Semi-circular bunds (for crops and forest/rangeland) [Нигер]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Dieter Nill
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
Demi-lunes (French)
technologies_1614 - Нигер
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Sani Mamadou Abdou
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP), Niamey, Niger
Нигер
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Герман1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/07/2012
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
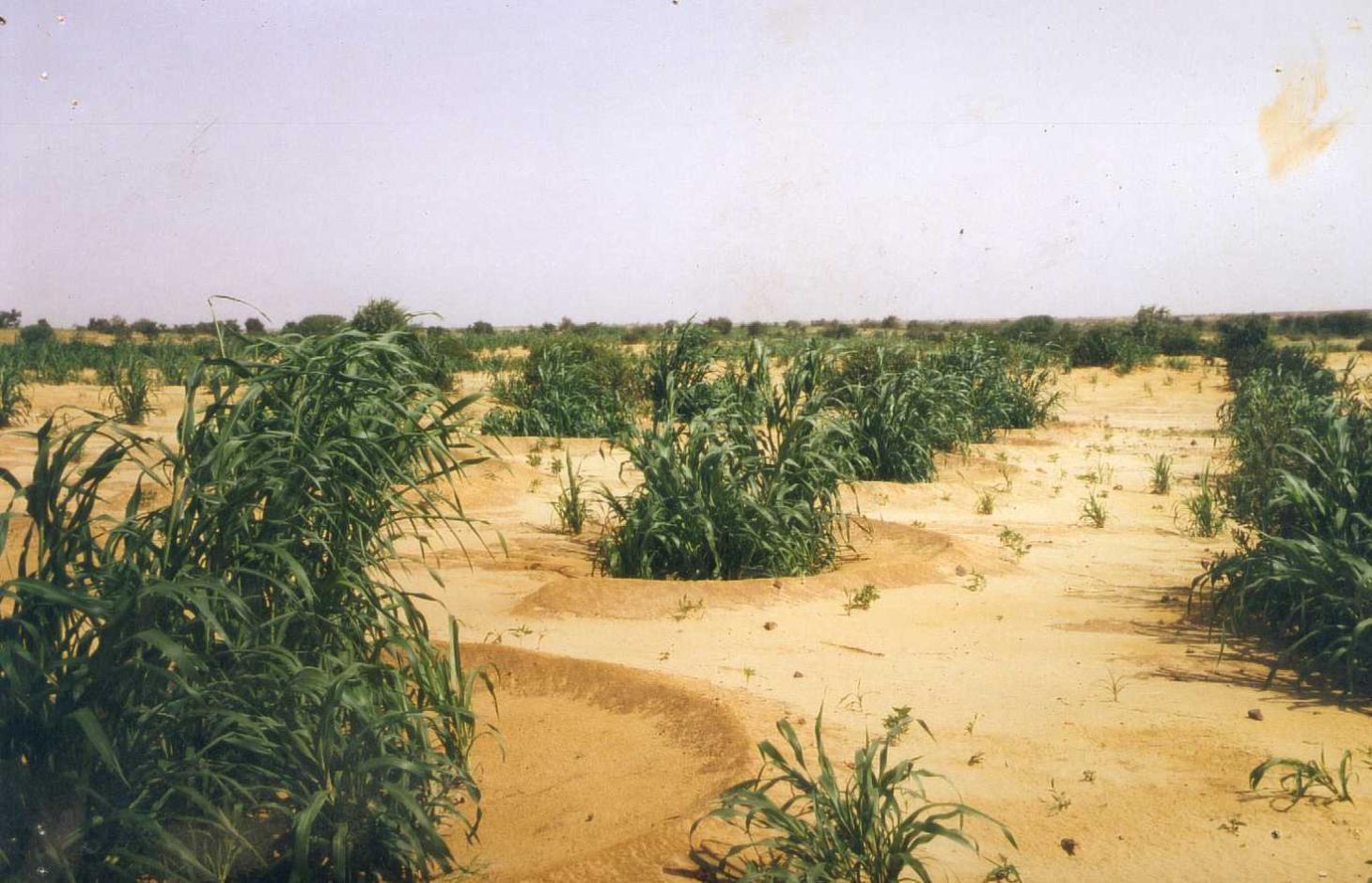
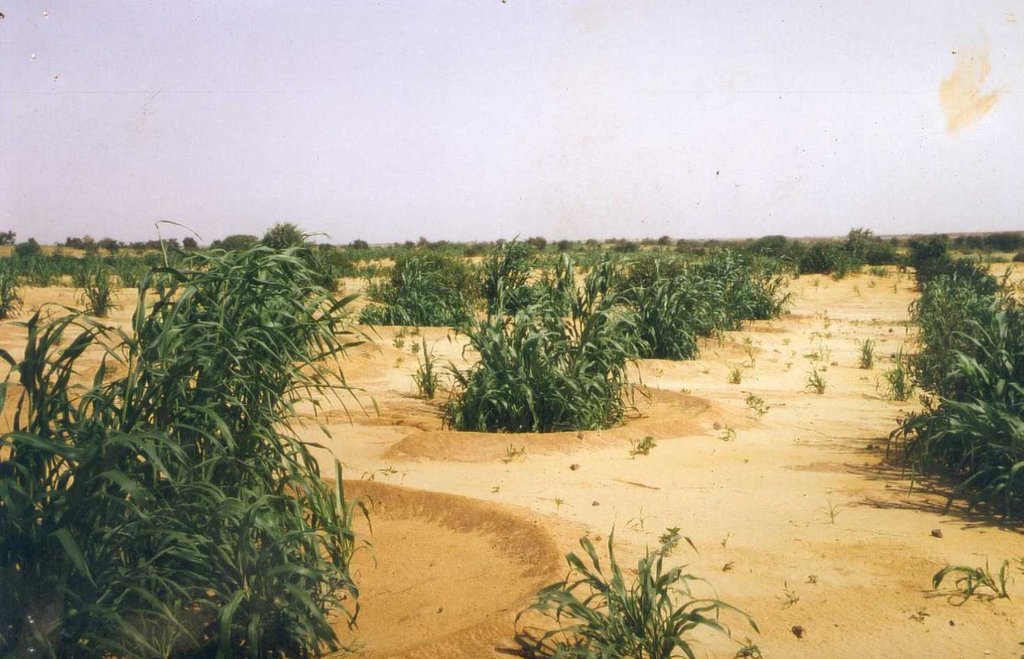
Semi-circular bunds are used to rehabilitate degraded, denuded and hardened land for crop growing, grazing or forestry.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
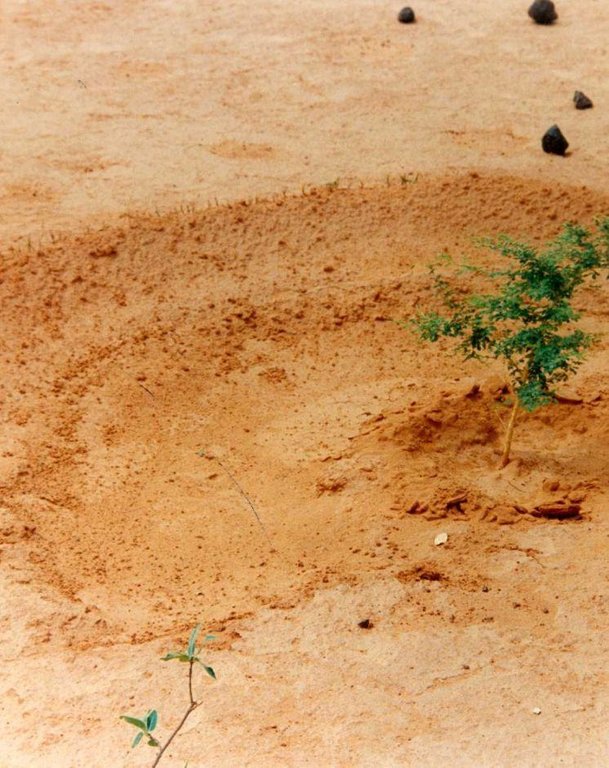
This technique involves building low embankments with compacted earth or stones in the form of a semi-circle with the opening perpendicular to the flow of water and arranged in staggered rows. They are constructed on gently to moderately sloping pediments and plateau areas in order to rehabilitate areas that are degraded, denuded and/or affected by soil crusting.
Depending on their purpose, the areas inside the semi-circular bunds, enriched with organic fertiliser, are used for growing cereals (crop crescents) and for planting trees, bushes and/or grasses (forestry and pastoral crescents). Semi-circular bunds slow down and capture runoff, providing the plants inside them with the water they need. They therefore reduce the loss of water and the fertile layers of the soil. This is particularly advantageous when rain is scarce, as the semi-circular bunds channel water towards the plants, increasing the moisture available to them. In the medium term, rich sediment builds up behind the semi-circular bunds, which helps to protect and restore the land. The bunds ensure that the manure placed around the plants inside them is not washed away by heavy rains, and the ridge of the bund protects young plants from the wind and wind erosion. When they are used for reforestation, they increase the rate of survival of the trees planted in them. Cropland bunds enable crops to survive dry spells. Earthen bunds are not, however, suitable in a scenario with heavy rainfall. They do not allow water to filter through, which can result in the soil inside them becoming waterlogged and the plants being flooded. This can lower yields in the case of crops that do not tolerate excess water. In such conditions, stone bunds are preferable.
To establish semi-circular bunds on cropland, the following activities are required: marking out the contour line, laying out the lines of the semi-circular bunds in staggered rows, digging the microcatchment, forming the ridge downhill of the microcatchment, applying organic fertiliser (around 1 t per ha per year).
To establish semi-circular bunds on forestland the same steps are required, however instead of applying fertilizer, other steps include digging the holes, planting the trees, and sowing grass on the ridges. The earthen ridges around cropland bunds need to be rebuilt each year. It is recommended that the ridges of forest/rangeland bunds be maintained each year and raised if overflowing has occurred. Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. This requires good community organisation. After dry years, forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds may have to be re-sown with grasses and replanted with trees.
The Sahel is a region where the population has always faced a high degree of climate variability, manifested both in terms of time (unexpected dry spells can occur during the rainy season) and in terms of space (rainfall can vary greatly from one area to another). The population is mainly composed of small farmers and livestock keepers.
Over the last two decades, the effects of climate change have exacerbated the already difficult conditions. Accord¬ing to projections made by climatologists, the Sahel will experience a rise in temperatures combined with highly variable rainfall and an increase in extreme weather events. The Soil and Water conservation and rehabilitation techniques have helped people in the Sahel to manage their ecosystems more effectively and improve their productive land. As a result, communities are better prepared to cope with environmental changes (changes in the climate, land degradation, etc.) and the im¬pact of shocks, particularly droughts.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Нигер
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Niger, Burkina Faso, Chad
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa in Niger; Bam region in Burkina Faso
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
(Таримал) байгалийн ой/мод бүхий газар:
- Сонгомол огтлол
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Жимс, самар
- Ойн бусад дагалт бүтээгдэхүүн
- Бэлчээрийн талбай/Хариулгатай бэлчээрлэлт
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): droughts, soil erosion, lack of water, surface runoff, soil crusting, unadapted land use methods, rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land, reduced or abandoned fallow periods, soil erosion, insecure access to land.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing, Improved pasture, agropastolralism
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
Малын нягт (шаардлагатай бол):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 10-100 км2
Тайлбар:
Also implemented in Burkina Faso and Chad
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa in Niger; Bam region in Burkina Faso
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population, increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed community land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
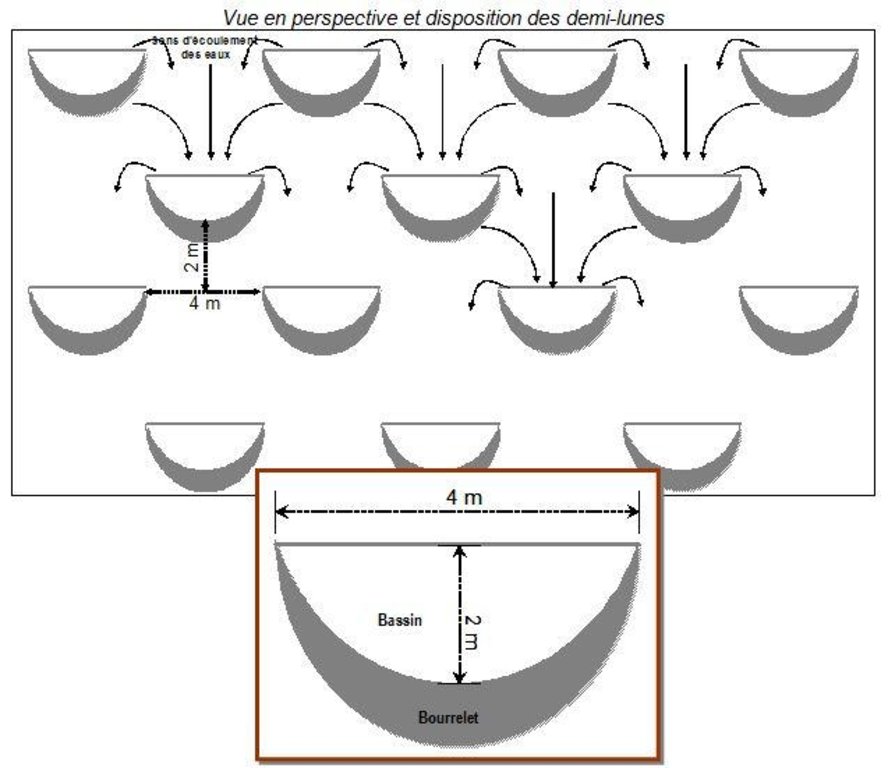
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Source: Ministère du Développement Agricole Niger (without date): Recueil des fiches techniques en gestion des ressources naturelles et de productions agro-sylvo-pastorales.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,15-0,20
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
CFA Franc
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
521.18
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the contour line | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 2. | laying out the lines of the semi-circular bunds in stag- gered rows | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 3. | digging the microcatchment | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 4. | forming the ridge downhill of the microcatchment | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 5. | applying organic fertiliser (around 1 t per ha per year) (only on cropland, this step is not required on forestland) | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 6. | digging the holes (only on forestland) | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 7. | planting the trees (only on forestland) | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 8. | sowing grass on the ridges (only on forestland) | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 201.5 | 201.5 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | ha | 1.0 | 17.3 | 17.3 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 218.8 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The earthen ridges around cropland bunds need to be rebuilt each year | Барилга байгууламжийн | each year |
| 2. | the ridges of forest/rangeland bunds be maintained each year and raised if overflowing has occurred. | Барилга байгууламжийн | each year |
| 3. | After dry years, forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds may have to be re-sown with grasses and replanted with trees. | Барилга байгууламжийн | after dry years |
| 4. | Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. | Барилга байгууламжийн | in the first two to three years |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
Тайлбар:
other costs for cropland semi-circular bunds: 10 cartloads of manure.
other costs for forestland semi-circular bunds:
• 625 tree seedlings
• 15 kg of grass seed
• cost of transporting 625 tree seedlings (2 cartloads)
• 120 seedlings to replace trees that die.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
In the case of forest/rangeland semi-circular bunds, the availability of tree and grass seeds and seedlings is a vital factor. In the PDRT and PASP projects in Niger, the villages had nurseries, and members of the village land manage- ment committees collected grass seeds from rangelands to sow in the semi-circular bunds.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seaonally carry out paid farm labour
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
traditional land use rights are prevailing. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Cropland bunds constructed on abandoned farmland increase millet yields by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. This requires good community organisation.
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Sites improved with semi-circular bunds for reforestation produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хэрэгцээ
Орлого, зарлага
ажлын хэмжээ
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
notably increses production of food, fodder and forest products
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
survival of planted trees
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | мэдэхгүй |
Тайлбар:
Physical structures can be biologically stabilized through planting of grass, bushes or trees. Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
Forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. Semi-circular bunds on forest/rangeland can achieve a remarkable regreening of the environment and promote biodiversity. Cropland bunds constructed on abandoned farmland increase millet yields by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year. Sites improved with semi-circular bunds for reforestation produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 50 -иас их %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 10-50%
Тайлбар:
60% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The techniques were implemented with food for work in the 1990s to 2000. Between 2000 and 2012 the work provided by land users was not compensated. Only small equipment and transportation were provided for free.
40% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support. Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Semi-circular bunds are applied for example in Niger, Burkina Faso, and Chad.
Some adoption (without support by the project) has been observed in some places. The level of replication is however limited to locations where stones are available nearby. Otherwise transportation becomes a problem.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Semi-circular bunds slow down runoff and enable the harvested water to be used to good effect. Soil moisture increases and the loss of fertile layers of the soil is reduced. |
| Cropland bunds enable crops to survive dry spells. On abandoned farmland millet yields may increase by 180 kg and straw yields by 400 kg per hectare per year. |
| Semi-circular bunds on forest/rangeland can achieve a remarkable regreening of the environment and promote biodiversity. When they are used for reforestation, they increase the rate of survival of the trees planted in them. Sites improved with semi-circular bunds produce one stere of wood per hectare per year after ten years. The value of this production can increase further from the fifth year onwards to around 850,000 CFA francs per hectare. |
| In the medium term, rich sediment builds up behind the semi-circular bunds, which helps to protect and restore the land. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| In the event of heavy runoff, a considerable amount of water accumulates inside the semi-circular bunds, and the ridges must be strong enough to withstand its weight. If the water overflows, it can create gaps in the bunds or cut out channels around the sides of them. | The land must be hoed each year. |
| At some sites, rainwater infiltration increases in the first year after the semi-circular bunds have been constructed, but if the land is not hoed, this effect declines considerably in successive years. | In such conditions, stone bunds are preferable. |
| Earthen bunds are not suitable in a scenario with heavy rainfall. They do not allow water to filter through, which can result in the soil inside them becoming waterlogged and the plants being flooded. This can lower yields in the case of crops that do not tolerate excess water (e.g. millet). | |
| Animal production may be reduced because forest/rangeland sites should be protected from grazing animals in the first two to three years, until the vegetation is well established. | |
| Labour-intensive work |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна