Silvo-pastoralism: Orchard with integrated grazing and fodder production [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Malgorzata Conder
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1554 - Тажикистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Киргизстан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Increased productivity of the land by planting fruit trees and conserving the land by restricting the access of livestock resulting in improved runoff retention
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
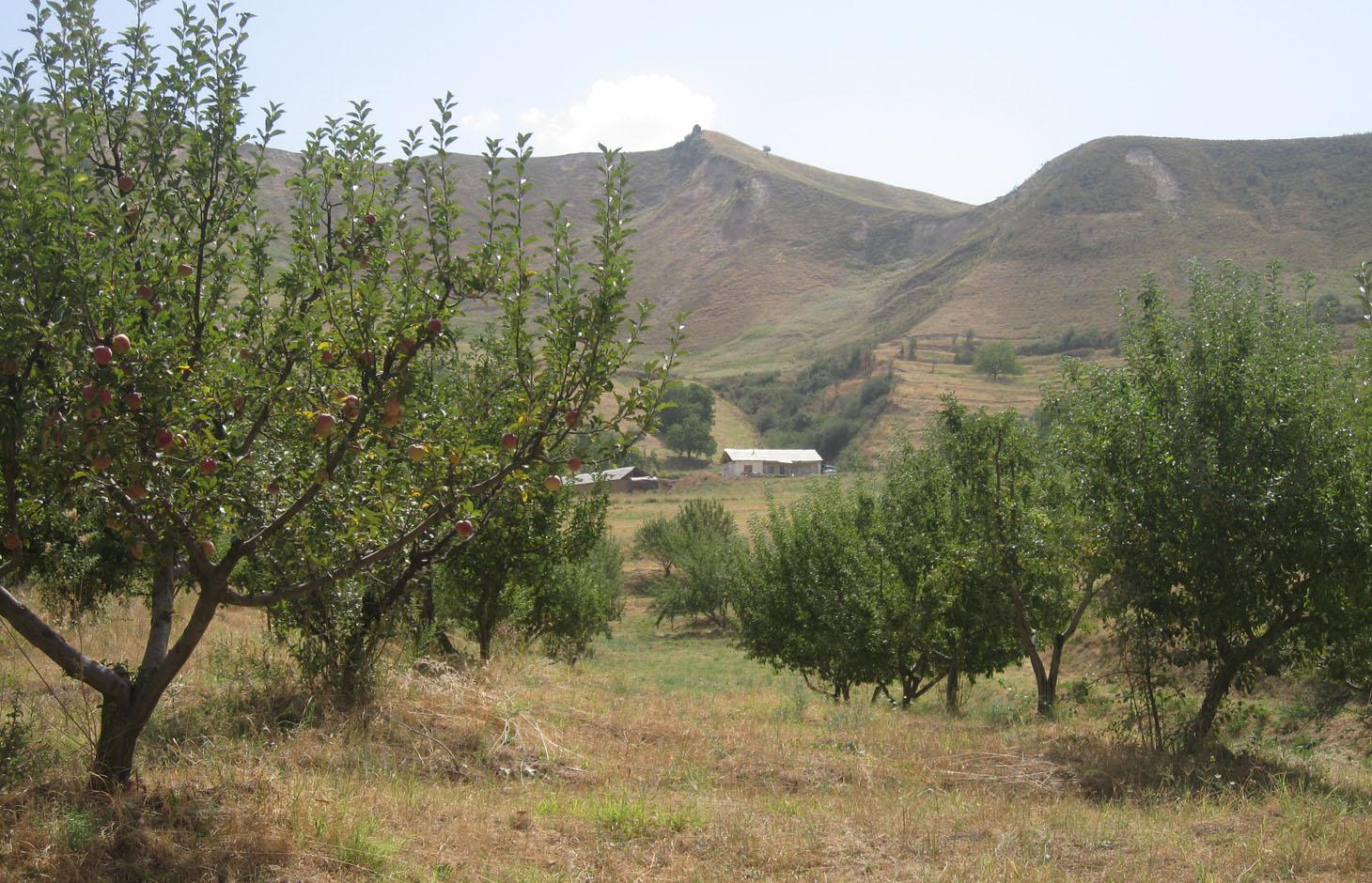
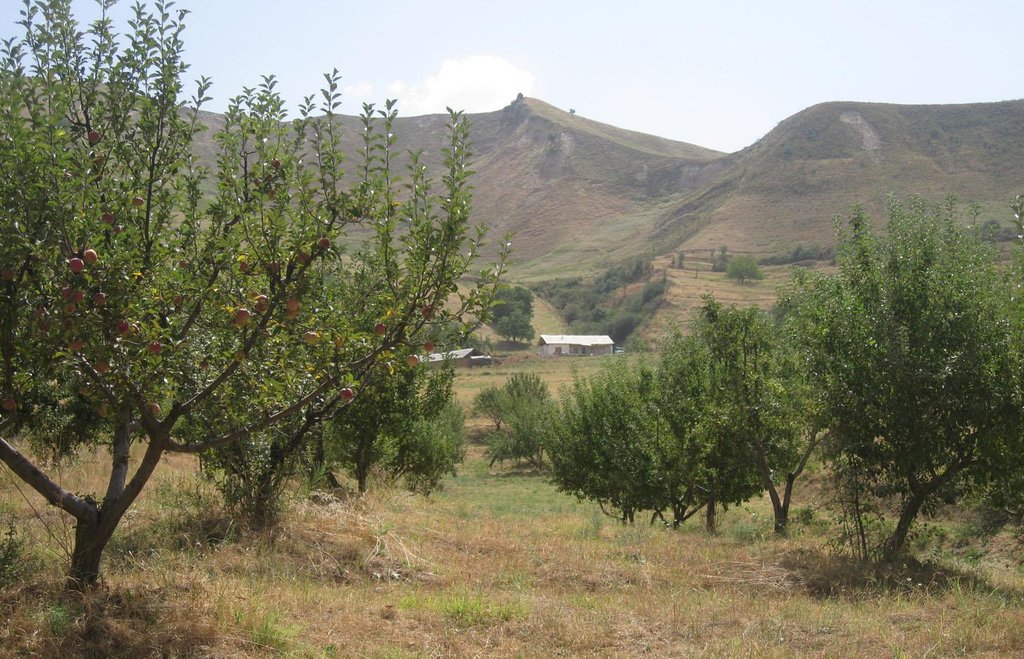
In Soviet times, this area of totally 40 ha comprised terraces and walnut trees in the steep foothills and pastures in the lower and flatter part. After the collapse of the Soviet Era, many similar areas got degraded due to uncontrolled grazing and overuse of natural resources. The area described in this documentation, in contrast, was taken over by a family in 1991. Within the whole area of 40 ha, roads were built to improve the access and 6000 trees were planted, whereof 1200 fruit trees were planted on the pasture, conversing it into an orchard.
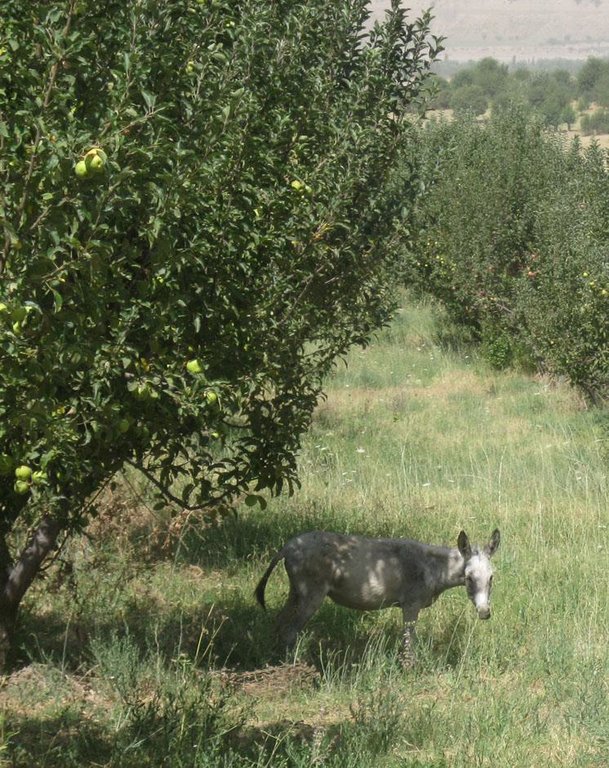
At present, the 6 ha of orchard are mainly consisting of three types of apple (white, golden and red), some pear and cherry trees. Several trees must have dried out or have been cut, as the farmer counts currently around 1000 fruit trees. The whole orchard is combined with pasture land. The farmer let his livestock graze in the orchard, and cuts the remaining grass in autumn, if there is still left.
The integrated orchard with pastureland and fodder production is partially fenced to hinder livestock entering his property. Furthermore, the orchard is within the range of vision which allows the farmer`s family to guard it.
The farmer who is managing the orchard today obtained the property of his father in order to continue the family project by his own initiative. By farming he ensures the livelihood of his family. Hence, he felt responsible to progress and improve the quality of life of his own family. The main reason for establishing the orchard within the grassland and to install fences, was to increase productivity of the land, bringin along beneficial effects on soil quality. According to his land users certificate, the main purpose of this land is to provide the local market with food products.
After planting, some of the seedlings were stolen or eaten by livestock from neighbouring farms. Initial labour input in the newly established orchard consisted of getting and planting the seedlings and applying pesticides. The trees are being maintained by pruning. Soil is loosened and drainage provided to increase water infiltration and to protect the trees additionally from parasites. The pasture is grazed by the livestock of the farmer. As the family only has a small number of livestock, grass is cut afterwards and used as fodder. Half of the fodder harvest belongs to the hired worker, the other half belongs to the farmer. The other tasks are executed by the farmer and his family.
The climate is semi-arid with precipitation (800mm totally) mainly during winter and spring time. Altitude is around 1380 m asl. The plot is located at the foothill, with the wider riverbed and fan downstream and overgrazed hills upstream. Bordering with the property from above, a steep slope with a dense vegetation of grafted fruit trees and walnut trees stabilizes the soil.The farmer is living with the family on the property, near the village of Momandion. In the past many livestock from nearby entered the property and grazed there. Through better control and fences less livestock is entering. The property is located directly on the road to Muminabad, the center of the District with a market- 2 km away.Considering the establishment costs of the orchard, the farmer is a fairly whealthy man, nevertheless he had to rely on his family and friends in terms of the working input.The establishment phase was a time and money consuming
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Muminabad
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- < 0.1 км2 (10 га)
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.06 km2.
Orchard is within the farmer's land property of totally 40 ha
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
22 years ago
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Мод, бут тариалах - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- жимс (алим, лийр г.м.)
- том үрт жимс (тоор, интоор, чавга г.м.)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Тайлбар:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): No major problems because of the early implementation of the technology which prevented the area of being (over)grazed without control
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The farmer is afraid of a possible landslide on his property. Another issue is the lack of a continuous fence, because still some unwanted livestock is able to enter the orchard. He installed a water point next to his house recently.
Other grazingland: agropastoralism: first grazing and if grass is left, then cut
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Тайлбар:
Grazing land: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (uncontrolled)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (increased livestock), governance / institutional (no or undeveloped pasture management after Soviet collapse)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
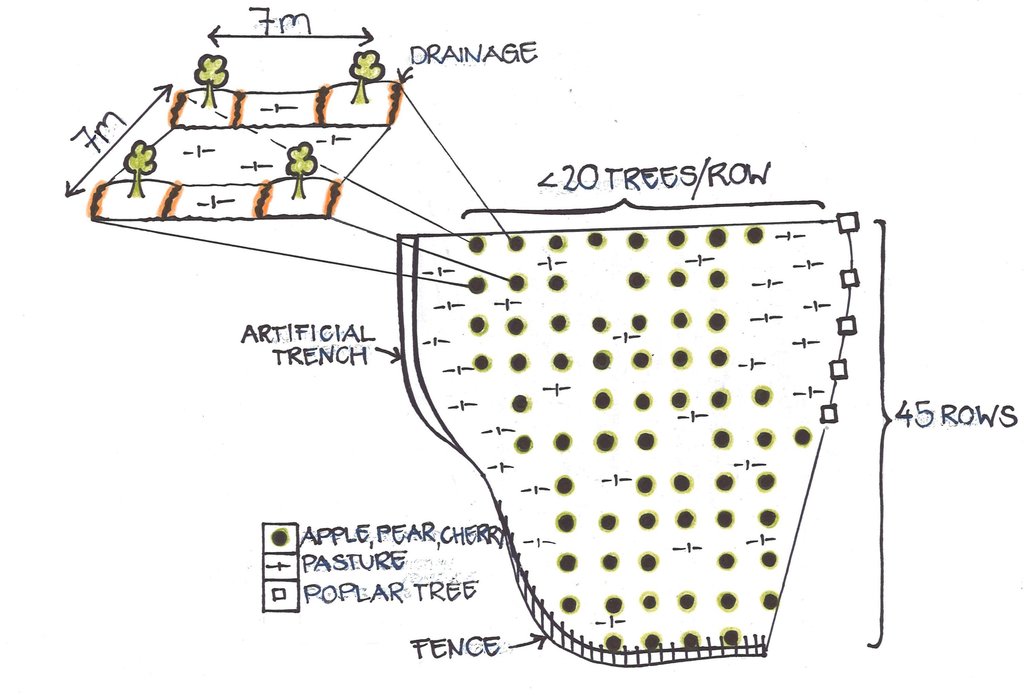
The orchard is situated within the farmers' property which is almost completely fenced by an artificial trench, thornbush fences, poplar trees and a natural steep slope. The orchard is 6 ha in size and consists of around 45 rows, with some 20 trees per row on average. In some places trees are missing due to drying out or cutting. Currently approximately 1000 fruit trees are growing. In between the tree rows and at the borders of the orchard, grass is growing and grazed by animals, and if not entirely grazed cut for haymaking in autumn.
The fruit trees grow at a distance of 7 meters. Around the trees the soil is loosened and a tiny trench is dug, the latter serving as a rainwater drainage.
Location: Momandion. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Date: 14.09.2012
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Good knowledge for planting required, knowledge about maintenance activities is probably more widespread amongst farmers, idea of fencing is lacking)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Aligned: -contour
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 7
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, pear, cherry
Change of land use type: change of pasture land into an orchard with integrated pasture land and fodder production (Silvopastoralism)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Fencing hence more extensive and controlled grazing
Зохиогч:
Conder Malgorzata
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Somoni
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
4.83
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
12.40
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying and transport of fruit seedlings (totally 6000 seedling, whereof 1200 seedlings on for the orchard of 6 ha) | once |
| 2. | Planting fruit tree seedlings (totally 6000 seedlings, whereof 1200 seedlings for the orchard), cost according to planted trees (3 TJS per tree) | once |
| 3. | Partial fencing (of around 200m) along the property, 10.5 days, 3-4 persons | 1991 |
| 4. | Building roads for access to the house | 1991 |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 194.9 | 194.9 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 207.0 | 207.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | fence | ha | 1.0 | 124.2 | 124.2 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 526.8 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 109.07 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning of 400 trees, ca. 40 days, 1 person, 3 TJS per tree (all trees pruned every 3 years) | spring/ once a year |
| 2. | Soil loosening around 1000 fruit trees, ca. 25 days (5 h/day), 1 person | spring/ once a year |
| 3. | Pesticides spraying once (should be done 2-3 times), 4 days (ca.5 h/d), 1 person | End of May/ once a year |
| 4. | After several years: Harvesting fruits (mainly apples) | September/every year |
| 5. | Cutting grass, by 10 people, one month, hours per day unknown. Half of straw harvest for owner, other half for the mowers as salary (4-5 Somoni/bundle). Total salary: 1000 bandles | End of summer |
| 6. | Guarding the orchard | all the time |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 383.3 | 383.3 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | pesticides | ha | 1.0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 391.1 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 80.97 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The structural fencing is adapted from T_TAJ047. Working hours are approximate as the work was done a long time ago, with the help of many relatives with different work times. No overview over the exact work and cost input exists, tools were mainly borrowed, prices unknown. Road building done in the past was not included, because current costs were difficult to estimate. Work as guardening is not monetarised. Apple harvesting as recurrent activity (vegetative measure) is derived from T_TAJ013. In the cost summary, the fencing was calculated proportionally to one ha.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Apart from the orchard, the whole property was rebuilt with roads, fences and tree planting which caused high initial costs during the establishment phase.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200m asl, weather station Muminabad)
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
As the area of the orchard with pasture is fenced it is not an communal pasture anymore as it was before
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
From pruning
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хэрэгцээ
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Products for market leading to higher income, sharing of some knowledge about management of private land enhances dissemination and exchange of information/knowledge.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
хөрс нягтрах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
түймрийн эрсдэл
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | муу |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | сайн |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
Family project to improve the quality of life of the family. Costs were high at the beginning with little outcomes, now there is less labour required and the outcome is high.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Even though they neighbours see the whealty orchard, the farmer din not see any other farmers adapting this Technology. Reasons are unknwon.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Giving good yield and "cash crop" hence having success in the project of the family |
| Better quality of fodder and less damages due to intrusive livestock |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Thanks to the establishment time, right after the collapse of the Soviet Union, when land was generally well conserved, the technology worked as a preventive measure. |
| Silvopastoralism not only raises productivity of the same plot as an orchard and pasture is combined, but also enables mutual benefits (p.e.rooting system raises soil moisture, which is again improving vegetation cover). |
| The technology might work as exemplary model for other farmers |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| There is always work to do, without input no (good) output. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| For the farmer, the economic benefit is more important than the ecologic benefit. Especially, there is missing sensibility of the farmer concerning the application of pesticides (quantity, type). | A workshop which provides guidelines on optimal use of pesticides (type and quantities of pesticides, timing and frequency of application etc.) |
| The establishment of orchards is more efficient on big plots of land, which often prevents poor farmers with small plots from establishing orchards. | Creating incentives to change land use, by combining plots from different land owners, which will allow to share costs for establishment and maintenance. Yields should be clearly attributed to the individual farmers. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
19/07/2012
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна