Tree windbreaks within irrigated agriculture in Central Asia [Киргизстан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Niels Thevs
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: Hayot Ibrakhimov
- Хянагчид: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5861 - Киргизстан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - Кени1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Agroforestry extension [Коста Рика]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Olman Quiros Madrigal
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
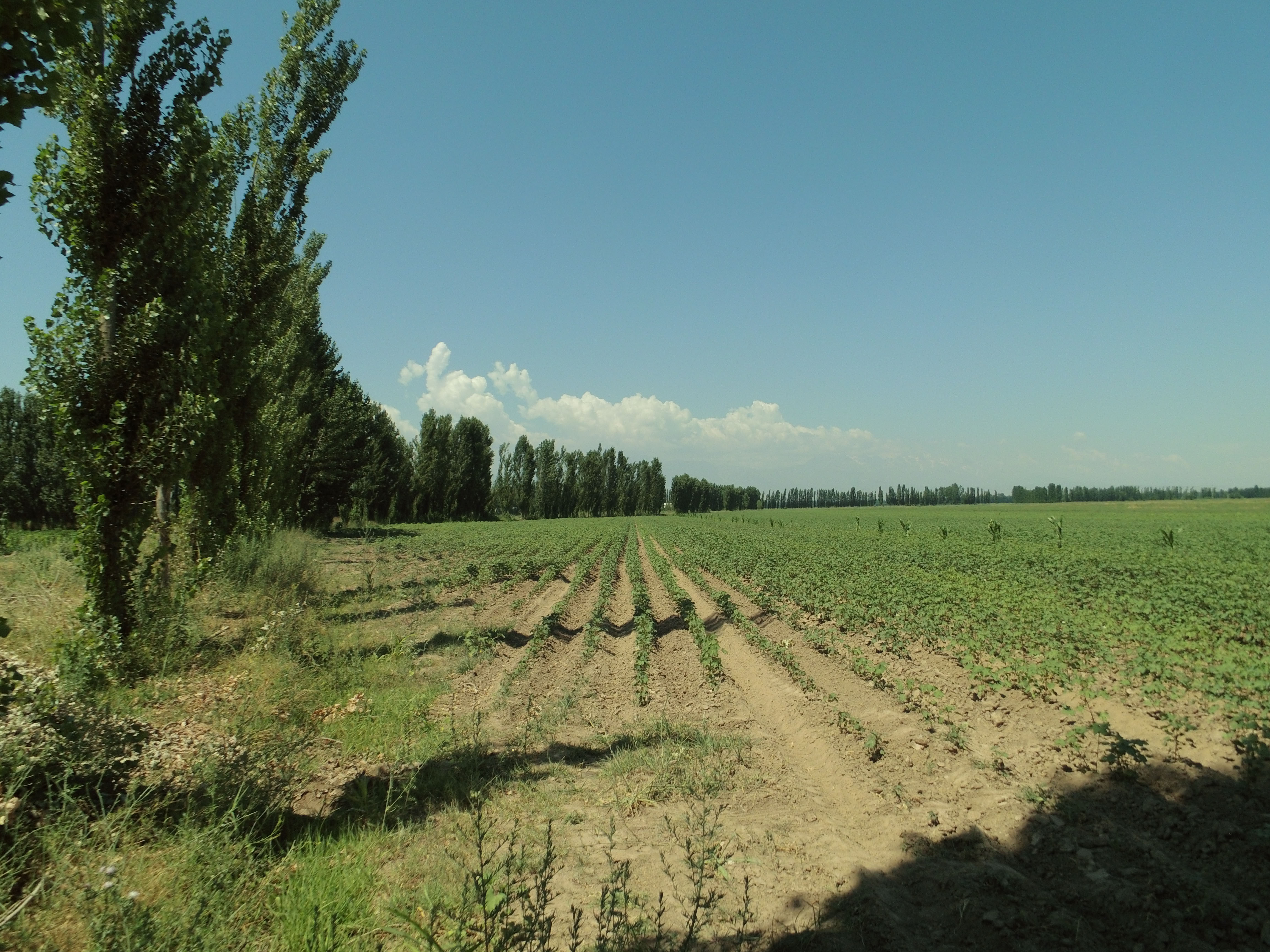
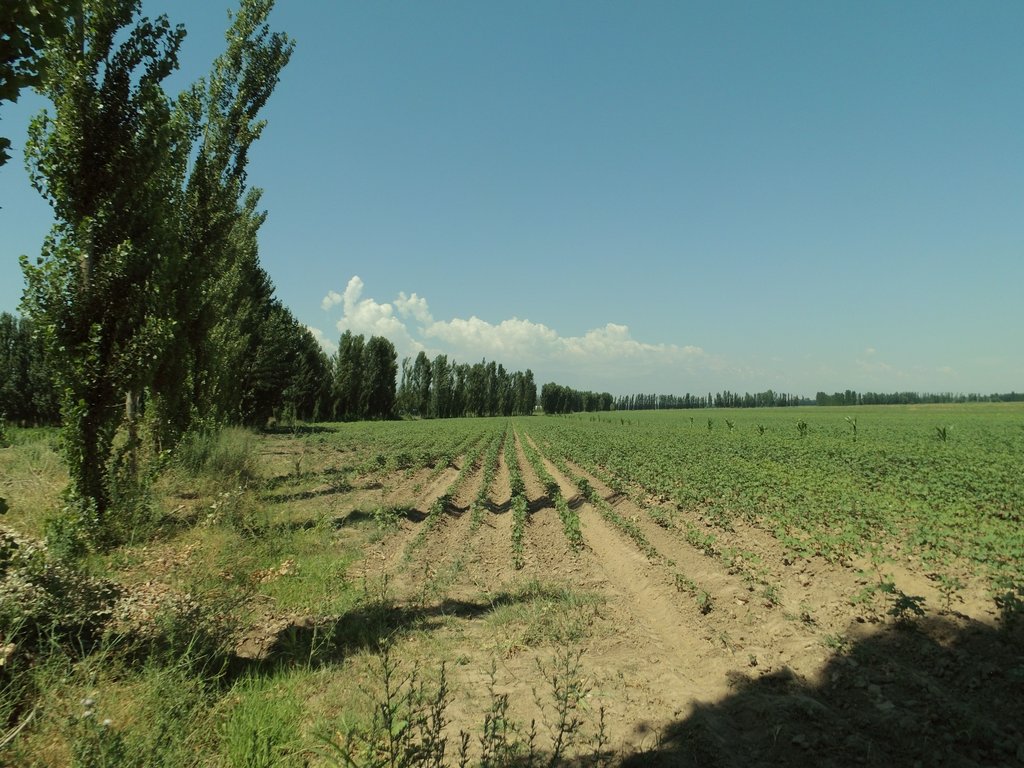
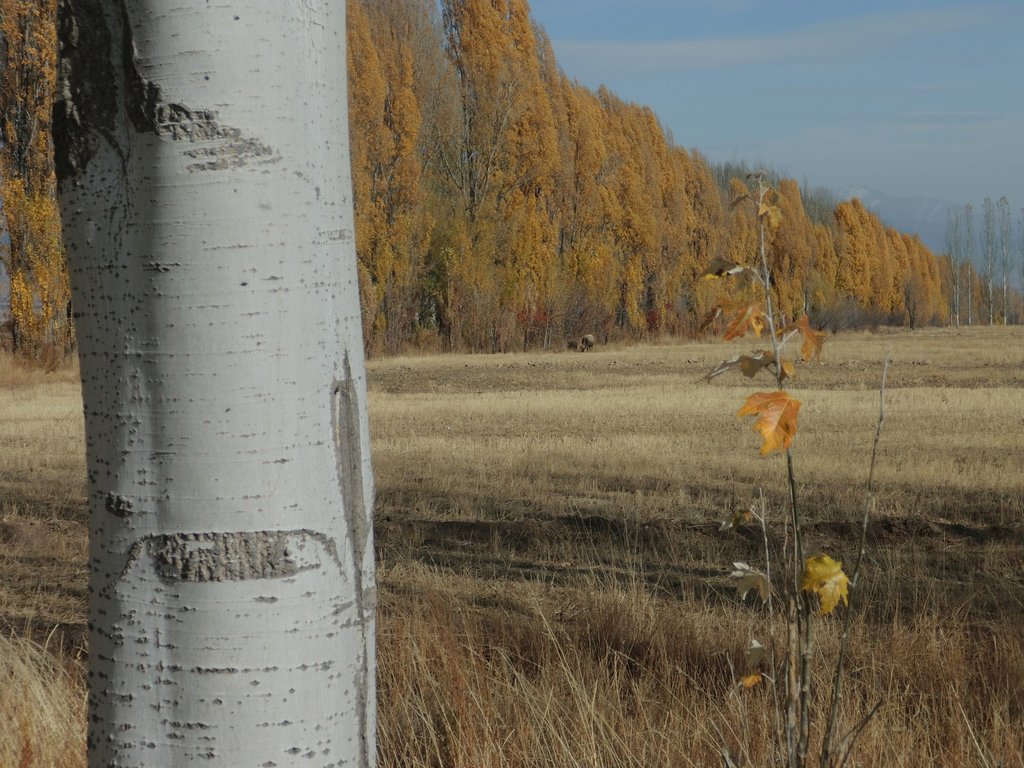
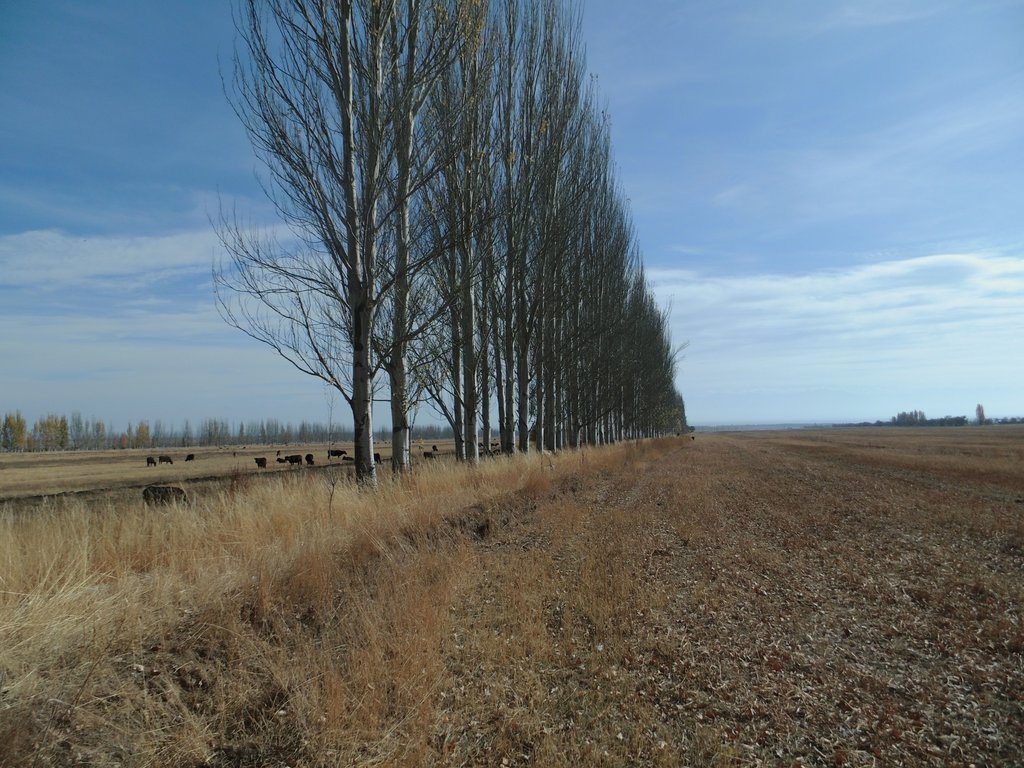
Windbreaks of poplar trees (Populus nigra pyramidalis) are a major agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture across Central Asia. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% and increase farm income by 10-15%.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
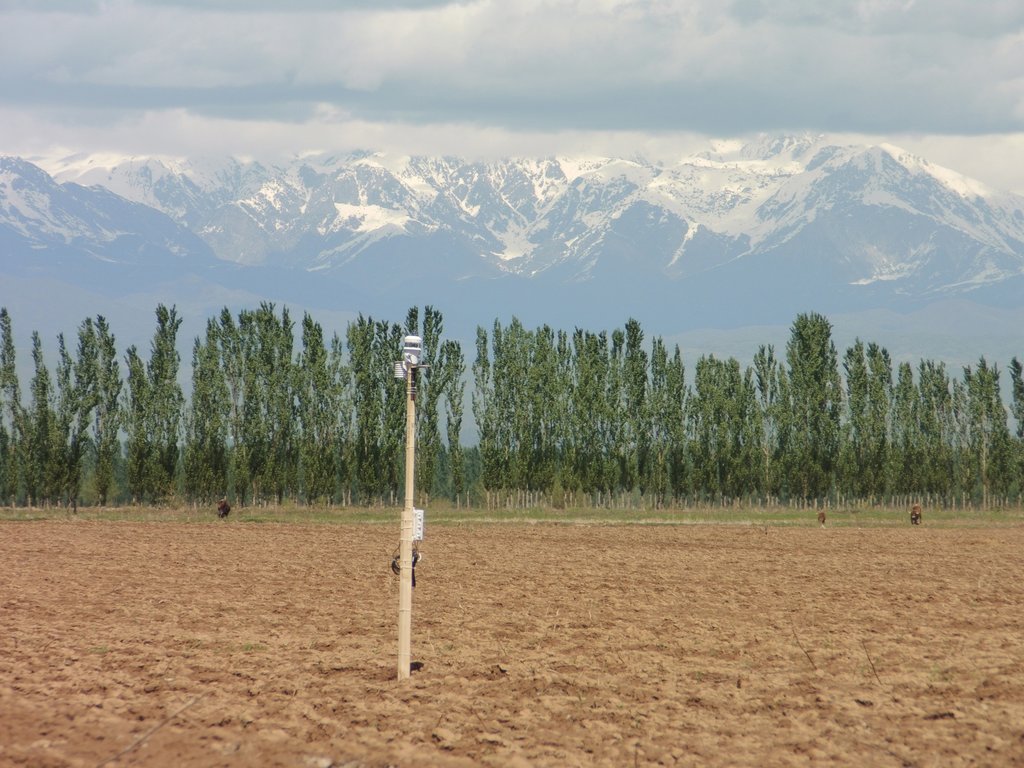
Windbreaks of trees are a major agroforestry system across Central Asia. The SLM technology presented here concentrates on windbreaks, chiefly of poplar trees (Populus nigra var. pyramidalis), within irrigated agriculture. These windbreaks of poplars have a long tradition as an agroforestry system in irrigated agriculture in the river basins of south and southeastern Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. In Kazakhstan and northern parts of Kyrgyzstan, poplars are partly replaced by Elm (Ulmus minor) windbreaks.
After those five countries had become independent, a large share of the windbreaks was cut down primarily for fuelwood and secondarily for timber, as the energy supply system had broken down in the course of the disintegration of the Soviet Union. Such windbreaks reduce the overall water consumption of irrigated agriculture by 10-20% compared to open field conditions, depending on crops and tree spacing (Thevs et al., 2019: doi:10.3390/land8110167). The trees serve as an additional source of income, chiefly from sustainable harvest of the trees for timber. Windbreaks also help to increase crop yields. In total, farm income is increased by 10-15% over the rotation period of the trees (Thevs and Aliev, 2021: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7). The rotation period of poplars is between 12 and 20 years, depending on the climatic conditions, e.g. poplars in the Ferghana Valles reach DBH (diametre at breast height) values of 22-27 cm and tree heights of 18 m after 13 years.
In this recent assessment, it was found that windbreaks of single tree rows with distances between trees of 1 m had the best effects on water saving and increasing farm income. The most suitable spacing between windbreaks was found to be around 200 m.
Windbreaks are perceived differently by land users depending on the region and knowledge (Ruppert et al., 2020: doi:10.3390/su12031093). For example, land users in the Ferghana Valley perceived windbreaks positively and were planting them primarily with the aim to have wood resources in the near future. In contrast, land users in the northern part of Kyrgyzstan were afraid firstly that windbreaks shaded their crops, consumed space, and competed for water and nutrients, and secondly that planting windbreaks may cause conflicts with neighbours due to those negative connotations. Farmers with larger field plots were more open towards them.
Windbreaks are planted with 2-year-old poplar saplings, which are locally available. The preferred place to plant is along irrigation ditches or other existing field boundaries. If windbreaks are planted along irrigation ditches, they simply tap water from the moist soil or elevated groundwater adjacent to those ditches. Otherwise, the trees need to be irrigated like the crops. As furrow irrigation is the dominant irrigation practice throughout Central Asia, poplars can be integrated without further adjustments in the field of irrigation. Alongside irrigation ditches poplars can withstand high water levels in those ditches as they occur during irrigation periods. If farmers switch to drip irrigation, and irrigation ditches are no longer present, the trees will need to be supplied with a dripline as well. The locally available poplar cultivars do not need additional fertilizer, but profit from the fertilizer applied to the crop. Only if high yielding modern cultivars were to be used, additional fertilizer application to the trees would be needed to unfold their full potential.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.4 Технологийн дүрс бичлэг
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт:
Video on Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
This video provides a concise introduction into tree wind breaks, including their advantages with regards to water consumption, building resiliance against climate change, and income.
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/09/2019
Байршил:
Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan
Зураглаачийн нэр:
Gino Carlo Garcia
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт:
This video on Youtube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Iv0VdPqBT9o, is part of a series on poplars. This part focusses on tree wind breaks with many statements of local acteurs. The other parts of this series introduce high yielding poplar cultivars and their options in agroforestry, woodlints, and value chains.
Он, сар, өдөр:
01/02/2020
Байршил:
Kyrgyzstan
Зураглаачийн нэр:
Lea Gerster and Stefanie Breunlich
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Киргизстан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Jalalabad Region, Chui Region, and Issyk Kul Region
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
Windbreaks are spread over large areas, but the spatial distribution can be described as pockets of between 10 and 1000 ha. Within those pockets, tree wind breaks are sometimes interrupted. Also outside those pockets with more or less contiguous windbreaks systems there are remnants of those systems.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- даавууны таримал - хөвөн
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (өвлийн)
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (эрт ургацын)
- үр тариа - цагаан будаа (чийгт газрын)
- үр тариа - арвай
- тэжээлийн ургамал - царгас
- үндэст/булцуут ургамал– төмс
- Poplars
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Үгүй
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 руу шилжинэ үү)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- бүрэн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
As the spatial distribution stretches over large parts of Central Asia, some locations where windbreaks are planted are rainfed and irrigated, but most parts need full irrigation.
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- Салхины хамгаалалтын ойн зурвас
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
- Hg: Гүний ус / уст үеийн усны түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
Тайлбар:
The main effect of windbreaks in the assessed areas is mainly reducing water consumption, and less wind erosion. Poplars could help to lower groundwater levels and thus contribute to combat salinization. But that did not play a role in the areas specifically assessed.
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
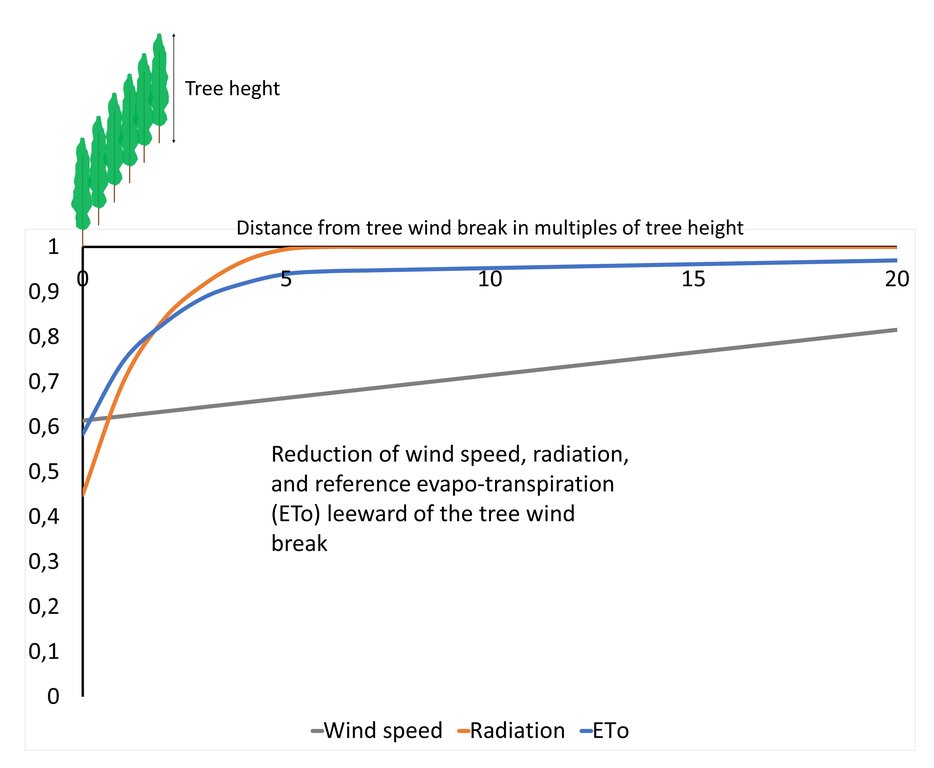
Windbreaks have their greatest impact when planted perpendicular to the main wind direction (or direction of the strongest winds). A whole grid of tree wind breaks running along all field plot borders will have a greater effect, as it prevents enhanced winds through a tunnel effect under changing wind directions. Tree wind breaks can be planted with distances of 50 m to 1000 m away from each other. The effect on the micro climate becomes less pronounced with increasing distance from tree wind breaks. Therefore, on a large field plot, say of 1000 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate averaged over the field plot will not differ much from the conditions without tree wind breaks. In contrast, on smaller field plots, say of 100 m width between windbreaks, the micro climate will differ significantly from open field conditions. This is also explained by the lines for temperature, air humidity, radiation, and in particular wind speed along an increasing distance from a given windbreak. Thereby, the distance from the windbreak is given in multiples of tree height.
In total, the best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption come with a spacing of 200 m between tree wind breaks.
The best effects with regard to economic return and reduced water consumption were achieved with single tree lines. So, only one line of poplar trees is planted along the field borders. The planting distance between trees is 1 m to 1.20 m.
Poplar trees are locally available as trees with a length of 2 m to 2.50 m. Those trees are planted, best along the small irrigation ditches that run along the field borders. The local cultivar which is mainly used is a Populus nigra var. pyramidalis cultivar under the local name Mirza Terek. In principle, modern high yielding cultivars can be used as well; first research has shown a 2-3 times faster growth compared to the locally available cultivars at similar water and nutrient requirements.
Зохиогч:
Niels Thevs
Он, сар, өдөр:
25/03/2021
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
1 ha
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
KGS
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
68.87
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
750
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | March (first year) |
| 2. | Maintenance of trees | April to September (first and second year) |
| 3. | Harvest of trees | December to February (last year of tree rotation - after 15 years) |
Тайлбар:
These entries refer to a windbreak system of poplars to be harvested at tree age of 15 years combined with cotton. Thereby, the activities related to trees, including the harvest, are considered as activities to establish windbreaks into an agrarian landscape where irrigated agriculture is ongoing. The annual crop related activities are therefore listed under maintenance. If cotton is rotated with corn or rice, the timing of the crop-related activities is similar.
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor costs for tree planting and maintenance (first year) | man-days | 3.0 | 750.0 | 2250.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor costs for tree maintenance (second year) | man-days | 3.0 | 650.0 | 1950.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Labor costs to harvest trees (at tree age 15 years) | man-days | 3.0 | 70.0 | 210.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Poplar saplings | sapling | 116.0 | 20.0 | 2320.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Transport of saplings | 500.0 | 1.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 7230.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 104.98 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Costs had been retrieved for the year 2017. Costs that appear in the second year and later were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5% based on costs as of 2017.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation and sowing of annual crop (cotton) | March to April / every year |
| 2. | Irrigation, fertilizer application and other farm operations for the crop | April to August / every year |
| 3. | Harvest of the crop (cotton) | September to October / every year |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor costs for soil preparation | man-days | 6.81 | 750.0 | 5107.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor costs for sowing | man-days | 2.5 | 750.0 | 1875.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Labor costs for irrigation | man-days | 23.64 | 750.0 | 17730.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Labor costs to apply fertilizer and plant protection | man-days | 3.34 | 750.0 | 2505.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Labor costs for harvest (cotton) | man-days | 32.78 | 554.0 | 18160.12 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine costs (rent) for soil preparation | ha | 1.0 | 10021.0 | 10021.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine costs (rent) for sowing | ha | 1.0 | 1316.0 | 1316.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine costs for fertilizer application | ha | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | kg | 50.0 | 101.0 | 5050.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | kg | 375.0 | 19.25 | 7218.75 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Plant protection | ha | 1.0 | 1517.0 | 1517.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Water fee | ha | 1.0 | 1014.0 | 1014.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 72714.37 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 1055.82 | |||||
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Labour costs are the largest single cost item. In fact, in the cotton system a lot of labour is unpaid family labour or mutual help among neighbours. All labour was calculated in monetary terms, as the share of unpaid labour differed much between farms. This cotton tree wind break system is wide spread in the south of Kyrgyzstan. In the north of the country, tree wind breaks are combined with wheat, barley, corn, or alfalfa (lucerne). There, labour costs are lower as more machines are used (e.g. for harvest).
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Precipitation maximum during spring and dry summers, which makes irrigation necessary.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Bazarkorgon, Kara Balta, Kemin
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
hot continental and semi-arid
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Tree windbreaks can be applied in a wide range of topographical situations. Though this particular entry focusses on windbreaks in irrigated agriculture so that the whole SLM technique, i.e. trees and crops, is distributed on flat land. As irrigation is tied to rivers as water sources, this SLM technique is distributed on river plains.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Tree windbreaks per se are not limited to specific soil types. In the region considered here, the soils that are irrigated and therefore are sites for this SLM technique were mostly formed by riparian deposits. Those soils silty to loamy. On most of those areas, where irrigation takes place, soils are classified as Fluvisols. On few areas, the soils are classified as Gleysols.
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
сайн
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Soil salinization and waterlogging do not play a role on the sites from where the information was collected for this introduction here. Though in parts of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, where this windbreak SLM technology is being applied and can be expanded as well, salinization and water logging do play a role.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
In Kyrgyzstan, the land users operate as households and can decide on their crops. Though, planting tree windbreaks does take place in agreement with neighbours. In Uzbekistan, where windbreaks are used as well, the freedom of farmers to chose their crops is limited, while tree windbreak planting partly follows governmental orders. In both countries as well as Tajikistan, labour migration is important for most rural families and remittances comprise a substantial share of the household income (off-farm income).
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
There is agreement in the scientific literature that tree windbreaks cause crop yield increases of 10-15%. Some references even claim crop yield increases of up to 40%.
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The leaves of the trees are partly used as fodder. But that additional fodder only is a minor contribution to the overall fodder demand.
модлогийн бүтээмж
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
none
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
53 m³/ha after 15 years
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Trees are harvested at an age of 15 years. Such trees have an average tree height and DBH of 19 m and 27 cm, respectively. Given a form factor of 0.42 one tree yields a stem volume of 0.457 m³. A number of 116 trees is assigned to 1 ha, which results in 53 m³/ha.
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
1 ha cropland
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
0.9 ha cropland
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Tree wind breaks occupy space so that the area available to the crop gets reduced. While the trees do not occupy substantial space during their first years of growth, they occupy about 10% of the cropland at and age of 10-15 years. This calculation was made for a spacing between tree wind breaks of 200 m.
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Tree windbreaks at a spacing of 200 m do not impede farm operations, while narrower spacing may disturb farm operations, in particular with machines.
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хэрэгцээ
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
904 mm over the cropping season
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
777 mm over the cropping season
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree windbreaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment below under evaporation)
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
There are expenses for tree planting material and labour associated to tree planting and maintenance during the first and second year.
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 214,000 KSG/ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
Accumulated NPV after 15 years: 232,000 KSG/ha
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The accumulated NPV over 15 years for cotton versus cotton and tree wind breaks were compared to assess the financial gain from tree wind break systems. 15 years is the tree age at which the tree wind breaks are harvested. Costs and revenues were discounted at a discount rate of 17.5%.
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Wood resources are added as additional income next to crops.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ууршилт
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
904 mm over the cropping season
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
777 mm over the cropping season
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
ETc (water consumption) of cotton is 904 mm over the whole cropping season. Tree win breaks (arranged as a rectangular grid with a spacing of 200 m) with cotton together consume 777 mm over the whole cropping season. (cf. comment above under irrigation water demand)
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
As tree wind breaks reduce evapotranspiration, they help to maintain soil moisture.
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Wind erosion did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia stronger winds prevail than in this very example. There, tree wind breaks do combat wind erosion.
давсжилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Salinity did not play a role in this example of cotton combined with tree windbreaks. Though in other parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia salinity does play a role. There, windbreaks, in particular poplar trees, help to lower the groundwater levels due to their high water consumption, which helps to combat soil salinization.
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The leaves of the trees partly end up as litter on the soil surface. The trees' root systems add to the below ground biomass. Both contribute to the formation of soil organic matter. Though, this is limited to a small area adjacent to the tree wind breaks and does not translate into the area of the cropland.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
As the evapotranspiration (water consumption) and the demand for irrigation water are reduced, the general availability of water is increased.
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Neighboring fields are partly shaded.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Glacier retreat which will result in reduced river flows and supply of water for irrigation |
Тайлбар:
There are two major effects of climate change on the region Central Asia: 1. Glacier retreat through rising temperatures and 2. increasing rainfall during winter and partly reduced snow. Currently, the melting glaciers cause elevated river flows so that there is more water available for irrigation. But, once the glaciers have reached a new equilibrium with smaller glacier volumes, they will deliver less water so that river flows are expected to drop during the second half of this century. Then, the supply of water for irrigation will become constrained. Tree windbreaks are one option to adapt to those conditions in the future.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Тийм
Дасан зохицох зорилгоор технологид хийсэн өөрчлөлт (хийц, материал, төрөл зүйл г.м.):
During the Soviet Union times, when tree windbreaks were promoted, multi-row tree windbreaks were planted. Today, farmers prefer single tree lines, in order not to sacrifice too much crop space.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks deliver wood resources for self consumption or to be sold on markets. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Tree windbreaks provide additional income as they deliver wood resources. |
| Tree windbreaks reduce overall water consumption in irrigated agriculture. |
| In more windy parts of Kyrgyzstan or Central Asia, land users see the advantage of reduced wind speed for crop quality and snow trap to build up soil moisture. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Tree windbreaks shade the crop. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks compete with the crops for nutrients and water. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks disturb farm operations. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect. |
| Tree windbreaks cause conflict with neighbours, as neighbours may share those negative perceptions. | Capacity building and explain that this is a minor effect and promote cooperation between neighbors to share benefits from tree wind breaks. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Financial resources are needed to establish tree windbreaks, while the revenue from the harvest of trees only can be realized in the future. | Access to suitable finance. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
Regular field visits (every 14 days) on three sites to collect climate, crop, and tree data to, among others, calculate crop and tree water consumption.
Field visit to two additional sites to collect data on tree growth.
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
62 household interviews to collect agro-economic numbers on crops and trees.
15 household interviews with wood traders and wood processors to collect information on markets and prices of wood from tree wind breaks.
80 semi-structured interviews on perception of tree wind breaks by farmers.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
compilation of literature on tree windbreaks, from Soviet Union and recent international literature.
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
14/07/2017
Тайлбар:
July 2017 was the most busy time to collect the interviews on agro-economy and wood markets. The interviews on farmers' perceptions of tree windbreaks were collected during September and October 2018. Crop and tree data (growth, water consumption) were collected during 2017 and 2018.
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K (2021): Agro-economy of tree windbreak systems in Kyrgyzstan, Central Asia. Agroforestry Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-021-00617-7
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Agroforestry Systems, EUR 37.40
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Ruppert D, Welp M, Spies M, Thevs N (2020): Farmers’ perceptions of tree shelterbelts on agricultural land in rural Kyrgyzstan. Sustainability 12:1093. doi:10.3390/su12031093
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/3/1093 - open access
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Thevs N, Gombert AJ, Strenge E, Lleshi R, Aliev K, Emileva B (2019): Tree wind breaks in Central Asia and their effects on agricultural water consumption. Land, 8: 167-183. https://doi.org/10.3390/land8110167
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://www.mdpi.com/2073-445X/8/11/167 - open access
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Strenge E, Thevs N, Aliev K, Eraaliev M, Lang P, Baibagysov A (2018): Water consumption of Populus alba trees in tree shelterbelt systems in Central Asia. Central Asian Journal for Water Resources 4, 48-62
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://www.water-ca.org/api/v1/articles/5955-water-consumption-of-populus-alba-trees-in-tree-shelterbelt-systems-in-central-asia.pdf - open access
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Thevs N, Aliev K, Lleshi R (accepted): Water Productivity of Tree Wind Break Agroforestry Systems in Irrigated Agriculture – an example from Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan. Trees, Forests, and People
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
will be open access
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
UNECE (2019): Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia – Challenges and Opportunities. Background paper for the Ministerial Roundtable on Forest Landscape Restoration in the Caucasus and Central Asia (21-22 June 2018, Astana, Kazakhstan)
URL:
http://www.unece.org/fileadmin/DAM/timber/publications/DP-72-flr-cca-en.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Agroforestry and Central Asia
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mAfQzO7MHg
7.4 Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
The questionaire guides the compiler through a number of questions through often standardized questions (ticking boxes). This is very helpful to avoid, possibly lengthy and not too concise descriptions. But with regard to agroforestry it should be made more clear where and how to address the trees.
In total it needs time to go through and fill in all sections, which surely is owed to the wish and need to collect information for a comprehensive description of each SLM technology. But, towards the end of projects, which have developed such technologies, the workload might be too high so that the entry into WOCAT is neglected. I guess one only can appeal to the motivation of projects or offer some sort of support for NGOs or so in need, but with very good SLM technologies to offer.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Agroforestry extension [Коста Рика]
Participatory extension of agroforestry systems, especially of shadegrown coffee, to promote sustainable and productive use of natural resources among small and medium scale farmers.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Olman Quiros Madrigal
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна