Participatory action research on drip irrigation [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2350 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre tecnologias da GST
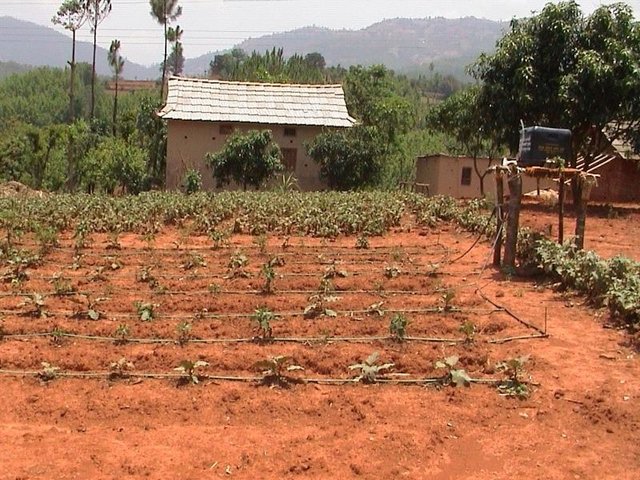

Low cost drip irrigation [Nepal]
An irrigation system which allows the slow and precise delivery of water to crops
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
Conducting participatory action research with farmers and line agencies for demonstrating, disseminating and scaling up drip irrigation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Most farming in the uplands of Nepal's midhills is rainfed with many fi elds remaining fallow during the dry season due to lack of irrigation water. The People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) water demand and supply survey identified scarcity of irrigation water as a major issue in Nepal's midhills. To assess the potential of drip irrigation to address this problem, the University of British Columbia (UBC) in 2000/2001, in collaboration with PARDYP, tested a low cost irrigation drip set and a more costly set in the Jhikhu Khola watershed; and PARDYP and Tribhuvan University's Institute of Engineering (Nepal) tested the low cost set with farmers at another site at Kubinde village, Kavre.
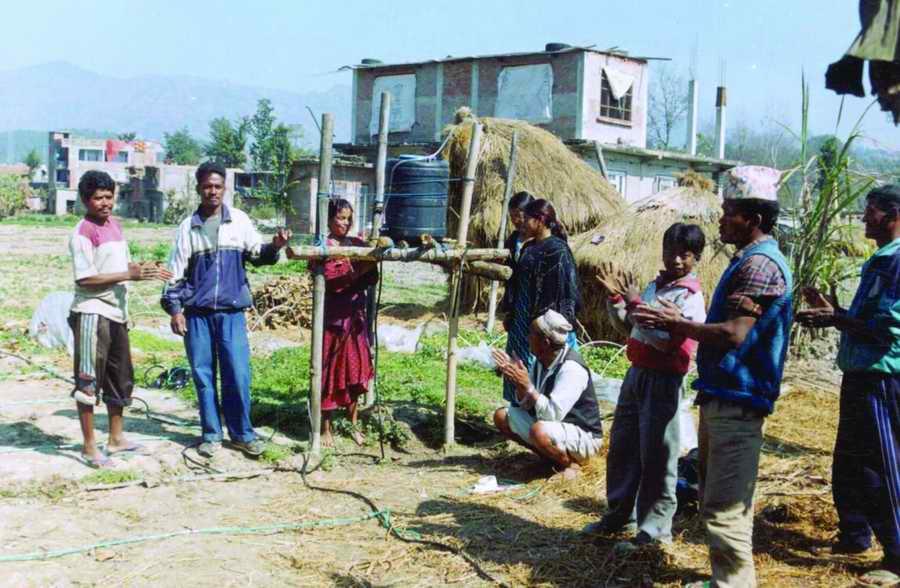
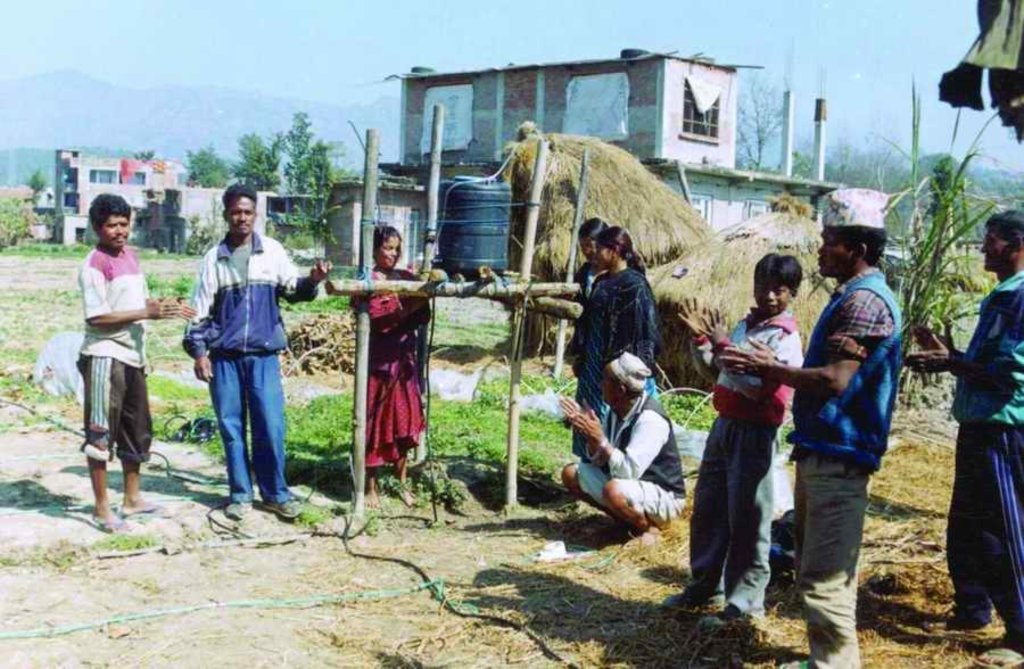
PARDYP started research on drip irrigation at an agricultural research station (the Spices Crop Development Centre at Tamaghat, Kabhrepalanchok) and brought different stakeholders, principally farmers, to the station to learn. After seeing the trials some farmers, especially those living near the research station, started testing drip irrigation on their farms. From 2001 to 2004, PARDYP subsidised 50% of the cost of the drip sets to most adopting farmers. PARDYP organised several farm visits for stakeholders to the research station and farmers’ fi elds. The number of interested farmers increased and many started testing and demonstrating the technology on their farms. PARDYP provided technical support during installation, advice about water application, and trouble shooting training to user farmers. Soon, many farmers started using drip irrigation with little or no technical support from PARDYP. Some collected quantitative and qualitative information on the performance of their systems. Results and experiences were shared regularly after cropping seasons through interaction meetings. Users’ experiences convinced many others to adopt the technology.
Interaction meetings were organised to communicate farmers’ feedback to the organisation and businesses involved in making the drip sets. Farmers from the watershed were taken to the drip set manufacturers to establish a direct link between them and to allow the project to phase out its support.
This approach emphasised on-station to on-farm research and demonstration to facilitate ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the performance of locally made drip sets.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Ano de término (caso a abordagem não seja mais aplicada):
2005
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (income generating activities, vegetable farming with micro irrigation system)
To test, demonstrate, and evaluate drip irrigation systems under local conditions with multiple stakeholders. To share results and experiences with communities to scale up the technology
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of systematic on-farm research on drip irrigation. - Weak institutional collaboration for developing, disseminating and scaling up drip technology. - Inadequate water available for agriculture alongside strong seasonality and poor irrigation facilities
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Inibitivo
Insufficient government incentives
Treatment through the SLM Approach: A Cost-effective technology and implementing approach
Quadro institucional
- Inibitivo
Weak institutional collaboration among line agencies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Participatory action research with several institutions - universities, local research centres, and farmers
Quadro jurídico (posse de terra, direitos de uso da terra e da água)
- Propício
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Because of private land owners there were no conflicts on land to implement the technology and for it's dissemination. and scaling up.
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Inibitivo
Promotion of micro irrigation was not a priority of line agencies in the study area
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Technology implemented with multiple stakeholders' participation
Outro
- Inibitivo
Lack of awareness on potential water-saving options
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Community-based training, discussions and field visits
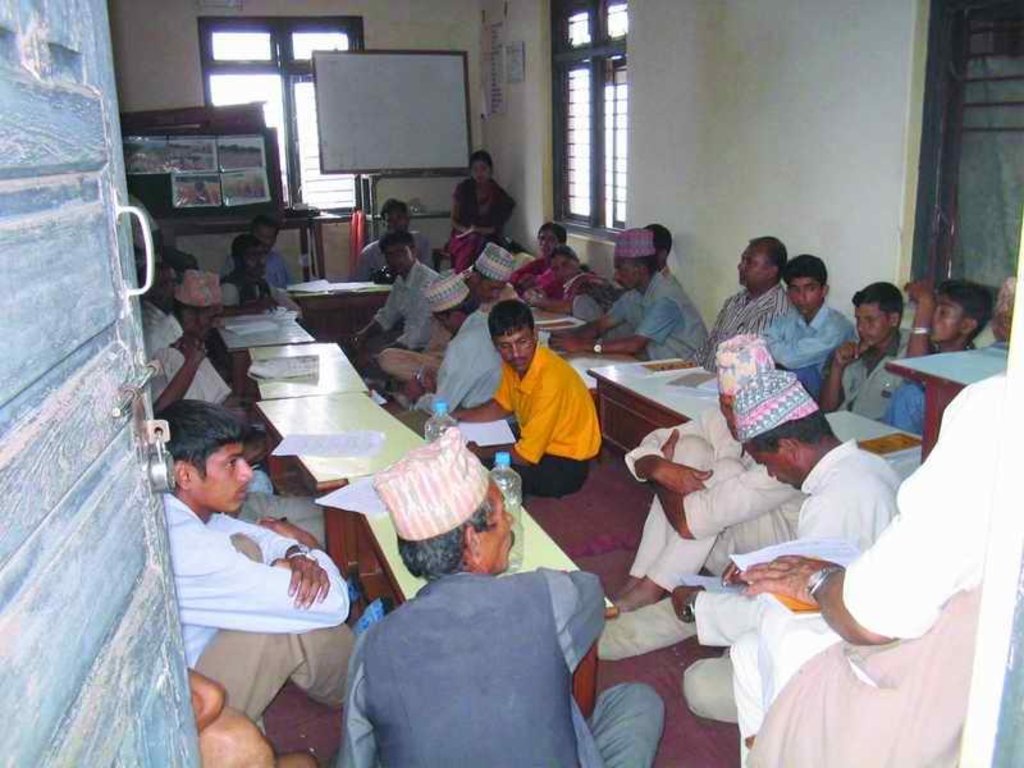
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
On farm research and demonstration
men and women worked equally
- Organizações comunitárias
existing groups of land users; community forest user group and terrace improvement committee
- Especialistas em GST/ consultor agrícola
Field technicians
- Organização não governamental
On station research
- Governo nacional (planejadores, responsáveis pelas decisões)
On station research
- Organização internacional
On station research
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Participativo | A water demand and supply survey identified problem of lack of water in the dry season for irrigating crops. The concept of drip irrigation was shared at public meetings and a demonstration plot established at a local agricultural research centre. Several farmer visits organised to the research cent |
| Planejamento | Participativo | Public meetings; farmers showed interest in drip irrigation. The project supported them by transporting drip sets to the nearest roadhead and subsidising the purchase costs |
| Implementação | Automobilização | Farmers implemented the technology and the project provided technical support |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Participativo | Mainly: measurements/observations, public meetings; partly: reporting; Farmers monitored the technology with project support. Evaluation was usually done at meetings and exchange visits. |
| Research | Automobilização | On-farm; The technology was tested at the local research centre during the first few years followed by on-farm research with farmers. Farmers collected and analysed quantitative and qualitative information themselves. |
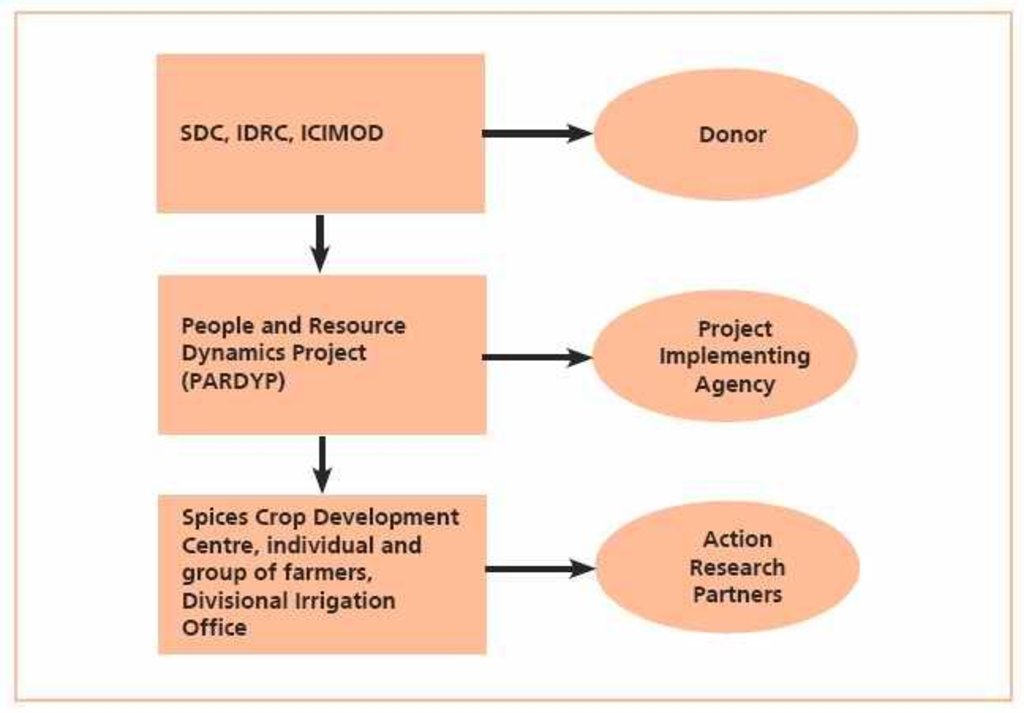
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
Descrição:
PARDYP project donors and implementing partners: SDC (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation); IDRC (International Development Research Centre); ICIMOD
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente especialistas em GST, após consulta com usuários da terra
Explique:
The project tested drip irrigation as a promising water-efficient technology.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. It was tested first in the research station to build confidence of the project staff and surrounding villagers, and was then taken to interested farmers' fields.
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Usuários de terra
- extensionists/trainers
Tipo de formação:
- Agricultor para agricultor
- Áreas de demonstração
- Reuniões públicas
Assuntos abordados:
Training programmes were organised on how to install and maintain the drip systems. Likewise farmers were trained on record keeping for water application, production, and cost-benefit analysis.
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Descreva/comentários:
Name of method used for advisory service: Farmer to farmer dissemination; Key elements: Interactive meeting, on-station and on-farm visits, workshops; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: non-governmental agency; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users, technicians/SLM specialists; Activities: interactive meeting, farm visits , workshops
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Government , NGOs and CBOs still continuing the activities.
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, significativamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Local
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Dê mais detalhes:
On-site training during drip installation provided to a local NGO (Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra) with vegetable seedling support.
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use change, crop rotation, soil surveys
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: water requirements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: socioeconomic surveys
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: cost-benefit production
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: area under drip irrigation
land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: number of drip users
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The subsidy system was withdrawn and work with groups rather than single households was started. In addition, interaction programmes were organised at different locations in the watershed.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation.
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
Action research was carried out to compare the water requirements, the cost-benefit, and the advantages and disadvantages of traditional and drip irrigation.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Caso o orçamento exato seja desconhecido, indique a faixa:
- 2.000-10.000
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour): 50.0%
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Equipamento
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Maquinário | ||
Se a mão-de-obra pelos usuários da terra foi uma entrada substancial, isso foi:
- Voluntário
Comentários:
Fifty percent subsidy on drip was provided by the project during initial stages (first two years) to a limited farmers.
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Land users started cropping land that was previously left fallow in the dry season and increased the area under cash crops - especially vegetables. Drip irrigation used only 60% of water compared to bucket irrigation.
Na Na
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A few institutions and district level line agencies like Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra, a local NGO, and the Divisional Irrigation Office Kabhrepalanchok started organising interactive meetings to discuss drip irrigation.
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Produção aumentada
increased vegetable production
- Carga de trabalho reduzida
less time required for irrgation, fertigation
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
Most of the land users continue to use drip irrigation and are maintaining the sets. A few farmers, including women, abandoned drip after using it for some time. The women who abandoned it said they did so because of 'lack of technical knowledge', 'not enough labour' and 'too far to get water'
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Regular interaction meetings provided land users with a platform to share ideas and for non-adopters to learn about drip from users. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| Farmer-to-farmer visits were helpful to build confi dence of farmers by seeing on-site results (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| On-site training on drip installation and maintenance helped build confi dence in using drip sets (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| This approach emphasises the participation of multiple stakeholders in researching, disseminating, and scaling up the use of the technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Identify and involve new interested stakeholders.) |
| On-station and on-farm research was important to get results from different locations and under different conditions. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue research to acquire in-depth knowledge on performance of drip irrigation under different conditions.) |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Women drip farmers' constraints were not sufficiently addressed. | Women's priorities and constraints must be better understood and addressed by programmes and projects on drip irrigation. |
| Many local land users remain unaware about the potential of drip irrigation technology. | Make more funds available to further promote the technology. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Shrestha-Malla, S. (2004). Adoption of Drip Technology and its Impact on Gender: a Case Study from Jhikhu Khola Watershed, Nepal. PARDYP/ICIMOD (unpublished)
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ICIMOD
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ICIMOD
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Low cost drip irrigation [Nepal]
An irrigation system which allows the slow and precise delivery of water to crops
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
Módulos
Não há módulos