Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Supplemental Irrigation Purpose in Dry Season [Непал ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Kabita Nhemhafuki
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Isabelle Providoli
Mato, Baluwa ra Cement bata Nirmit Sinchai Pokhari - Nepali
technologies_5684 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Shah Ram Deo
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED)
Непал
Газар ашиглагч :
Gautam Laxmi
Непал
Газар ашиглагч :
K.C Prashuram
Непал
Газар ашиглагч :
Neupane Kumar
Непал
Газар ашиглагч :
Adhikari Apsara
Непал
Газар ашиглагч :
Shrestha Jay Ram
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Resilient Mountain Solutions Initiative, ICIMOD (RMS initiative)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
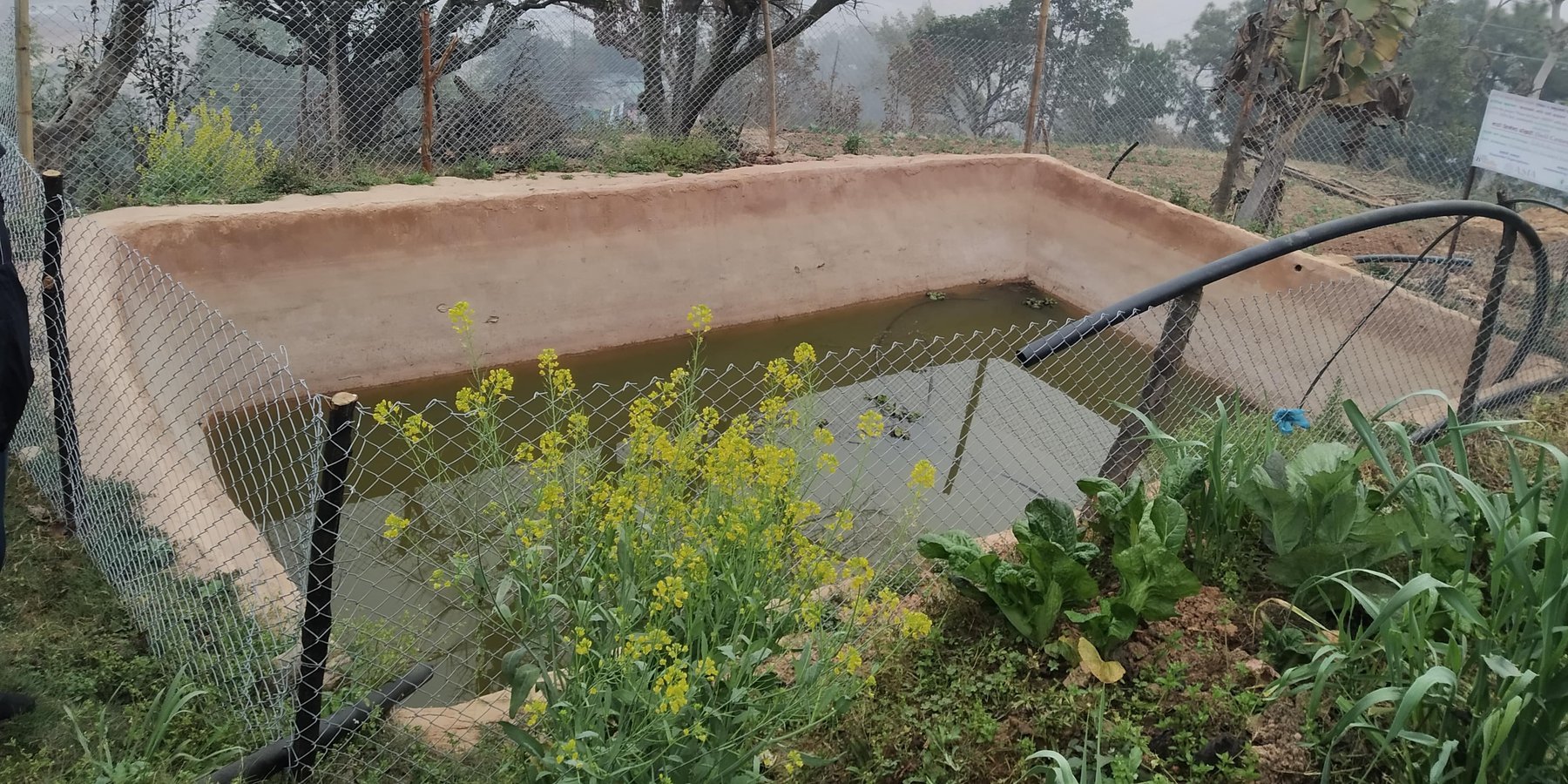
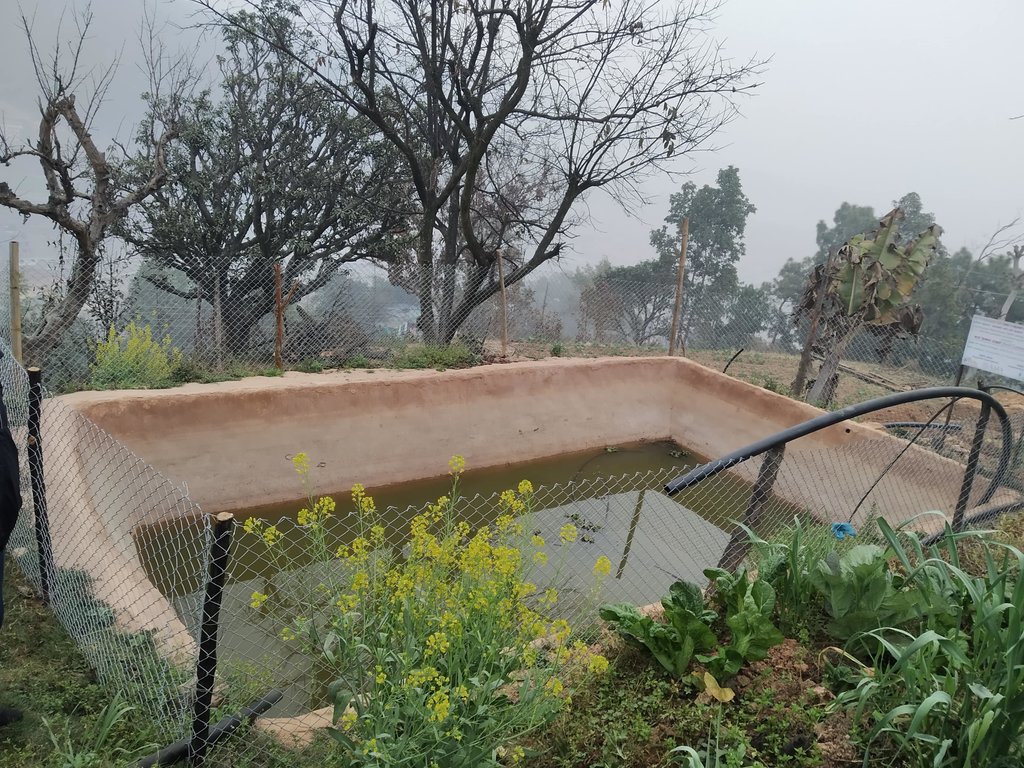
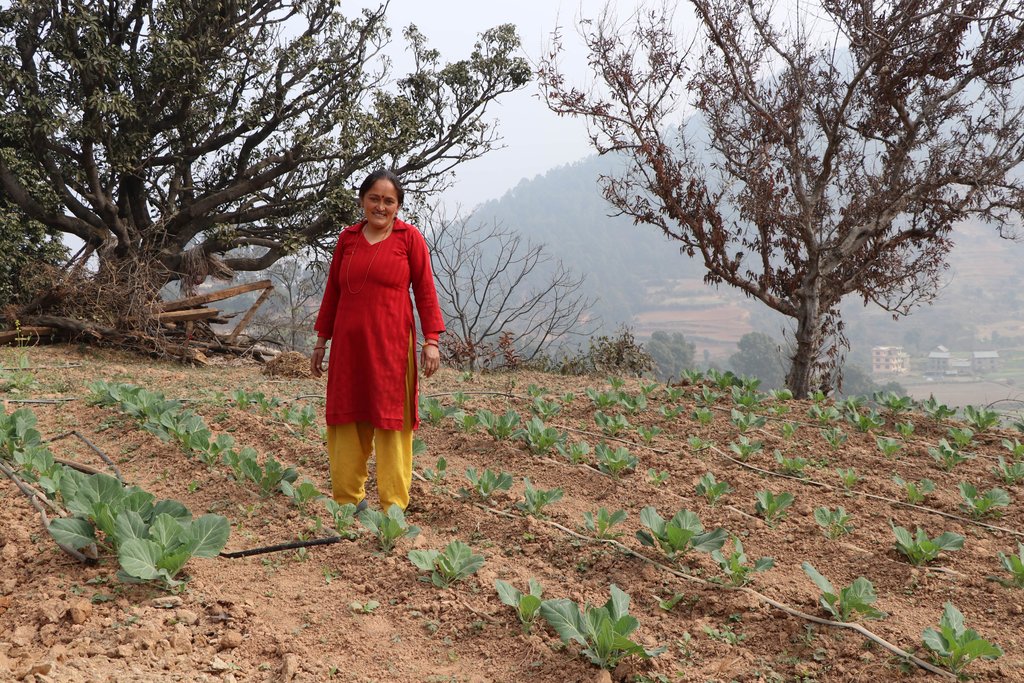
A soil cement water collection pond to store rainwater, runoff and household kitchen waste water free from soap and detergent for supplemental irrigation purpose during dry seasons.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
In Nepal's mid-hills mountain farmers face problems during dry seasons to irrigate their fields, as they entirely depend on rain- water. Soil cement water collection pond are ideal to tackle this challenge, as they can capture excess rainfall during monsoon, which is later available during prolonged seasonal water shortage.
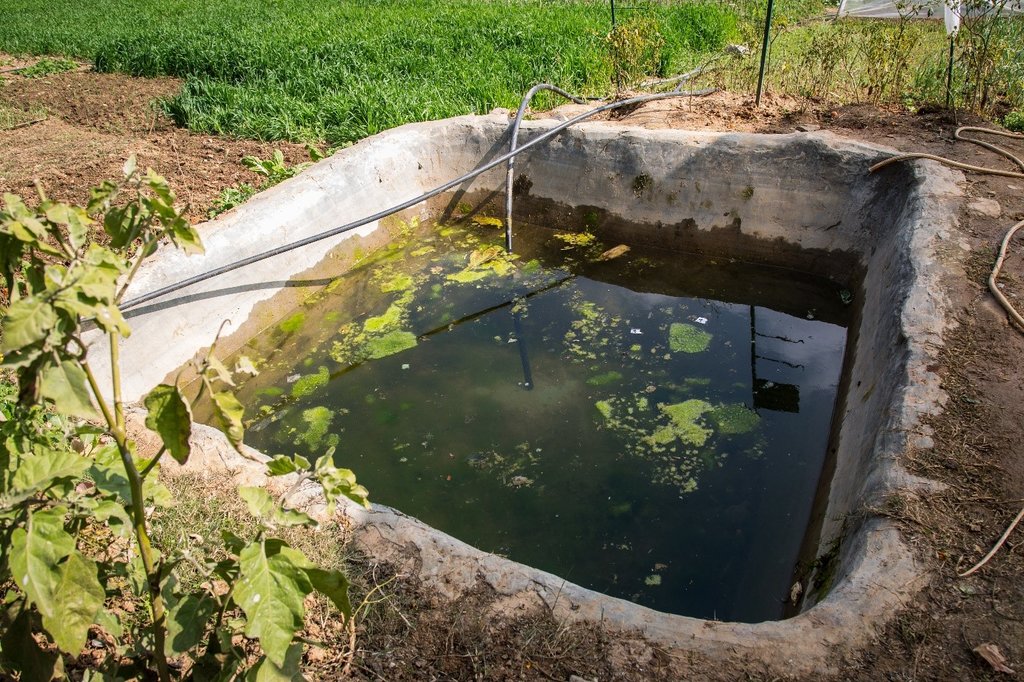
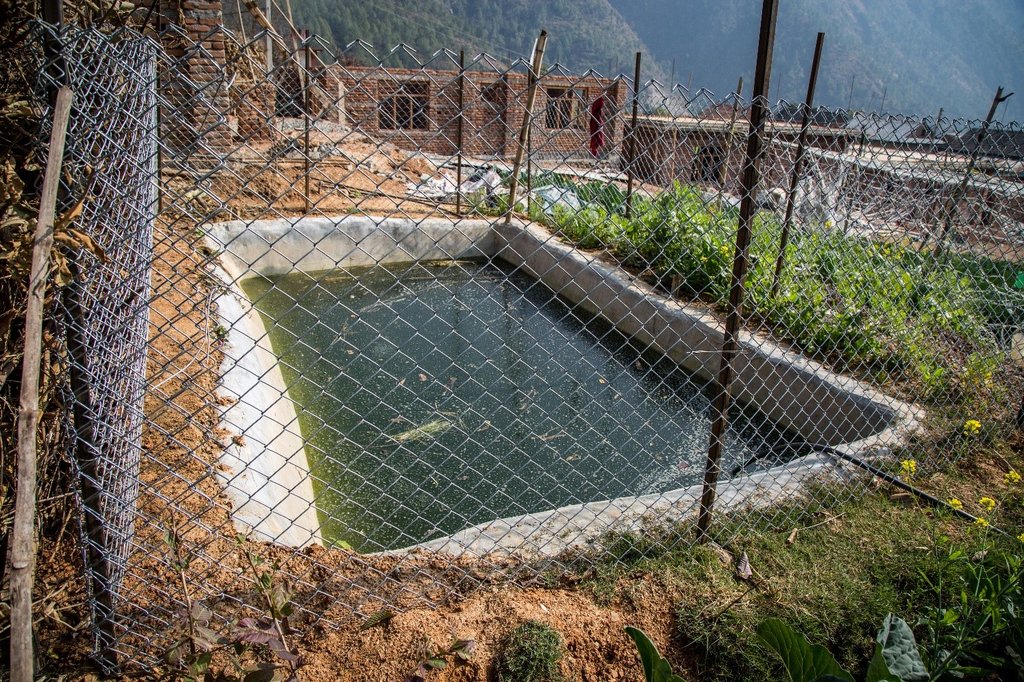
The Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project of ICIMOD together with its local partner, CEAPRED tested and demonstrated soil cement ponds with a capacity of 24000 liters. The conservation ponds were used for irrigating high value off-season horticultural crops (vegetables, fruit, and spices). These crops were irrigated with drip irrigation and micro sprinklers. The ponds were fed from rainwater, upland springs and taps, and household wastewater from kitchen free from soap and detergent. They were established during the dry season during 3 months. They were prepared by selecting a suitable site with a sufficient catchment; mapping out the area and depth of the pond; digging out the soil; removing protruding stones and roots; and compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond. Then gravel and pebbles were used for the base and the floor and side walls were leveled off. Initial mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1) was applied to roughly plaster all the side walls and gravel was mixed in the mixture while plastering the floor. The following day, the roughly plastered pond was watered and was covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This was continued for 3-4 days. Then again a second mixture of soil, sand and cement (2:2:1) was applied to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. The pond was watered for the next 3-4 days and was covered with wet jute sacks. Around 4-5 days after the second plaster, the pond was filled with water. For safety, pond was enclosed with a gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using any locally available material). The total establishment cost for a soil cement pond with 24000 liters capacity was USD 311.
The main maintenance activity was to maintain the gabion wire/bamboo fence to prevent livestock and people from entering the pond, and to remove the sediment that accumulates in the pond. The sediment has to be removed once a year carefully by hand and if cracks occur, it should be sealed with a mixture of soil, sand and cement (3:3:1). The total annual maintenance cost for 24000 liters soil cement tank was USD 68.
This technology has somehow helped small-land holding farmers to irrigate their rain-fed land during dry months which has increased the crop production and their income as well.
Land user's particularly liked that their production increased and that they were able to grow up to three crops per year. Trough this the farmers were able to diversify their crops, and they were less vulnerable to the dry season. In addition, soil cement water ponds are more efficient than plastic-lined conservation ponds which are easily damaged by rats. Although cost effective, the fixed price for this technology is quite high, particularly for smallholder farmers. To lessen this financial burden, local governments can provide subsidies to women and marginalized groups interested in this technology. Self-help groups with a revolving grants system would help expand the use of these ponds and ensure sustained use across Nepal.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
Гэрэл зурагтай холбоотой ерөнхий тэмдэглэл:
Size of soil cement pond depends upon the area of land to be irrigated.
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Непал
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Province no: 3
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk District, Nepal
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай байнгын хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
ICIMOD demonstrated this technology through the program of Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) with the help of its implementing local partner, The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) in its pilot project sites in Kavrepalanchok district.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- Improve water availability during dry seasons
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- үр тариа - цагаан будаа (өндөр газрын)
- буурцагт ургамал - шош
- үндсэрхэг/булцуут таримал - төмс
- үрт ургамал - гүнжид, намуу, гич бусад
- хүнсний ногоо - навсит ургамал (салат, байцаа, бууцай, бусад)
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 3
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар таримлыг сөөлжлөн тариалдаг вэ?
Tomato and raddish
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 хариулт руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Ус хураах
- Усжуулалтын менежмент (усан хангамж, ус зайлуулалт зэрэг.)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S4: Шаталсан шуудуу, нүх, хэвгий
- S7: Ус хуримтлуулах, усаар хангах, усалгааны төхөөрөмж
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
- Hs: Гадаргын усны хэмжээ багасах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
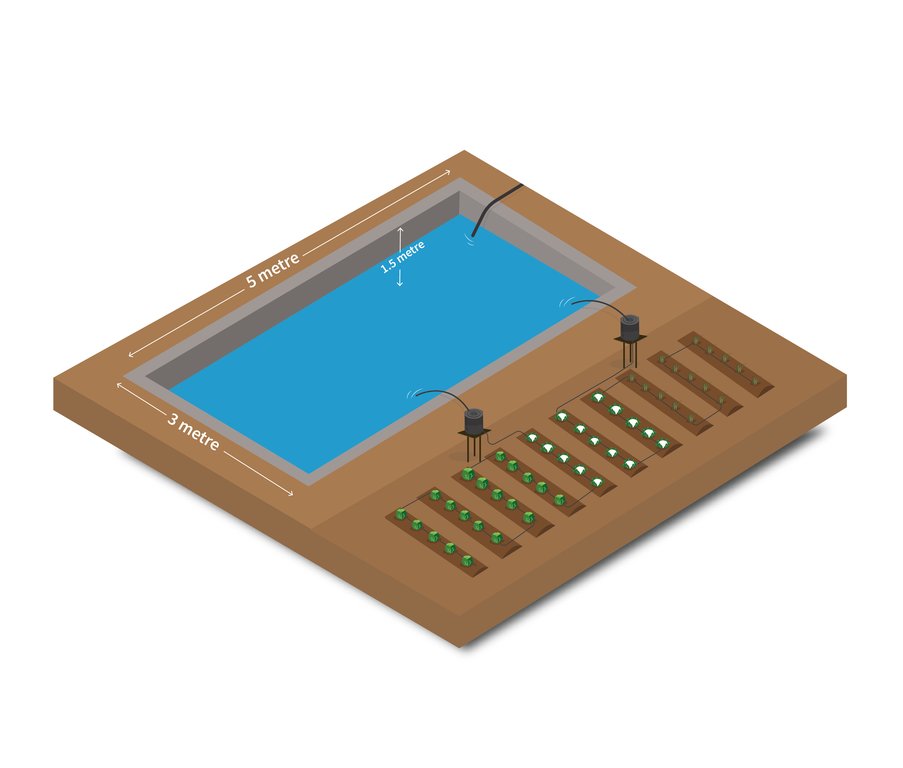
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
Soil Cement Water Collection Pond for Irrigation Purpose in Dry Seasons
Location: Charange fedi, 03, Namobuddha Municipality, Kavrepalanchowk
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5
Capacity of the tank= 24000 litres.
Construction material (earth): Clay
Construction material (other): Cement, sand and water-proofing liquid
Зохиогч:
Kabita Nhemhafuki, Ram Dev Shah
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/12/2020
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Хэмжээ ба нэгж талбайг тодорхойл:
0.0024 ha
Хэрэв өөрийн уламлалт талбай хэмжээг ашиглаж байгаа бол нэг гектарт шилжүүлэх коэффициент (жишээ нь 1 га = 2.47 акр): 1 га =:
1 ha = 10000 square metres
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
5.68
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a preferably stable ground with a sufficient catchment area | dry months |
| 2. | Measure the area to be irrigated and estimate the size of the pond | dry months |
| 3. | Measure and mark out the pond | 1st day |
| 4. | Dig out the soil to the pre-determined depth and remove protruding stones and roots | 1st day |
| 5. | Compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond | 2nd day |
| 6. | Apply initial mixture of soil, sand, cement (3:3:1) to roughly plaster all the the side walls and mix gravel in the mixture while plastering the floor. | 2nd day |
| 7. | The following day, the roughly plastered pond should be watered and covered with wet jute sack to keep it moist. This should be continued for 3-4 days. | 3rd day |
| 8. | Apply a second mixture of soil, sand, and cement (2:2:1) to smoothly plaster the floor and side walls. | 5th day |
| 9. | Water the pond for the next 3-4 days and cover with wet jute sack. | 8th day |
| 10. | Around 4-5 days of second plaster, fill the pond with water. | 13th day |
| 11. | For safety, the pond can be enclosed with gabion wire/ bamboo fence (or using other locally available materials) | 14th day |
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Dig out pond | persons/unit | 7.0 | 5.68 | 39.76 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Stone soiling | persons/unit | 1.0 | 8.74 | 8.74 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Cementing | persons/unit | 10.0 | 8.74 | 87.4 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Wiring | persons/unit | 2.0 | 8.74 | 17.48 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Spade | piece | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Measuring tape | piece | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | piece | 3.0 | 7.0 | 21.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Hammer | piece | 3.0 | 4.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Cement mixing iron pan | piece | 2.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Trowel | piece | 3.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Sand | bags | 24.0 | 0.87 | 20.88 | |
| Барилгын материал | Cement | bags | 6.0 | 7.43 | 44.58 | |
| Барилгын материал | Water proofing liquid | bottle | 1.0 | 2.62 | 2.62 | |
| Барилгын материал | Gabion wire sheets | sq.ft | 120.0 | 0.31 | 37.2 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 311.66 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 311.66 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагчаас нийт өртөгийн 100%хүрэхгүй зардал гарсан бол хэн үлдсэн хөрөнгө оруулалтыг хийснийг тодорхойл.
The Center for Environmental and Agricultural Policy Research, Extension and Development (CEAPRED) covered the remaining cost
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintain and repair wire fence to prevent livestock and humans from entering the pond | once in a year |
| 2. | Removing accumulated sediment once a year carefully by hand | dry months/once in a year |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Clean and maintaining the pond | persons/unit | 3.0 | 5.68 | 17.04 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintain and repair wire fence | persons/unit | 2.0 | 7.0 | 14.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Gabion wire | sq.ft | 120.0 | 0.31 | 37.2 | 100.0 |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 68.24 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 68.24 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The cost given above is for unit technology having 24000 liters capacity as in 2020.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
Cost of cement and sand
Members of a household contributed as labour in all sites.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
1584.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- шаардлагагүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын болон ул хөрсний ус
Усны давсжилт асуудал болдог уу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үер усанд автдаг уу?
Үгүй
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water source is mainly spring.
More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: spring
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Их
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Nepal harbors 3.2 % and 1.1 % world's known flora and fauna respectively despite occupying only 0.1 % of global area. Particularly, beta diversity is high in Nepal (BCN and DNPWC, 2011).
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын % 10-50 хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Ядуу
- Дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Хүнд хүчир ажил
- Амьтны зүтгүүр
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- Дунд нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 154 - 453 persons per km2 ( Census, 2011)
Annual population growth : 2% - 3%
Among 100% land users, 80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (ranked by land users). 20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification:
Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages.
Due to loss of farmland and increasing urbanization and loss of farmlands many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns.
The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi.
Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Vegetables- commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labor consists of planting, irrigation , harvesting, while field preparation is carried out by animals, also machines but just in valley bottom.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, цол эргэм бүхий
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Газар ашиглалтын эрх уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилдаг уу?
Тийм
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
Waste management:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
Тайлбар:
Health facilities: There are nine health facilities centre in Namobuddha municipality, Kavre. The main health facilities are Methinkot Hospital, which is a 15-bed district level government hospital, and Dapcha Health Center, which is run by Kathmandu.
Education: There are eight academic institutes for higher studies ( higher secondary schools and colleges). The main academic institutes are:
Dapcha Krishna
Multiple Campus (community), Dapcha;
Janahit Secondary School (public), Khanalthok
Janak Multiple Campus (community), Methinkot
Janak Secondary School (public), Methinkot
Kanpur Campus(community), Kanpur and
Kanpur Secondary School
(public), Kanpur.
Employment ( off-farm): Due to loss of farmlands and increasing urbanization, many people are switching from agriculture to non-farm occupations such as working in brick kilns. The opening of the BP Highway has led to the establishment of many hotels and restaurants and the development of local market places such as Bhakundebesi. Most local businesspersons are small entrepreneurs with limited investment capacity.
Market: Bhakundebesi is the emerging marketplace due to its strategic location in the middle of the municipality astrid the BP Highway. Most local business activities in the municipality take place in Bhakundebesi bazaar. It is a major place for local people to purchase consumer goods.
Energy
Cooking fuel:
In 2011, 88% of households mainly used firewood for cooking, followed by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) (4.92%). In Puranogaun Dapcha, almost all households (99.8%) relied on firewood for cooking. LPG was relatively popular in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (10.3%) and Khanalthok (11.5%). Less than 6% of households used biogas for cooking, with its use relatively high in Mathurapati Fulbari (19.3%) and Methinkot (15.9%) (CBS, 2011).
Lighting :
93% of households used electricity for lighting while 5% depended on kerosene. Dependency on kerosene was relatively high in Khanalthok (8.1%) and Methinkot (7.4%). There was little solar lighting except for in Khanalthok where 3% of households relied on it (CBS, 2011).
Roads and Transportation:
Namobuddha Municipality is easily accessible by motorable road from neighboring areas via the BP Highway, which splits the municipality into almost two equal halves . The highway, which runs from Banepa to Bardibas in the Terai, is the shortest route from the Kathmandu Valley to the eastern hills and Terai. The limited width of the road and its sharp bends mean that public transportation along the BP Highway is mostly by small buses and jeeps.
Drinking water and Sanitation:
In 2011, about 60% of households had access to taps or piped water with accessibility varying across the municipality. While about 80% of PuranogauDapcha households had taps or piped water, only 37.5% of households in Simalchour Syampati enjoyed such services. Other sources of drinking water were covered wells (12.3%), uncovered wells (20.2%) and water spouts (6.3%). Methinkot (40.8%) and Simalchour Syampati (31.4%) residents were most reliant on uncovered wells. Covered wells served sizeable household populations in Dapcha Chatrebhanjh (35.3%) and Simalchour Syampati (23%) (CBS, 2011).
Toilet facilities: In 2011, about 63% of households had accessto toilet facilities, with about 40% overall having flushtoilets. The least toilet coverage was in Kanpur Kalapaniand Simalchour Syampati VDCs where 63% and 58% ofhouseholds respectively did not have their own toilets. Almost all households in Puranogaun Dapcha had their own toilets, mostly flush toilets (CBS, 2011).
Waste Management: – Namobuddha is in the early phase of urbanization with no systematic waste management.The Municipality Office is searching for a landfill site.
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Before they used to plant only one crop per year but now due to adoption of this technology, crop production has increased as they plant three crops per year.
үр тарианы чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Crop quality has become good due to availability of more water for irrigation and integration of this technology with bio-pesticide jholmol and mulching.
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to availability of water for irrigation, farmers have turned many fallow land into agricultural land.
Усны хүртээм ба чанар
усалгааны усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Water needed for irrigation has increased as all the waste water from households, rainwater and taps waters are stored in this tank for irrigation in dry seasons.
Орлого, зарлага
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Irrigation water availability has increased crop production in turn farmer income has increased by selling those crops in market.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийгөө хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Farmers are becoming more self sufficient due to high production of crops.
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to informal network of farmers with pond has strengthened community institutions.
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Farmers share their knowledge and experiences with each other and discuss on how they can overcome the challenges they have been facing recently.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to availability of more irrigation water.
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Most of the fallow land are turned into crop land.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Доод урсгалын үер
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to trapped runoff
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Орон нутгийн аадар бороо | Сайн |
| Орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Дунд зэрэг |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Сайн биш |
Бусад уур амьсгалын өөрслөлт болон уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
| Бусад (тодорхойлно уу) | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? |
|---|---|
| reducing growing period | Сайн |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- > 50%
Технологийг өөрийн талбайд нэвтрүүлсэн бусад иргэдээс хэд нь үүнийг өөрийн хүчээр, өөрөөр хэлбэл ямар нэг материал, техникийн дэмжлэг, төлбөр авалгүй хийсэн бэ?
- 11-50%
Тайлбар:
Till now 24 land user families of Namobuddha Municipality have adopted this technology.
Among 24 land user families, 18 have adopted this technology with external material support through Resilient Mountain Village (RMV) project and 6 land users families have adopted this technology without any external support.
Comments on spontaneous adoption (Through survey results) : There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the technology because this technology is quiet expensive, compared to plastic- lined conservation pond.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Хувьсан өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд Технологид сүүлд ямар нэг шинэчлэл хийгдсэн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Water stored in this tank is sufficient to irrigate 2-3 ropani (1 ropani = 508 sq.m.) land in one season. |
| This technology can be enhanced by sharing the advantages of this technology with large number of people. |
| It is more sustainable and efficient than plastic-lined conservation pond. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Good income can be achieved even from a small piece of land by sales of vegetables in the dry season . |
| These ponds are fed with rainwater and household kitchen wastewater free from soap and detergent and from springs and taps. The pond water was mainly used for micro irrigation including drip irrigation and micro-sprinkler. |
| It helps to promote the use of other water conserving techniques like mulching when using the harvested water. |
| It has reduced the dependence on large scale water supply schemes. |
| How can they be sustained / enhanced? Harvest all possible sources of water. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Soil cement tank is expensive for poor farmers. | Subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| It is unsafe for small children. | Protection structures should be constructed. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Cement and sand rate is very expensive for poor farmers. | Make it available in the local market at a subsidized cost for poor farmers. |
| The ponds attract insects, mainly mosquitoes, that cause disease; and the ponds are unsafe for small children. | Regularly clean the pond and fence them. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
6
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
5
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
1
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
2
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
20/02/2020
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2018) Building Mountain Resilience: Solutions from the Hindu Kush Himalaya. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICIMOD
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
SCWMC (2004) Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Measures and Low Cost Techniques. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Component - Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
DSCWM, Kathmandu
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Namobuddha Municipality, Nepal Situation Analysis for Green Municipal Development, 2018
URL:
https://gggi.org/site/assets/uploads/2018/07/GGGI_GMD-Assessment_Namobuddha.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Farmers in Kavre reaping benefits from soil cement tanks, 2021
URL:
https://www.icimod.org/article/farmers-in-kavre-reaping-the-benefits-of-soil-cement-tanks/
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна