Earth checks for Gully reclamation [ອີທິໂອເປຍ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Daniel Danano
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1069 - ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Estifanos Zena
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Desta Hiwot
Boditi, Department of Agriculture and Rural Development
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ອີຕາລີຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - ອີທິໂອເປຍ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
30/05/2011
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
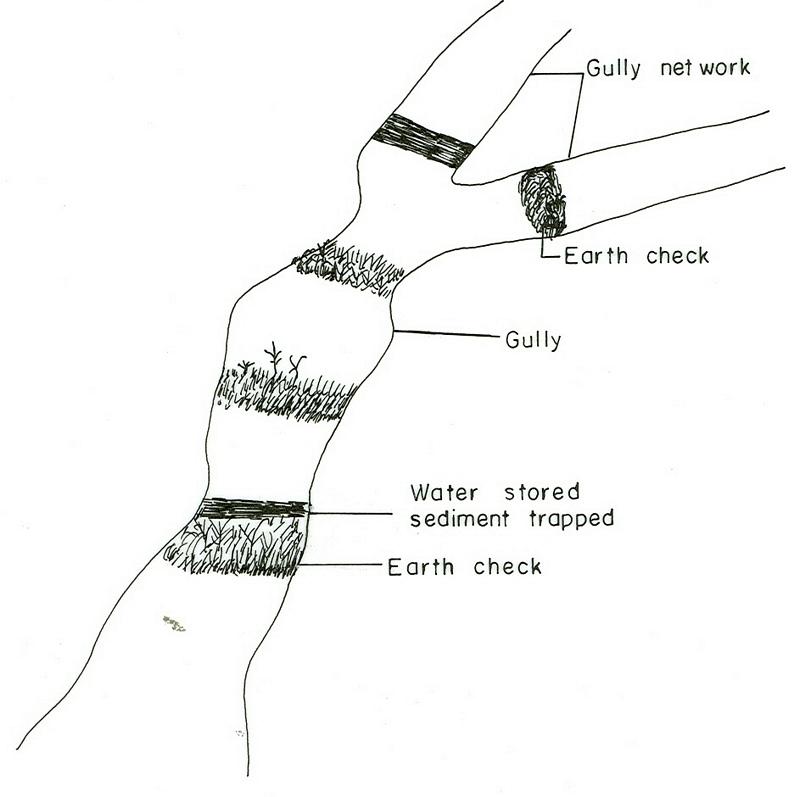
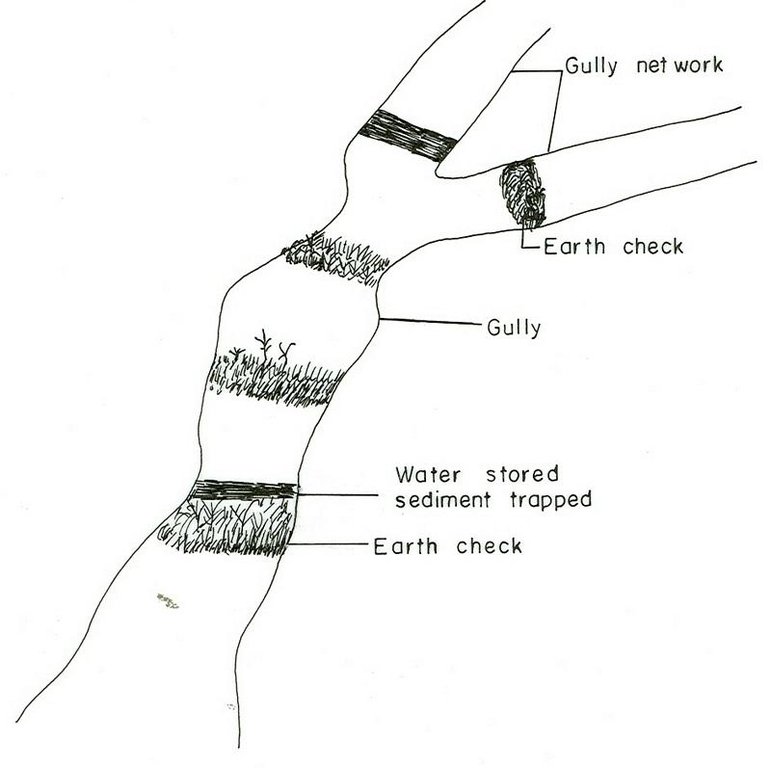
Earh-checks are constructed of earth embankment put across in a deep gully in such a way to trap sediment and store water passing by it.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
Active deep gullies are plugged by digging earth from the bottom as well as gully sides and embanked forming a barrier to runoff passing through it. The embankment is reinforced by planting useful plants such as banana, sesbania, gravillea, gesho, etc., The purpose is to rehabilitate gullies having depth and expand along sides and towards the head. By constructing earth checks the water is stored in the checks. The water percolates down the ground enriching the ground water. The soil is trapped in the checks and later brings up the gully gradient higher. As a result, a cultivable/cropable strip is formed. Weeding and cultivation done to plants established.The gully fence and breaks are repaired. The technology is seen to be suitable to humid highlands where land loss by gully is a serious problem and land under cultivation and grazing is getting here and there. In brief it is suitable in areas where land degradation problem is increasing with currently cultivated and grazed lands are encroched by gully expansion.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ອີທິໂອເປຍ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
SNNPR
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
SNNPR/Damot Galle/Bilate
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- ຕໍ່າກວ່າ 10 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ (ມາເຖິງປະຈຸບັນ)
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The technology is introduced but highly modified by adjesting design, layout and by increasing use of locally available materials for construction.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
- ພືດຢືນຕົ້ນ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນໄມ້)
- ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ໄມ້ພຸ່ມ ຈາກການປູກພືດ
ການປູກພືດຫຼັກ (ທີ່ສາມາດສ້າງລັບຮັບ ເປັນເງິນສົດ ແລະ ເປັນພືດສະບຽງອາຫານ):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Teff
Major food crop annual cropping: Maize, sweet potato, enset
Major other crop annual cropping: Taro, potato
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Sugar cane
Major cash crop tree and shrub cropping: Sugar cane
Major other crop tree and shrub cropping: Fruit trees

ປະສົມປະສານ (ການປູກພືດ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້), ລວມທັງ ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Monocropping, soil erosion, fertility mining, overgrazing, improper runoff management.
Grazingland comments: Livestock such as cows, oxen, donkeys and horse are thethered at a very small piece of land left infront of houses usually meant for social purposes. Some farmers thether their animals in a piece of land left uncropped in the field. The most part of livestock feed comes from crop residue which is collected from crop fields. Maize stalk, teff straw and enset leaves are fed stall.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize-sweet potato-Teff-potato-sorghum
3.3 ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
ຈໍານວນ ລະດູການ ປູກໃນປີໜຶ່ງ:
- 2
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 180 Second longest growing period from month to month: Aug - Jun
3.4 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ມາດຕະການ ຕັດຂວາງ ກັບຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ
- ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
3.5 ການຂະຫຍາຍເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 51.2 m2.
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ປ້ອງກັນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main goals: Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
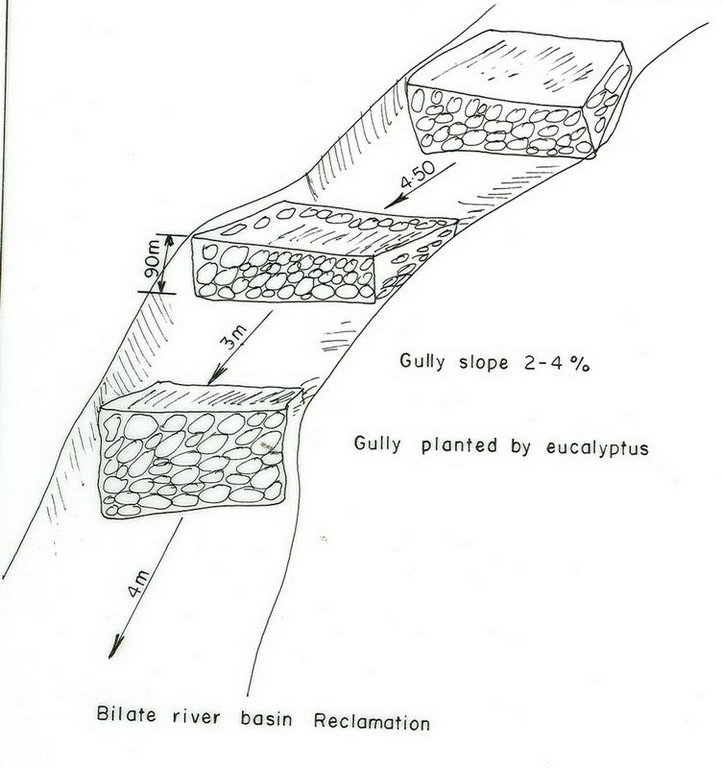
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
4.2 ການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດອະທິບາຍເຕັກນິກ
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Early planting
Material/ species: maize
Quantity/ density: 85000/ha
Remarks: sawn in lines
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize-sweet potato/haricot bean
Remarks: inter cropped & strip cropped
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize-taro-enset
Mulching
Material/ species: enset
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: maize, potato, sweet potato, traro
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Teff, maize, sorghum
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: maize-tarro-sorghum
Remarks: only rotations
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: primary and secondary oxen tillage
Contour tillage
Remarks: tillage done following contour
Agronomic measure: harrowing
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2-4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5x1.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2x2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena, Sesbania, Grevillea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, papaya, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Casava
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 8.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-75
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Construction material (earth): Most of the structural measures are made by earth involving excavation and embankment.
Construction material (stone): Stone is mainly used for demonstration.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: The land after treatment is closed
Control / change of species composition: Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
4.3 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ສະກຸນເງິນອື່ນໆ / ປະເທດອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸ):
Birr
ລະບຸ ອັດຕາແລກປ່ຽນ ຈາກໂດລາ ເປັນເງິນຕາທ້ອງຖີ່ນ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ): 1 ໂດລາ =:
8.5
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
0.60
4.4 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | September, october |
| 2. | Sugar cane planting | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | November |
| 3. | Sugar cane cultivation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | January/August |
| 4. | Casava planting | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | April |
| 5. | Casava cultivation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | June |
| 6. | Maize planting | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | January-1st plough, April 2nd plough |
| 7. | Maize cultivation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | June |
| 8. | Sweet potato planting | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | September |
| 9. | Sweet potato cultivation | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | October |
| 10. | Fruite trees | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | June |
| 11. | Digging foundation | ໂຄງສ້າງ | November-February |
| 12. | Forming embankment | ໂຄງສ້າງ | November-February |
| 13. | Side wall shaping | ໂຄງສ້າງ | November-February |
| 14. | Planting trees and shrubs | ໂຄງສ້າງ | March-1st planting & June 2nd planting |
| 15. | Excluding animals by fencing and guarding | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | all year |
| 16. | Construct cutoff drain | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | dry season |
| 17. | Establish buffer zone between Area enclosure and crop land by strip of plantation | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | June/July |
| 18. | Construct earth checks and trenches in the gully | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | dry season |
4.5 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 282.3 | 282.3 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 270.6 | 270.6 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸໃນການປູກ | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 117.6 | 117.6 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 670.5 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ປະເພດ ມາດຕະການ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | ພືດ | september, october / 2 times |
| 2. | Sweet potato planting | ພືດ | September / each cropping season |
| 3. | Sweet potato cultivation | ພືດ | October / each cropping season |
| 4. | Maize planting | ພືດ | January/April / each cropping season |
| 5. | Maize cultivation | ພືດ | June / each cropping season |
| 6. | Teff sawing | ພືດ | |
| 7. | Teff weeding | ພືດ | |
| 8. | Prunning | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | october /once |
| 9. | Mulching | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | october /once |
| 10. | Thining | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | october /once |
| 11. | Fencing | ການບໍາລຸງລ້ຽງ | any time /once |
| 12. | Weeding | ໂຄງສ້າງ | June/each cropping season |
| 13. | Cultivation | ໂຄງສ້າງ | March/each cropping season |
| 14. | Replanting | ໂຄງສ້າງ | June/each cropping season |
| 15. | Repair in breaks | ໂຄງສ້າງ | November-February/each cropping season |
| 16. | Fence | ໂຄງສ້າງ | each cropping season |
| 17. | Repair breaks on cutoff drain and earth checks | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | dry season / 2 years |
| 18. | Prunning, weeding and cultivation | ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ | end of rains / each cropping season |
4.7 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Machinery/ tools: spade, hoe
Length and width of structure
4.8 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Factors affecting costs in this technology are the depth and width of gully, steepness of slope, planting and replanting of vegetative materials.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄີ່ງຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, about 70%), gentle and rolling (both ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ປານກາງ (1-3 %)
ຖ້າເປັນໄປໄດ້ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ຕິດຄັດ ການພັນລະນາດິນ ຫຼື ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະຂອງດິນ, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ປະເພດຂອງດິນ, ຄ່າຄວາມເປັນກົດ / ເປັນດ່າງຂອງດິນ, ສານອາຫານ, ດິນເຄັມ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ.
Soil depth on average: Deep (Soils are very deep (75%))
Soil texture: Medium (fertile loam soils)
Soil fertility is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (ranked 1, in the crop lands), low (ranked 2, degraded areas) and high (ranked 3, around the homestead)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1, on crop land) and high (ranked 2, on flat plateau land)
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ປະສົມ (ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ / ເປັນສິນຄ້າ
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- 10-50 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ສະເລ່ຍ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
- ສັດລາກແກ່
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich.
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
40% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have SWC measures on their land produce more and hence have better financial income, which could allow them get involved in petty trade and other activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, crop lands) and manual work ( ranked 2, homstead and gully lands)
Market orientation of cropland production system: subsistence (self-supply, maize) and mixed (subsistence/ commercial, sweet potato, teff, coffee)
5.7 ພື້ນທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ເຊົ່າໂດຍຜູ້ໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha (more than 80% of farmers) and 1-2 ha
grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (communal grazing lands are severly degraded)
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Shortage of grazing land: Animals are thethered in a small plots
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
teams are formed
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
many wants to be beneficiaries but only the poor given the opportunities
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
Biodiversity enhancement
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
all runoff retained
ການທັບຖົມ ຂອງດິນຕະກອນ ຢູ່ເຂດລຸ່ມນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
all soil trapped
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກເລັກນ້ອຍ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ