Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields [Веьтнам]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Justyna Sycz
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff
technologies_1277 - Веьтнам
- Бүрэн хураангуйн PDF хувилбар
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр хэвлэх
- Хөтөч дэх бүрэн хураангуй
- Бүрэн хураангуй (форматгүй)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 05 1-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 29 4-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 03 5-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Water saving through reuse of return flow in paddy fields: 11 8-р сар 2019 (public)
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Land-use intensity and Ecological Engineering – Assessment Tools for risks and Opportunities in irrigated rice based production systems (LEGATO / GLUES)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Technische Hochschule Köln (TH Köln) - Герман1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
03/08/2015
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Return flow from paddy fields is strategically collected before being lost to rivers and is reused as an effective source of agricultural water.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
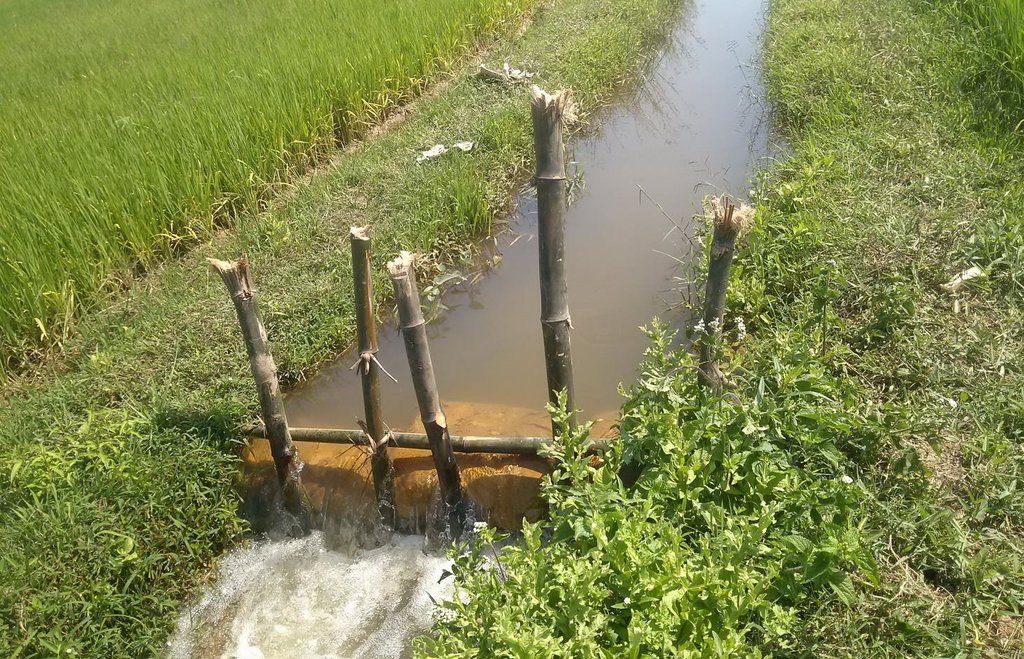
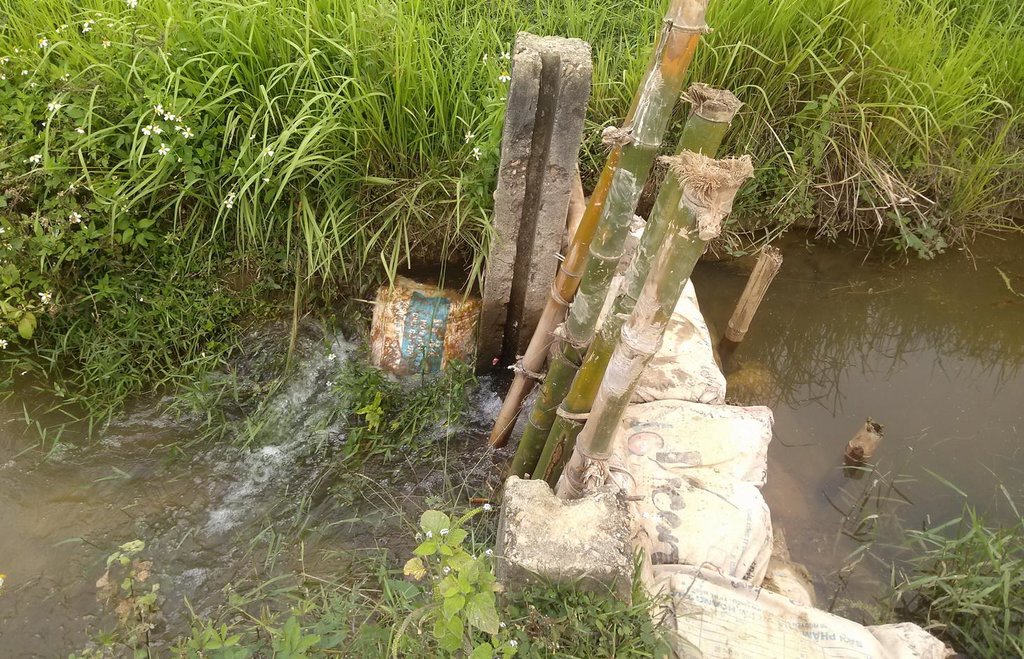
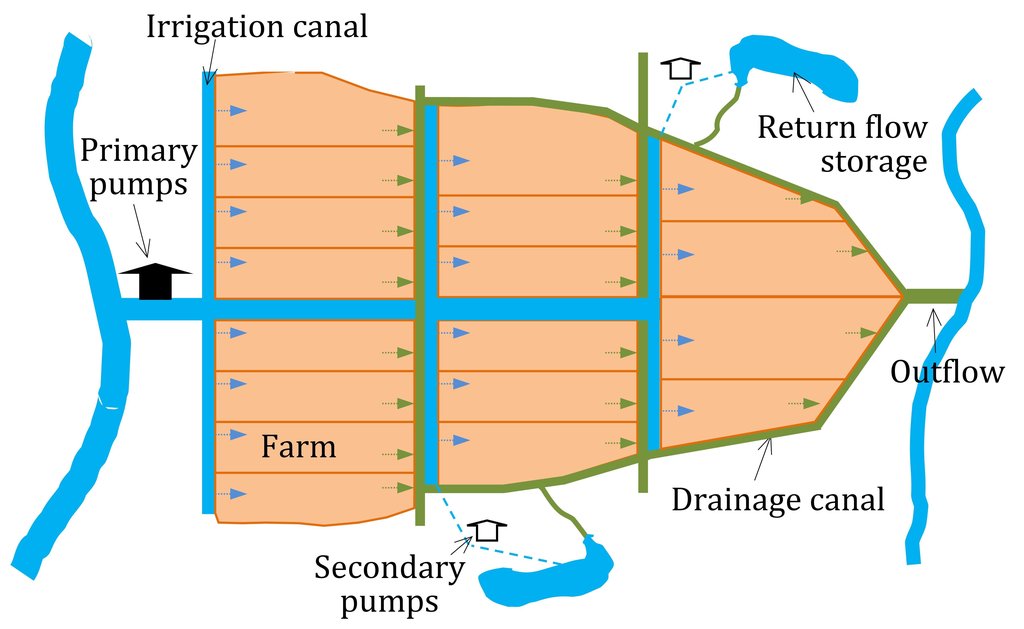
Return flow from paddy fields is defined as applied water that is not lost by evapotranspiration but returns to an aquifer or surface water body (Womach, 2005). The two types of return flow are surface and sub-surface. Surface return flow accounts for the major proportion. If surface return flow is strategically collected before entering rivers, it can be used as an ‘extra’ effective source of agricultural water supply (Phil King, 2008; Simons et al., 2015). Because paddies effectively purify water by absorbing nitrogen and phosphorus, this produces return flow of an acceptable quality for irrigation purposes. Return flow can be collected by drainage canals and stored in ponds and reservoirs, and then returned to pumps for reapplication. This technology offers one solution towards overcoming a deficit of irrigation water.
The goal of this technology is to store and reuse surface return flow from paddy farms to enhance irrigation efficiency. The purpose of constructing temporary barriers in drainage canals is to minimise water wastage and optimise the possibility of collecting and recycling surface return flow. Return flow from irrigation system is stored in surrounding ponds and reservoirs Return flow can only be used when it is captured in a storage structure or drain which has a hydraulic link to the irrigation source: thus an integrated framework for the reuse system consisting of both hydraulic, and management, links should be established. Within the scope of this study, the Water Management Unit (WMU) is understood as an integrated irrigation and drainage system consisting of four components: (i) the hydrological catchment which covers both non-irrigated and irrigated area; (ii) the source scheme generating return flow; (iii) the reuse scheme that is hydraulically connected with the source scheme; and (iv) a drainage system functioning as a harvesting as well as a supply structure.
Before implementing such a system it is recommended to analyse the correlation between irrigation efficiency and reuse of return flow, as well as developing a framework for managing and recycling return flow. Investigation aims at identifying the potential of return flow for irrigation; determining its quantity and quality; and developing an efficient and sustainable reuse framework. Water balance calculations, field measurements, water quality sampling and interviewing are all used for this purpose.
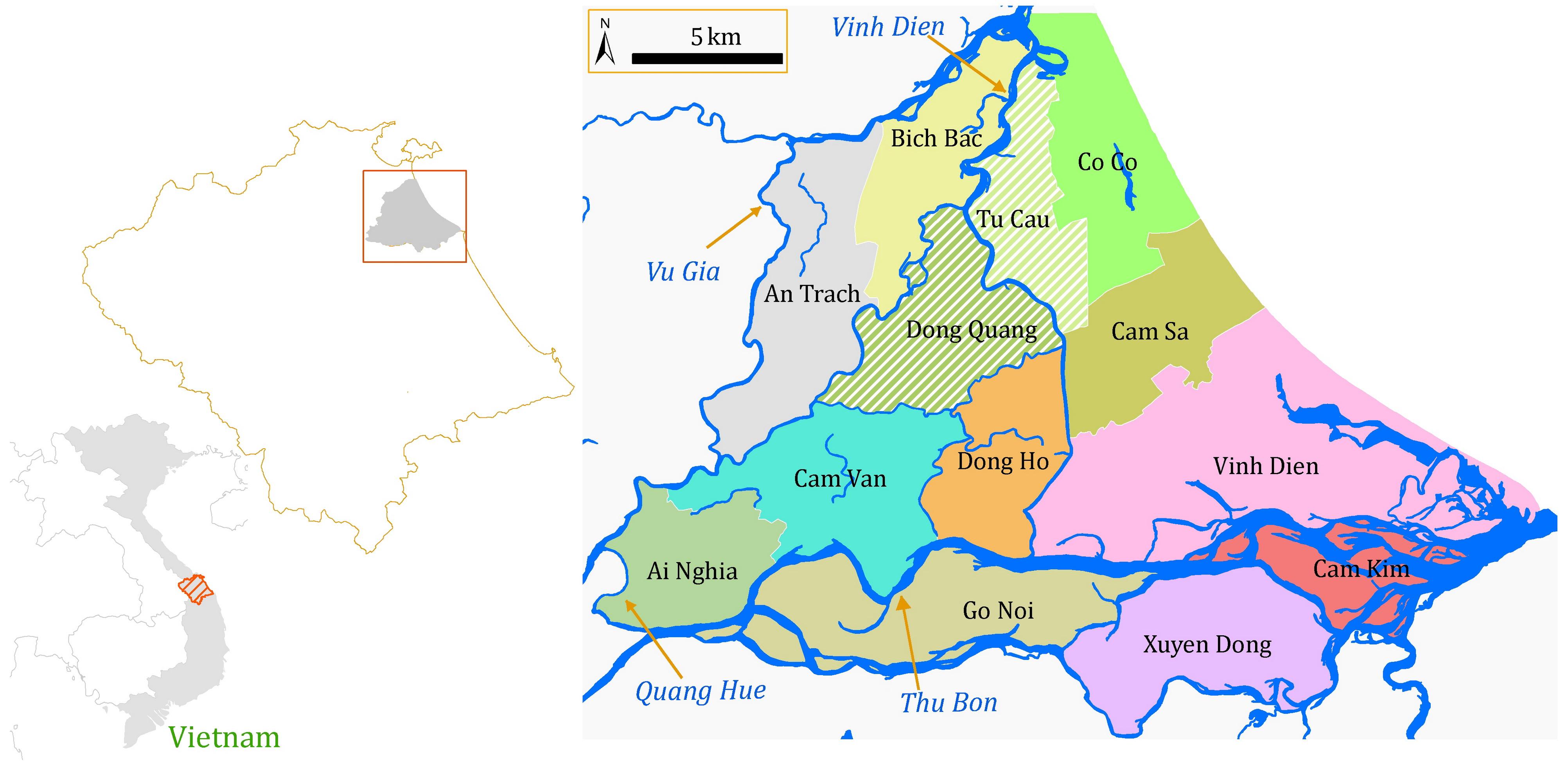
In the study area, long dry seasons cause severe water shortages and problems with saline intrusion. The study area is mainly covered by paddy, vegetables and other annual crops such as maize, sweet potatoes, peanuts and sugarcane. Paddy rice, which consumes a high proportion of the freshwater, is the dominant crop. Agricultural land in the downstream area is irrigated through gravity or pump irrigation systems. Here results indicate that the irrigation efficiency can be improved significantly: the irrigation efficiency of Tu Cau and Thanh Quyt irrigation schemes is projected to increase respectively by 1.8 and 1.4 times.
Reuse of return flow can be applied in all WMUs where the drainage canals are connected with storage tanks. Scientific and technical support tools are offered by the Vu Gia Thu Bon River Basin Information Centre. The centre was established in Danang providing a comprehensive information service to farmers and other water users – it includes capacity building and consulting services also.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Веьтнам
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Quang Nam
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Dien Ban
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The lowland part of Vu Gia Thu Bon is an intensive agricultural area. Rice cultivation, which consumes a high proportion of fresh water, accounts for 70% of total agricultural land (Ribbe et al., 2011). Since 2005, due to the impacts of droughts and saltwater intrusion, water for irrigation during the dry seasons has become an increasing problem in the lowland area of this basin. Simultaneously, the irrigation efficiency of this region is relative low. Various measures are applied to address water scarcity for irrigation. Reusing return flow is regarded as a potentially new measure to reduce the severity of the irrigation deficit in dry periods.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Based on the information provided by the Department of Natural Resources and Environment (DONRE) for Quang Nam Province, this basin now faces the problem of temporarily insufficient irrigation water. This situation is caused by droughts, insufficient reservoir capacity, salinity intrusion and ineffective irrigation management.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- бүрэн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 130, Longest growing period from month to month: 20th December to 28th April; Second longest growing period in days: 110, Second longest growing period from month to month: 20th May to 06th September
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Ус хуримтлуулах
- гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг, гол, нуур, тэнгис гэх мэт)
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.916 m2.
The research area is located in the downstream of the Vu Gia Thu Bon Basin (VGTB), Central Coast of Vietnam. Based on the hydraulic connectivity, the lowland of the VGTB is divided into 13 Water Management Units (WMU) (Viet, 2014). Of which, the Dong Quang and Tu Cau WMUs are selected to conduct the field survey and water quality sampling.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S5: Далан, усан сан, цөөрөм
- S6: Хашаа, саад, явган хашлага, хашаа

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
- M6: Хог хаягдлын менежмент (дахин боловсруулах, эргүүлэн ашиглах эсвэл бууруулах)
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

усны доройтол
- Hs: Гадаргын усны хэмжээ багасах
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Paddy rice requires huge amounts of water. Meanwhile, the coefficient of irrigation return flow from paddy field is also quite high.), industrial activities and mining (Hydropower construction reduces water availability for irrigation), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (It causes water waste and reduces irrigation efficiency.), change of seasonal rainfall (It affects the paddy water balance and actual irrigation need.), droughts (It causes saltwater intrusion.)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (It relates to evapotranspiration.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …), governance / institutional
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
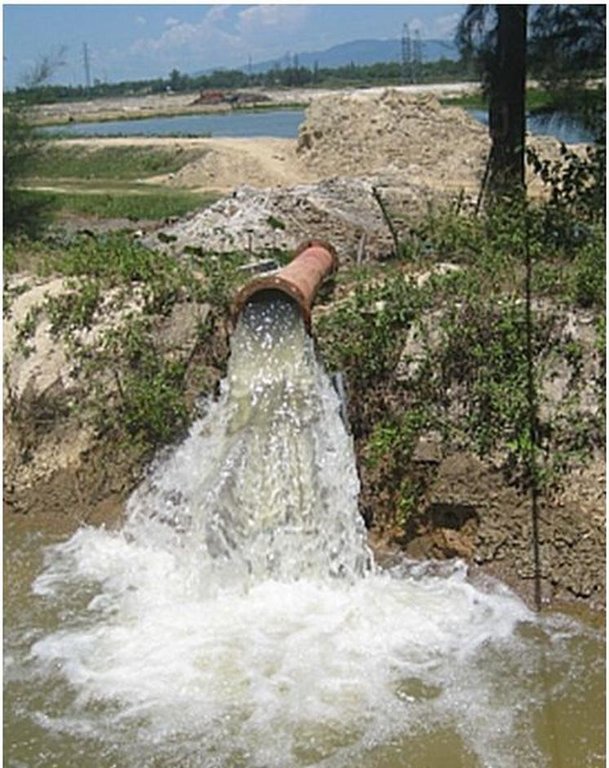
Methods of recycling return flow from paddy fields: The surface return flow can be captured by drainage canals and stored in tanks: return water from these reservoirs is pumped back into irrigation canals.
In 2012, the first on-farm irrigation structure was initially implemented in the Tu Cau WMU in order to use return flow for irrigation purposes. The existing Sen Pond was enlarged and a temporary pumping station was installed to pump water into the irrigation canal system.
According to the pumping diary of Tu Cau station (in Winter-Spring crop 2013), there were totally 7 irrigation periods (8-11 days/period). Total input water (including effective rainfall) during the measuring period from 01 March to 10 April was about 28,000 m3. Meanwhile the total volume of return flow of the Tu Cau site was 16,176 m3. This amount of return flow has the potential to irrigate the agricultural area for about 16 days, equivalent to one and a half irrigation periods. The overall efficiency of the irrigation system will be significantly improved.
Location: Lowland area of VGTB Basin. Quang Nam Province
Date: January 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 194.9
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 399.4
Wall/ barrier
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.26
Construction material (other): Stone, sandy bags and bamboo sticks
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 116764.59m3
Catchment area: 77860 m²m2
Beneficial area: 30 ham2
Other type of management: Return flow is the part of drainage flow, it is necessary to enhance the institutional link to develop the reuse framework for the study area. Think about reforming IMC to IDMC with D is drainage.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
VND
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
20828.0
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building temporary barrier in drainage canal | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 2. | Dredging and expanding Sen Pond | Барилга байгууламжийн | 12 months |
| 3. | Installing and operating the temporary pump at Sen Pond, P is 15KW (Q=520-600m3/h) | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | 1.0 | 3046.52 | 3046.52 | ||
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | 1.0 | 5344.09 | 5344.09 | ||
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | hammer, iron wire | 1.0 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 100.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Stone,sandy bags,bamboo sticks | 1.0 | 6.45 | 6.45 | 100.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Earth, concrete | 1.0 | 1335.8 | 1335.8 | ||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 9735.26 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Temporary barrier | Барилга байгууламжийн | each cropping season |
| 2. | Temporary pump | Барилга байгууламжийн | annually |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 30.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | 1.0 | 38.41 | 38.41 | ||
| Барилгын материал | Stone,sandy bags,bamboo sticks | 1.0 | 3.22 | 3.22 | 100.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 65.63 | |||||
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Prices of the material and equipment; the approval procedure and disbursement process of the project of “Dredging and expanding Sen Pond”; the compensation cost for the farmers; the cost of operating and maintaining temporary pump; the cost of reinforcing the drainage canals.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Average annual rainfall in period 1978-2010 of research area is 2105mm. February to April is driest period as rainfall in this period accounts only 3-5% of annual rainfall.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics. humid tropical monsoon climate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 3% of the land.
2% of the land users are rich and own 7% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
2% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is a large industrial park located near the study site and a large part of the working population in the region is earning income by working in the factories.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- farmer, individual
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- farmer, individual
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
A small farming area within an irrigation scheme will be used to store drained water.
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The technology helps to minimise negative impacts of saltwater intrusion on irrigation
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хэрэгцээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The technology helps to reduce water abstracted from river in dry periods when saltwater intrusion occurring
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Increased irrigation efficiency
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
37%
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
68%
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The irrigation efficiency is improved significantly (increasing about 1.8 times) in the case of recycling return flow
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
This technology helps to minimise the damage to agricultural production caused by excess salt during the dry periods. It brings the benefits for the farmers by increasing the crop yields and helps to improve their livelihoods.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less freshwater is used for irrigation purposes
гадаргын урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
давсжилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
50/270 ha of the Tu Cau Irrigation scheme is additionally supplied water in the dry periods as rivers are affected by saltwater intrusion
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Loss of land for enlarging the Send Pond
contamination of reused water by agro-chemicals
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | муу |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 50-90 %
Тайлбар:
By applying the technology, the potential reuse area of return flow is estimated about 33% of the study area (30.4ha of agricultural area is potentially irrigated by return flow). However, estimating the number of land user families that have implemented the technology is not the initial aim of the study. Therefore, it requires further detailed investigation and social survey as well.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increases the water depth in paddy fields which helps to improve paddy productivity |
| Beneficial/ endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Using return flow is helpful to improve irrigation efficiency. The amount of extracting water for irrigation and the cost of operating an irrigation system can be reduced. |
| The measure contributes to mitigating negative impacts of drought and salt intrusion. During the dry season the river water becomes more and more saline due to salt water intrusion. Salinity also builds up from not leaching out salts in the subsoil |
| Take advantages of available drainage canals, ponds, reservoirs to reduce the investment costs |
| Acceptable water quality because of the purification function of paddies which removes nutrients from the water |
| Low costs of conveyance systems because of short distance. More flexibility of allocation because of stable return flow. Less conflict between sectors. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Temporal and spatial variation causes difficulty in using return flow. The differences in soil type, terrain, storage capacity of the paddy fields and irrigation method (e.g. irrigation techniques, the amount of input water and pumping intervals) are major factors influencing the quantity of return flow | Constructing temporary barriers in the drainage canal helps to minimise the water wastage and optimise the possibility of collecting and recycling surface return flow. |
| Using return flow might spread diseases, and weed seeds from affected farms to safe farms | Encourage farmers to comply with the principles of prevention and control diseases in agricultural production. It is necessary to implement preliminary tests and analyses the quality of return water before recycling for irrigation purposes. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Kim, H. K. et al. (2009) Estimation of irrigation return flow from paddy fields considering the soil moisture
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Agricultural Water Management, 96(5), 875–882.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Phil King (2008) Return Flow Efficiency
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Simons, G.W.H. et al. (2015) Water reuse in river basins with multiple users: A literature review
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Journal of Hydrology. 558–571
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Ribbe et al. (2011) Annex 2 to Milestone Report 2011 - Description of the Study Region including an updated stakeholder analysis,
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
LUCCi project. ITT, Cologne University of Applied Sciences
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна