nipple(no) 0.2 materials 1*10 inch GI nipple(no) 0.2 materials 1inch end cap (no) 0.7 materials GI socket (no) 0.2 materials thread seal tap (no) 0.1 Additional info Q 3.1.1.4: - less chance of disputes over turns to fetch water - medium General comments: Water harvesting is an ancient practice. The system used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed comes from Thailand, so the technology is often called ‘Thai jar’. In Nepal, the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Support Programme (RWSSSP) introduced it in the water deficit districts of western Nepal.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning the jar | dry months/one or twice in a year |
| 2. | Flushing contaminated water | After a long dry spell/whenever required |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Cleaning the system | Persons/unit | 7,0 | 2,1 | 14,7 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 14,7 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 14,7 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Machinery/ tools: hacksaw, steel scissors, hammer, pliers, wrench, trowel, steel pan bucket, and jug
Per unit cost of structure. The above mentioned cost is for unit water harvesting system. It can not be converted into hectare basis. It was estimated in 2006.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
The mould and tools were provided by the project and can be used to install many water harvesting systems. Therefore, the cost of tools are not included here. Material costs fluctuate from time to time. The transport costs will vary according to the remoteness of the site. During 1999/2000, the cost of a system varied from US$80 to US$120, of which land users contributed about US$40 by providing the unskilled labour and locally available materials like sand and fine aggregates (calculated at an exchange rate of US$1 = NRs 73).
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
មតិយោបល់ និងបញ្ចាក់បន្ថែមអំពីសណ្ឋានដី :
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលគ្មានគុណភាព (តម្រូវឱ្យមានការសំអាត)
មតិយោបល់ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសផ្សេងៗទៀតលើគុណភាព និងបរិមាណទឹក :
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- 10-50% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីលក្ខណៈពាក់ព័ន្ធផ្សេងទៀតអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
15% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
50% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land (as ranked by the land users).
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតមធ្យម
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
by the house to accommodate the water jar
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកបរិភោគដែលអាចទាញយកមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
in dry seasons
harvested water can be used during busy periods ( field preparation, vegetable planting, rice harvesting, and festivals).
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
បន្ទុកការងារ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
1 hour
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
5 minutes
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
greatly reduced time needed to fetch water
reduced women's workload i.e. per day water fetching time reduced from about 12 hours to about 1 hour ( for the households having ~10 family members).
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គមផ្សេងៗ
Water is available near the house
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
A house hold having 10 family member require about 12 gagree ( 1 gagree is equivalent to15 litre)
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ស្ថាប័នសហគមន៍
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
together with adopters, other potential local adopters have started discussing options
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
through training, demonstration, and knowledge sharing
livelihood and human well-being
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved heath condition due to clean water availability
Sanitation
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
more water avilable forwashing leading to improved health
Risk of injury from carrying water along slippery and steep tracks
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ទឹកជំនន់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
a little portion of rainfall traped directly from the roof and collected at the courtyard
កំណកល្បាប់ខ្សែទឹកខាងក្រោម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
reduced eroded materials from the courtyard.
availability of water for neighbours during scarce period
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះភ្លៀងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | ល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយអាកាសធាតុ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| រាំងស្ងួត | មិនល្អ |
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយទឹក
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ទឹកជំនន់ទូទៅ (ទន្លេ) | ល្អ |
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
ផលវិបាកដែលទាក់ទងនឹងបរិយាកាសផ្សេងៗទៀត
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| កាត់បន្ថយពេលដាំដុះ | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
មតិយោបល់:
Although the initial investment is high, the users immediately get more water. The high cost of installing the system means that the short term benefits are slightly negative.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
46 households in an area of 1 - 10 sq km (200 - 500 persons/sq km)
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 11-50%
មតិយោបល់:
74% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
34 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
26% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
12 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The number of households applying the technology is increasing without further incentives being provided.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
|
The stored water can be kept for use in emergencies such as to prepare food for guests during busy times like rice planting and harvesting, and during festivals. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Share experiences to extend adoption of the technology |
|
Harvested water is tastier due to being cooler compared to the water collected in the polythene tank. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Laboratory analysis of the harvested rainwater in different time period, i.e. from 1st month of harvest to 12th month could help to know the quality status. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
|
Harvested rainwater has saved almost one workday per day per family due to reduced water fetching time in this case referring to the rainy season, however water will generally be used during the dry season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Publicise the economic benefits of the technology through experience sharing programmes. |
|
Women are responsible for fetching water and so the technology reduces their workloads. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Implement a larger scale programme to promote the technology. |
|
The jars are more durable than plastic tanks. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Carry out regular maintenance to keep systems in good working order. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| The technology is expensive for poor households. | External support is needed for poor households to afford this system. |
| The height of the tap is very low which makes it inconvenient to collect water in the gagree. | It was designed to use collected water efficiently, the tap height can be raised, which means that the dead storage is increased, i.e. more water is unavailable for use. |
| There are chances of the jar’s base plate subsiding due to lack of compactness of foundation. | The area of base plate should be made more compact. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| 2,000 litre capacity jars barely meet the dry season needs of a household. | Larger sized jars or more than one jar need to be built to meet most household’s requirements. |
| Microbiological contamination (total and faecal coliform bacteria) and levels of phosphate above the EC maximum were found in a number of the jars caused by bird droppings and dust particles from the roof. | Regularly clean catchment roofs and treat water before drinking by boiling or chlorinating. Rainwater has a low mineral content which can be harmful for the human body, if taken in large quantities (due to reverse osmosis process). |
| This technology is not suitable for temple roofs because such roofs are usually home to large numbers of pigeons, and their excreta will contaminate rainwater that falls there. | Avoid badly contaminated catchments. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Sharma, C. (2001) Socioeconomic IndicativeImpact Assessment and Benchmark Study on Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting, Kabhrepalanchok District, Nepal, a report submitted to ICIMOD, Kathmandu, Nepal
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
ICIMOD (2000) Water Harvesting Manual, unpublished manual prepared for PARDYP Project, ICIMOD
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Lessons Learned from the People and Resource Dynamics Project , PARDYP/ICIMOD. 2006.
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Nakarmi, G.; Merz, J.; Dhakal, M. (2003) ‘Harvesting Roof Water for Livelihood Improvement: A Case Studyof the Yarsha Khola Watershed, Eastern Nepal’. In News Bulletin of Nepal Geological Society, 20: 83-87
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
Nakarmi, G.; Merz, J. (2001) Harvesting Rain Water for Sustainable Water Supplies to Rural Households in the Yarsha Khola Watershed, a report submitted to Kirchgemeinde Zuoz, Switzerland and ICIMOD, Kathmandu, Nepal
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
ICIMOD
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល