Orchard-based agroforestry [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Loes Masselink
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Laura Ebneter, Olga Andreeva, Lisa Soloveva, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli
technologies_1017 - Тажикистан
- Бүрэн хураангуйн PDF хувилбар
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр хэвлэх
- Хөтөч дэх бүрэн хураангуй
- Бүрэн хураангуй (форматгүй)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 14 8-р сар 2019 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 02 11-р сар 2021 (public)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 04 4-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 19 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 17 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 17 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 17 7-р сар 2017 (inactive)
- Orchard-based agroforestry: 09 3-р сар 2017 (inactive)
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Soil Science Institute (Soil Science Institute) - Тажикистан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/01/2004
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
An agroforestry system where legumes and cereals are planted in fruit orchards, giving simultaneous production and conservation benefits.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
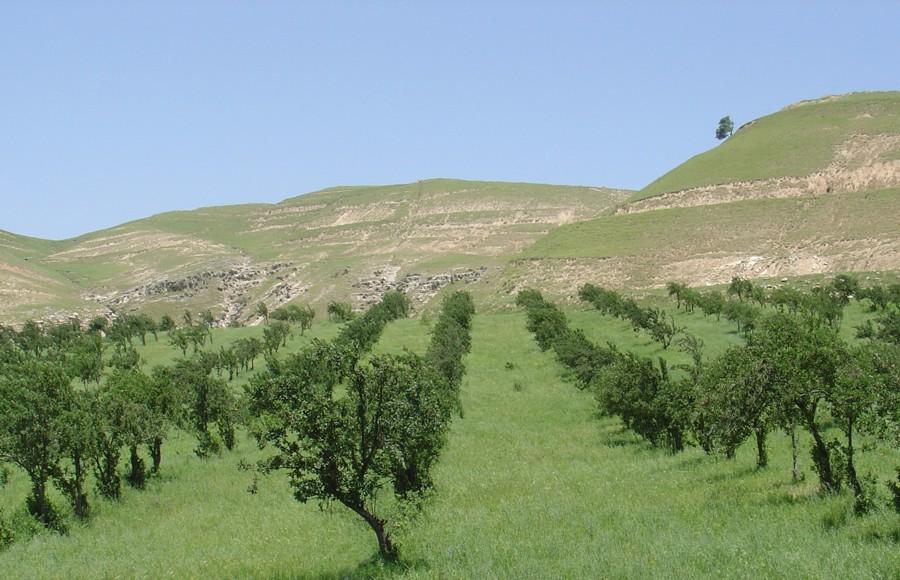
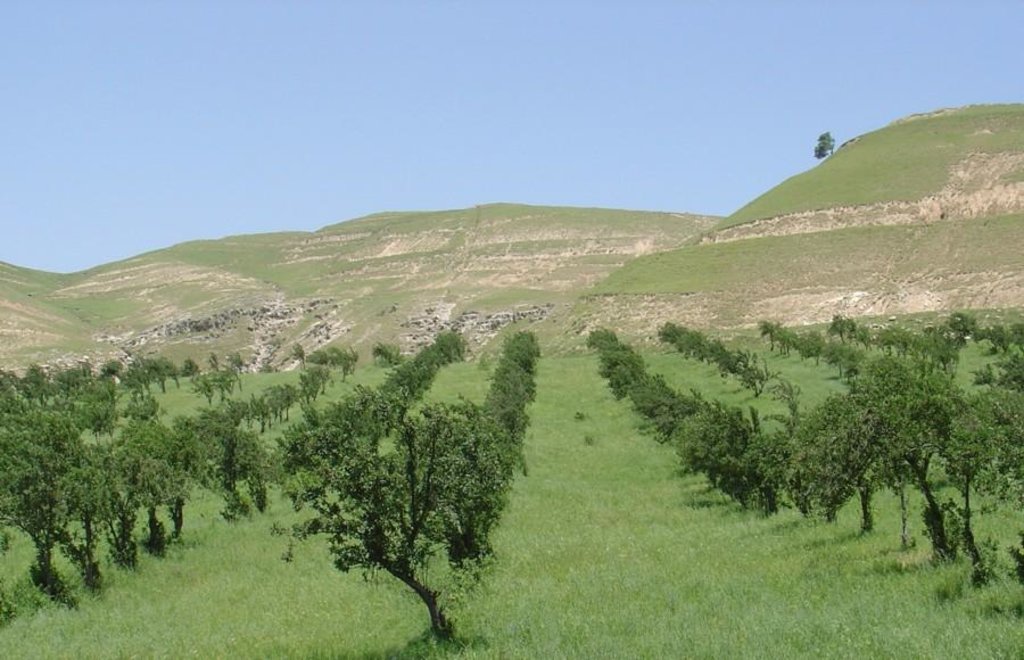
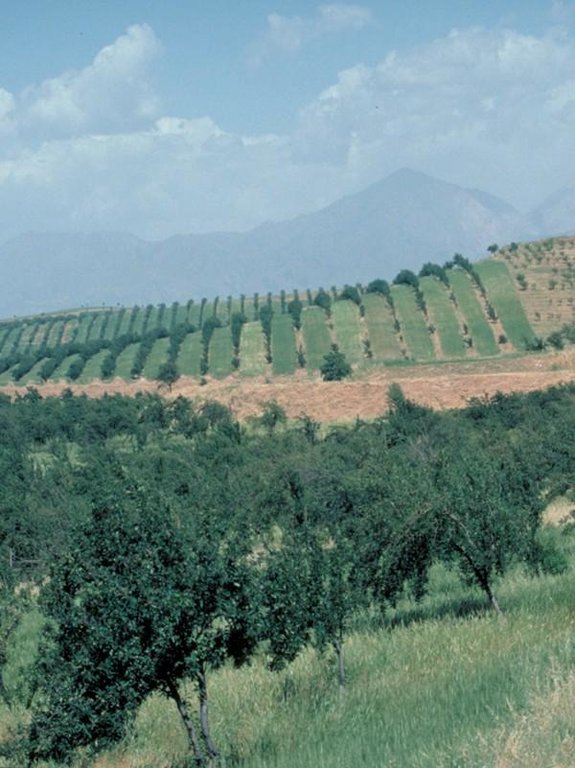
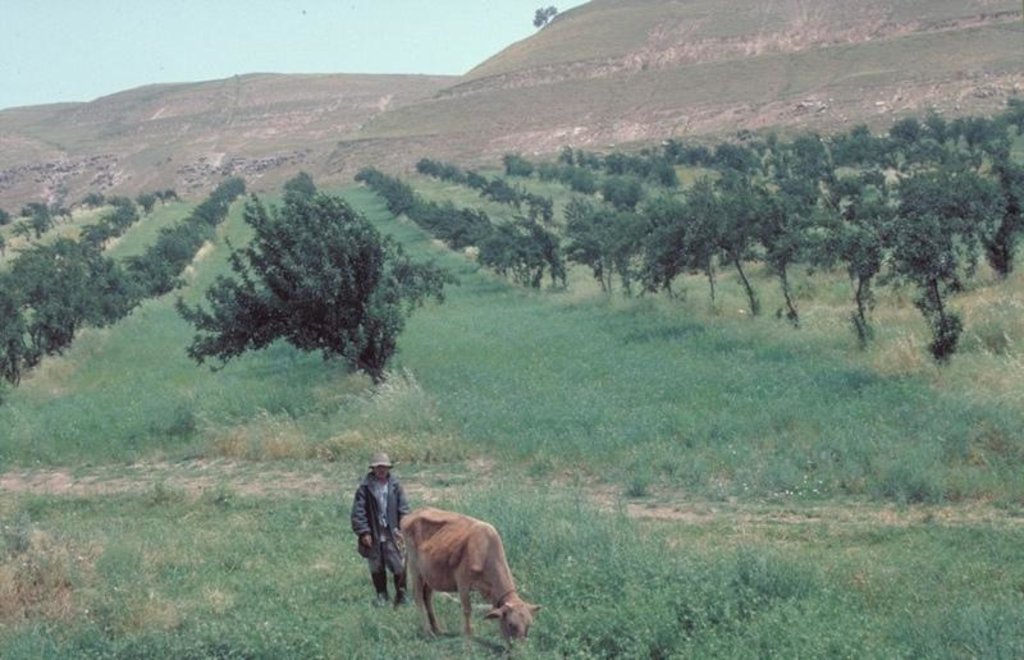
In the Faizabad region, Tajikistan, an area which is characterised by hilly topography, and deep but highly erodible loess soils, farmers traditionally cultivate beans and wheat in combination with fruit trees. This was a rather unsystematic agroforestry system, and during Soviet times (in the 1980s) fruit production was intensified. Pure-stand orchards were established: the land was levelled and on slopes exceeding 20%, terraces were constructed mechanically. The density of trees was increased, and the little space remaining between was used for hay production. Annual cropping was stopped.
Purpose of the Technology: After the Soviet era, farmers reduced the number of trees, allowing room for inter-cropping. They also established new orchards according to this same pattern. Those who farm rented land merely inter crop wheat, whereas the few farmers who own their land, rotate crops with two years of wheat, followed by one of legumes (beans or lucern). Crops are grown both for home consumption and sale.
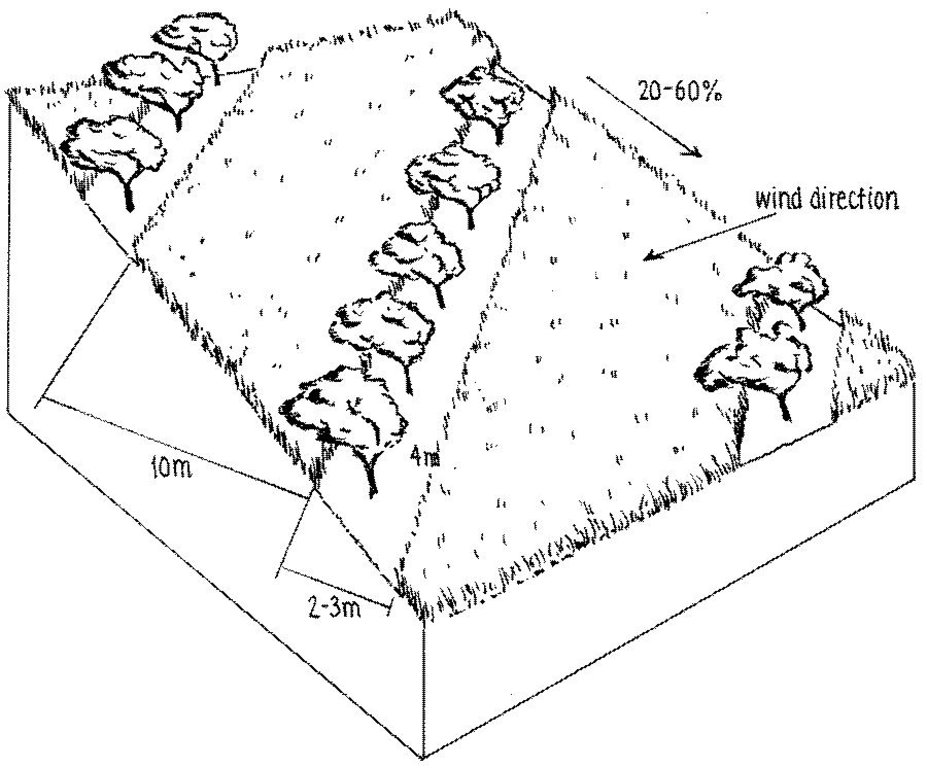
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The density of apples was reduced by expanding the spacing from approx 5 m to 10 m between rows, and from 2 m to 4 m within rows. Along each row of trees a 2-3 m strip of grass was left to grow. The layout of fruit trees in lines is a compromise between being along the contour, and against the prevailing wind. After harvesting of the fruit, between August and October, farmers sow their annual crops.
Natural / human environment: This agroforestry system provides protection against strong winds, heavy rains and flooding. Soil erosion (by water) has been reduced due to improved soil cover by the inter cropping, and through leaf litter, which is left to decompose on the ground. Furthermore, after harvesting, about three quarters of the crop residues are left on the field as mulch. The remainder is used as fodder. Soil organic matter within the current agroforestry system is considerably higher than in the surrounding grazing areas. Soil fertility has improved also: beans can fix 60-80 kg/ha/year of nitrogen. Compared with other crops, wheat provides the best erosion protection. Since the lateral rooting system of the apple trees reaches only 1-1.5 m from the trunk, competition for nutrients is not a major problem. Neither is there a problem with shade, since during the crop establishment period the trees have lose their leaves. In order to increase production, farmers plan to apply supplementary irrigation where possible.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Tajikistan, Faizabad
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Холимог (тариалан/бэлчээр/мод), үүнд. ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
Гол бүтээгдэхүүн/ үйлчилгээ:
major cash crop: apples, wheat, beans
major food crop: apples, wheat, beans
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Most of the rains fall in late autumn and early spring, and the rains coincide with very strong winds. The topsoil is therefore exposed to erosion during this period if left uncovered, and without a windbreak. A particular problem during the soviet period was that the intensive orchard system meant annual food crops were left out of the production system: soil cover was reduced and there was less food.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: two years of wheat followed by one of legumes (beans or lucerne)
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: October-JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 270Second longest growing period from month to month: November-July
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Салхины хамгаалалтын ойн зурвас
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 45 m2.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А6: Бусад

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, rotations / fallows
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Et: loss of topsoil, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (The suplementary irrigation system could not be maintained after state farms stopped recieving government support. Thus, it became more interesting to increase crop production through intercropping.)
Secondary causes of degradation: governance / institutional (With the transformation of the planned economy to a market economy, for the state farm areas new forms of management had to be found.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Fruit trees intercropped with wheat (or beans): note the fruit trees are aligned in a 'compromise' position between the direction of the prevailing wind and the slope.
Location: Faizabad. Faizabad, Tajikistan
Date: 25-07-2004
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, improvement of soil fertility (with crop rotation incl. Beans+lucerne)
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), water harvesting / increase water supply, retain/trap concentrated runoff (prevention of gully erosion)
Mulching
Material/ species: leaf litter, crop residues
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat, legumes
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2-6
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2-3
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-60%
terrace: forward sloping: earth
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of fruit orchard | Ургамлын | |
| 2. | Thinning: doubling the spacing between trees (by farmers, after Soviet period) | Ургамлын | |
| 3. | Hand planting of fruit tree seedlings | Ургамлын | |
| 4. | planting fruit trees | Ургамлын | |
| 5. | 1. Levelling of steep land into terraces with graders | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 6. | Planting of fruit orchards | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Planting of fruit orchard | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Thinning and hand lanting | ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 | |
| таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | pesticides | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 570.0 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Applying organic manure for crops and trees | Агрономийн | (November to March) |
| 2. | Ploughing to depth of 25–30 cm for annual crops | Агрономийн | (November to March) |
| 3. | Disc ploughing and harrowing . | Агрономийн | (March) |
| 4. | Chemical fertiliser application to crops | Агрономийн | (once during season). |
| 5. | Pest management with chemicals | Агрономийн | (two-three times where possible/affordable) |
| 6. | harvesting: wheat is the only crop, which can be harverted if tractor and petrol is available | Агрономийн | |
| 7. | mulching trees (humus cover) | Агрономийн | |
| 8. | cutting trees | Агрономийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | applying organic manure for crops and trees | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | ploughing | ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | labour animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | labour harvesting | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | labour mulching and cutting | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 220.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Cost calculation refers to farmers who established new agroforestry plots (without receiving any incentives). These are farmers who have rented land from state farms. However, conversion of Soviet orchards is more common than the establishment of new agroforestry plots (information on costs not available).
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Landforms also mountain slopes.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- механикжсан / мотортой
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: trade and business; young men often migrate to Russia (seasonally or for several years) to search for jobs
Level of mechanization manual work: pruning of trees, harvesting, applying herbizids
Level of mechanization animal traction: ploughing if no fuel for tractors is available
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: Disc ploughing and harrowing, if petrol is available
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology also 2-5 ha
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
модлогийн бүтээмж
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
trees hinder farm operations
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
difficult to apply pesticides using machinery and pesticides are very expensive.
Pruning is important, but farmers are new to the system and don’t always have the skills required
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
nutrient use efficiency
water use efficiency
soil fertility
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Also biodiversity enhancement is medium (20-50%)
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 10-50%
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
3500 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support in an area of 45 km^2
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 90-100 %
Тайлбар:
3500 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Adoption rate is high: 3,500 households in the region, who rented the orchards, have converted them themselvs without any incentives.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Easy to convert orchards How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land reform from state to private ownership would assist the process and strengthen farmers' associations. |
| Helps provide employment (mainly self- employment, partial employment of additional labourers) and increased self-sufficiency. With the cultivation of wheat, some farmers can solve their food problems and do not need an off-farm income. |
|
Improvement of soil fertility and soil organic matter content How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use all the crop residue and leaves of trees as cover (mulch). |
|
Considerable reduction of soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Adopt cover crop and rotate with other legumes and minimum tillage system. |
|
Wider spacing between the rows of trees (to 10 m) is best for the agroforestry How can they be sustained / enhanced? Remaining orchards with the original Soviet spacing of 5m between the rows should be thinned. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The irrigation system established during Soviet times required high maintenance inputs due to siltation of the canals. During the period of the civil war systems ceased to function, the canals filled up with sediments and finally overflowed during rain storms causing gully formation | Control of water flow within the orchard using cutoff drains and drainage ditches. |
| Lines of trees which are planted up and down the slope to provide wind. | Compromise in layout design (see description). |
| Orchards managed by state farms are often not well looked after. | Leasing of land and awarding landholder certificates leads to improved orchard management. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.3 Цахимаар олж болох хэвлэлийн холбоос (ж.нь ном, тайлан, видео г.м.)
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Loes Masselink. 2012. Monitoring SLM Practices in Tajikistan. BSc thesis, Land Degradation and Development Group, International Land and Water Management at Wageningen University. The Netherlands.
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/fileadmin/user_upload/documents/Theses/Masselink2012.pdf
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна