Improved grazing land management [Этиоп]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Daniel Danano
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano, Donia Mühlematter
Gitosh masheshal
technologies_1049 - Этиоп
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ИталиТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - Этиоп1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/07/2003
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
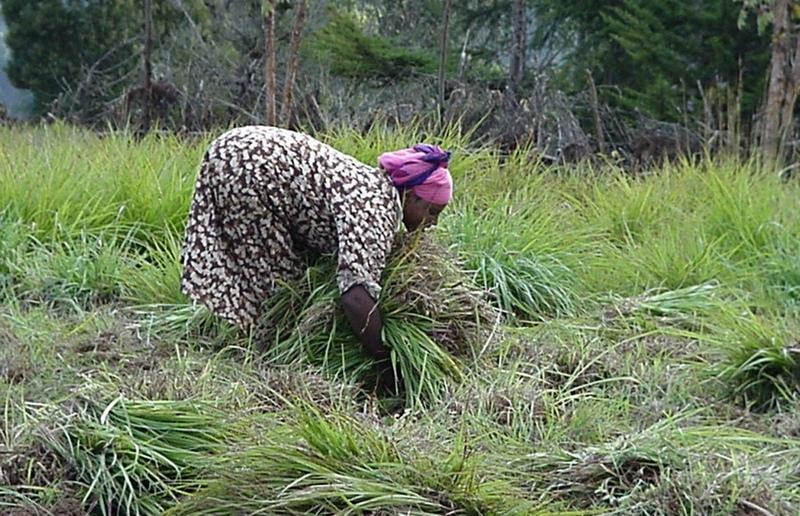
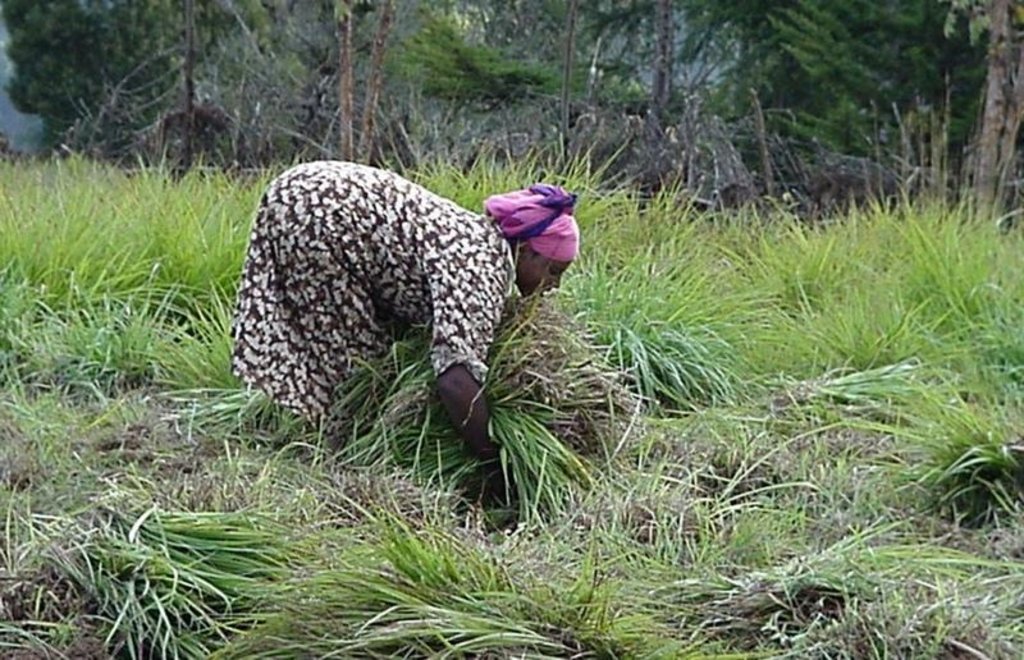
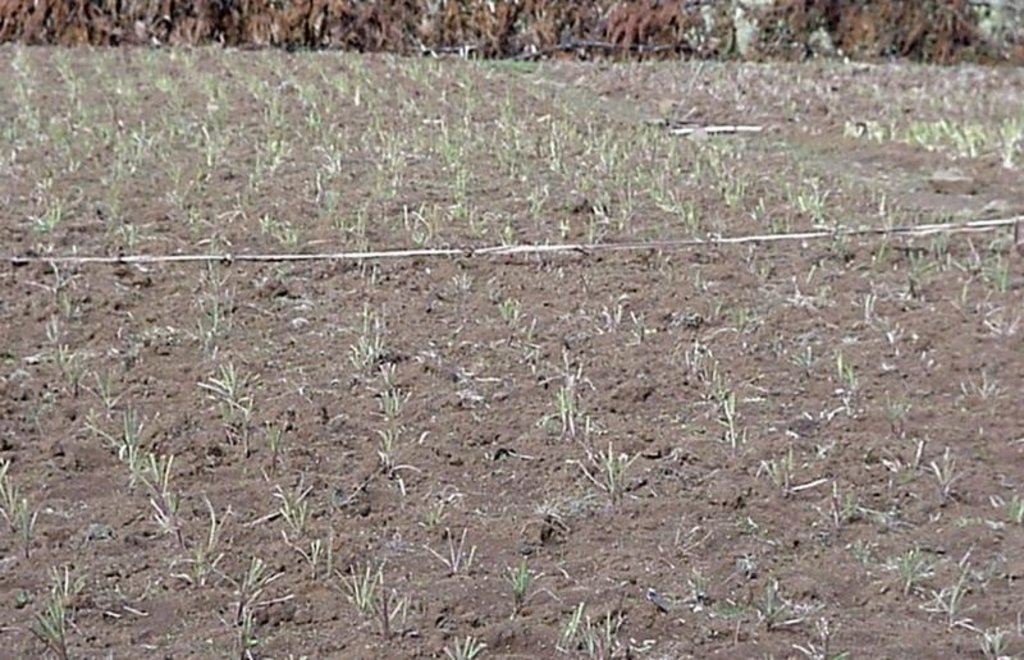
Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands, through planting of improved grass and fodder trees and land subdivision, to improve fodder and consequently livestock production.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
This case study focuses on the highly populated, humid highland regions of Ethiopia that experience serious shortages of pasture. Due to rapid population growth, communal grazing areas are increasingly being converted into cropland. This has led to enormous pressure on the little remaining grazing land, through overstocking of dairy cows and oxen, and thus overgrazing, resulting in considerably decreased productivity.
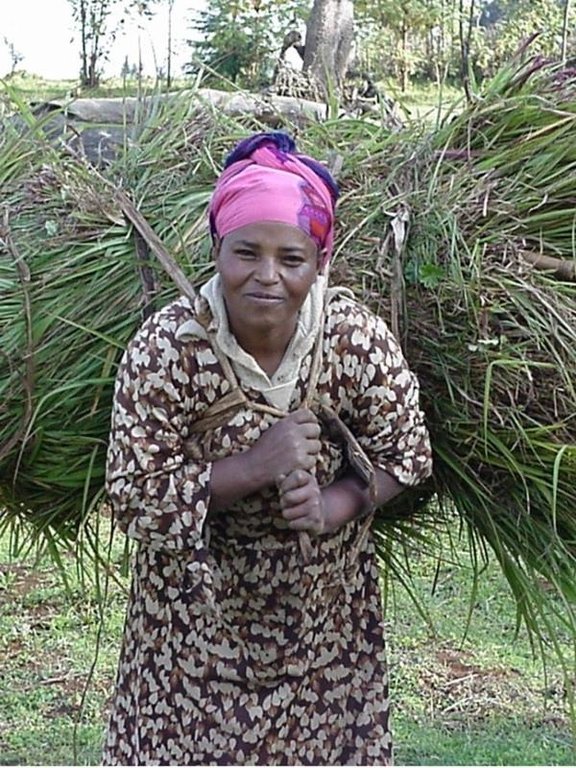
Improved grazing land management is vital to increase food security and alleviate poverty, as well as to bring environmental rewards. To address these problems, the national SWC programme in Ethiopia initiated a grazing land management project over a decade ago. Implementation of the technology includes the initial delineating of the grazing land, and then fencing to exclude open access. This is followed by land preparation, application of compost (and, if necessary, inorganic fertilizers) to improve soil fertility, then planting of improved local and exotic fodder species, including multipurpose shrubs/trees such as Leucaena sp. and Sesbania sp. and the local desho grass (Pennisetum sp.). Desho has a high nutritive value and regular cuts are ensured. It is planted by splits, which have high survival rates and establish better than grasses which are seeded. Other grass seeds, as well as legumes, including alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa) and clovers in some cases, are mixed with fodder tree seeds and then broadcast.
Maintenance activities such as weeding, manuring and replanting ensure proper establishment and persistence. Fodder is cut and carried to stall-fed livestock. Once a year, grass is cut for hay, which is stored to feed animals during the dry season. Experience shows that such grazing land is best managed when individually owned and used. In the study area, the community has distributed small plots (<0.5 ha) of communal grazing land to individual users to develop, manage and use.
The overall purpose of the intervention is to improve the productivity of grazing land and control land degradation through the introduction of productive techniques and improved fodder species, which consequently improve livestock production. Commercialisation of animals and marketing of their products increases the income of farmers. The government provides technical assistance, close follow-up, and some inputs for initial establishment. Land users are trained in compost/ manure application, planting of seeds, splits and seedlings, and general maintenance.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Этиоп
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Chencha
Map
×2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
- Сайжруулсан бэлчээр
Голлох малын төрөл ба бүтээгдэхүүн:
before SWC

Холимог (тариалан/бэлчээр/мод), үүнд. ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Ой-мал аж ахуйн систем
Гол бүтээгдэхүүн/ үйлчилгээ:
After SWC - cut-and-carry (desho gras (Pennisetum sp.)), legumes (alfalfa, lucerne: Medicago sativa), trees (Leucaena sp, Sesbania sp.)
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Population growth has resulted in a substantial reduction in land holdings (<0.5 ha per family) and this in turn has led inevitably to encroachment onto communal grazing lands for cultivation. Livestock numbers on the other hand have remained unchanged, and this has led to overstocking of the few areas left. Livestock production, which accounts for 40% of the average household income, is thus reduced and farmers’ income declines correspondingly.
Хэрэв технологи нэвтрүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан бол технологи нэвтрүүлэхээс өмнө байсан газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг тодорхойлно уу:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: March - September
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Газар нутаг чөлөөлөх (ашиглалтыг зогсоох, нөхөн сэргээх)
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- ургамлын сорт / малын үүлдэр сайжирсан
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Splits of desho grass (Pennisetum pedecillatum) are plantet in lines, using a hand hoe, after good seedbed preparation. Spacing between grass splits is 10 x 10 cm. The white line is a boundary between two households' plots (width of plot: 15-20 m). Trees are planted at rirregular spacing (around 5 m apart), layout is not specified.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of dispersed runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, improvement of soil structure, control of concentrated runoff
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: animal manure, leaf litter, wood ash, soil
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena sp., Sesbania sp.
Grass species: Desho grass (Pennisetumsp.), alfalfa (lucerne: Medicago sativa)
Other type of management: change of intensity level
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delineation of the area to be conserved and establishment of a fence | Ургамлын | before the onset of rain |
| 2. | Subdivision of communal land into individual plots of 0.3–0.5 ha. | Ургамлын | |
| 3. | Planting material preparation in nurseries: grass splits (desho) | Ургамлын | |
| 4. | Good seedbed preparation | Ургамлын | (at the onset of the rains). |
| 5. | Planting of grass splits and tree/shrub species in lines; sowing of grass | Ургамлын | (early in the rainy season). |
| 6. | Weeding. | Ургамлын |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 320.0 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | |
| таримал материал | Grass splits (tillers) | ha | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 55.0 | 55.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1052.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Compost/manure preparation. Material used includes animal manure, | Агрономийн | / initial establishment |
| 2. | Compost application | Агрономийн | / one month after planting, initial establishment |
| 3. | Cut-and-carry, to stall-fed animals, begins when fodder is ready. | Ургамлын | (after 2–3 months growth) /2 -4 times |
| 4. | A final cut for hay is taken early in the dry season when the grass has matured well. | Ургамлын | (end of October) / |
| 5. | Weeding | Ургамлын | /each year. |
| 6. | Compost/manure application, mixed with soil, during seedbed preparation (only where plants have died and need replacement and fertilisation). | Ургамлын | |
| 7. | Enrichment planting and gap filling | Ургамлын | after a year / repeated each year. |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Deadwood for fencing | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 126.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Seedlings are given by the government for initial establishment. For further extension of area and replanting, the
land users set up their own nurseries. After 2-3 years maintenance costs decrease substantially as the grass cover closes up and maintenance activities such as replanting/enrichment planting and compost application are reduced or cease. The local daily wage is about US$ 0.70 a day, but varies depending on the intensity of the work. In this calculation the standard rate has been applied.
Farmers usually cannot afford fertilizers. Milk production compensates for some of the high investment costs (previously, production was low).
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Local term: wett dega
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and foot slopes (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and rolling (ranked 3)
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 2) and low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: source of off-farm income includes petty trade and weaving
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
1-2 ha: Ranked 1
< 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha: Both ranked 2
2-5 ha: Ranked 3
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increase in livestock production
модлогийн бүтээмж
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increase in the availability of livestock products on the market
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Decrease in size of grazing plots due to land fragmentation
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Selling animals and their products
ажлын хэмжээ
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Dependence on incentives
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Initially high. Incentives such as free seeds, seedlings, tools
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Improvement in household diets (milk)
олон нийтийн институц
үндэсний институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increased willingness
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Biodiversity
Soil fertility
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Sediment transport
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 50 households who accepted the technology in the initial phase, did so with incentives. They were provided with planting materials (seeds, seedlings, grass splits) and hand tools.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The rate of spontaneous adoption is very high. At present over 500 households have taken up the technology and the total area covered is about 20 km2.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increased national income due to export of animals and their products. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Availability of fodder (grass, hay, shrubs) in sufficient quantities, and all year round How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increase the area under such development. |
|
Reduction in soil loss and land degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain adequate cover by planting more grass. |
|
Introduction of high yielding species as well as increase in land productivity and livestock production How can they be sustained / enhanced? ntroduce bigger variability of quality species and improve maintenance activities such as weeding and cultivation. |
|
Improved diet: livestock by-products such as milk, butter and cheese are essential food items required by the households How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep on increasing/improving quantity/quality of livestock feed. |
|
Increased income through commercialisation and marketing of animals and their by-products. Meets financial needs for paying taxes, school fees, clothes etc. |
| Rehabilitation of communal grazing lands is both a technical and social challenge. Here is a promising example from Ethiopia that is spreading quickly. The key is subdivision of land into individual plots where cut-and-carry of grass and stall-feeding of livestock is practiced. This is only a possible option, however, where rainfall is favourable. land use rights: individual for cropland, open access (unorganised/communally used) for grazing land, except for the case study area where the rights to rehabilitated grazing land are given to individuals |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| At the initial stage of establishment it is very labour intensive | Use of improved land preparation methods such as oxen ploughing. |
| Substantial cash for inputs, particularly seedlings, is required | Produce seedlings of improved species and making compost in backyards. |
| Needs high fertilizer application | Focus more on organic fertilizers. |
| High pressure on remaining grazing areas | Keep animals in stall (stable) or park, at least part of the day and during the night, and introduce cut-and-carry more widely. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Adane Dinku, Chencha Wereda, Natural Resources Management Annual Report,. 2001 and 2002.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна