Plastic mulching for cash crops [ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Tshering Yangzom
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Kuenzang Nima
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6864 - ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Rai Pratap Singh
ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
Mulching in agriculture helps conserve moisture, prevent water and wind erosion, control weeds, and regulate soil temperature. While it has these benefits, it also poses environmental concerns related to soil contamination and waste accumulation. Plastic mulches are a significant source of microplastic pollution in agricultural soils. The residual microplastics in the soil negatively affect soil health. Used plastic mulches are eventually burned and the burning releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and global warming. Additionally, the residues left behind after burning plastic mulches can persist in the soil for extended periods thereby contaminating the soil. Though mulching helps increase crop yields, it has negative effects on the natural environment and thus the use of mulching necessitates careful consideration.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
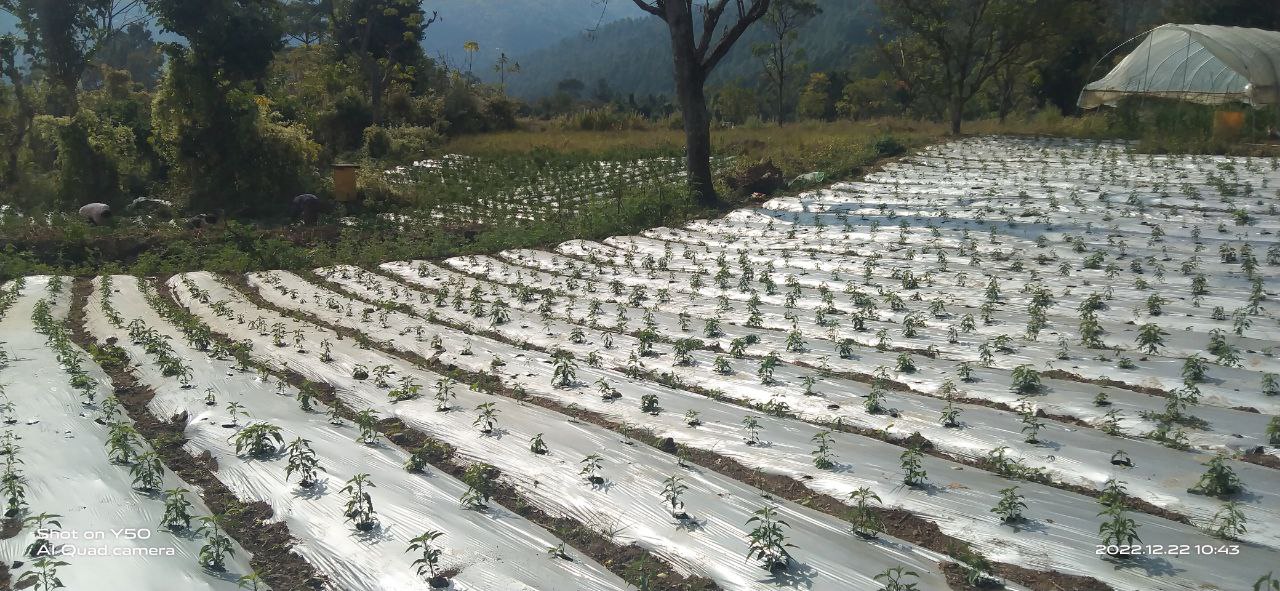
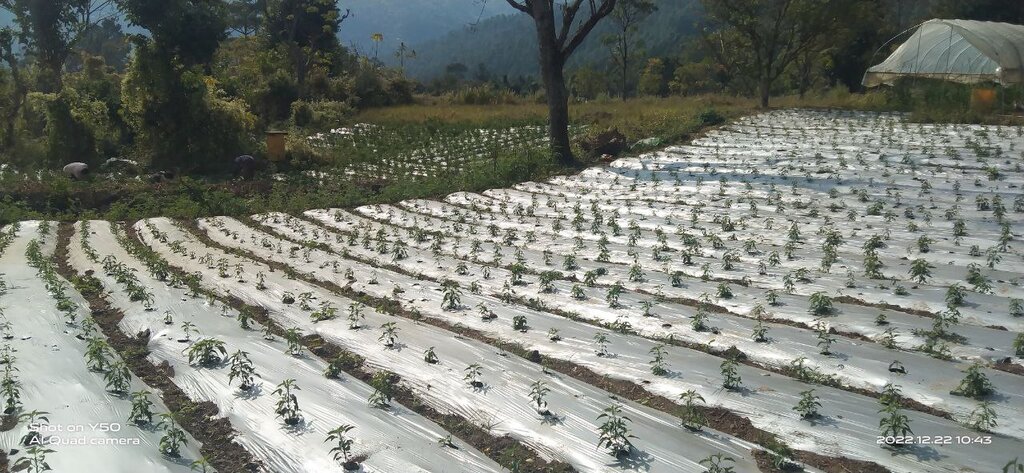
Plastic mulching comprises thin plastic sheets laid out on raised soil surfaces around plants to help conserve soil moisture, prevent water and wind erosion, control weeds, and regulate soil temperature. It is used in agriculture to increase crop yields. However, there are environmental concerns about soil contamination and waste disposal.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
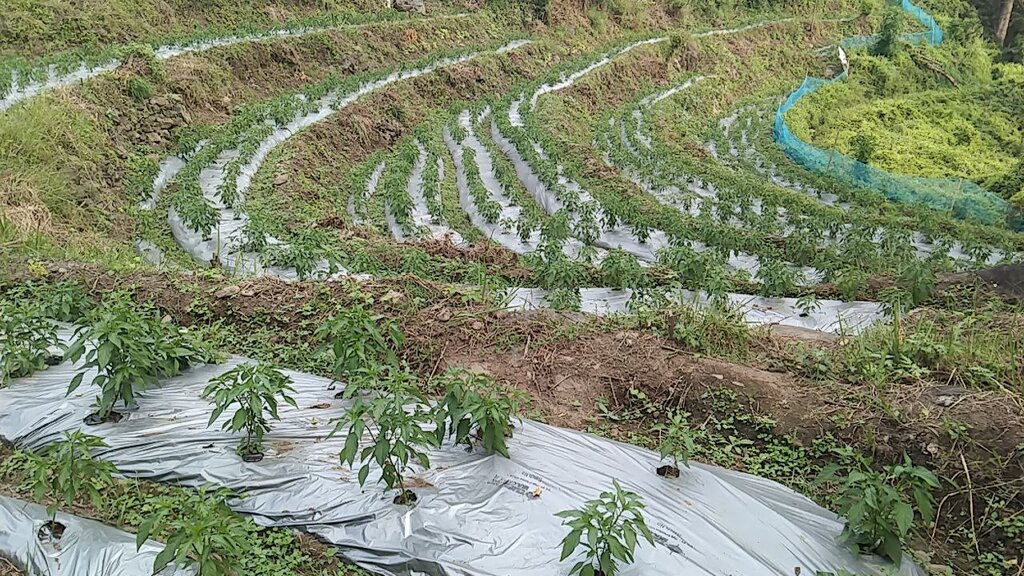
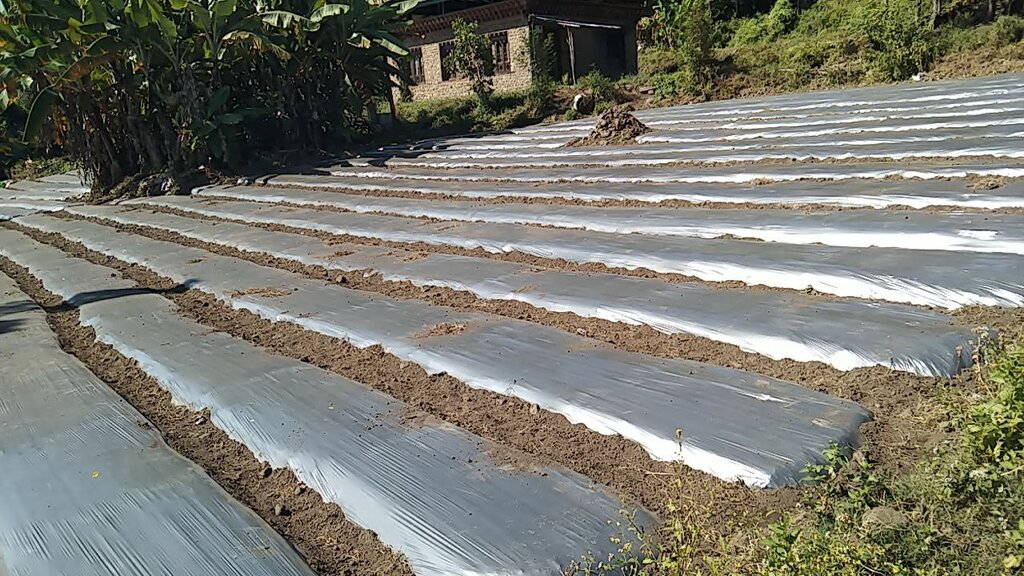
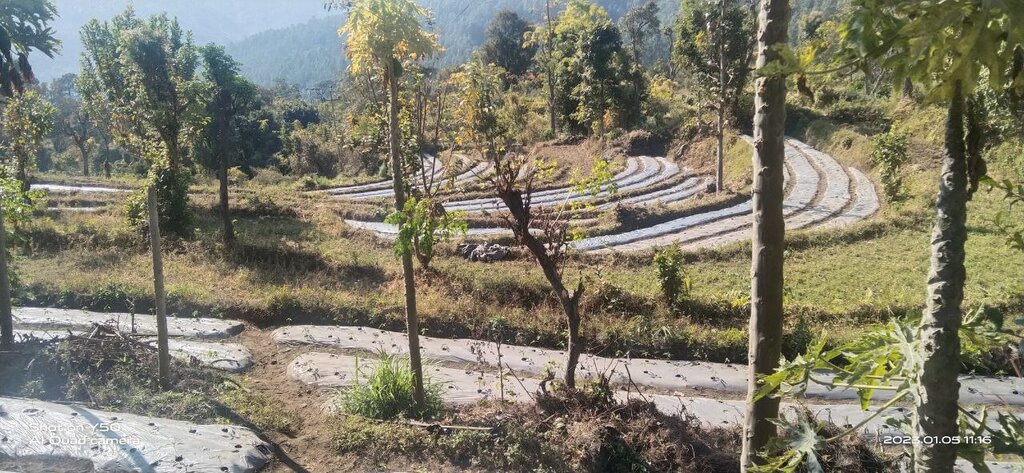
Plastic mulching is a widely used agricultural practice in Bhutan, primarily employed in the cultivation of cash crops. Farmers have adopted plastic mulching to enhance crop production and address specific agricultural challenges. It allows farmers to optimize water usage by reducing evaporation and maintaining soil moisture levels, which is crucial in regions where water resources are limited. It also helps suppress weed growth, minimizing competition for nutrients and ensuring healthier crop growth. Additionally, the regulation of soil temperature through plastic mulching can extend the growing season and improve crop quality and yields. These benefits are particularly valuable in Bhutan's mountainous terrain and varied climatic conditions.
However, the application of plastic mulching can have both direct and indirect impacts on the natural environment. Improper disposal or management of plastic mulch can lead to environmental pollution, including soil contamination and plastic waste accumulation. Therefore, sustainable practices and appropriate waste management techniques are crucial to minimize the potential negative effects on the natural environment.
Plastic mulching serves several purposes and functions in agricultural practices. One of its primary functions is moisture conservation, as it helps prevent water evaporation from the soil surface by acting as a barrier. Additionally, plastic mulch controls weeds by blocking sunlight and inhibiting weed seed germination, reducing competition for nutrients. Another important function is soil temperature regulation, as plastic mulching traps heat from the sun, raising soil temperatures in cooler climates and promoting faster plant growth. Overall, plastic mulch contributes to enhanced crop performance.
Furthermore, it helps prevent soil erosion by protecting the soil surface from wind and water erosion, thus maintaining soil structure and fertility, and creating a barrier between plants and the soil, reducing the risk of soil-borne pests and diseases affecting the crops. It can also deter certain pests by disrupting their habitat and limiting access to plants.
Plastic mulching involves the use of thin sheets or films made of polyethylene or similar materials, which come in various colours and thicknesses. Manual tools are utilized to lay the sheets evenly over the prepared soil. Before laying the plastic mulch, the soil is typically ploughed, levelled, raised, and cleared of debris to create a smooth surface. To prevent displacement by wind or other factors, the plastic mulch needs to be securely anchored to the ground. Plastic mulching can be combined with drip irrigation systems to provide water and nutrients directly to the plant roots.
Some specific advantages pointed out by the land user include the opportunity to achieve higher returns on agricultural investments. It reduces the need for manual weeding or herbicide application, saving time, labour, and resources. Additionally, it reduces the frequency of irrigation. It also extends the growing season expanding options and potential profits. There are many advantages of mulching but there are some serious disadvantages of the technology. Plastic mulching poses environmental concerns related to soil contamination and waste accumulation. Plastic mulches are a significant source of microplastic pollution in agricultural soils and these microplastics negatively affect soil health. The disposal of plastic mulches is a challenge as recycling options are limited resulting in waste accumulation on farms. These accumulated wastes are eventually burned and release greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and global warming. Additionally, the residues left behind after burning plastic mulches can persist in the soil for extended periods thereby contaminating the soil. Also, the cost of purchasing plastic mulch can prove to be too high for farmers if the land area is huge. Though mulching helps increase crop yields, it has negative effects on the natural environment - thus the use of mulching necessitates careful consideration.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសប៊ូតង់
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Sergithang, Tsirang
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- ត្រូវបានផ្សព្វផ្សាយត្រឹមតំបន់មួយ
ប្រសិនបើមិនច្បាស់ពីទំហំផ្ទៃដី សូមធ្វើការប៉ាន់ប្រម៉ាណ:
- < 0.1 គម2 (10 ហិកតា)
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
The land user uses plastic mulching on 1 acre of land for chili production.
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2018
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
- It was introduced by the gewog Agriculture Extension Officer and through exposure to social media.
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំ:
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ពោត
- ធញ្ញជាតិ - ស្រូវ (តំបន់ដីសើម)
- ឬស/ដំណាំមើម - ដំឡូងបារាំង
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកស្លឹក (សាលាដ ស្ពៃក្តោប ផ្ទី ផ្សេងៗ)
- បន្លែ - ត្រសក់ផ្អែម ល្ពៅ ពពួកបន្លែទ្រើង
- បន្លែ - បន្លែយកមើម (ការ៉ុត ខ្ទឹមបារាំង ឆៃថាវម្យ៉ាង ផ្សេងៗ)
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ផ្លែប៊ឺ
- ផ្លែឈើផ្សេងៗ
- ផ្លែស្វាយ/ផ្លែមង្ឃុត/ផ្លែត្របែក
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 2
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ប្រសិនបើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទដំណាំដែលដាំចន្លោះគ្នានោះ:
Vegetable crops are intercropped for self-consumption.
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើបាទ/ច៎ា សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Vegetable crops are rotated.

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ព្រៃ (ពាក់កណ្តាល) ធម្មជាតិ/ ដីព្រៃ
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃល្បោះចម្រុះ/ ព្រៃស្រោង
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- អុស
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- ទេ (បន្តទៅសំណួរ 3.4)
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
The land users of Sergithang face water shortage problems.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- Weed management
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការផ្សេងៗ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Plastic mulching may fall under structural measures.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការបាត់ដីដោយសារខ្យល់
- Et: ការបាត់បង់ដីស្រទាប់លើ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bp: ការកើនឡើងនូវសត្វល្អិត ឬជំងឺ បាត់បង់នូវសត្វមានប្រយោជន៍

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hs: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅលើផ្ទៃដី
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់:
Plastic mulching prevents soil and water erosion and conserves soil mositure.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
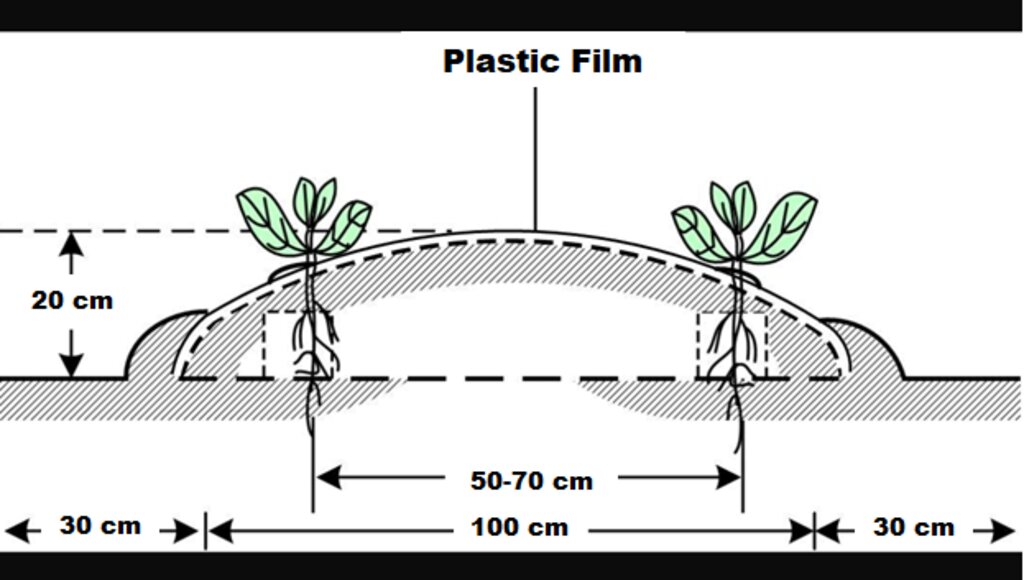
This diagram shows a cross-section of a raised bed using plastic mulching. The plants grow through the punctured holes in the plastic. The length of the bed varies from farm to farm and is 1 m wide and spaced 30 cm apart (bed-bed spacing) for easy access/movement. The bed is usually raised to 20 cm in height. The planting distance shown in the diagram is for chilies, 50-70 cm. The distances will vary according to the crop/variety.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Thinley Penjor Dorji
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
20/07/2023
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
1 acre
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
Ngultrum
បើពាក់ព័ន្ធសូមកំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (ឧ. 1 ដុល្លារ = 79.9 រៀលនៃរូបិយប័ណ្ណប្រេស៊ីល) ៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
82,1
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
Nu 400
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field preparation (tilling) | Winter |
| 2. | Field preparation (rotary tilling) | Winter |
| 3. | Manure application | Winter |
| 4. | Bed preparation | Winter |
| 5. | Laying of plastic mulch | Winter |
| 6. | Making holes in the plastic | Winter |
| 7. | Transplantation | Winter |
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Field preparation (tilling) | Person/day | 5,0 | 400,0 | 2000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Manure application and rotary tilling | Person/day | 8,0 | 400,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Bed preparation, laying of plastic mulch and making holes | Person/day | 12,0 | 400,0 | 4800,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Transplantation | Person/day | 8,0 | 400,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Power tiller (tilling) | Per day | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Power tiller (rotary tilling) | Per day | 1,0 | 2500,0 | 2500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Seeds | Packet | 5,0 | 15,0 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Plastic mulch | Rolls | 4,0 | 2800,0 | 11200,0 | 100,0 |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Food and Refreshment | per person | 33,0 | 350,0 | 11550,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 41025,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 499,7 | |||||
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
មតិយោបល់:
No maintenance work has been carried out.
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
ប្រសិនបើមិនអាចបំបែកតម្លៃដើមក្នុងតារាងខាងក្រោមទេ សូមផ្តល់នូវតម្លៃប៉ាន់ស្មានសរុបក្នុងការថែទាំបច្ចេកទេសនោះ:
29823,0
មតិយោបល់:
The plastic mulch is reused and hence there is no expenditure on the plastic mulches.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Higher cost of plastic mulching and hiring a power tiller.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Falls under Humid Sub-tropical Zone with an annual rainfall of 1200-2500 mm
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under. Bhutan is divided into AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- សើម
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ខ្ពស់ (>3%)
បើអាចសូមភ្ជាប់ការពណ៌នាពីដីឱ្យបានច្បាស់ ឬព័ត៌មានដែលអាចទទួលបាន ឧ. ប្រភេទដី, pH ដី/ ជាតិអាស៊ីត, សមត្ថភាពផ្លាស់ប្តូរកាចុង, វត្តមាននីត្រូសែន, ភាពប្រៃ ។ល។:
Moisture content-4.46%
Organic matter-5.85 %
Organic carbon-3.40%
pH-6.15
Electrical conductivity-853.00 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.17
Phosphorus-1.92
Potassium-198.73 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Silt Clay Loam
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
- គ្រឿងយន្ត/ ម៉ាស៊ីន
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
1 acre or 0.404 ha
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
The land use rights in Bhutan are based on a traditional legal system guided by formal land-act rules and regulations.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The production of winter chili has increased to 700-800 kg following the use of mulching.
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Crop quality has increased due to reduced competition from weeds.
ហានិភ័យនៃភាពបរាជ័យរបស់ផលិតកម្ម
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The risk has decreased as mulching helps conserve moisture, prevent water and wind erosion, control weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Mulching reduces soil erosion.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The farm income from chilli has increased resulting from mulching
បន្ទុកការងារ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Workload has decreased due to a reduction in weeding requirements.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
សន្តិសុខស្បៀង/ ភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់ខ្លួនឯង
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The land user produces enough for self-consumption as well as for commercial purposes.
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Soil moisture is retained and the need for frequent irrigation is reduced.
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Soil erosion has reduced due to mulching.
បញ្ជាក់ពីការប៉ាន់ស្មាននៃផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស (វាស់វែង):
These are the on-site impacts that have been shared by the land user. The land user has reused the mulches. He is unaware of the soil contamination caused by the plastics due to residual microplastics in the soil but is well aware of the wastes that will be generated. For the lack of better waste disposal options, like many other land users of the community the land user will opt to burn the wastes.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវរងា | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | រដូវក្តៅ | កើនឡើង | ល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
អវិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
មតិយោបល់:
In the long run, the benefits will be negative, as the land user has to invest in additional costly plastic mulch. Furthermore, the existing mulching plastic is not durable.
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- > 50%
បើអាច សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីបរិមាណ (ចំនួនគ្រួសារ និង/ ឬតំបន់គ្របដណ្តប់):
All the land users of Sergithang have implemented the technology.
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 91-100%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Plastic mulching technology increases crop production. |
| The workload is reduced as there is reduction in the need of weeding. |
| It isn't a very complex technology and can be adopted easily. |
| Controls weeds. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| It aids off-season (winter) crop production. |
| Conserves moisture. |
| Reduces erosion (wind and water). |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Plastic mulching poses environmental concerns related to soil contamination and waste accumulation. | Disposal of plastic mulch is a challenge as recycling options are limited resulting in waste accumulation on farms. But one thing that the land users can do is switch to biodegradable plastic mulches or even better organic mulches (straw and Artemisia myriantha). In Bhutan straw and Artemisia myriantha mulches are very common. |
| Plastic mulching can prove to be very expensive if the land area is huge. | Opt for other more environmentally friendly alternatives such as straw and Artemisia myriantha mulching. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
19/07/2023
7.3 ការភ្ជាប់ទៅកាន់ព័ត៌មានពាក់ព័ន្ធលើប្រព័ន្ធអនឡាញ
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Vegetable cultivation Theme 3 Mulching
វេបសាយ:
http://rcbajo.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Veg-Theme-03-Mulching-printing.pdf
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល