Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd production [ເນໂປ]
- ການສ້າງ:
- ປັບປູງ:
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Richard Allen
- ບັນນາທິການ: –
- ຜູ້ທົບທວນຄືນ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Karela kheti ma thopa sinchai ko satha ma pasu mutra ko prayog (Nepali)
technologies_1751 - ເນໂປ
ເບິ່ງພາກສ່ວນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດ1. ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປ
1.2 ຂໍ້ມູນ ການຕິດຕໍ່ພົວພັນ ຂອງບຸກຄົນທີ່ສໍາຄັນ ແລະ ສະຖາບັນ ທີ່ມີສ່ວນຮ່ວມ ໃນການປະເມີນເອກກະສານ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
ເນໂປ
ຜຸ້ຊ່ຽວຊານ ດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
ເນໂປ
ຊື່ໂຄງການ ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ/ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)ຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - ເນໂປຊື່ສະຖາບັນ (ຫຼາຍສະຖາບັນ) ທີ່ອໍານວຍຄວາມສະດວກ ໃນການສ້າງເອກກະສານ / ປະເມີນ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ເງື່ອນໄຂ ກ່ຽວກັບ ການນໍາໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນເອກະສານ ທີ່ສ້າງຂື້ນ ໂດຍຜ່ານ ອົງການພາບລວມຂອງໂລກ ທາງດ້ານແນວທາງ ແລະ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການອານຸລັກ ທໍາມະຊາດ (WOCAT)
ຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ແລະ ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ ທີ່ໃຫ້ຂໍ້ມູນ (ຫຼາຍ) ຍິນຍອມ ຕາມເງື່ອນໄຂ ໃນການນຳໃຊ້ຂໍ້ມູນ ເພື່ອສ້າງເປັນເອກກະສານຂອງ WOCAT:
ແມ່ນ
1.5 ແບບສອບຖາມທີ່ອ້າງອີງເຖີງແນວທາງ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ (ໄດ້ເຮັດເປັນເອກະສານທີ່ໃຊ້ WOCAT)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [ເນໂປ]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [ເນໂປ]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Richard Allen
2. ການອະທິບາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ຂອງການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
2.1 ຄໍາອະທິບາຍສັ້ນຂອງ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການກຳໜົດຄວາມໝາຍ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
2.2 ການອະທິບາຍ ລາຍລະອຽດ ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ການພັນລະນາ:
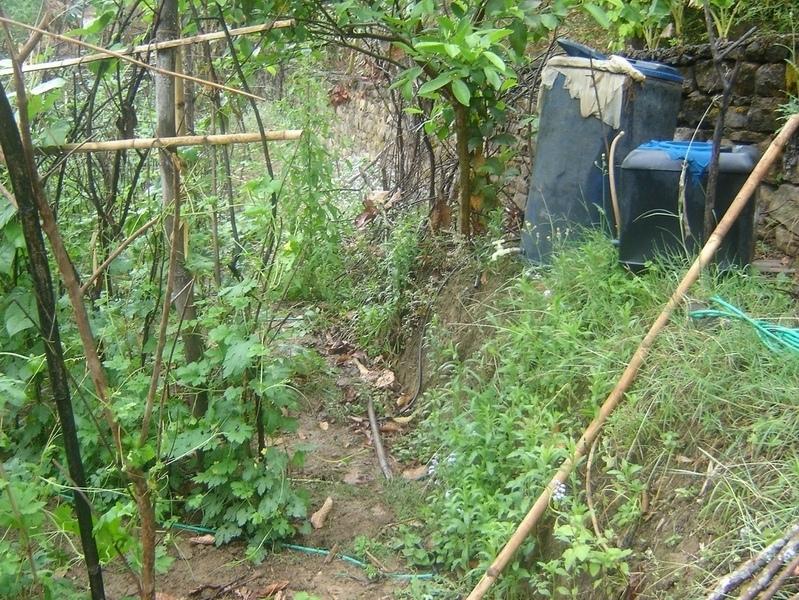
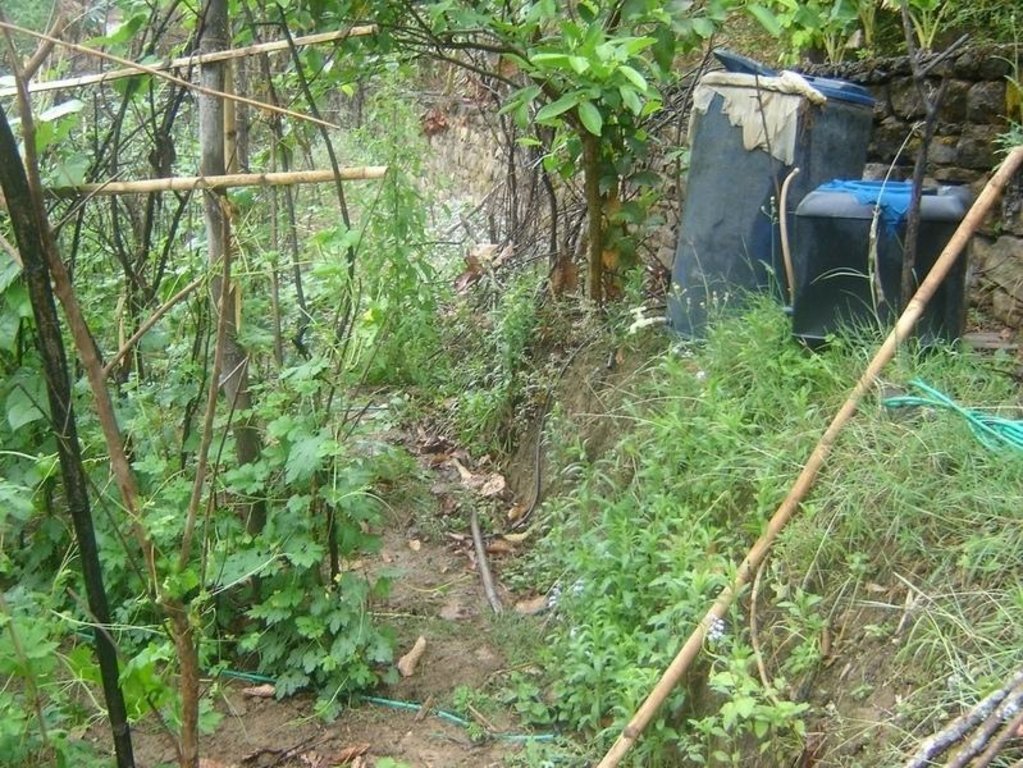
Bitter gourd vegetables fetch a high price in the off-season and respond well if grown with drip irrigation. This crop is planted in December/January and harvested from May through to July/August. The growing period mainly falls in the driest period of the year and therefore requires irrigation.
In addition to water, the plants need fertiliser to ensure healthy growth and good production. Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants and high crop productivity can only be achieved if sufficient nitrogen is available. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in most areas of Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure; but in many places this is being supplemented or entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser, mainly urea. However, fertiliser prices have increased substantially in recent years and this type of fertiliser is often not available in sufficient quantities in areas away from the roadheads. At the same time cultivation practices are intensifying with greater cropping intensities and more nutrient demanding crops as local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are introduced. This can easily lead to nutrient mining and soil fertility decline unless there is an equivalent increase in inorganic or mineral fertilisation.
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser; it is nitrogen rich. The urine is collected in improved cattle sheds (fact sheet on urine collection QT NEP1). For constant fertiliser application and to reduce the water requirement, the collected urine can be added to the irrigation water in the drip irrigation tanks (fertigation). Farmers who have tried this say it has increased the yield of bitter gourd and other cash crops, in some cases by as much as 100%. Other crops that can be grown using drip irrigation with a water-urine mixture are cauliflower, cucumber, and other types of gourd.
2.3 ຮູບພາບຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
2.5 ປະເທດ / ເຂດ / ສະຖານທີ່ບ່ອນທີ່ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຮັບການນໍາໃຊ້ ແລະ ທີ່ຖືກປົກຄຸມດ້ວຍການປະເມີນຜົນ
ປະເທດ:
ເນໂປ
ຂໍ້ມູນເພີ່ມເຕີມຂອງສະຖານທີ່:
Midhills districts of Nepal
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ການແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ:
- ແຜ່ຂະຫຍາຍຢ່າງໄວວາໃນພື້ນທີ່
Map
×3. ການໃຈ້ແຍກ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໃນການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
3.1 ຈຸດປະສົງຫຼັກ (ຫຼາຍ) ຂອງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ປັບປຸງ ການຜະລິດ
3.2 ປະເພດການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃນປະຈຸບັນ() ທີ່ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ໄດ້ຖືກນໍາໃຊ້

ດິນທີ່ປູກພືດ
- ການປູກພືດປະຈໍາປີ
ການປູກພືດປະຈຳປີ - ລະບຸປະເພດພືດ:
- ຜັກ-ໝາກໂມ, ໝາກອື, ໝາກບວບ ຫຼື ໝາກນ້ຳ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater. Also, irrigation water is in short supply during 6 to 8 months of the year. Fertigation allows about 20 to 30% of the irrigation water to be replaced by urine.
3.5 ການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ຢູ່ໃນກຸ່ມການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ
- ການຈັດການອຸດົມສົມບູນ ຂອງດິນປະສົມປະສານ
3.6 ມາດຕະການ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ທີ່ດິນແບບຍືນຍົງ ປະກອບດ້ວຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ມາດຕະການ ທາງດ້ານການຄຸ້ມຄອງ
- M2: ການປ່ຽນແປງ ການຈັດການຄຸ້ມຄອງ / ລະດັບຄວາມໜາແໜ້ນ
3.7 ປະເພດດິນເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຫຼັກທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ

ການເຊື່ອມໂຊມ ຂອງດິນ ທາງເຄມີ
- Cn: ຄວາມອຸດົມສົມບູນ ລົດໜ້ອຍຖອຍລົງ ແລະ ສານອິນຊີວັດຖຸລົດລົງ (ບໍ່ແມ່ນສາເຫດມາຈາກການເຊາະເຈື່ອນ)
3.8 ການປ້ອງກັນ, ການຫຼຸດຜ່ອນ, ຫຼືການຟື້ນຟູຂອງການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ເປົ້າໝາຍ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ທີ່ພົວພັນ ກັບຄວາມເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ:
- ຫຼຸດຜ່ອນການເຊື່ອມໂຊມຂອງດິນ
4. ຂໍ້ກໍາໜົດ, ກິດຈະກໍາການປະຕິບັດ, ວັດຖຸດິບ, ແລະຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
4.1 ເຕັກນິກ ໃນການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງເຕັກນິກ (ທີ່ກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ ກັບການແຕ້ມແຜນວາດ ທາງດ້ານເຕັກນີກ):
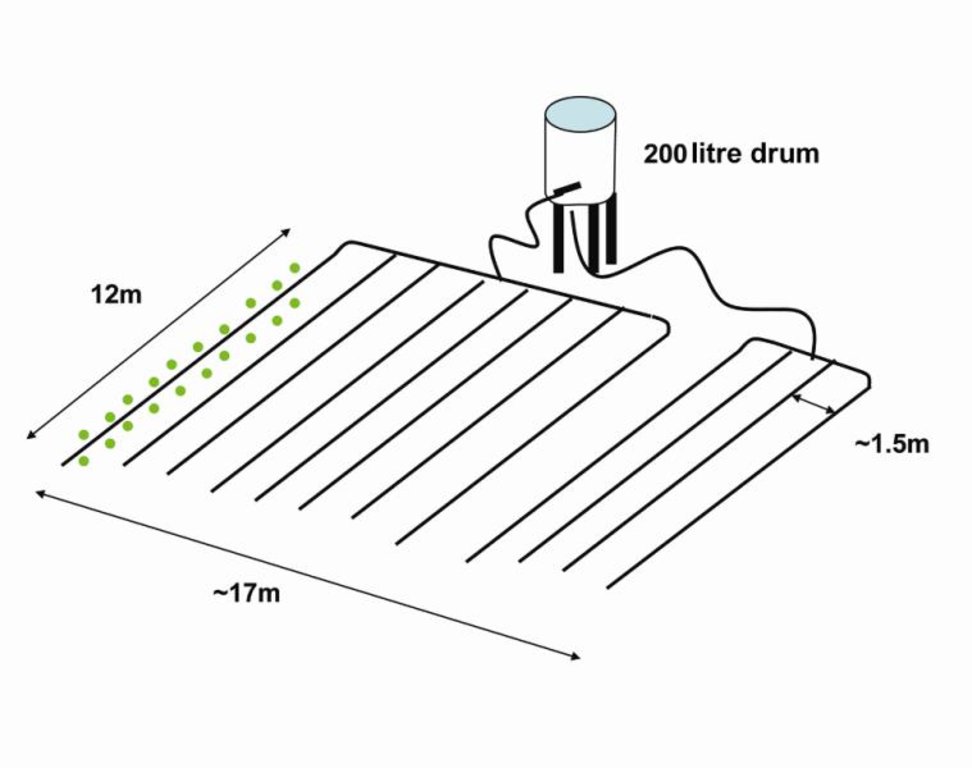
The following setup was used in Iman Singh Basnet’s fi eld:
- two drip irrigation sets: one set with
8 lines, one with 4 lines
- a 200 l plastic drum
- 20 bitter gourd plants per line with
1.5m spacing between lines
- approximate area covered: 200m2
Note that the drum was not delivered with the drip irrigation set. Mr Basnet uses the same drum for irrigating other crops where drip irrigation is not feasible, in which case he connects a pipe with a rose to the drum.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: supplementary irrigation, constant and slow supply of nutrients, increase in soil fertility & increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: pest control
4.2 ຂໍ້ມູນທົ່ວໄປກ່ຽວກັບການຄິດໄລ່ປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າໃນການຜະລິດ ແລະ ມູນຄ່າອື່ນໆ
ລະບຸ ວິທີການ ຄຳໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ທີ່ໄດ້ຄິດໄລ່:
- ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸຫົວໜ່ວຍ:
Drip irrigation system
ກໍານົດຂະຫນາດຂອງຫົວນ໋ວຍ (ຖ້າກ່ຽວຂ້ອງ):
200 l plastic drum; 20 bitter gourd plants per line with 1.5m spacing between lines
ລະບຸ ສະກຸນເງິນທີ່ໃຊ້ສໍາລັບ ການຄິດໄລ່ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ:
- USA
ລະບຸ ຄ່າຈ້າງ ຄ່າແຮງງານສະເລ່ຍ ຕໍ່ ວັນ:
2.00
4.3 ການສ້າງຕັ້ງກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare and place stakes | |
| 2. | Collect urine (see WOCAT fact sheet ‘Improved cattle shed for improved urine collection – QT NEP1) | |
| 3. | Grow bitter gourd seedlings | |
| 4. | Set up drip irrigation set and prepare field | |
| 5. | Transplant seedlings |
4.4 ຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ປັດໄຈຂາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນໃນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Collect urine and prepare irrigation system | persons/unit | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Drip set | unit | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| ອຸປະກອນ | Drum | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| ວັດສະດຸກໍ່ສ້າງ | Stakes | unit | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ໃນການຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 50.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການສ້າງຕັ້ງເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 50.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 ບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ / ແຜນຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ກິດຈະກໍາ
| ກິດຈະກໍາ | ໄລຍະເວລາ / ຄວາມຖີ່ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear drip holes | |
| 2. | Double filter the urine – once when taking out of the collection tank, and again when pouring into the drip irrigation tank | |
| 3. | Irrigate every alternate day with 160 l water and 40 l urine. | |
| 4. | Fix shoots to the stakes | |
| 5. | Raise ridges for better irrigation efficiency | |
| 6. | Harvest the crop |
4.6 ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ແລະ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າທີ່ຈໍາເປັນສໍາລັບການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາກິດຈະກໍາ / ແຜນປະຕິບັດ (ຕໍ່ປີ)
| ລະບຸ ປັດໃຈ ນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລີດ | ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ປະລິມານ | ຕົ້ນທຶນ ຕໍ່ຫົວໜ່ວຍ | ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ຂອງປັດໃຈຂາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດ | % ຂອງຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ຈ່າຍເອງ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ແຮງງານ | Maintain drip irrigatio nsystem and apply urine | persons/unit | 15.0 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| ຕົ້ນທຶນທັງໝົດ ທີ່ໃຊ້ໃນການບໍາລຸງຮັກສາ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ | 30.0 | |||||
| ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍທັງໝົດ ສຳລັບການບົວລະບັດຮກສາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ເປັນສະກຸນເງີນໂດລາ | 30.0 | |||||
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Cost calculated in January 2007.
5. ສະພາບແວດລ້ອມທໍາມະຊາດ ແລະ ມະນຸດ
5.1 ອາກາດ
ປະລິມານນໍ້າຝົນປະຈໍາປີ
- < 250 ມີລິແມັດ
- 251-500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 501-750 ມີລິແມັດ
- 751-1,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,001-1,500 ມີລິແມັດ
- 1,501-2,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 2,001-3,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- 3,001-4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
- > 4,000 ມີລິແມັດ
ເຂດສະພາບອາກາດກະສິກໍາ
- ຄວາມຊຸ່ມ
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 ພູມິປະເທດ
ຄ່າສະເລ່ຍ ຄວາມຄ້ອຍຊັນ:
- ພື້ນທີ່ຮາບພຽງ (0-2%)
- ອ່ອນ (3-5 %)
- ປານກາງ (6-10 %)
- ມ້ວນ (11-15 %)
- ເນີນ(16-30%)
- ໍຊັນ (31-60%)
- ຊັນຫຼາຍ (>60%)
ຮູບແບບຂອງດິນ:
- ພູພຽງ / ທົ່ງພຽງ
- ສັນພູ
- ເປີ້ນພູ
- ເນີນພູ
- ຕີນພູ
- ຮ່ອມພູ
ເຂດລະດັບສູງ:
- 0-100 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 101-500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
- > 4,000 ແມັດ a.s.l.
ຄຳເຫັນ ແລະ ຂໍ້ມູນສະເພາະ ເພີ່ມເຕີມ ກ່ຽວກັບ ພູມີປະເທດ:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.6 ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ທີ່ໄດ້ນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ລະບົບ ການຕະຫຼາດ ແລະ ຜົນຜະລິດ:
- ກຸ້ມຕົນເອງ (ພໍພຽງ)
- ການຄ້າ / ຕະຫຼາດ
ບຸກຄົນ ຫຼື ກຸ່ມ:
- ບຸກຄົນ / ຄົວເຮືອນ
ໃຫ້ລະບຸ ຄຸນລັກສະນະ ຂອງຜູ້ນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 ເນື້ອທີ່ສະເລ່ຍຂອງດິນ ທີ່ຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ ໃຊ້ເຮັດເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- <0.5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 0.5-1 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1-2 ເຮັກຕາ
- 2-5 ເຮັກຕາ
- 5-15 ເຮັກຕາ
- 15-50 ເຮັກຕາ
- 50-100 ເຮັກຕາ
- 100-500 ເຮັກຕາ
- 500-1,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- 1,000-10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
- > 10,000 ເຮັກຕາ
5.8 ເຈົ້າຂອງທີ່ດິນ, ສິດໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ, ແລະ ສິດທິການນໍາໃຊ້ນໍ້າ
ເຈົ້າຂອງດິນ:
- ບຸກຄົນ, ບໍ່ມີຕໍາແໜ່ງ
ສິດທິ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ:
- ເຊົ່າ
- ບຸກຄົນ
6. ຜົນກະທົບ ແລະ ລາຍງານສະຫຼຸບ
6.1 ການສະແດງຜົນກະທົບ ພາຍໃນພື້ນທີ່ ທີ່ໄດ້ຈັດຕັ້ງປະຕິບັດ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ຜົນກະທົບທາງເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມ
ການຜະລິດ
ການຜະລິດພືດ
ລາຍໄດ້ ແລະ ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ
ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍ ປັດໄຈນໍາເຂົ້າ ໃນການຜະລິດກະສິກໍາ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
reduced expenses for agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
ຜົນກະທົບທາງດ້ານເສດຖະກິດສັງຄົມອື່ນໆ
Allows organic production of high value crops
establishment costs
ຜົນກະທົບດ້ານວັດທະນາທໍາສັງຄົມ
social prestige as a progressive farmer
requires handling of dung and urine
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດ
ຜົນກະທົບຕໍ່ລະບົບນິເວດອື່ນໆ
application of agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
eutrophication, nitrification of water bodies due to uncontrolled outflow of urine
6.2 ຜົນກະທົບທາງອ້ອມ ຈາກການນໍາໃຊ້ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
ມົນລະພິດ ທາງນໍ້າ / ນໍ້າໄຕ້ດິນ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ / ລະບຸແຈ້ງ:
reduced influx of nutrients into water bodies
dependence on costly external inputs
6.4 ການວິເຄາະຕົ້ນທຶນ ແລະ ຜົນປະໂຫຍດ
ຈະເຮັດປະໂຫຍດເພື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍກັບສິ່ງກໍ່ສ້າງ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຈະໄດ້ຮັບຜົນປະໂຫຍດເມື່ອປຽບທຽບກັບ / ຄ່າໃຊ້ຈ່າຍໃນການບຳລຸງຮັກສາທີເ່ກີດຂື້ນອິກ (ຈາກທັດສະນະຄະຕິຂອງຜູ້ນຳໃຊ້ທີ່ດິນ) ໄດ້ແນວໃດ?
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະສັ້ນ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຜົນຕອບແທນ ໃນໄລຍະຍາວ:
ຜົນກະທົບທາງບວກ
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser and the high price that bitter gourd fetches means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, a major reduction in fertiliser costs and improved income leads to increased benefits.
6.5 ການປັບຕົວຮັບເອົາເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
- ກໍລະນີດຽວ / ການທົດລອງ
ທັງໝົດນັ້ນ ແມ່ນໃຜ ໄດ້ປັບຕົວເຂົ້າ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ, ມີຈັກຄົນ ທີ່ສາມາດເຮັດເອງໄດ້, ຕົວຢ່າງ, ປາດສະຈາກ ການຊ່ວຍເຫຼືອ ທາງດ້ານອຸປະກອນ / ການຈ່າຍເປັນເງິນ?
- 91-100%
ຄວາມຄິດເຫັນ:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some farmers in Surkhet district started to use the technology in 2006, after seeing Iman Singh Basnet's innovation of applying urine through drip irrigation in 2005.
6.7 ຈຸດແຂງ / ຂໍ້ດີ / ໂອກາດ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ
| ຈຸດແຂງ / ຈຸດດີ / ໂອກາດ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ |
|---|
|
Urine as a liquid manure is applied at the same time as irrigation (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation or other forms of small scale irrigation needs to be promoted |
|
The on-farm use of collected urine reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing cash expenditure and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the technology to increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less acceptable How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the use of urine and show that there is no problem with using human urine |
6.8 ຈຸດອ່ອນ / ຂໍ້ເສຍ / ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ໃນການນໍາໃຊ້ ເຕັກໂນໂລຢີ ແລະ ວິທີການແກ້ໄຂບັນຫາ
| ຈຸດອ່ອນ/ຂໍ້ບົກຜ່ອງ/ຄວາມສ່ຽງ ຈາກທັດສະນະຂອງຜູ້ປ້ອນຂໍ້ມູນ ຫຼື ບຸກຄົນສຳຄັນ | ມີວິທີການແກ້ໄຂຄືແນວໃດ? |
|---|---|
| The initial establishment costs for a drip irrigation set may hinder adoption |
Prepare a business plan and calculate the cost-benefi t to convince farmers of the technology’s benefi ts |
| Lack of availability of urine may inhibit the commercial application of urine with drip irrigation | Urine needs to be established as a tradeable good produced by livestock farmers and bought by vegetable farmers to apply to their crops |
7. ເອກະສານອ້າງອີງ ແລະ ການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່
7.1 ວິທີການ / ແຫຼ່ງຂໍ້ມູນ
ຂໍ້ມູນການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່ ແລະ ເນື້ອໃນ
ຂະຫຍາຍທັງໝົດ ຍຸບທັງໝົດການເຊື່ອມຕໍ່

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [ເນໂປ]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [ເນໂປ]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- ຜູ້ສັງລວມຂໍ້ມູນ: Richard Allen
ເນື້ອໃນ
ບໍ່ມີເນື້ອໃນ