Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar [ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ Ahmad Khalid Wiyar
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ Megha bajaj, Mohammad Ajmal Rahimy, Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د ځنګل رغونی او کرنیزی ځنګلداری لپاره د پمپ په واسطه د ابه خور سیستم
technologies_7473 - ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
- សង្ខេបជា PDF
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញជាទម្រង់ PDF សម្រាប់បោះពុម្ព
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញទម្រង់អ៊ីនធឺនេត
- សេចក្តីសង្ខេបពេញលេញ (មិនមានទម្រង់ជាក់លាក់)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 5 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 24 ខែ មិនា ឆ្នាំ 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 18 ខែ ឧសភា ឆ្នាំ 2025 (inactive)
- Using lift irrigation for afforestation and agroforestry in Kunar: 9 ខែ កក្កដា ឆ្នាំ 2025 (public)
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកជំនាញឯកទេស SLM:
Safi Sharifullah
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Safi Mohammad Afzal
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Safi Qiamuddin
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Safi Farhad
Managi Forest Management Association (FMA)
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in Afghanistanឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
No, the technology described here is not problematic with regard to land degradation. In fact, it promotes sustainable land management by enhancing soil health, preventing erosion, and supporting afforestation efforts. This technology contributes to the restoration and conservation of forest ecosystems.
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
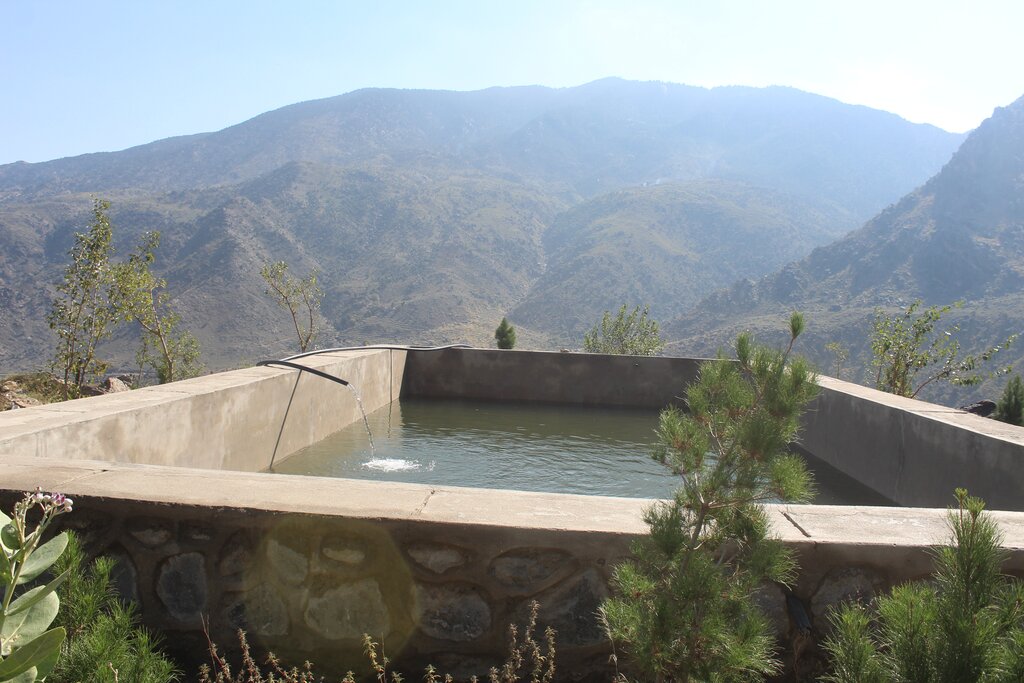
Water exploitation is a major issue in Afghanistan. The lift irrigation technology helps to irrigate an afforestation/agroforestry area (demonstration plot) using surface water (rivers) and solar-powered submersible pump. The construction of reservoirs at the demo plot ensures efficient water storage and use for irrigation purposes without relying on groundwater. A well-designed pipe irrigation scheme is implemented to distribute water evenly across the site, supporting plant irrigation and growth.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
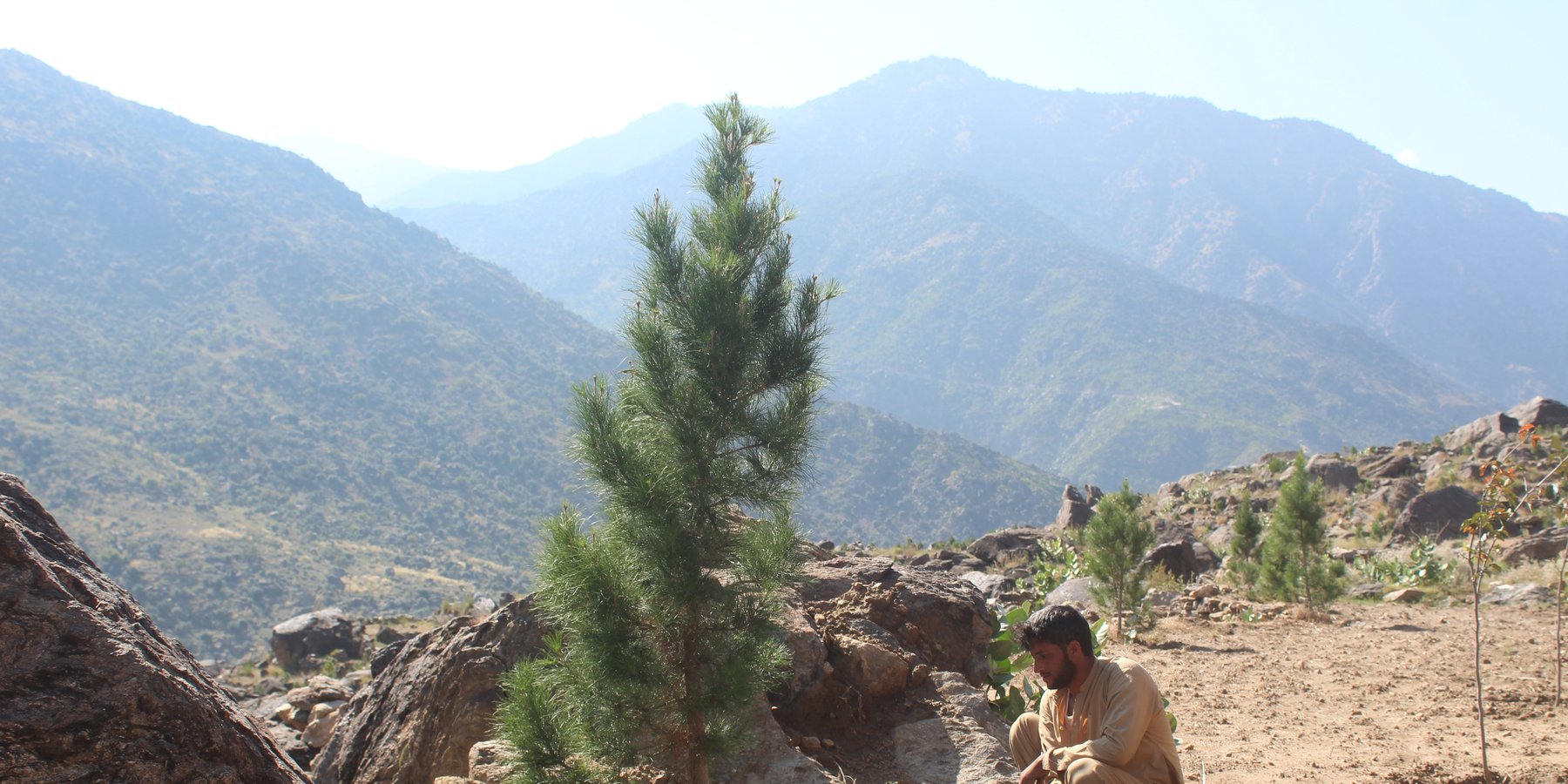
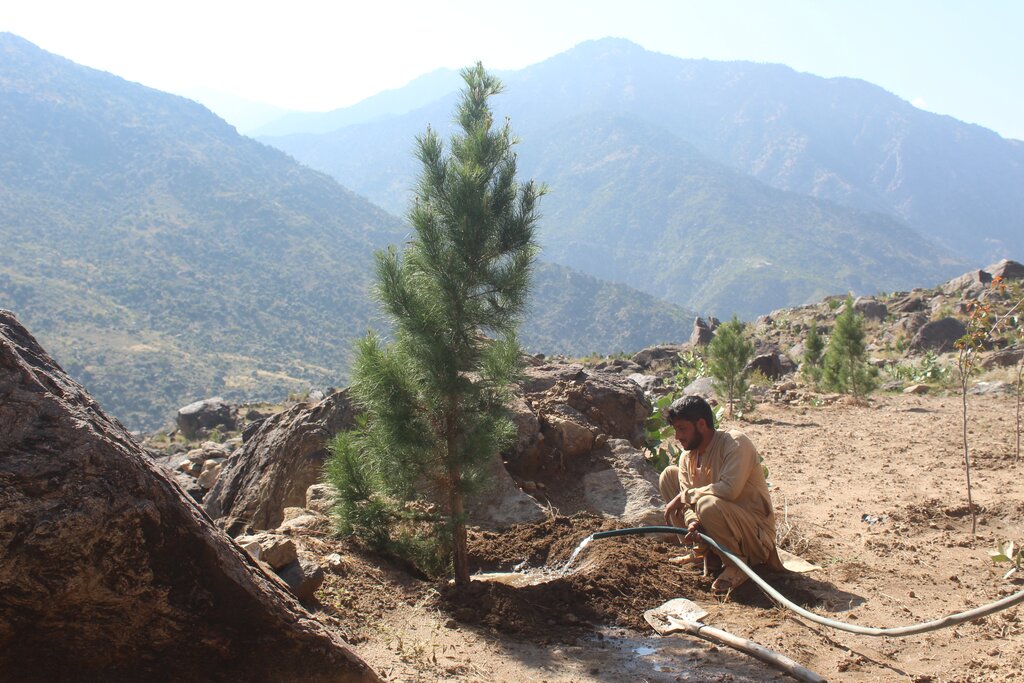
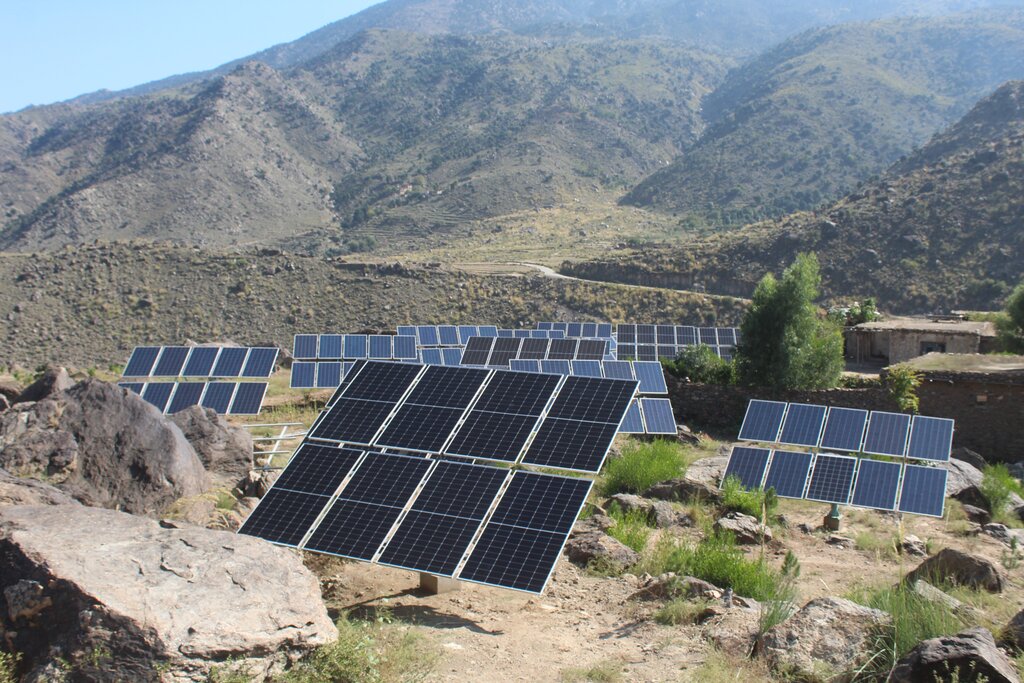
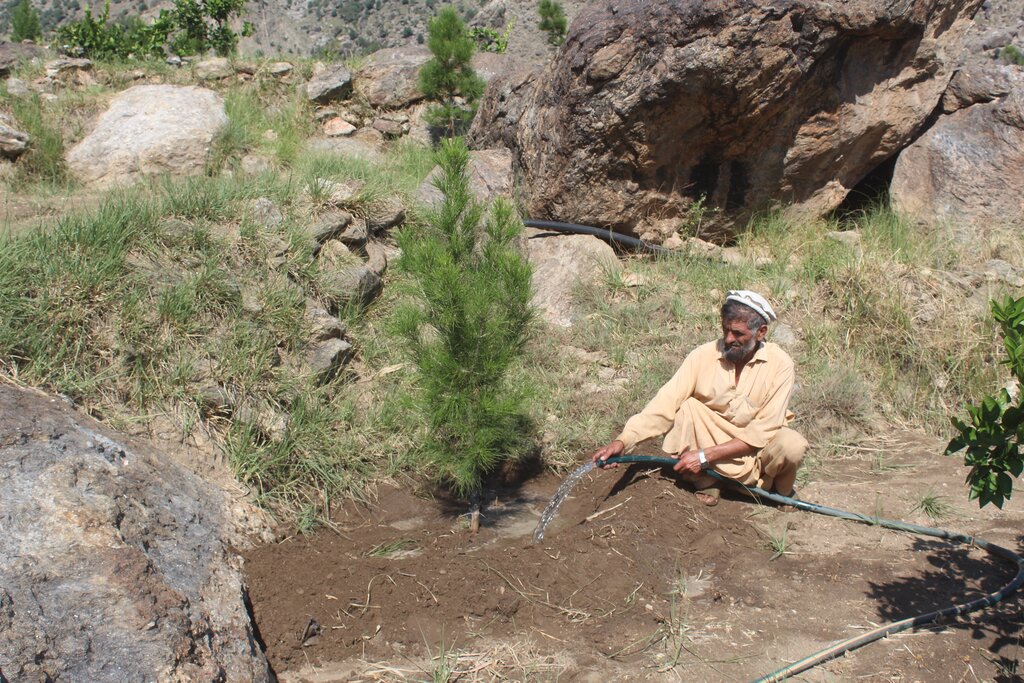
Water exploitation is a critical issue in Afghanistan, and the project aims to address this challenge through innovative and sustainable technology. The technology involves the use of solar panels and submersible water pumps to efficiently lift water from a nearby river to reservoirs constructed uphill, which is then distributed by gravity with the help of a pipe system to irrigate planted saplings in the afforested and agroforestry area. For afforestation, Pinus eldarica (Afghan pine) was planted due to its adaptability and soil stabilization properties. Additionally, citrus and persimmon trees are introduced for agroforestry, combining tree cultivation with agricultural benefits. This integrated technology promotes biodiversity, soil health, and sustainable land use, making the site a model/ demonstration site for afforestation and agroforestry practices. This is a significant advancement in the local area, utilizing clean energy to promote sustainable land and forest management and environmental restoration. The project is implemented on communal land, covering 50.25 hectares of land.
The primary purpose of this technology is to create an efficient irrigation system that extracts and transports water to support afforestation and agroforestry activities. By doing so, it aims to restore forest cover, mitigate environmental challenges such as land degradation, and promote long-term ecological and socio-economic sustainability. The technology includes key components such as solar panels, water pumps (submersible), polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes, water reservoirs, and saplings. Additionally, it requires labor, technical assistance, capacity-building programs, and construction materials for its establishment and maintenance.
The benefits of this technology are substantial. It has successfully irrigated previously barren land, achieving an impressive 85% survival rate for the saplings that were planted in the plot, while preventing land degradation and improving soil health. Without this technology, survival rates would drop to zero due to the arid conditions. Furthermore, the project has enhanced the capacities of local farmers/community members, enabling them to replicate and demonstrate the technology within their community. This has fostered a sense of ownership and empowerment among land users.
Land users have expressed both appreciation and concerns regarding the technology. On the positive side, they value its efficiency and reliability, as the solar panels provide a consistent water supply, especially during the hot/sunny season, leading to increased greenery and healthier trees. The cost-effectiveness of solar energy, with its low operational costs compared to traditional diesel pumps, has also been a significant advantage. Additionally, the environmentally friendly nature of the technology aligns with their desire for sustainable practices. The capacity-building programs provided by organizations like FAO have further empowered users to manage the system effectively.
However, some challenges have been noted. The initial investment costs for purchasing, installing and construction of the technology are high, making it difficult for smallholder farmers to replicate. Technical issues, such as inverter failures or battery malfunctions during extreme weather conditions (e.g., cloudy weather), can disrupt operations. Additionally, not all community members are equally informed about the technology’s benefits, highlighting the need for increased outreach and engagement efforts to ensure broader adoption and understanding.
In summary, this solar-powered irrigation technology represents a groundbreaking innovation in the area, combining clean energy with sustainable land management practices. While it has demonstrated significant environmental and agricultural benefits, addressing the challenges of initial costs, technical reliability, and community engagement will be crucial for its long-term success and scalability.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ទីតាំង:
N/A
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
N/A
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
ប្រទេសអាហ្វហ្គានិស្ថាន
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
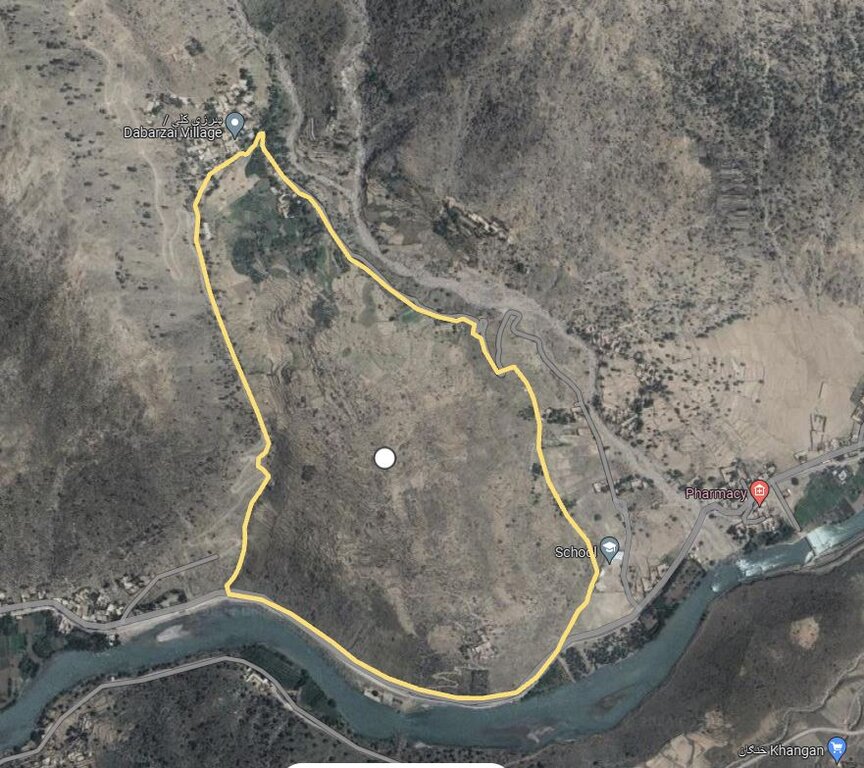
Kunar
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Managi village of Manogi district
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
តើបច្ចេកទេស (មួយ ឬច្រើន) ទាំងនោះស្ថិតនៅក្នុងតំបន់ការពារជាអចិន្ត្រៃយ៍ណាមួយដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
មតិយោបល់:
The area is about 50.25 ha, and the coordinate has been taken from the center of the site, where technology has been implemented:
34.9419930°N71.0119714°E
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2022
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
GEF-06 Community based Sustainable Land and Forest Management in Afghanistan
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- បន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងផលប៉ះពាល់របស់វា
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
បាទ/ចា៎
បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទដីច្រើនប្រភេទ (ដីដាំដំណាំ/ដីចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ/ដីព្រៃឈើ):
- កសិរុក្ខកម្ម

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ - បញ្ជាក់ប្រភេទ:
- ពពួកក្រូច citrus
- Persimmon
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំចន្លោះ?
ទេ
តើជាការអនុវត្តន៍ដំណាំវិលជុំ?
ទេ

ដីព្រៃ/ដីដាំដើមឈើ
- ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំព្រៃឡើងវិញ
ការដាំដើមឈើ ការដាំដើមឈើឡើងវិញ៖ បញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទក្នុងតំបន់ និងប្រភេទលុប:
- ឯកវប្បកម្មដែលប្រើពូជក្នុងតំបន់
ប្រភេទដើមឈើដែលដាំនៅកន្លែងដែលមិនធ្លាប់មានឈើពីមុន :
- ព្រៃស្ងួតដាំតំបន់ពាក់កណ្តាលត្រូពិច - Pinus spp.
ប្រភេទឈើ:
- Pinus species (pine)
តើប្រភេទឈើខាងលើជាប្រភេទឈើក្នុងព្រៃល្បោះ ឬស្រោង?
- ព្រៃស្រោង
ផលិតផល និងសេវាកម្ម:
- ការអភិរក្ស/ការការពារធម្មជាតិ
- ការកំសាន្ត/ទេសចរណ៍
- ការពារពីគ្រោះធម្មជាតិ
3.3 បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
បន្ទាប់ពីអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើដីប្រើប្រាស់មានការប្រែប្រួលដែររឺទេ?
- បាទ/ច៎ា (សូមបំពេញសំណួរខាងក្រោមពីស្ថានភាពដីប្រើប្រាស់មុនពេលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស)
ដីប្រើប្រាស់ចម្រុះនៅលើដីតែមួយ:
ទេ

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
5 decades ago, the area was a forest area, but due to war, smuggling and drought the area become barren land.
3.4 ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង និងប្រព័ន្ធស្រោចស្រព
មតិយោបល់:
The saplings planted in the area have been supplementary irrigated. Prior to the implementation of this technology, the land was barren, and seasonal rains led to soil erosion.
3.5 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- គ្រប់គ្រងការដាំព្រៃឈើ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងគម្របដី/ ដំណាំគម្របដី
- បច្ចេកទេសប្រើប្រាស់ថាមពលមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការរុក្ខជាតិ
- V1: ឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S5: ទំនប់ ថ្លុក ស្រះ
- S7: ការប្រមូលទឹកស្តុកទុក/ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹក/ សម្ភារៈស្រោចស្រព
- S10: វិធានការសន្សំថាមពល

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
- M3: ប្លង់យោងទៅតាមធម្មជាតិ និងបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ
មតិយោបល់:
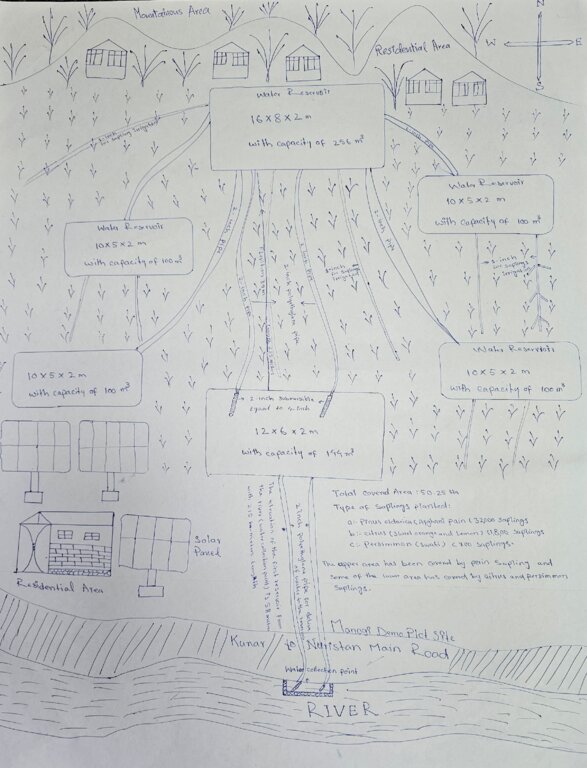
The project has successfully implemented afforestation by planting trees and promoting agroforestry through the cultivation of fruit trees. To improve irrigation management, the project installed a 1-inch underground pipeline system with connected taps, enabling the attachment of flexible hoses. This efficient setup ensures optimal watering of saplings while significantly reducing water waste. By implementing this approach, the project has enhanced vegetative cover and successfully planted approximately 32,000 saplings. Additionally, the project constructed 14 rotating mounting structures for solar panels, installed 134 solar panels, established pipe schemes for manual irrigation of saplings, and constructed 6 water reservoirs with different capacities. The integration of trees at optimal spacing, combined with regular cultural practices, has further supported the project's goals.
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bl: ការបាត់បង់មីក្រូ និងម៉ាក្រូសរីរាង្គរបស់ដី

ការបាត់បង់ទឹក
- Ha: ការថយចុះសំណើមដី
- Hg: ការប្រែប្រួលបរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រោមដី
មតិយោបល់:
The planting pits are specially designed for planting of saplings. Additionally, farmers construct small barriers near plants (eye-brows and trenches), known as micro-catchments, to collect and retain water. It is important to note that these micro-catchments are distinct structures, separate from pits and reservoirs, and are specifically built to support water retention for plants. The enhanced vegetation cover and the establishment of micro-catchments for water collection significantly reduce soil erosion. Soil improvement and enrichment, as well as habitat enhancement, are supported through these practices. Additionally, they contribute to groundwater recharge and help control runoff.
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការជួសជុល/ ស្តារឡើងវិញនៃឱនភាពដីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ
មតិយោបល់:
The human-induced causes of land degradation include deforestation, overgrazing of livestock, and unsustainable agricultural practices. In response, following the implementation of a specific technology, local communities established regulations rooted in their customs and traditions to protect the site, which is quarantined for five years. These regulations prohibit herders from grazing animals, cutting trees, engaging in unsustainable agricultural practices, and uprooting bushes for fuelwood. Additionally, the community has constructed rainwater harvesting structures, such as eyebrows and trenches, across the site to address natural causes of land degradation through runoff by enhancing water infiltration. As a result, the site is now effectively protected from both human-induced and natural land degradation.
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ទាក់ទងនឺងគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស):
According to the technical specifications from the project engineer, 6 reservoirs have been constructed with varying dimensions and water holding capacities as follows:
1.First reservoir: Dimension of 12x6x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 144 m³.
2.Central reservoir: Dimensions of 16x8x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 256 m³.
3.Four additional reservoirs: Each measuring 10x5x2 meters, with a water holding capacity of 100 m³
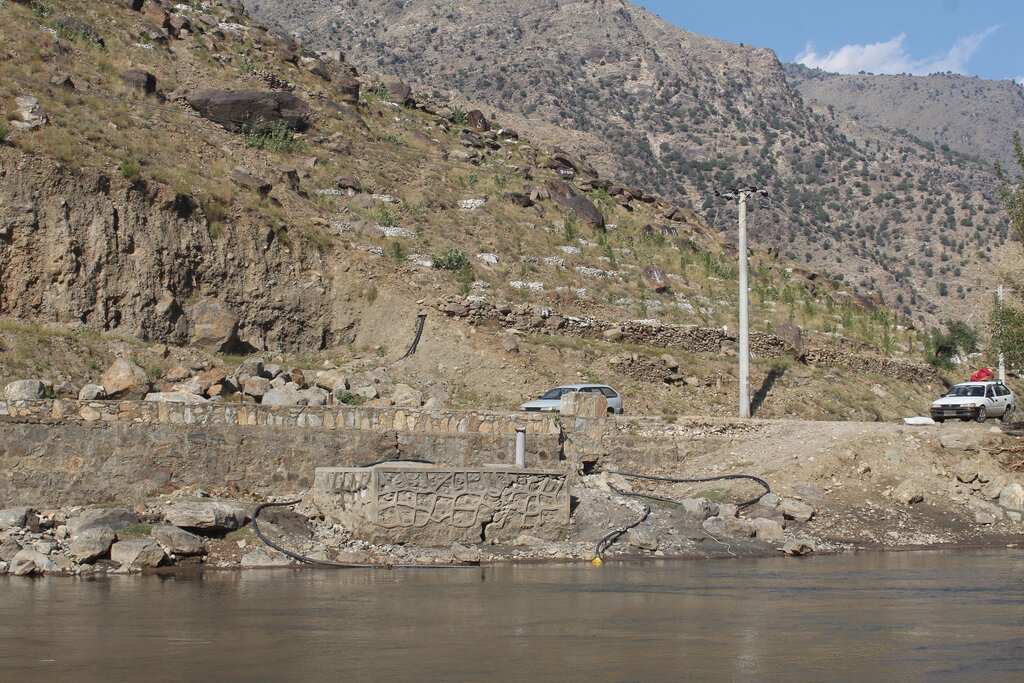
In total, the reservoirs will hold 800 m³ of water, ensuring a reliable water supply for irrigation of the area. Two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs by gravity.
Furthermore, excavation and backfilling for 2-inch polyethylene pipes should be done to a depth of 80 cm with a width of 50 cm. For 1.5-inch pipes, excavation and backfilling should be 40 cm deep. The installation of 1.5-inch polyethylene pipes, including all elbows, joints, connectors, and valves, should be carried out every 30 meters on both sides, connecting to 1-inch pipes, in accordance with specifications and to satisfaction.
Additionally, 32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghan Pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings were planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. The saplings are spaced 5 meters apart, both plant-to-plant and row-to-row, as part of afforestation and agroforestry initiatives. This effort aims to restore ecosystems, enhance biodiversity, and improve soil conservation.
ឈ្មោះអ្នកនិពន្ធ:
Hafizullah Naeemy
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
01/03/2022
4.2 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
50.25 Hectares
កំណត់រូបិយប័ណ្ណសម្រាប់ថ្លៃដើម:
- ដុល្លារ
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
5 USD
4.3 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | រយៈពេល (រដូវកាល) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Awareness and mobilization of the community | Aug-2021 |
| 2. | Survey and site selection followed by feasibility study | Sep to Oct-2021 |
| 3. | Stakeholder consultation | Aug-2021 till Sep-2022 |
| 4. | Preparation of technical design, drawings, and Bill of Quantities (BoQ). | Nov to Dec-2021 |
| 5. | Initiation of procurement process for required tools and equipment | Jan to Feb-2022 |
| 6. | Excavation and construction of water reservoirs, setting up pipe system and installation of solar panels for irrigation. | Mar to Sep-2022 |
| 7. | Capacity building of the target communities | Aug- 2021 till date |
| 8. | Practical interventions: production or purchase of saplings, digging planting pits, transplatation and irrigation of saplings and establishment of micro-catchments | Feb to Mar-2023 |
មតិយោបល់:
The awareness-raising session on Sustainable Land Management (SLM) and Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) was successfully held to improve understanding of land and forest management practices and conservation efforts. Community members were actively mobilized to support the project, aiding in the completion of construction and installation work.
4.4 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Unskilled labor for planting of saplings | Man/day | 450,0 | 5,0 | 2250,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Skilled labor for installation of irrigation system and constuction of reservoirs | Man/day | 50,0 | 10,0 | 500,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Water Pump 2 inch - 10HP/7500w | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Solar Panel minimum size 400W and 270W | Number | 132,0 | 82,0 | 10824,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | DC to AC Inverter 7.5-11KW | Number | 4,0 | 450,0 | 1800,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Polyethylene Pipes 2 Inch and 1.5 Inch with all elbows, joints, connectors and valves after 30 meter for both sides to connect pipes. | Meter | 4300,0 | 2,75 | 11825,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Rotating PV panels mounting structure (manual) | Number | 28,0 | 270,0 | 7560,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | DC and AC current wire | Meter | 1800,0 | 2,5 | 4500,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Distribution board | Number | 2,0 | 70,0 | 140,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈ | Flexon 1 inch rubberize pipes | Meter | 5500,0 | 1,4 | 7700,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Saplings procured & transported | Sapling | 32000,0 | 0,775 | 24800,0 | |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | Planting tools | lump sum | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Organic fertilizers for transplanted saplings added through community | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | 6 reservoirs constructed by a construction company (cement, stone, sand excavation, etc.. | lump sum | 1,0 | 35000,0 | 35000,0 | |
| ផ្សេងៗ | Patrolling, irrigating and quarantine of the site | lump sum | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 111799,0 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 111799,0 | |||||
ប្រសិនបើអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីមិនមានថ្លៃដើម 100% សូមបញ្ជាក់ថានរណាដែលចំណាយថ្លៃដើមដែលនៅសល់:
The remining cost were covered by the project.
មតិយោបល់:
The first two 2-inch submersible pumps draw water from the river to supply the first reservoir. From there, two additional 2-inch submersible pumps transfer water from the first reservoir to the central reservoir. The water then flows to the other four reservoirs through gravity.
4.5 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Patrolling | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump (submersible) | Ad hoc /Annually |
| 4. | Plot maintenance (Pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding,). | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacement of failed saplings | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing micro-catchments | Spring/annually |
4.6 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labor for cleaning of sedimentation of reservoirs | Man/day | 60,0 | 5,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labor for patrolling | Man/day | 360,0 | 5,0 | 1800,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labor for repairing micro-catchments | Man/day | 20,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Manage the solar system operations | Man/day | 360,0 | 2,77 | 997,2 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labor for weeding and mulching | Man/day | 30,0 | 5,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Pump submersible, PVC pipe, fittings | lumpsum | 3,0 | 500,0 | 1500,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Shovels | lumpsum | 1,0 | 140,0 | 140,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈដាំដុះ | saplings | Sapling | 2000,0 | 0,6 | 1200,0 | 100,0 |
| ជី និងសារធាតុពុល | Organic fertilizers (cows dungs) | Kg | 16000,0 | 0,1 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 7787,2 | |||||
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេសគិតជាដុល្លារ | 7787,2 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
The community has hired an individual to manage the solar system operations. This person is responsible for both operating the solar system for lifting water and overseeing the distribution of water for irrigation purposes among community members.
4.7 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
All equipment are imported and has resulted into higher cost.
Natural hazards, floods and windstorms will increase the costs of repairs and replacement
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
300,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Most of rain occur in the months of Feb, Mar, Apr, July and Aug.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
The data has been collected based on the farmers observation and local practices.
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងតិចតួច
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- សណ្ឋានដីផត
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- ទាប (<1%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
> 50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
កម្រិតមធ្យម
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក គឺផ្តោតទៅលើ៖:
ទាំងទឹកក្រោមដី និងលើផ្ទៃដី
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
ភាពទៀងទាត់:
ញឹកញាប់
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- កម្រិតមធ្យម
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម)
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មិនល្អ
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ជាក្រុម/ សហគមន៍
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីប្រើប្រាស់ដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី ក្នុងការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
មតិយោបល់:
The area where the technology is applied covers 50.25 hectares and is managed by 112 land users.
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ភូមិ
- ឯកជន មានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
- ឯកជន
តើកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី គឺផ្អែកលើប្រព័ន្ធច្បាប់បែបបុរាណ?
បាទ/ចា៎
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
In Afghanistan, the traditional land use system involves the equitable distribution of deserts and barren land among the local residents. The decisions made by the elders are respected and adhered to by all members of the community.
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
fruit production (citrus and persimmon)
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as part of the agroforestry system and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people. Based on the production, the socio-economic status of the community members is expected to improve.
ផលិតកម្មឈើ
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
A total of 32,000 forest saplings (Pinus species) were successfully planted
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
32,000 Pinus eldarica (Afghani pine) and 2,500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted across 50.25 hectares of degraded land. Following agronomic practices, the four Ds—dead, diseased, damaged, and dying—branches will be pruned and utilized for shelter and fuel.
ផ្ទៃដីផលិតកម្ម
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0 fruit trees
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
Approximately 1,200 fruit trees, including sweet orange and persimmon species, have been planted
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The 2500 citrus and persimmon saplings have been planted as a agroforestry and will bear fruit in line with the demand and needs of the people.
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
The area was once barren and occasionally used for rainfed cultivation, where most farmers grew wheat. Now, with the introduction and implementation of the technology farmers can also intercrop beans, mung beans, and others. Farmers who have more than 1 hectare of land hire labor for agronomical practices.
ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
ទឹកប្រើប្រាស់សម្រាប់ស្រោចស្រព
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
0
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
100%
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
With the adoption of this technology, irrigation for planted saplings is now available 100% throughout all seasons of the year.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ភាពសម្បូរបែបប្រភពប្រាក់ចំណូល
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Timber Production, Non-Timber Forest Products, Ecotourism, Agroforestry, Wildlife Conservation and Fuelwood and Biomass
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើវប្បធម៌សង្គម
ឱកាសនៃការបង្កើតថ្មី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Recreational opportunities that benefit both local communities and visitors such as nature trails allowed individuals to engage with nature, promoting physical activity and wellness. The reforestation efforts have led to the restoration of habitats for various wildlife species, this provides opportunities for wildlife observation and photography, and contributing to local ecotourism.
ចំណេះដឹង SLM / ការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Improved due to workshops and on job trainings
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
វដ្តទឹក/លំហូរ
លំហូរទឹកលើផ្ទៃដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to better soil coverage by plantation of saplings and micro-catchment structures
ដី
សំណើមដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to the availability of irrigation water and the establishment of micro-catchments to harvest water and enhance water infiltaration soil moisture for sapling growth has increased
គម្របដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to natural regeneration and plantation of saplings and intercrops
ការបាត់បង់ដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to better soil coverage and less water runoff
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃរុក្ខជាតិ
ការកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យនៃគ្រោះមហន្តរាយ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃទឹកជំនន់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
better soil cover reduced water runoff and ultimately flooding
6.2 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្រៅបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ខូចខាតដល់ហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសាធារណៈ/ឯកជន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Soil erosion was reduced and has been better controlled
ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃឧស្ម័នផ្ទះកញ្ចក់
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to plantation
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | កើនឡើង ឬថយចុះ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំរដូវកាល | និទាឃរដូវ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយធម្មជាតិ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ព្យុះកំបុតត្បូងតាមតំបន់ | មធ្យម |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមានតិចតួច
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមានខ្លាំង
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- 1-10%
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 0-10%
មតិយោបល់:
The community economic condition is not good. So, without receiving incentives they are not able to adopt such technology easily.
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| Improved water availability with minimized fuel cost and decreased pollution as well as minimum operational cost |
| Opportunities/ potential for upscaling of the technology |
| Use of clean energy to contribute to mitigate climate change |
| Reduce greenhouse emission through carbon sequestration |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The technology is highly efficient and suitable for adoption by land users. It promotes clean energy, reduces greenhouse gas emissions through carbon sequestration, and contributes to climate change adaptation. |
| The area has been successfully afforested, restoring its natural beauty and original landscape. |
| The vegetation cover on the previously degraded land has been significantly enhanced. |
| This technology with its approach for implementation represents an effective solution for the restoration of degraded soils. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Inadequate maintenance and repair services of the technology | Linkage to the service provider and maintenance services. Nation wide technology transfer |
| Solar water lifting relies on fully sunny days for operation, which can sometimes be a limitation, especially when weather conditions are cloudy or during periods of low sunlight. This can result in insufficient water being lifted to meet the irrigation needs of the site. | Backup charging system/battery system |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Solar water lifting depends on sunny days for operation, which can sometimes fall short of meeting irrigation needs during cloudy periods. | Combining solar power with backup energy (like batteries or grid connection) |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
10
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
15
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកជំនាញ/ ឯកទេស
2
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
28/11/2024
មតិយោបល់:
The data has been collected during Oct and Nov 2024
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល