Small level bench terraces [Тайланд]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Samran Sombatpanit
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Fabian Ottiger
Khan ban dai din khanard lek (Thai)
technologies_1404 - Тайланд
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Cheewinkuntong Wichai
Wang Put Tan, Ban Santikiri, Amphur Mae Fa Luang, Chiang Rai 57110
Тайланд
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
World Association of Soil and Water Conservation (WASWC) - Хятад1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
30/05/2000
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
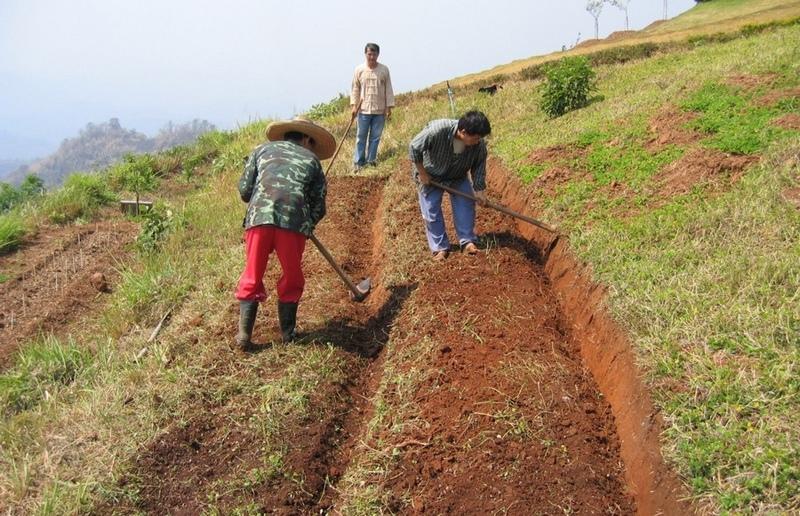
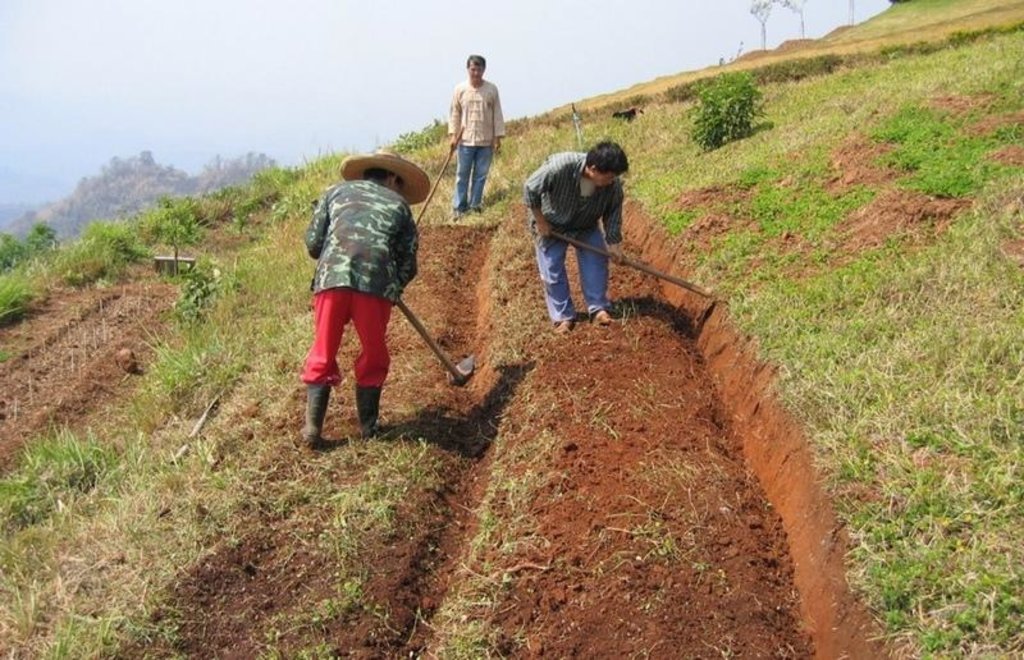
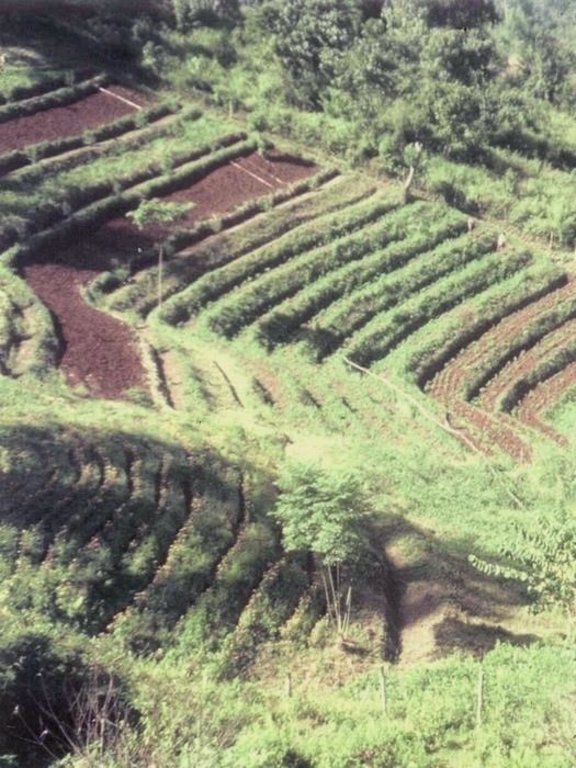
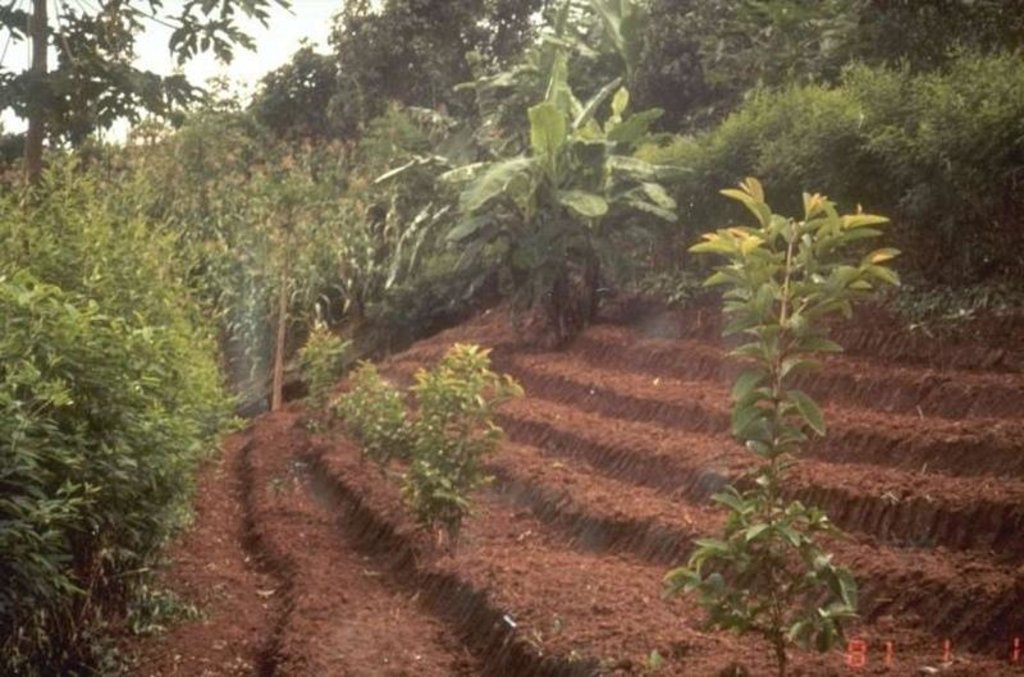
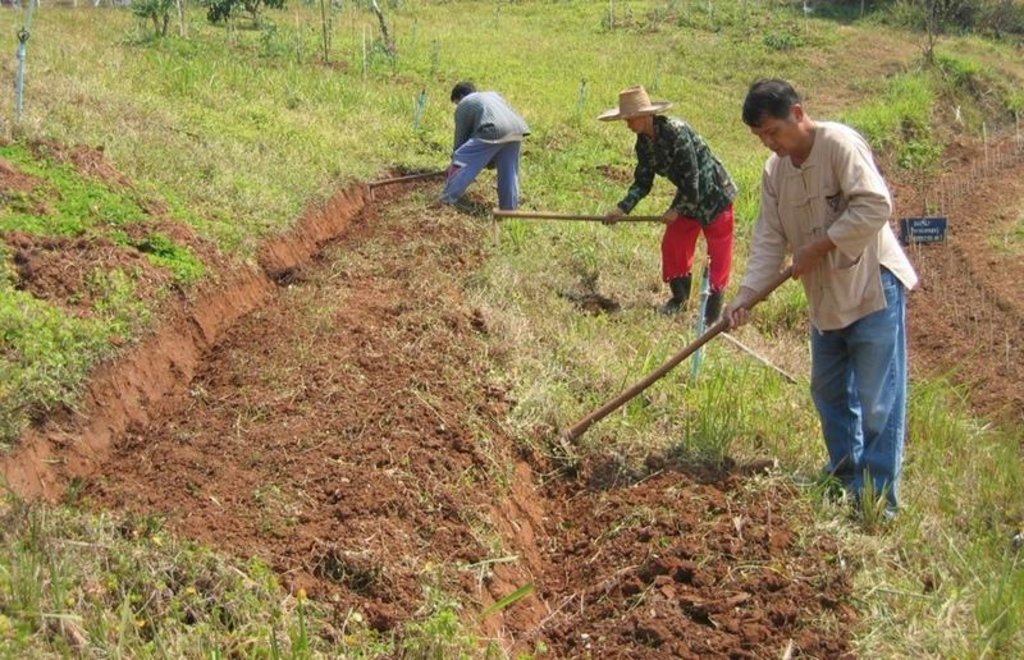
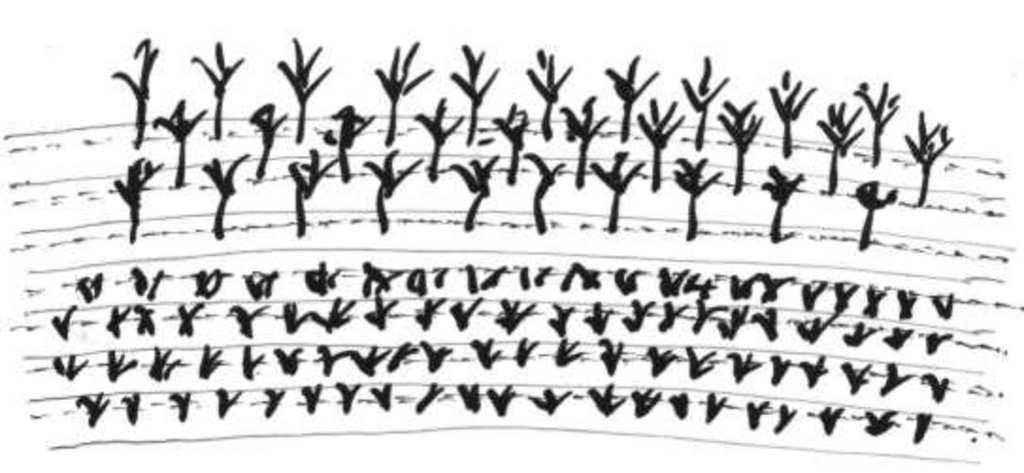
Terraces with narrow beds, used for growing tea, coffee, and horticultural crops on hillsides cleared from forests.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
The terraces described in this case study from northern Thailand are found on hilly slopes with deep soils. The climate is humid and tropical, with 1,700-2,000 mm of rainfall annually. The main aim of the terraces is to facilitate cultivation of tea or coffee on sloping land: erosion control is secondary. Coffee and tea, as well as flowers and vegetables, are good alternatives to opium poppies - which it is government policy to eradicate.
Purpose of the Technology: After clearing natural and secondary forests by slash and burn, terraces are aligned by eye - and constructed by hoe. The width of the bed is 1.0-1.5 m depending on slope, though there are no specific technical guidelines. The length of each terrace can be up to 25 m. Down the slope, after every 3-4 terraces, there are lateral drainage channels, approximately 20-30 cm wide and 10 cm deep. Situated at the foot of a riser, each channel has a gradient of 0.5% or less. Excess water - some of which cascades over the terrace risers, with some draining through the soil - is discharged through these channels, generally to natural waterways. The risers are steep, with a slope of above 100%, and without a defined lip.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Natural grass cover develops on the risers: this is cut back by hand hoe or machete, or completely removed. The grass is often burned. After harvest (of annual crops), the land is left until immediately before the next rainy season. The terraces at this stage are covered by weeds and grasses. Land is then tilled by hoe. The weeds and grasses are removed and heaped in piles outside the cropped area. They are not composted or used for mulching - and here an opportunity is missed. Where soil fertility is a problem, chemical fertilizers are used. Maintenance includes building up/repairing of risers and levelling of terrace beds as required.
Natural / human environment: The technology was pioneered, and continues to be practiced, by refugee immigrants from China looking for new areas to start farming. These immigrants first came in the 1950s, and cultivated simply through slash and burn techniques. During the 1970s they visited relatives in Taiwan and brought back the idea of small terraces. Originally they settled illegally, but eventually they were given official permission to stay. However, official title deeds to their land have not yet been allocated.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тайланд
Улс/аймаг/сум:
ChiangMai
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Amphur Mae Fa Luang
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Taiwan.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Tee, coffee
Major cash crop perennial (non-woody) cropping: Vegetables, flowers
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - soil erosion on cultivated hillsides
- practical difficulties in tending tea, coffee, vegetables and flowers on sloping land: farming is much easier on levelled land
- Lacking of land ownership (The whole area is reserved forest.)
- Low price of agricultural produce.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Lacking of land ownership. 2. Landusers do not have Thai citizenship; less than 20% have ID cards (not citizenship).
Forest: before SWC measures
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Dec - Apr
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
- Усны урсац зохицуулах болон салаалах
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 1-10 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 km2.
This practice has been done by tribal people such as E-kaw, Lahu, Lisu, Mien, Khin, Thai Yai, Haw Chinese, H'mong
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Lack of enforcement of legislation or authority
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural activities), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
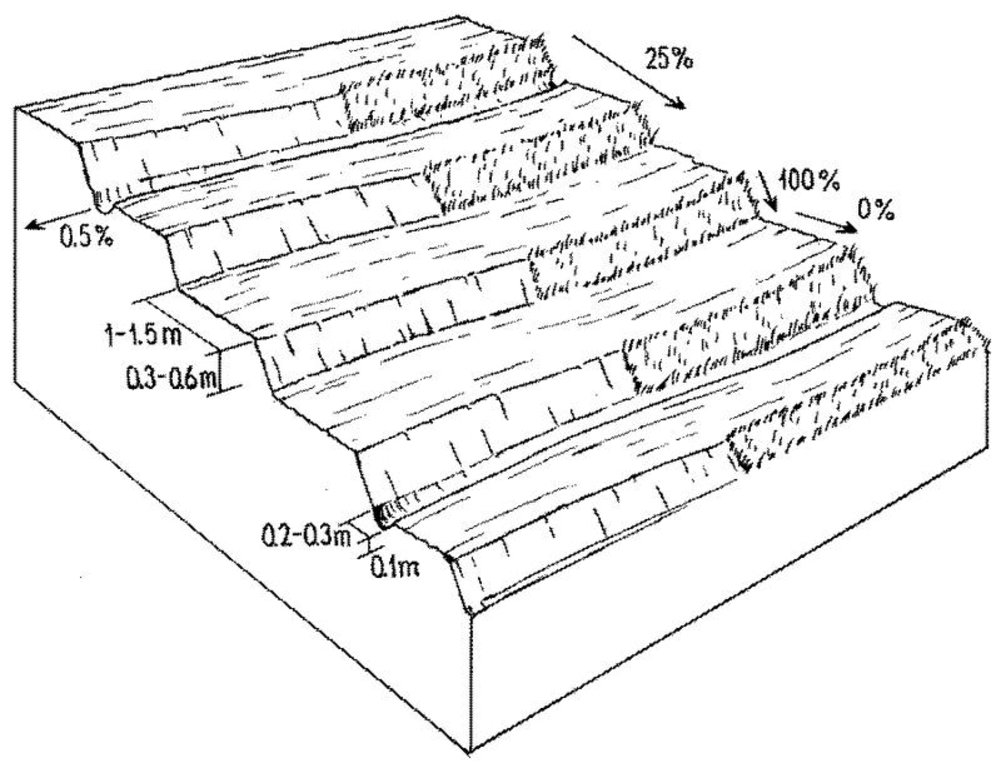
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Layout of small level bench terraces. After every third or fourth terrace a lateral drainage channel is built. Later, protective grass cover is established on the risers (right).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Vegetative measure: grass on risers (optional)
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.4
Spacing between structures (m): 0.3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 25
Structural measure: drainage channels
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): .02 - .3
Construction material (earth): It is the earth dug in situ.
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Baht
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
37.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.16
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout is simply by eye and best judgment. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 2. | Work begins on the lower part of the slope, and then progresses uphill. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 3. | Farmers cut into the hillside with hoes and drag the soil down to formthe risers and level the terrace beds. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 4. | Risers are then stabilised/compacted by hoe. | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 270.0 | 270.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 275.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeds and grasses are removed and piled outside the cropping area. | Ургамлын | |
| 2. | Land is prepared through tillage by hoe. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 3. | Risers are built up/repaired where necessary. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 4. | Terrace beds may need levelling. | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 90.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Clearing of forest is not included in the cost calculations. This calculation is based on a typical slope of approximately 20%, with risers of 0.2 m in height and beds 1.0 m wide. Maintenance costs include basic land preparation (for annual crops) or weeding etc for perennial crops.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The slope factor affects most because it will require longer time to construct.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Average 1600-1800 mm
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Slopes on average: Also steep (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1) and very low (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, good drainage though being cleyey soil) and good (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low (both ranked 1)
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
6% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
24% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: farmers spend much time as farm labourers on other farms or in food processing factories - and some have jobs at construction sites, for example road building
Level of mechanization: Manual work (ranked 1) and animal traction (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Commercial/market (ranked 1, tea, coffee, vegetable and flower production) and subsistence (ranked 2)
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 2-5 ha if farmers may farm at 2-4 plots far apart from each other.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
- illegal (initially) (see Annex T3)
- illegal (initially) (see Annex T3)
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Production is not decreased.
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
газрын менежмент
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
эдийн засгийн ялгаат байдал
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Ease of cultivation. Can walk and work in the farm easier
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Input constraints
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
үндэсний институц
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
20
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
15
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
During dry spells due to increased infiltration
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
50
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
10
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Soil erosion is reduced
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
500
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 50-90 %
Тайлбар:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
450 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a little growing spontaneous adoption: for example in the Mae Salong area farmers accept these terraces increasingly, but fruit growers tend to prefer intermittent ‘orchard terraces’ - terraces spaced apart, with 5 m or more of undisturbed land in-between. The benches in this case are backward sloping.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| For facilitating picking of tea leaves |
| For using as farm path |
| For increasing soil fertility |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
A relatively cheap method of terracing which makes cultivation easier and provides erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Should be further promoted by extension agencies (in areas where cultivation is officially allowed). Allocation of official title deeds to land will speed up the adoption automatically. |
| For improving/maintaining soil fertility |
|
For increasing the yield of tea leaves How can they be sustained / enhanced? Inspecting the field during/after rain to see how efficient they are in conserving soil and water and repair as needed |
| For using as farm path |
| Compared with normal bench terraces, construction does not bring infertile subsoil to the surface. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Farmers have to pay for its construction. | The government may be able to help in the future. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Does not lend itself to mechanisation: the terrace beds are narrow and only suited to hand hoeing. | Teach farmers techniques of composting and/or mulching. |
|
In this situation grasses and weeds are merely piled and burned rather than being used to improve soil fertility |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
No references
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна