Vallerani System [ເບີກິນາ ຟາໂຊ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Sabina Galli Vallerani
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: Brigitte Zimmermann, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1528 - ເບີກິນາ ຟາໂຊ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Long Allain
Reach Afrique, NGO
ເບີກິນາ ຟາໂຊ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Lindo Grandi
Deserto Verde Burkinabé, NGO
ສະວິດເຊີແລນ
ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Boureima Amadou
Reach Afrique
ເບີກິນາ ຟາໂຊ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Reach Africa (Reach Africa)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Reach Italia (Reach Italia) - ອີຕາລີ1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.4 ແຈ້ງການວ່າ ດ້ວຍຄວາມຍືນຍົງຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ດັ່ງກ່າວໄດ້ອະທິບາຍ ເຖິງບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນບໍ? ຖ້າບໍ່ດັ່ງນັ້ນ ມັນບໍ່ສາມາດ ຢັ້ງຢືນໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນເຕັກໂນໂລຊີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ? :
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
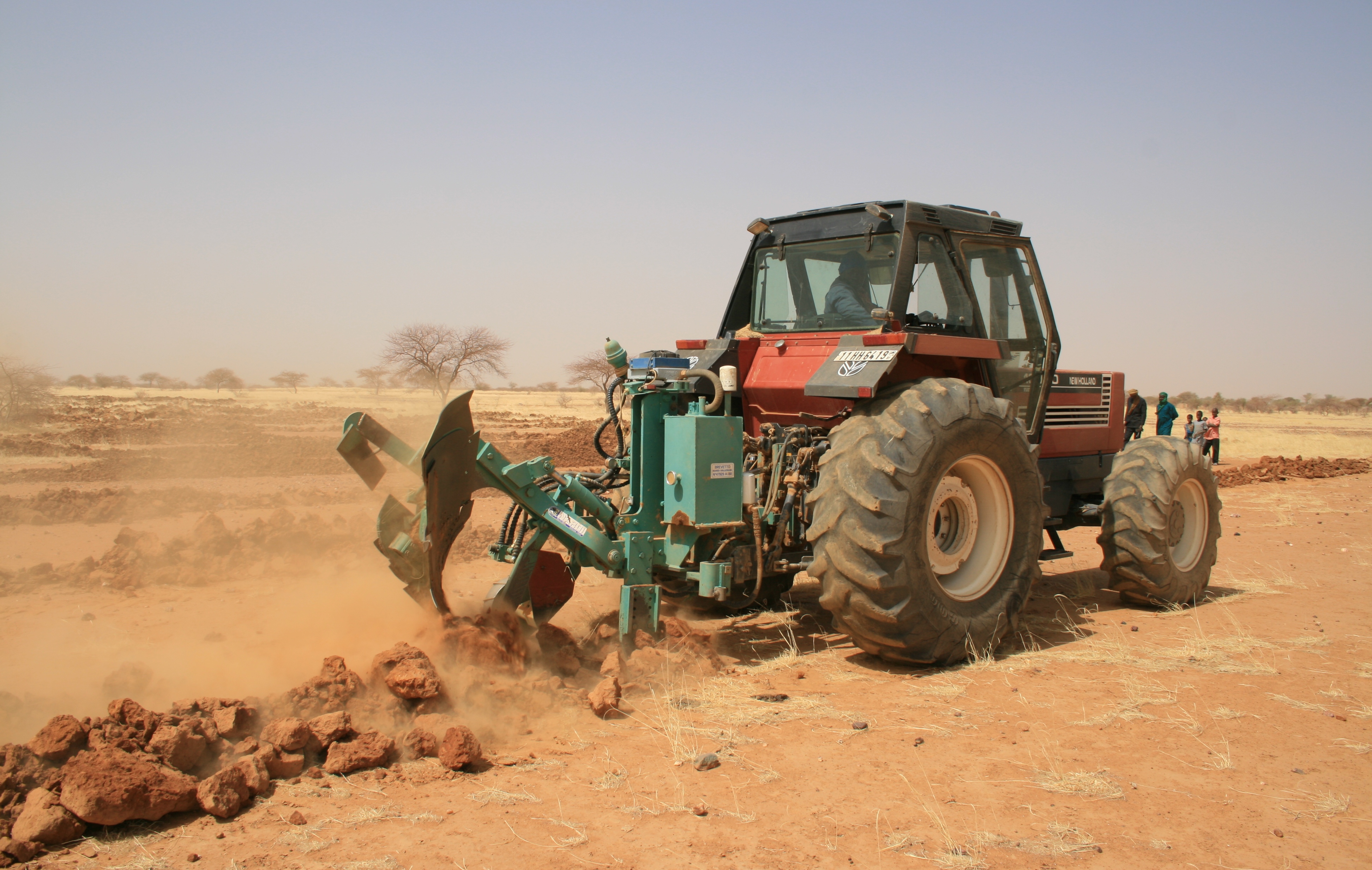
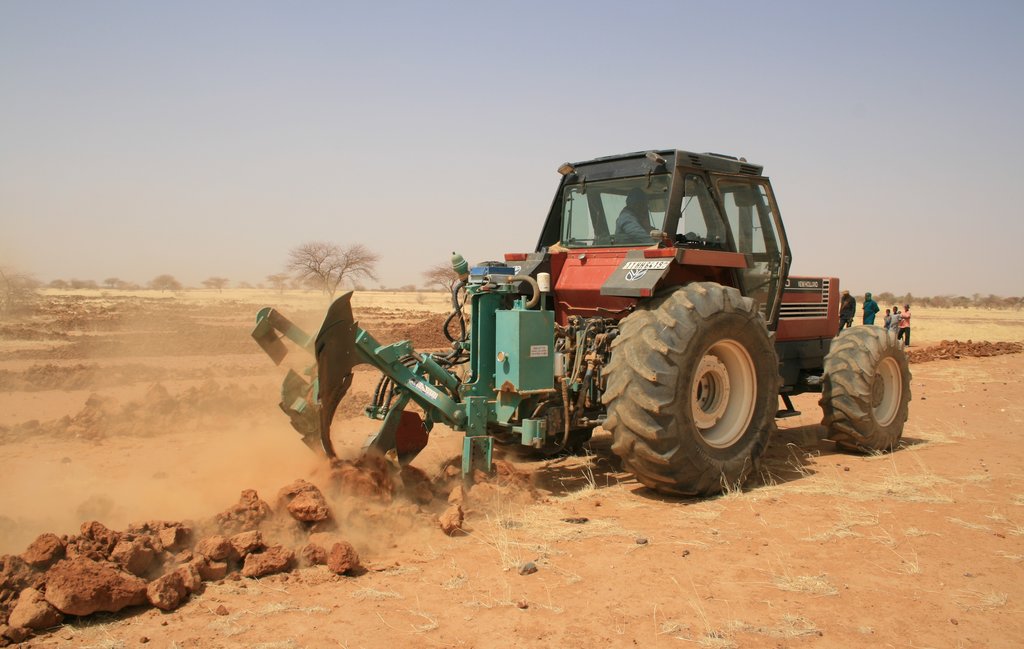
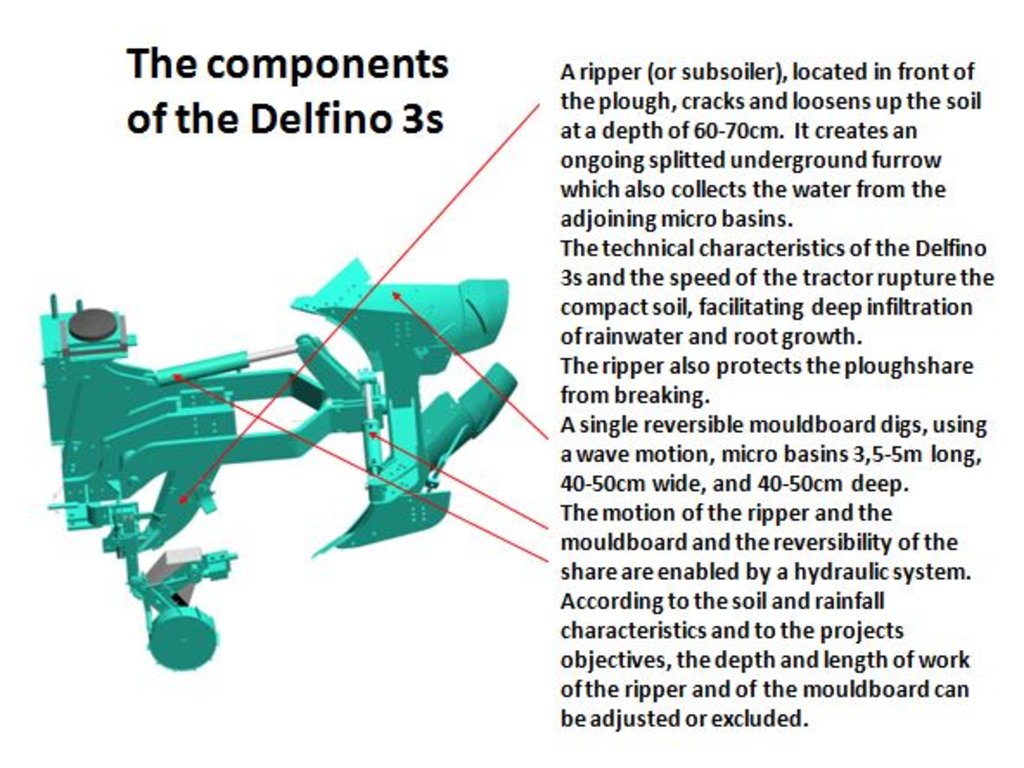
A special tractor-pulled plow that constructs micro-catchments. It combines the traditional techniques of rainwater harvesting with mechanization for large scale land rehabilitation.
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
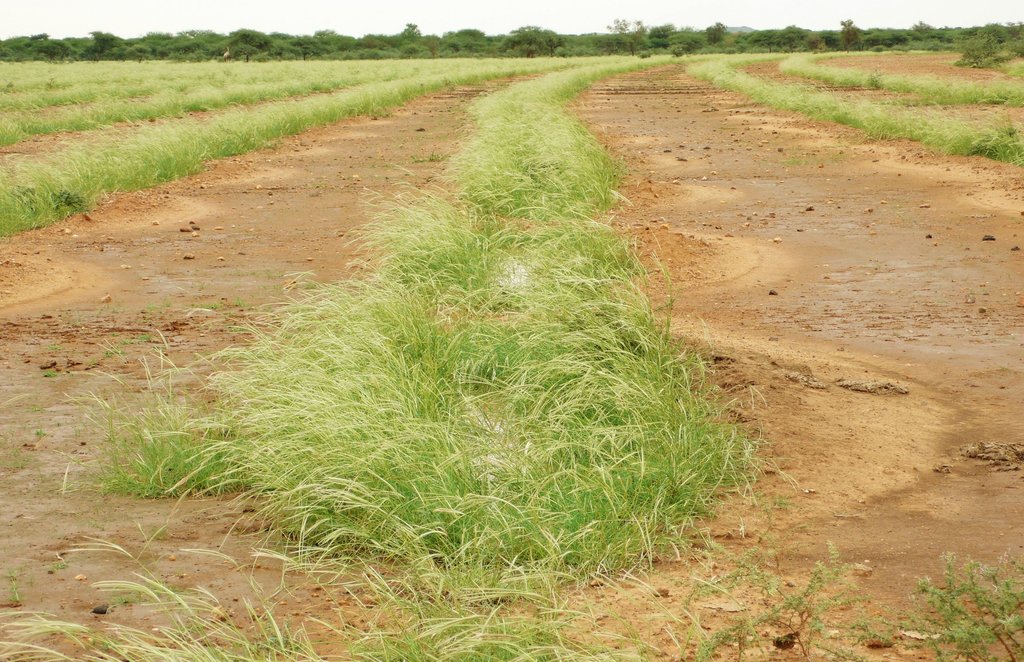
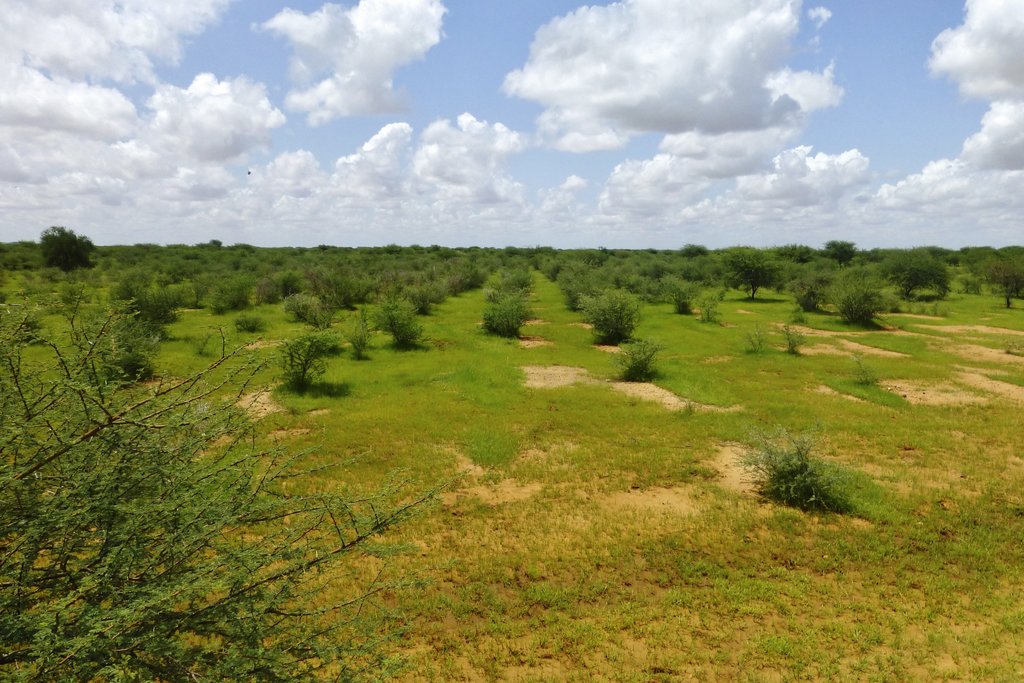
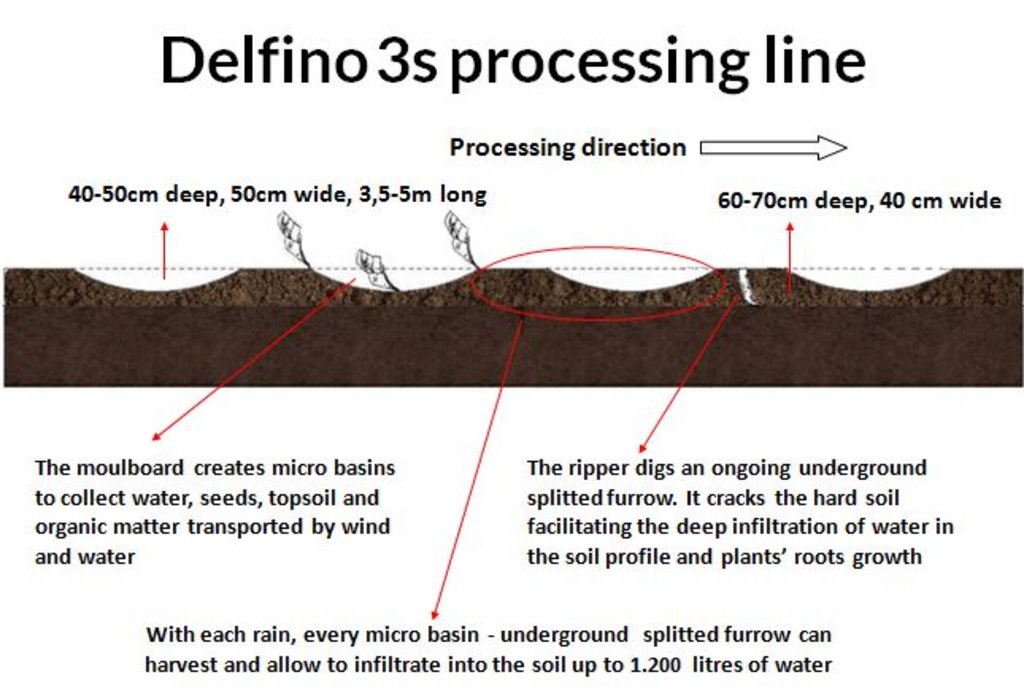
The Technology mechanizes the traditional technique of zai and semi circular bunds for water harvesting using a modified plow named Delfino3s pulled by a 180hp tractor. A normal plow on flat land excavates a symmetrical, continuous furrow, and earth piles up equally on both sides of the furrow. The Delfino3s plow has a single reversible plowshare that creates an angled furrow and piles up the excavated soil in half moon shaped ridges only on the downhill side. The plowing must be done along the contour to collect and slows down runoff water as it flows downhill. The plow’s blade moves in and out of the soil creating micro basins about 5 meters long, 50 cm deep, 50 cm wide and spaced 2-3 m. The ripper placed before the plow cracks up the soil to a depth of 70 cm facilitating the infiltration of water into the soil profile and the growth of deep roots. After plowing, the local population sows seeds of plants of indigenous species. They are sown along the ridges of the basins and in the furrow of the ripper. While for most species seeds are collected by the local population, for species rarely present in the region, seeds are purchased from tree nurseries. Sowing the manure of goat containing seeds has also been very successful with about 95% of all micro basin having at least one tree growing. The intervention on a big scale, the effects of water infiltration in depth, erosion reduction and vegetation growth, boost a long lasting rehabilitation process. Each day the Delfino plow can plow up to 20 ha, digging 6.000-7.000 micro basins. The speed, the capability to plow hard, abbandoned land, the effectiveness of the Delfino3s plow are its major advantages for the ecosystem rehabilitation process but require a big commitment. To make the best out of it, a great motivation and organizational work is necessary to: find great availability of land; train accuratelly the technicians; have well-rooted Subjects in the region. The technological aspect is just part of the recovery process, an important work with the Communities is required upstream and downstream. Communities are involved in the management process – in identifying the areas to be restored, clarifying the land uses of the affected areas, planning and implementing e.g. gathering and keeping seeds of local ecotypes, sowing, in the management of plantations and in the monitoring and evaluation of the results. Rules for SLM are adopted and respected by all. The Technology is applied in a degraded agro-sylvo-pastoral area of the Sahel Region, in the north east of Burkina Faso with 200-500 mm of annual rainfall. The soil is sandy-loam, strongly degraded with surface crust. The population is mainly composed of semi-nomadic herders. At the beginning of the project, the NGO Reach Italia was promoting schooling; they soon realized that during the dry season most kids left school and that to avoid it they should face food security and pasture improvement. So they started applying the Vallerani System and developped the participatory approach. The vegetation growth reduces the need for fodder search and long-range transhumance which also allows children to go to school regularly.The ecosystem rehabilitation effect of the technology help the communities to become more concious and resilient to the effects of climate change and prepared to cope with the socio-economic-environmental changes they are faced with.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.4 ວິດີໂອ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
A short video that introduces the Vallerani System.The video has been shot in the project area.
ວັນທີ:
14/05/2014
ສະຖານທີ່:
Oudalan, Burkina Faso
ຊື່ຂອງຜູ້ຖ່າຍວີດີໂອ:
Jonathan van Laamsverde
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
ICARDA Vallerani –Technology transfer from Morocco to Jordan.
The presentation of the ICARDA Minared project applying the Vallerani System for rangeland rehabilitation in the Jordan Badia.
ວັນທີ:
16/06/2016
ສະຖານທີ່:
Badia, Jordan
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ, ຄໍາອະທິບາຍຫຍໍ້:
REACH – DESERTO VERDE BURKINABe' Vallerani - Recupero Terre in Burkina Faso Sicurezza Alimentare.
Reach Italia and Deserto Verde Burkinabé present the project of soil rehabilitation and food security in Burkina Faso. Italian text.
ວັນທີ:
01/09/2009
ສະຖານທີ່:
Oudalan, Burkina Faso
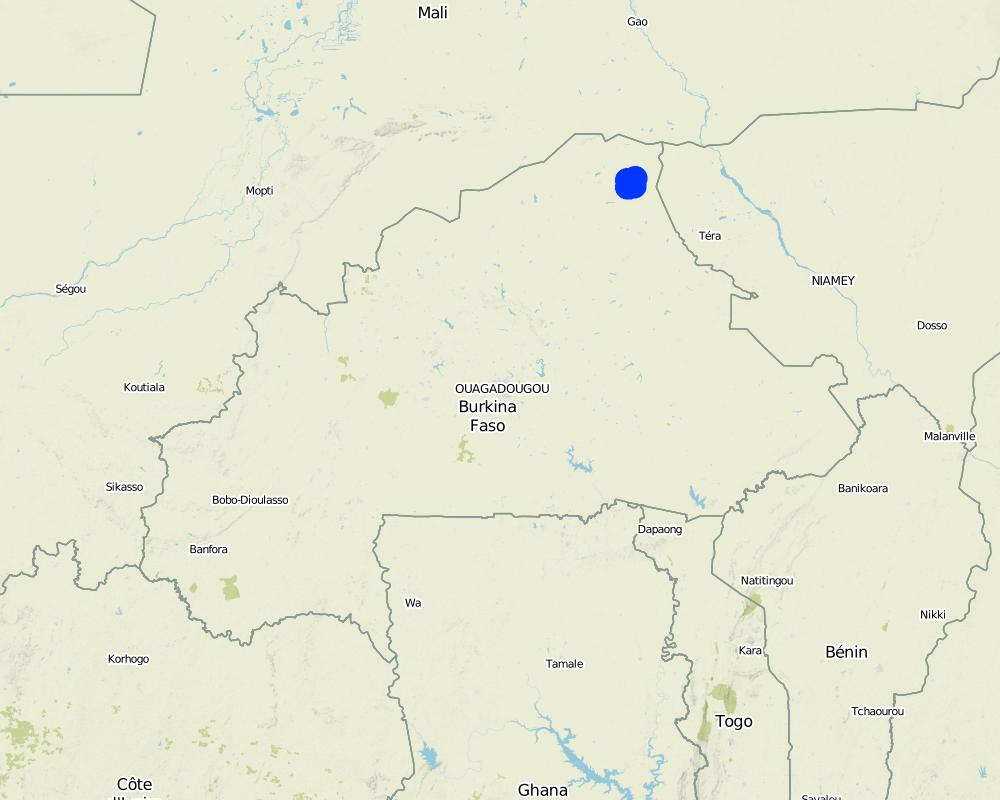
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເບີກິນາ ຟາໂຊ
ພາກພື້ນ / ລັດ / ແຂວງ:
Sahel Region
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ກະຈາຍໄປທົ່ວພື້ນທີ່, ໃຫ້ລະບຸເນື້ອທີ່ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມ (ເປັນ ກິໂລຕາແມັດ):
25.6
ຖ້າຫາກບໍ່ຮູ້ເນື້ອທີ່ທີ່ແນ່ນອນ, ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເນື້ອທີ່ໂດຍປະມານ ທີ່ໃກ້ຄຽງ:
- 10-100 ກມ 2
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
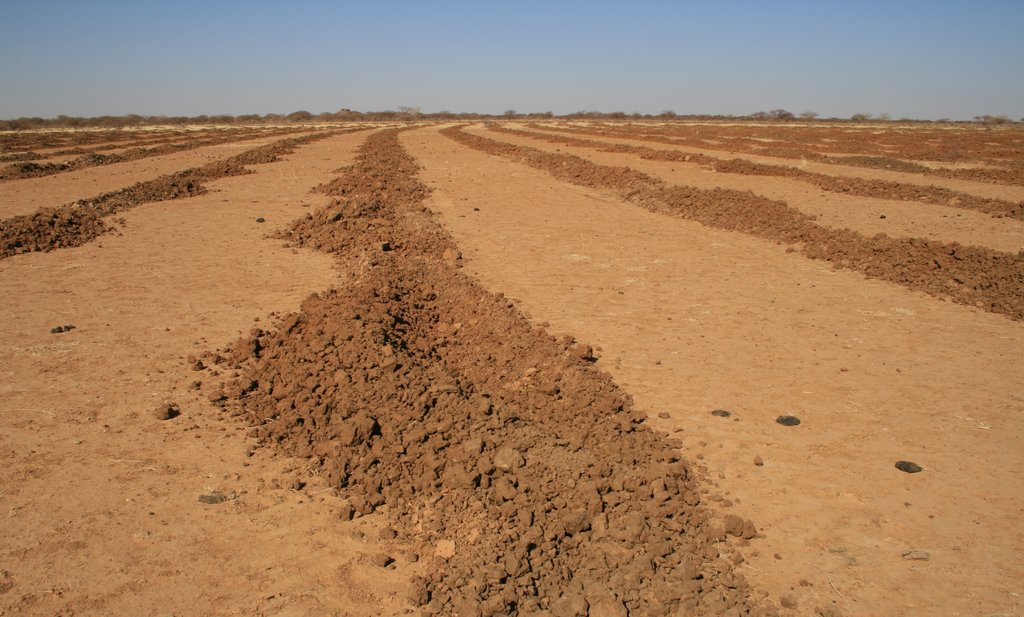
Since the project is going on since 2002, it is possible to see implemented sites in different stadium of rehabilitation. The plowing lines are clearly visible.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology in the Region is about 25.600 hectares up to 2017.
Map
×2.6 ວັນທີໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າ ບໍ່ຮູ້ຈັກ ປີທີ່ຊັດເຈນ ແມ່ນໃຫ້ປະມານ ວັນທີເອົາ:
- 10-50 ປີ ຜ່ານມາ
2.7 ການນໍາສະເໜີ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດຄືແນວໃດ?
- ໃນໄລຍະການທົດລອງ / ການຄົ້ນຄວ້າ
- ໂດຍຜ່ານໂຄງການ / ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອຈາກພາຍນອກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ (ປະເພດ ໂຄງການ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The Technology was introduced in the Region in an agro-sylvo-pastoral pilot project to fight against desertification by FAO in 1996-97.
3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ປ້ອງກັນ, ຟື້ນຟູ ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ປົກປັກຮັກສາ / ການປັບປຸງຊີວະນາໆພັນ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຄວາມສ່ຽງ ທາງໄພພິບັດທໍາມະຊາດ
- ປັບຕົວຕໍ່ກັບການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ / ທີ່ຮ້າຍແຮງ ແລະ ຜົນກະທົບ
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນຜົນກະທົບ ຈາກການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທາງເສດຖະກິດ ທີ່ເປັນປະໂຫຍດ
- ສ້າງຜົນກະທົບ ທີ່ເປັນທາງບວກ ໃຫ້ແກ່ສັງຄົມ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້
ການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ປະສົມພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ດຽວກັນ:
ແມ່ນ
ລະບຸການນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນແບບປະສົມ (ຜົນລະປູກ / ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ / ຕົ້ນໄມ້):
- ປ່າໄມ້-ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ

ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບປ່ອຍ ຕາມທຳມະຊາດ:
- ການລ້ຽງສັດແບບເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດແບບສຸມ / ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ:
- ປັບປຸງ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າ
ປະເພດສັດ:
- ສັດໃຫ່ຍ-ງົວພັນຊີ້ນ
- ແບ້

ປ່າໄມ້ / ປ່າ
- ການປູກຕົ້ນໄມ້, ການປູກປ່າ
ປະເພດຂອງຕົ້ນໄມ້:
- ຕົ້ນກະຖິນ
- ຕົ້ນກະຖິນ ເຊເນກາວ
- ຕົ້ນກະຖິນ
- ຕົ້ນກະຖິນ
- Balanites aegyptiaca
- Ziziphus mauritiana

ດິນ ທີ່ບໍ່ອຸດົມສົມບູນ
ລະບຸ ຊະນິດ:
Hard abbandoned land
ຂໍ້ສັງເກດ:
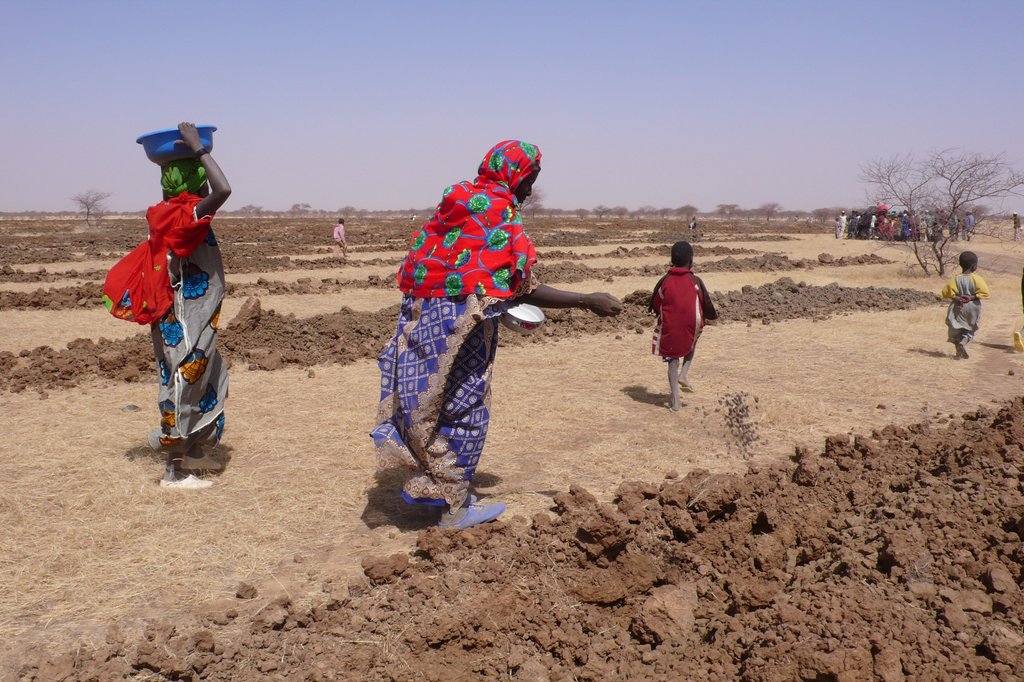
Especially at the beginning of the project, some communities agreed to try the system on their most unproductive land. After seeing the results, they started to request the intervention on less degraded soil and on fields that are closer to their villages.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation-desertification with reduction of vegetation cover in terms of plant density and species diversity is the main problem: disappearance of grasses and trees, reduction of the size of the plants that are resistant and of the biological activity of the soil. Runoff, water and wind erosion increase. Drought and irregular precipitation have heavy consequences on soil fertility, availability of water for humans and livestock, and recharging groundwater.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
3.4 ການສະໜອງນ້ຳ
ການສະໜອງນໍ້າ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ນໍ້າຝົນ
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ກະສິກໍາ-ປ່າໄມ້ ແບບປະສົມປະສານ
- ການຄຸ້ມຄອງສັດລ້ຽງ ແລະ ທົ່ງຫຍ້າລ້ຽງສັດ
- ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງການກະສິກໍາ
- A1: ພືດ / ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງດິນ
- A3: ການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
- A4: ການບໍາລຸງ ປົກປັກຮັກສາ ຊັ້ນຮອງໜ້າດິນ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານພືດພັນ
- V1: ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ ແລະ ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງໄມ້ພຸ່ມ
- V2: ຫຍ້າ ແລະ ພືດສະໝູນໄພທີ່ເປັນໄມ້ຢືນຕົ້ນ

ມາດຕະການໂຄງສ້າງ
- S2: ຄັນຄຸ, ແຄມຕາຝັ່ງ
- S4: ລະດັບຮ່ອງ, ຂຸມ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M1: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ປະເພດ ການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
- M3: ອີງຕາມສະພາບແວດລ້ອມ ທາງທຳມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍນໍ້າ
- Wt: ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ / ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຜິວໜ້າດິນ
- Wg: ການເຊາະເຈື່ອນຮ່ອງນ້ຳ / ຫ້ວຍ
- Wo: ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ພາຍນອກ

ດິນເຊາະເຈື່ອນ ໂດຍລົມ
- ການສູນເສຍຊັ້ນໜ້າດິນ
- Eo: ຜົນກະທົບຈາກການເຊື່ອມໂຊມທາງອ້ອມ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງກາຍະພາບ
- Pc: ການອັດແໜ້ນ
- Pk: ການບັນເທົາ ແລະ ການປົກຄຸມຂອງເປືອກໂລກ
- Pu: ການສູນເສຍ ການທໍາງານ ຂອງຊີວະພາບຜົນຜະລິດ ເນື່ອງຈາກການກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນໆ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ທາງຊີວະພາບ
- Bc: ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
- Bh: ການສູນເສຍ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊິວິດ
- Bq: ປະລິມານ / ອິນຊີວັດຖຸຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bs: ຄຸນນະພາບ / ການອັດແໜ້ນ ຂອງສາຍພັນຫຼຸດລົງ
- Bl: ການສູນເສຍ ຈຸລິນຊີໃນດິນ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງນໍ້າ
- Ha: ສະພາບແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
- Hg: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ລະດັບນ້ຳໃຕ້ດິນ ຫຼື ນ້ຳບາດານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use , such as wood cut for cooking, to feed livestock or as building material, overgrazing, low contribution of animal dejections that are used as cooking fuel, change of seasonal rainfall, droughts. Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), low environmental awareness and support services such as forestal or veterinary assistance.
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
- ການຟື້ນຟູ / ຟື້ນຟູດິນທີ່ຊຸດໂຊມ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
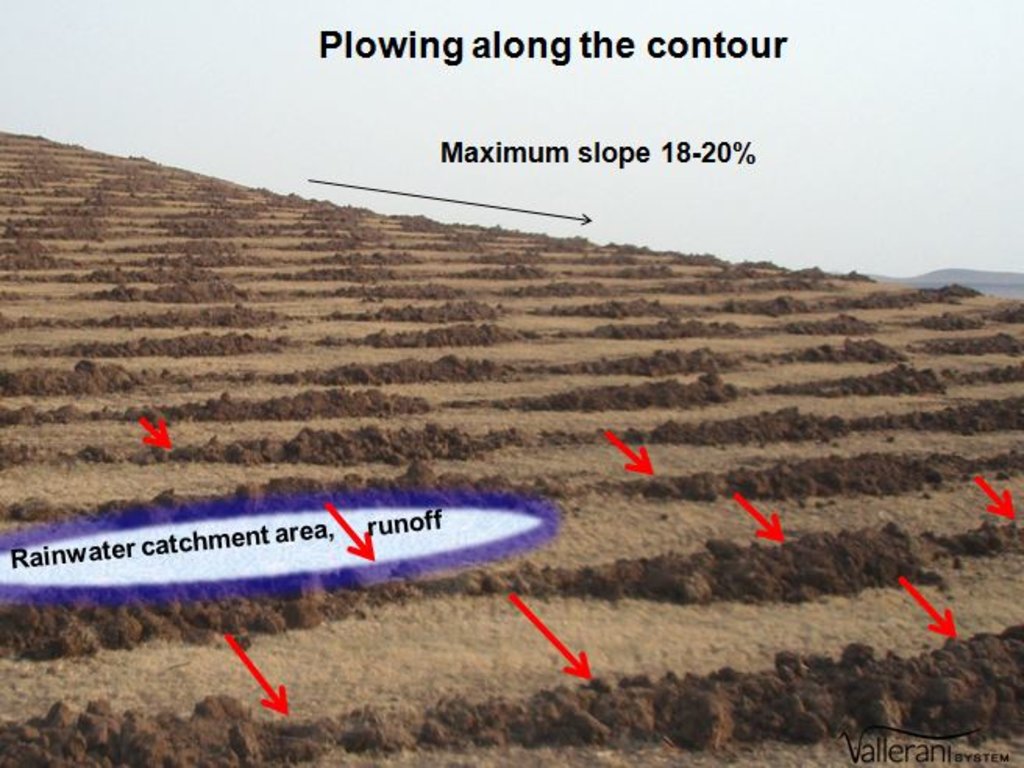
Drawing 1) A. The land chosen together with the local population is plowed with the special Delfino3s plow. The spacing between the plowed lines depend on: slope, soil and rain characteristics, purpose of the project. In average the inter-line is 4-6m wide. B. Local people sow seeds (collected from local trees or bought if species are rare) or goat dung containing seeds (collected in the night enclosures after feeding the goats shaking trees with ripe seeds). C. The micro basins collect the rain that falls into the crescents and up to 90% of the runoff water. The water easily penetrates into the soil profile, remains available to plant roots without risk of evaporation and eventually infiltrates to the groundwater.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Patrizia Kolb
ວັນທີ:
10/10/2013
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Drawing 2) All plowing measures are adjustable. Total length of work: 4/8 m. Tractor required: 180hp. Working speed: 4/7 Km/h which correspond to 1,5/2.5ha per hour. Weight of the plough: 1800 Kg.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Sabina Vallerani
ວັນທີ:
04/04/2017
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
Drawing 3) To optimize run off harvesting and reduce water erosion, the ploughing must always be done along the contour. The bare soil between the tilled lines works as catchment area for the collection of runoff. To facilitate the execution of the plowing along the contour, nowadays there are new technologies such as laser guidance systems or GPS assistence.
ຜູ້ຂຽນ:
Sabina Vallerani
ວັນທີ:
25/04/2018
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ ຂະໜາດ ແລະ ເນື້ອທີ່:
100 hectares
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
2.5
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Project planning, consulting and training | Before starting |
| 2. | Plowing with the Delfino plow | Dry season |
| 3. | Seed harvesting and storage | When seeds are ripe |
| 4. | Missing seeds purchase in local markets or nurseries | When seeds are ripe |
| 5. | Direct sowing | Dry season |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The NGO REACH AFRICA which implements the project is also supported by REACH ITALIA which mainly works for foundraising. They have many different founders. After the first years, thanks to the collaboration and founding by the Swiss Association Deserto Verde Burkinabé and the good results achieved, founders are more likelly to be found. The main are: different NGO's, some Italian Municipalities, a Swiss school, the Gouvernement of Burkina Faso, FAO, international cooperation agencies of Luxembourg and Belgium, a mining company and others.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The actual (2018) total cost of each implemented hectare is $ 170. This cost can be considerably reduced by around 22% in the case of an optimal use of the Technical Mechanization Unit, ie 800-1000 hours of work per year. This means that an operator who works with the plow Delfino has a gross investment cost which can vary according to its technical and organizational experience and by the amount of the plowed surface each year.
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pasture management to avoid overgrazing | After the rain and in the dry season |
| 2. | Vegetation growth management | During the first 3-5 years |
| 3. | Woodcut management | After 4-7 years |
| 4. | Equipment maintenance (plow, tactor) | Daily, weekly, seasonal |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
ຖ້າຫາກຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ນຳໃຊ້ມູນຄ່າຕ່ຳກວ່າ 100% ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ແມ່ນໃຜເປັນຜູ້ຊ່ວຍ ໃນລາຍຈ່າຍທີ່ເຫຼືອ:
The NGO REACH AFRICA which implements the project is also supported by REACH ITALIA which mainly works for foundraising. They have many different founders. After the first years, thanks to the collaboration and founding by the Swiss Association Deserto Verde Burkinabé and the good results achieved, founders are more likelly to be found. The main are: different NGO's, some Italian Municipalities, a Swiss school, the Gouvernement of Burkina Faso, FAO, international cooperation agencies of Luxembourg and Belgium, a mining company and others.
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Maintenance costs of plow and tractor greatly depend from the attention and technical skills of tractor drivers and mechanics and from the diligence and frequency of the maintenance activities of the implements. No other maintenance costs are forseen for the Technology.
4.7 ປັດໄຈ ທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ໃຫ້ອະທິບາຍ ປັດໃຈ ທີ່ສົ່ງຜົນກະທົບ ຕໍ່ຕົ້ນທຶນ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ:
Upfront costs for the aquisition of the required implements are around 40,000 EUR for the plow and 75,000 EUR for the tractor. Depending on the maintenance activities, the spares and fuel costs can be reduced. Fuel, oil and spares also greatly depend from the characteristics of the soil and the purpose of the project.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ / ຄວາມເຫັນກ່ຽວກັບ ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນ:
Dry season from oktober to may, rainy season from june to september. There's a great climate variability with unexpeced dry periods or areas in the rainy season. In the last years climate change effects are experienced in the region with raise in temperature, droughts and rain variability increase. Some Community claim that since the rehabilitation of big degraded areas it rains more regularly and abbundant.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຊື່ສະຖານີ ອຸຕຸນິຍົມ ເພື່ອເປັນຂໍ້ມູນອ້າງອີງ:
Dori, Burkina Faso
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ເຄິ່ງແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
- ແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Average temperature 30°C
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ໄດ້ຖືກນຳໃຊ້:
- ບໍ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ
5.3 ດິນ
ຄວາມເລິກ ຂອງດິນສະເລ່ຍ:
- ຕື້ນຫຼາຍ (0-20 ຊັງຕີແມັດ)
- ຕື້ນ (21-50 ຊຕມ)
- ເລີກປານກາງ (51-80 ຊຕມ)
- ເລິກ (81-120 ຊມ)
- ເລິກຫຼາຍ (> 120 cm)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ໜ້າດິນ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ເນື້ອດິນ (ເລິກຈາກໜ້າດິນ ລົງໄປຫຼາຍກວ່າ 20 ຊັງຕິແມັດ):
- ຫຍາບ / ເບົາ (ດິນຊາຍ)
- ປານກາງ (ດິນໜຽວ, ດິນໂຄນ)
ຊັ້ນອິນຊີວັດຖຸ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
- ຕໍາ່ (<1 %)
5.4 ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ລະດັບ ນໍ້າໃຕ້ດິນ:
> 50 ແມັດ
ການມີນໍ້າ ເທິງໜ້າດິນ:
ປານກາງ
ຄຸນນະພາບນໍ້າ (ບໍ່ມີການບໍາບັດ):
ບໍ່ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ (ຮຽກຮ້ອງໃຫ້ມີການບຳບັດນ້ຳ)
ມີບັນຫາ ກ່ຽວກັບນໍ້າເຄັມບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ເກີດມີນໍ້າຖ້ວມ ໃນພື້ນທີ່ບໍ່?
ບໍ່ແມ່ນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ກໍານົດ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ຄຸນນະພາບ ແລະ ປະລິມານ ຂອງນ້ຳ:
Generally the watertable is lowering. Surface water is collected in boulies (ponds) for livestock and household activities. Its quality deteriorates during the dry season and its quantity decreases fast.
5.5 ຊີວະນາໆພັນ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງສາຍພັນ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ທາງດ້ານ ທີ່ຢູ່ອາໃສ ຂອງສິ່ງທີ່ມີຊີວິດ:
- ຕໍ່າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ ແລະ ລັກສະນະສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມກ່ຽວກັບ ຊີວະນາໆພັນ:
Up to 30-50 years ago biodiversity was rich and soil coverage higher.
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຢູ່ປະຈຳ ຫຼື ເຄື່ອນຍ້າຍຕະຫຼອດ:
- ແບບເຄີ່ງຂັງ-ເຄີ່ງປ່ອຍ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
ລາຍຮັບ ທີ່ບໍ່ໄດ້ມາຈາກ ການຜະລິດ ກະສິກໍາ:
- ໜ້ອຍກ່ວາ 10 % ຂອງລາຍຮັບທັງໝົດ
ລະດັບຄວາມຮັ່ງມີ:
- ທຸກຍາກຫຼາຍ
- ທຸກຍາກ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ກຸ່ມ / ຊຸມຊົນ
ລະດັບ ການຫັນເປັນກົນຈັກ:
- ການໃຊ້ແຮງງານຄົນ
ເພດ:
- ຜູ້ຍິງ
- ຜູ້ຊາຍ
ອາຍຸ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ຊາວໜຸ່ມ
- ໄວກາງຄົນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
During the dry season men often migrate(d) to the nearby mines or cities for off-site income. After the implementation of the Technology the need for seasonal migration reduced. Difference in gender involvement: the project involves reforestation and pasture improvement for the grazing of livestock which is a men dominated activity. Since 2010 women have sown and protected from grazing some special plants for medical and domestic use and as raw material for handcrafts. Population density: 10-50 persons/km2. Annual population growth: 3% - 4%. Off-farm income specification: The only activity people of the region are engaged in is goat and cattle breading. Crop production is practiced only for subsistence use.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
ຖືໄດ້ວ່າ ເປັນຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ, ກາງ ຫຼື ໃຫຍ່ (ອີງຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ສະພາບຄວາມເປັນຈິງ ຂອງທ້ອງຖີ່ນ)? :
- ຂະໜາດນ້ອຍ
- ຂະໜາດໃຫຍ່
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The Technology is applied on land that remains in use to the local population (it's mainly land owned by the State, the Region or the Municipality and given in use to the local Communities). the amenaged sites vary from 40 ha to 150ha in each Village. Up to december 2017 a total of more than 25.600ha have been amenaged.
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ລັດ
- ຊຸມຊົນ / ບ້ານ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ:
- ເປີດກວ້າງ (ບໍ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
- ຊຸມຊົນ (ທີ່ມີການຈັດຕັ້ງ)
5.9 ການເຂົ້າເຖິງການບໍລິການ ແລະ ພື້ນຖານໂຄງລ່າງ
ສຸຂະພາບ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການສຶກສາ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ດ້ານວິຊາການ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການຈ້າງງານ (ຕົວຢ່າງ, ການເຮັດກິດຈະກໍາອື່ນ ທີ່ບໍ່ແມ່ນ ການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ):
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຕະຫຼາດ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ພະລັງງານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ຖະໜົນຫົນທາງ ແລະ ການຂົນສົ່ງ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການດື່ມນໍ້າ ແລະ ສຸຂາພິບານ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
ການບໍລິການ ທາງດ້ານການເງິນ:
- ທຸກຍາກ
- ປານກາງ
- ດີ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
2-4 times
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Crop production and biomass augmented 2-4 times compared with traditional cultural techniques.
ການຜະລິດອາຫານສັດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
90kg/MS/ha
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
1250kg/MS/ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Grass fodder production increased by a factor of 5–30 compared with unmanaged land. The production of herbaceous biomass varied from 420 kg to 2.090 kg (dry matter) per ha; thus, on average, 1.250 kg of herbaceous biomass (dry matter) per ha developed on sites where the Vallerani system was deployed, compared with an average of 90 kg (dry matter) per ha in control plots. Vegetation is mainly distributed inside and around the micro basins.
ຄຸນນະພາບຂອງອາຫານສັດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
12 floral species
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
44 floral species
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The application of the Technology boosts a regenaration process increasing year by year. Compared to the surrounding control rangelands, fodder quality and biodiversity increased with a high proportion of grassland species of good forage value, such as Panicum laetum and Schonefeldia gracilis, and the return of legume species such as Alysicarpus ovalifolius and Zornia glochidiata also testify the improvement of the quality of the reconstituted pastures.
ຜົນຜະລິດຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The increase of fodder quantity and quality represents a surplus of 22–106 grazing days per tropical cattle unit per hectare. This extra fodder supply reduces the need to make long-range transhumance or cut shrubs to meet livestock needs for fodder, even in years where pasture is low. Livestock is fed with more and better quality fodder so its productivity and market price increase.
ຜົນຜະລິດໄມ້
ປ່າໄມ້ / ຄຸນນະພາບປ່າໄມ້
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
20 trees/ha of 6 species
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
700 trees/ha of 14 species
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Significant improvement in forest cover (700 live trees and shrubbs per ha, on average) and biodiversity: trees are capable of spontaneous growth even with open access to grazing and in years of high water stress.
ປ່າຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Berries, gum arabica, resins, fruits.
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຕໍ່ຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The increased fodder quantity, quality and biodiversity, the deep root system of the sown plants, increase resilience of the ecosystem and reduce the risk of production failure. The increased biodiversity, soil moisture and fertility increase the resilience of plants to attacks by pests, deseases and drought. Even in the case of severe drought, there are some plants that can be used as "emergency food" by humans and animals.
ຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ ຂອງຜົນຜະລິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The implementation of the Technology gives the opportunity to diversify the production. Next to animal breeding, agriculture has intensified and in some villages the production of handicrafts, food processing, hunting and tourism activities are developping. Berries, gum arabica, resins, fruits enrich the family diet or can be sold at markets. Wild animals, insects, reptiles and birds have returned after decades and greatelly increased.
ເນື້ອທີ່ການຜະລິດ
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
25.600ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
By the end of 2017 about 25.600 hectares of severelly degraded, abbandoned land has been rehabilitated.
ມີນໍ້າ ແລະ ຄຸນນະພາບ
ມີນໍ້າດື່ມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Local people attest that the rehabilitation of large areas of bare soil augmented the local rain amount and the water level in the wells.
ມີນໍ້າ ໃຫ້ສັດລ້ຽງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The rain collected in the micro basins is available for livestock during the rainy season. The augmented rainfall also increases water availability in boulies (ponds).
ຄວາມຕ້ອງການ ນໍ້າຊົນລະປະທານ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
No water is needed for the Technology except for rain.
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The implementation cost of the technology is not entirelly sustainable by Communities. donors and founders sustain the project. Large-scale application reduces the cost per hectare and increases the impact of actions in reversing the degradation–desertification trend. The cost of each plowed hectare.
ລາຍຮັບ ຈາກການຜະລີດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Fodder increase in quality and quantity, improve animal health and productivity as well as their market price.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍ ຂອງແຫຼ່ງລາຍຮັບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The Technology increases income for herders and their families also thanks to diversification. More land is also used for agriculture. Selling or transformation of other products such as berries, fruits, gums, resins; hunting; new job opportunities in disadvantaged areas such as tractor drivers, social promoters, seed collectors...The community raises awareness and a potential for small business activities occurs, mainly among women.
ຄວາມແຕກຕ່າງ ທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Disadvantaged groups such as women start new economic activities such as mat production and sale at markets, medical plants and food production. They diversify their income and improve their status in the community.
ມີວຽກໜັກ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
5 micro basins/day
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
6.000 micro basins/day
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Each man can dig 5 micro basins per day doing a heavy work. The plow can dig 6.000-7.000 micro basins per day. As most rangelands, the area of the project has a low human density (29 inhabitants/km2) so people are responsible for seed collection and storage, sowing, the livestock management during the first growing phase, monitoring activities, a.s.o.
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
Migration
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increased and improved fodder availability reduces the need for long-range tranhumance and seasonal or definitive migration to areas with more work opportunities (e.g. mines), cities or other countries.
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
ການຄໍ້າປະກັນ ສະບຽງອາຫານ / ກຸ້ມຢູ່ກຸ້ມກິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Food security improves with increased and diversified productivity and income. The increased fodder and crop quantity, quality and biodiversity, the deep root system and soil fertility, increase the resilience of the whole ecosystem. Even in the case of severe drought, there are some plants that can be used as "emergency food" by humans and animals.
ສະພາບທາງດ້ານສຸຂະພາບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Improved health especially due to better nutrition also for disadvantaged groups such as children and old people: bigger amounts, diversification, milk, vegetables. The reduction of dust storms also improves the health situation.
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ຫຼື ນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Awareness rising and discussion of the theme are essential. Due to the great productivity of former degraded and often abandoned land, land use rules and water rights are clearly discussed and defined at the beginning of the project. Rules for SLM are adopted and respected by all; for example, it is forbidden to install camps in or near restored areas, to cut trees, and to mow for commercial purposes.
ໂອກາດ ໃນການພັກຜ່ອນຢ່ອນໃຈ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Shadow, green areas near the villages increase recreational opportunities.
ສະຖາບັນ ການຈັດຕັ້ງຊຸມຊົນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
It is essential to involve and give responsibility to local people in every step of the process. Comities and groups such as the women or seniors groups gain relevance and become essential for the sustainability of the project.
ສະຖາບັນແຫ່ງຊາດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Collaborations with national institutions such as forestry direction, ministery of environnement and agricolture, research institutes, etc
ຄວາມຮູ້ກ່ຽວກັບ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ / ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
All communities are involved in the management process – identifying the areas and the use of the sites to be restored, planning, and implementing (e.g. gathering and keeping seeds of local ecotypes, manure and sowing). Local villages are involved in the care and defence of new plantations and in the monitoring and evaluation of the results of vegetation growth. Ultimatelly they become responsable for the sustainable management of the whole area.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຂໍ້ຂັດແຍ່ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
If land use and water rights are clearly defined, the increased availability of fodder reduces conflicts with neighbours and farmers.
ສະຖານະການຂອງສັງຄົມ ແລະ ກຸ່ມດ້ອຍໂອກາດທາງເສດຖະກິດ
Community well being
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
People have more confidence in the future, dignity and hope. The Community cohesion and identity is strenghtened and the community becomes more resilient to conflicts and disasters.
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ວົງຈອນນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າ
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
360.000l/ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
With each rain, each micro basin can collect up to 1.200l of water. Each hectare collects an average of 360.000 liter of rain, runoff included. Collected in the micro basin, the water has enough time to infiltrate in the soil profile and eventually in the water table. Local people assert that after the implementation of the Technology, the water level in the wells has raised.
ການຂຸດຄົ້ນ / ການເກັບກັກນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The Technology allows to harvest 100% of the rain falling in the micro basin and on the ripped furrow as well as up to 90% of the rain falling between the tilled lines. The bare soil between the tilled lines is essential as catchment area, to recieve rainfall and process runoff downstream. The micro basins collect up to 95% of rainfall.
ການໄຫຼ ຂອງນໍ້າໜ້າດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
5-15%
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
90%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Plowing is done along the contour. This is essential to collect the runoff that flows between the tilled lines (catchment area). The distance between the lines can be between 4m and 12m depending from: slope, rain characteristics (quantity, intensity), soil type, surface roughness (runoff coheficient), the purpose of the project (type of plants desired). The technology allows to collect up to 90% of the runoff.
ຊັ້ນນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ / ນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Local people assert that after the implementation of the technology, the water level in the wells has raised.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The rain collected in the micro basins infiltrates in the soil profile being accessible for seeds and roots without evaporating. After the first rains, the micro basins are quickly covered with high grasses that contribute to reduce evaporation.
ດິນ
ຄວາມຊຸ່ມຂອງດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Improved soil hydrodynamic properties: the relative size of capillaries by different soil levels increased and the soil water-retaining capability improved.
ການປົກຄຸມຂອງດິນ
ການສູນເສຍດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Reduced soil loss through runoff reduction and wind erosion.
ການອັດແໜ້ນຂອງດິນ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
423
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
70
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
At different depth soil compactness reduces from 6 (0 to 20cm) to 1.3 times (40 to 60cm)
ວົງຈອນ ຂອງສານອາຫານໃນດິນ
ອິນຊີວັດຖຸໃນດິນ / ຢູ່ລຸ່ມຊັ້ນດິນ C
ຊີວະນານາພັນ: ສັດ, ພືດ
ການປົກຫຸ້ມຂອງພືດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Vegetation cover increase 5 to 30 times. Vegetation grows mainly inside and around the micro basins.
ມວນຊີວະພາບ / ຢູ່ເທິງຊັ້ນດິນ C
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
70 to 110kg/MS/ha
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
420 to 2090 kg/MS/ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The biomass production increases 5 to 30 times compared to the nearby unplowed soil. On implemented sites, biomass varies from 420 to 2090 kg / DM / ha, on average between 1000 and 1200 kg / ha against 70 to 110kg / DM / ha on control plots.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງພືດ
ປະລິມານ ກ່ອນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
14 herbaceous, 6 woody species/ha
ປະລີມານ ຫຼັງການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
44 herbaceous, 14 woody species/ha
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Floral diversity increases from 14 to 44 species. With a high proportion of graminaceous species of good forage value and the return of more leguminous species. Concerning the diversity of woody plants the results show an average per hectare of 14 species on implemented sites and an average of 6 species on control plots.
ຄວາມຫຼາກຫຼາຍຂອງສັດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
A great increase of animal biodiversity: insects, birds, reptiles and mammals (such as squirrel, jackals, gazelle...) are observed in the implemented sites.
ການຄວບຄຸມສັດຕູພືດ / ພະຍາດ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The increased vegetal and animal biodiversity, deep root system, soil fertility and water availability, increase the health and resilience capacity of the whole ecosystem.
ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄພພິບັດ ແລະ ອາກາດປ່ຽນແປງ
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງນໍ້າຖ້ວມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Through water harvesting the rain is retained in the precipitation area and flood risk decreases. If flood occurs in the plowed area before the vegetation is well established, the micro basins can be washed out.
ຜົນກະທົບ ຂອງໄພແຫ້ງແລ້ງ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Increased biodiversity, vegetation cover and soil fertility, deep root system and water storage in the soil profile, increase the resilience to drought of the whole ecosystem. During the project, in years of extreme drought, plants have reduced their growth but most of them survived, were used to feed animals and started growing again in the following rainy season.
ການລະເຫີຍອາຍກາກບອນ ແລະ ອາຍຜິດເຮືອນແກ້ວ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Minimal production of carbon dioxide compared with the potential gain.
ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກໄຟໄໝ້
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The implementing area remains open to lifestock (regulated pasture) to reduce the high production of grass that could favor the spread of a fire, herders also monitor the territory. There is a high level of community involvement and a growing ecological awareness.
ຄວາມຮູນແຮງ ຂອງລົມ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
The great number of growing trees reduce the wind speed.
ການປ່ຽນແປງ ອາກາດ ໃນວົງແຄບ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Local people attest that the Technology locally increased the amount of rain and reduced dust storms in number and intensity.
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ສາມາດເຂົ້າເຖິງແຫຼ່ງນໍ້າ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Local people tell that the rehabilitation of large areas of bare soil augmented the local rain amount and the water level in the wells.
ລົມ ທີ່ພັດເອົາຕະກອນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
Wind intensity and dust storms reduction thanks to soil coverage and wind brake effect by trees and shrubs.
6.3 ການປ້ອງກັນ ແລະ ຄວາມບອບບາງ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢິ ໃນການປ່ຽນແປງສະພາບດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ແລະ ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງກັບອາກາດທີ່ມີການປ່ຽນແປງທີ່ຮຸນແຮງ / ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ (ຮັບຮູ້ໄດ້ໂດຍຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ)
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
ການປ່ຽນແປງດິນຟ້າອາກາດ ເທື່ອລະກ້າວ
| ລະດູການ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ ຫຼື ຫຼຸດລົງ | ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ອຸນຫະພູມປະຈໍາປີ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ | |
| ອຸນຫະພູມລະດູການ | ລະດູແລ້ງ | ເພີ່ມຂື້ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ | |
| ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນຕາມລະດູການ | ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ / ລະດູຝົນ | ຫຼຸດລົງ | ດີ |
ອາກາດ ທີ່ກ່ຽວພັນກັບຄວາມຮຸນແຮງ (ໄພພິບັດທາງທໍາມະຊາດ)
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸຕຸນິຍົມ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ພະຍຸຝົນ | ປານກາງ |
| ພາຍຸຊາຍທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
| ພາຍຸລົມທ້ອງຖິ່ນ | ດີຫຼາຍ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງອຸທົກກະສາກ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ນໍ້າຖ້ວມຮູນແຮງ | ບໍ່ດີ |
ໄພພິບັດທາງຊີວະພາບ
| ການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ສາມາດ ຮັບມື ໄດ້ຄືແນວໃດ? | |
|---|---|
| ແມງໄມ້ / ການລະບາດຂອງພະຍາດ | ດີ |
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກຫຼາຍ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The system includes the use of a heavy duty tractor and a special plow whose costs are high though difficult to sustain by the local population. Most financial costs are covered by founders and donors, the land user's partecipate to the project with their work so even if the benefits in the short term are fewer than in the mid and long-term, for them it is still very positive.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- 11-50%
ຖ້າຫາກວ່າມີ, ປະລິມານ (ຈໍານວນຂອງຄົວເຮືອນ / ເນື້ອທີ່ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ):
330 villages and around 33.000 beneficiaries
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 51-90%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Except for plowing, the other activities part of the Technology are practicable by the population under an initial guidance of a promoter with specific training. These are done without any material incentives/payments. The technology is well known in the Region and there is an active participation of the local people and a strong demand for new interventions.
6.6 ການປັບຕົວ
ໄດ້ມີການດັດປັບ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເພື່ອໃຫ້ແທດເໝາະກັບເງື່ອນໄຂ ການປ່ຽນແປງບໍ?
ແມ່ນ
ອື່ນໆ (ລະບຸແຈ້ງ):
technical
ລະບຸການຮັບຮອງເອົາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ການອອກແບບ, ອຸປະກອນການ / ຊະນິດພັນ ແລະ ອື່ນໆ):
The design of the plow has been adapted to increase the performance of the implement and reduce the running costs of plowing. The reversibility of the plowshare reduces the need for empty rides. The different parts of the plow are adjustable to adapt it to the needs of the project and the soil characteristics.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ |
|---|
| Higly degraded, abandoned land becomes fertile and rentable again. Fodder increases in quantity and improves in quality and lasts all year round. Food security also in drought years. Herds are healthier and more productive. Fodder and water availability for animals is closer to the villages. Some plants can be sown for different uses: crops, medicine or for the production of mats or other handcrafts products that can be sold. |
| Better life conditions, more income opportunities and diversification. Food is diversified and more nutritious. Less hunger and deseases. |
| Greater community cohesion and less migration, better environnemental conciousness and commitment, education and security. People gain back dignity, confidence in the future and hope. |
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
| The Technology allows the rehabilitation of rangeland and highly degraded areas in a fast and natural way on a large scale. This can boost a longlasting effect and the shift of the whole ecosystem. The Technology confers drought resilience and reduces the effects of climate change. It allows the sequestration of CO2 and can contribute to achieve the Land Degradation Neutrality Goals. |
| The partecipatory approach is essential for the sustainability of the project. The local Communities improve their life quality, awareness, cohesion and resilience. The need for migration is reduced and people has the chance to stay in their Lands. |
| The sown tree and shrub species are mainly indigenous and locally adapted species. Each specie can follow it's own growing laws and adaptation strategies. Through the tillage process the technology offers the highest degree of efficiency in the first years from processing. Its effects last for a long time so it does not need to be repeated on the same site. |
| The VS does not use any water (except rain) in countries where water is rare and precious. |
| The use of a mechanized implement allows to rehabilitate very hard, degraded and abbandoned land on large areas with reduced population. As the Delfino3s can plow strongly degraded land, the local people often ask to work their worse land which they would never be able to use. |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງໃນມຸມມອງຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| Land that was unproductive and nobody claimed becomes productive: it can lead to misunderstandigs and conflicts. | Land use and production exploitation rules must be cleared and accepted by all Subjects at the beginning of the project. |
| Good pasture attracts animals and herders from the nearby Region (also from far away and abroad). | Rules must be clear. |
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The investmentand running costs for the machinery are high and cannot be covered by single land users or small Communities. | The projects must be financed by donors or founders. The Community can partecipate to some extent to cover the running costs. |
| The speed and effectiveness of the Delfino3s plow are its major advantages in the ecosystem rehabilitation process but can also be its major limitation. To make the best out of it, it is necessary to have a great availability of land (1.000-1.800ha) every year. | A big organizational capacity is needed. The spreading "like wildfire" that has characterized the case study was possible by the presence on the territory of an NGO already active and rooted in the territory for many years and by perseverance, respect and competence of all involved subjects. |
| Since great extentions will be processed, a big organisation is needed for all connected activities (awareness raising, seed collection and stockage, training, logistics, etc), | Must be well organized and should operate already before starting with plowing. |
| The professional level of the tractor drivers and the mechanics as well as the lack of a well-organized mechanical workshop and spares stock can lead to long interruptions of the work and high extra costs. | Professional technical trainings and monitoring are very important. The organization of a well managed mechanical workshop and spares stock are essential. This can also be a great development opportunity for the Region. |
| The increased amount of fodder can induce the shepherds to increase the number of animals. | An important work with the Communities is essential to achieve shared and sustainable management goals. |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
- ການໄປຢ້ຽມຢາມພາກສະໜາມ, ການສໍາຫຼວດພາກສະໜາມ
4
- ການສໍາພາດ ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ
30
- ສໍາພາດ ຊ່ຽວຊານ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
8
- ການລວບລວມ ບົດລາຍງານ ແລະ ເອກະສານ ອື່ນໆ ທີ່ມີຢູ່ແລ້ວ
5
ເມື່ອໃດທີ່ໄດ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ (ຢູ່ພາກສະໜາມ)?
2012/2018
7.2 ເອກກະສານອ້າງອີງທີ່ເປັນບົດລາຍງານ
ຫົວຂໍ້, ຜູ້ຂຽນ, ປີ, ISBN:
Un "delfino" rinverdisce i deserti, Venanzio Vallerani, ISBN 978-88-95858-05-0
ມີຢູ່ໃສ?ມູນຄ່າເທົ່າໃດ?
info@vallerani.com
7.3 ເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ກັບຂໍ້ມູນທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງໂດຍກົງ
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Récupération des sols fortement dégradés à des fins sylvo-pastorales, CILSS 2009
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Rapport-Reach-Cills-2009.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
GIZ, Good practices in soil and water conservation, pag. 22 seg.
URL:
https://www.giz.de/fachexpertise/downloads/giz2012-en-soil-water-conservation.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Using Mechanized Water Harvesting System (The Vallerani System ) for Rehabilitation of Degraded ASALs in Kenya
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Meshack-Muga-Paper-25-Final.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Report for the Sino-Italian cooperation project, SFA, China
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/Report_in_English-10.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Global guidelines for the restoration of degraded forests and landscapes in drylands FAO, pag. 104 seg.
URL:
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i5036e.pdf
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Improved rainwater harvesting for fodder shrub production and livestock grazing: the Vallerani micro-catchment system in the Badia of Jordan
URL:
http://www.fao.org/family-farming/detail/en/c/1040697/
ຫົວຂໍ້ / ພັນລະນາ:
Conedera, M., N. Bomio-Pacciorini, et al. 2010. Reconstitution des écosystèmes dégradés sahéliens. Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2). Bois et Forêts des Tropiques 304(2). Bois et Forêts des Tropiques
URL:
http://www.vallerani.com/images/Reconstitution.pdf
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ບໍ່ມີຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ