Area closure for rehabilitation [Этиоп]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Daniel Danano
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Fabian Ottiger, Donia Mühlematter, Alexandra Gavilano
Meret mekelel
technologies_1048 - Этиоп
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - Этиоп1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
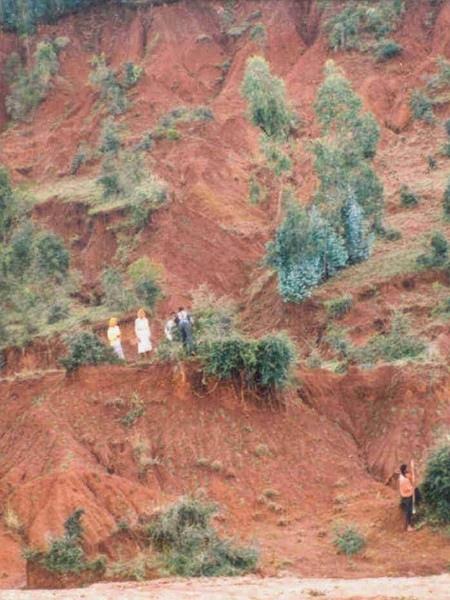
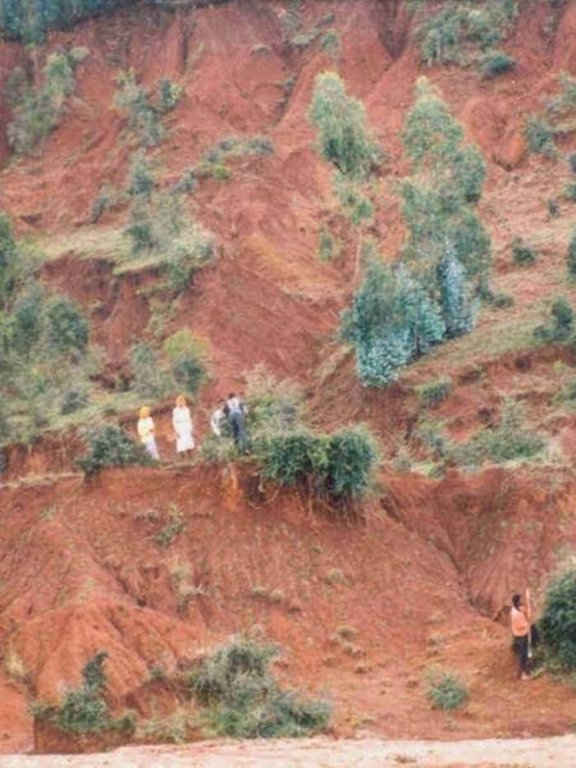
Enclosing and protecting an area of degraded land from human use and animal interference, to permit natural rehabilitation, enhanced by additional vegetative and structural conservation measures.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
Area closure involves the protection and resting of severely degraded land to restore its productive capacity. There are two major types of area enclosures practised in Ethiopia: (1) the most common type involves closing of an area from livestock and people so that natural regeneration of the vegetation can take place; (2) the second option comprises closing off degraded land while simultaneously implementing additional measures such as planting of seedlings, mulching and establishing water harvesting structures to enhance and speed up the regeneration process. The focus of this case study is on this second type.
The selection of measures chosen for rehabilitation depends mainly on the land use type, and to a lesser extent on climate, topography and soil type. Degraded croplands with individual land use rights are normally treated with additional structural measures to retain soil moisture and trap sediment, and with agronomic measures to restore soil fertility. Open access grazing lands are closed for natural regeneration while partly treated with additional measures, and open access woodlands are simply closed. In the case study area 60% of the enclosed area is under treatment with additional conservation measures and 40% is under natural regeneration. First, the area to be closed is demarcated and protected with fencing, usually live fences, and a site guard may be assigned to further ensure protection. Structural measures such as micro-basins, trenches, and bunds that enhance water infiltration and soil moisture may be constructed to increase survival rate of vegetative material planted. Hillside terraces, spaced at a 1 m vertical interval with a width of 1 m are constructed on steep slopes (exceeding 20%). Nitrogen-fixing and multipurpose shrubs/trees (for fodder, fuel) such as Acacia saligna, Sesbania sesban, Leucaena leucocephala as well as local grass species such as napier (Pennisetum purpureum) and rhodes (Chloris gayana) are planted as additional measures for conservation.
The maintenance of area enclosures involves activities such as replanting, maintaining of fences, pruning of trees and weeding. After one year, cut-and-carry of grass for stall-feeding can be partly practiced - which is of economic benefit to the farmers. Rehabilitation normally takes about 7-10 years depending on the level of degradation and intensity of management. Land use is limited to selective cutting of trees, collection of dead wood and cut-and-carry of grass for livestock fodder. On individually owned enclosures land users start cutting trees after three years (for eucalyptus) and after 7–8 years (for other trees), while on communal land farmers are allowed to collect dead wood after 3-–4 years, and the community decides about the use of trees.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Этиоп
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Alaba, South Ethiopia
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Bilate River Catchment (Rift Valley)
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
Map
×2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Сильво-пасторализм

Тариалангийн газар
- Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан
- Мод, бут тариалах
- napier (Pennisetum purpureum), rhodes (Chloris gayana)
- Acacia saligna, Sesbania sesban, Leucaena leucocephala, Eucalyptus, Grevillea robusta
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Sep

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн бэлчээр / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Over 30% of the land in the study area is degraded, resulting in low crop yields and poor livestock production. Severe water erosion is the main cause of land degradation on all slopes, followed by fertility depletion due to intensive cultivation practices and overgrazing. Serious gully formation and a high sediment load in the Bilate River threaten Lake Abaya. Communal grazing lands, woodlands with open access, and cultivated lands on steep slopes without conservation measures are particularly affected. By tradition, land users in rural Ethiopia can own as many livestock as they wish, which encourages overstocking.
Ranching: (before SWC)
Other grazingland: mixed silvo-pastoral (after SWC): cut-and-carry, trees
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- газар нутаг чөлөөлөх (ашиглалтыг зогсоох, нөхөн сэргээх)
- Налуугийн хөндөлн огтлолын дагуух арга хэмжээ
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

Хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим болон органик агууламж буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
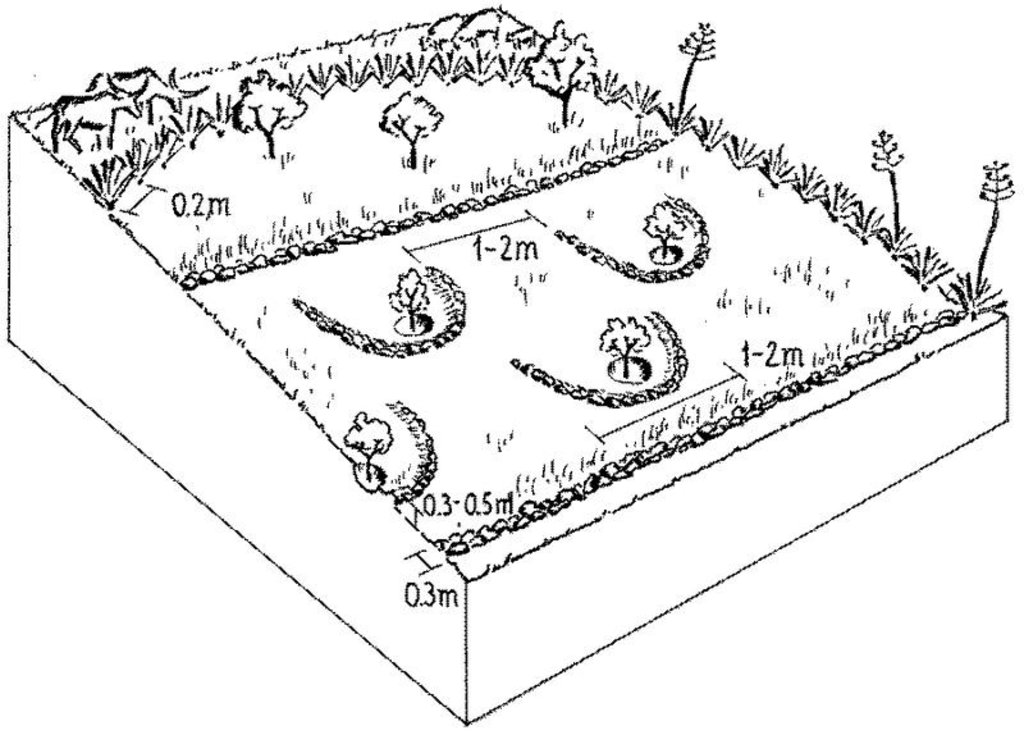
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
Rehabilitation of degraded land based on enclosure with live fence. Natural regeneration of vegetative cover is supported by water harvesting structures and planting of nitrogen-fixing/multipurpose shrubs and trees as well as local grass species. On steeper slopes hillside terraces may be established.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, control of dispersed runoff, control of concentrated runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, less sediment deportation
Mulching
Material/ species: tree leaves/grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: oversowing grasses
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Acacia saligna, Sesbania sesban, Leucaena leucocephala, Eucalyptus spp., Grevillea robusta
Grass species: nepier (Pennisetum purpureum), rhodes (Chloris gayana)
Structural measure: micro-basins (opt.)
Structural measure: terraces (opt.)
Structural measure: bunds (opt.)
Other type of management: land use change, enclosure,, cut-and-carry
Зохиогч:
Mats Gurtner
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of trees (Eucalyptus spp., Grevillea robusta) as well as | (early rainy season). |
| 2. | Oversowing/interplanting with local grass species: napier grass | (early rainy season). |
| 3. | Marking the boundary and establishment of live fences: digging pits | early rainy season (before June). |
| 4. | Construction of structural measures such as micro- basins, trenches, bunds or hillside terraces. | before rains |
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 175.0 | 175.0 | 50.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | |
| Таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Stone | ha | 1.0 | |||
| Барилгын материал | Wood | ha | 1.0 | |||
| Бусад | site guard (kg grain/ha/year) | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 391.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 391.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mulching with tree leaves/grass around newly planted trees, before | before rains / initial establishment |
| 2. | Replanting/gapping up live fence and trees during rains in the early | during rains / |
| 3. | Harvesting grass | during rainy season. / |
| 4. | Pruning of trees | in the dry season. / |
| 5. | Weeding | after rains. / |
| 6. | Repairing breaks in structures | before rains./ |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | |
| Бусад | site guard (kg grain/ha/year) | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 91.0 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 91.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Labour for establishment activities: 250 person days per ha for structural measures and planting of trees, plus guarding. Labour for maintenance: 50 person days for replanting/weeding. A common daily wage is US$ 0.70 (= 6 Ethiopian Birr), however in this case the site guards were given 3 kg of grains per ha per year. They can control over 200 ha.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
751-1,000 mm (ranked 1)
1,001-1,500 mm (ranked 2)
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Гадаргын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Altitudinal zone: Also 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l. (ranked 2) and 2001-2500 m a.s.l. (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and moderate (ranked 3)
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Сийрэг/хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Low
Topsoil organic matter: Also medium and high (both ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Very high
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: from petty trade, weaving, etc
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- Хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
(cut-and-carry of grass)
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
(cut-and-carry of grass)
модлогийн бүтээмж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduction of grazing area leads to high pressure on remaining grazing areas
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н хөрөнгө оруулалтын зардал
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
(selling grass/wood)
хөдөлмөр хүчний хэмжээ
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Unequal share of benefits, some illegal cutting of vegetation is involved
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
илүүдэл ус урсгах
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
>50%
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
>80%
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
initially 50% reduction, after 2–3 years
Бусад экологийн үр нөлөө
Soil fertility
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
increased organic matter, nitrogen fixing shrubs
Biodiversity
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
recovering disappearing local species
competition between (grass)species
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
competition between naturally regenerating and oversown (grass)species
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсгал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Also groundwater recharge
Доод урсгалын үер
урсацын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдана
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less sediment transported
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Технологийг өөрийн талбайд нэвтрүүлсэн бусад иргэдээс хэд нь үүнийг өөрийн хүчээр, өөрөөр хэлбэл ямар нэг материал, техникийн дэмжлэг, төлбөр авалгүй хийсэн бэ?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
300 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Adoption rate has considerably increased owing to improved ownership feeling and immense benefits obtained through the practice. However, if labour-intensive structural measures are required people rely on food-for-work incentives.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Reduction of on-site and off-site land degradation, reclamation of degraded non-productive land (regenerating fertility) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Strengthen maintenance and protection to increase biomass production of enclosure. |
|
Fodder shortage is reduced through cut-and-carry of grass in enclosures (after 1 year) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Introduce more productive and nutritious grass/legume species. |
|
Collection of dead wood from enclosures (after 3–4 years) mitigates fuelwood shortage How can they be sustained / enhanced? Introduce alternative fast growing multi-purpose tree species such as Grevillea robusta (fodder for smallstock in very dry periods). |
|
Cutting wood for construction of houses and wooden farm implements (after 7–8 years) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue planting of multipurpose trees. |
|
Increased honey production through increased bee activity in enclosures Emerge of springs, which have disappeared due to deforestation/land degradation Income generation: farmers sell grass/wood collected from area enclosures; they make profit despite seven years enclosure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve beehives, ‘bee feed’ (bee-friendly plants), and access to market. Maintain proper ground cover to improve infiltration and percolation of rainwater. Better management of planted grass, making of hay, improve market systems. |
|
Emergence of springs, which have disappeared due to deforestation/land degradation -> Maintain proper ground cover to improve infiltration and percolation of rainwater. - Income generation: farmers sell grass/wood collected from area enclosures; they make profit despite seven years enclosure -> Better management of planted grass, making of hay, improve market systems. Editors’ comments: Protecting degraded land against grazing is a common practice worldwide. In Ethiopia it is the second most important SWC practice after structural conservation measures. About 1.2 million hectares of degraded lands have been closed for rehabilitation in Ethiopia during the past three decades. As this case study shows, results are encouraging both in terms of effective protection and enhanced production. Land use rights: open access on woodlands and grazing lands (communal land use rights), individual on cropland |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| On highly eroded areas and in areas with low rainfall the survival rate of trees and shrubs is low and as a result the benefits only come after a very long period. This situation becomes unacceptable to the land users |
Select suitable local and exotic multipurpose tree/shrub species adapted to the local conditions (Acacia spp., Eucalyptus spp., Grevillea robusta etc). Construct water-harvesting structures (trenches, micro-basins). Raise awareness among land users through meetings and training. |
| Investment costs are rather high for land users | Credits, loans, cooperatives. |
| Inequitable share of benefits | Awareness should be increased through enhancing the LLPP approach. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Chadokar PA: Multipurpose Plant Species for Soil and Water Conservation. Assistance to Soil and Water ConservationProgramme. ETH/81/003. 1985.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Betru Nedassa: Biological Soil Conservation Measures. Land Rehabilitation and Reforestation Project. Project 2488MOA/WFP. 1995.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна