Participatory action research on drip irrigation [Непал]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Madhav Dhakal
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Laura Ebneter
approaches_2350 - Непал
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
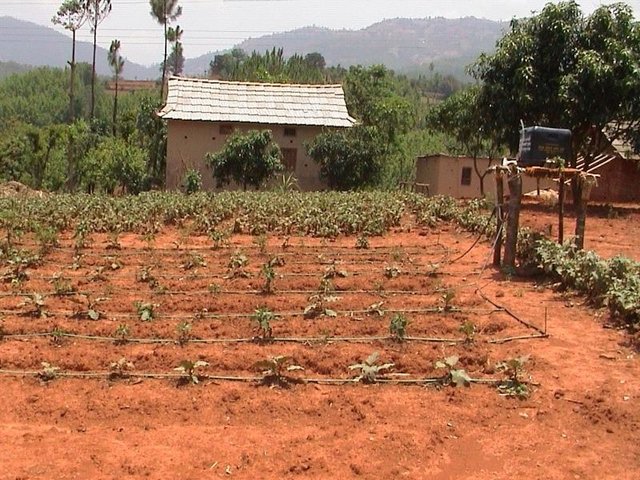

Low cost drip irrigation [Непал]
An irrigation system which allows the slow and precise delivery of water to crops
- Составитель: Madhav Dhakal
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Conducting participatory action research with farmers and line agencies for demonstrating, disseminating and scaling up drip irrigation.
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
Most farming in the uplands of Nepal's midhills is rainfed with many fi elds remaining fallow during the dry season due to lack of irrigation water. The People and Resource Dynamics Project (PARDYP) water demand and supply survey identified scarcity of irrigation water as a major issue in Nepal's midhills. To assess the potential of drip irrigation to address this problem, the University of British Columbia (UBC) in 2000/2001, in collaboration with PARDYP, tested a low cost irrigation drip set and a more costly set in the Jhikhu Khola watershed; and PARDYP and Tribhuvan University's Institute of Engineering (Nepal) tested the low cost set with farmers at another site at Kubinde village, Kavre.
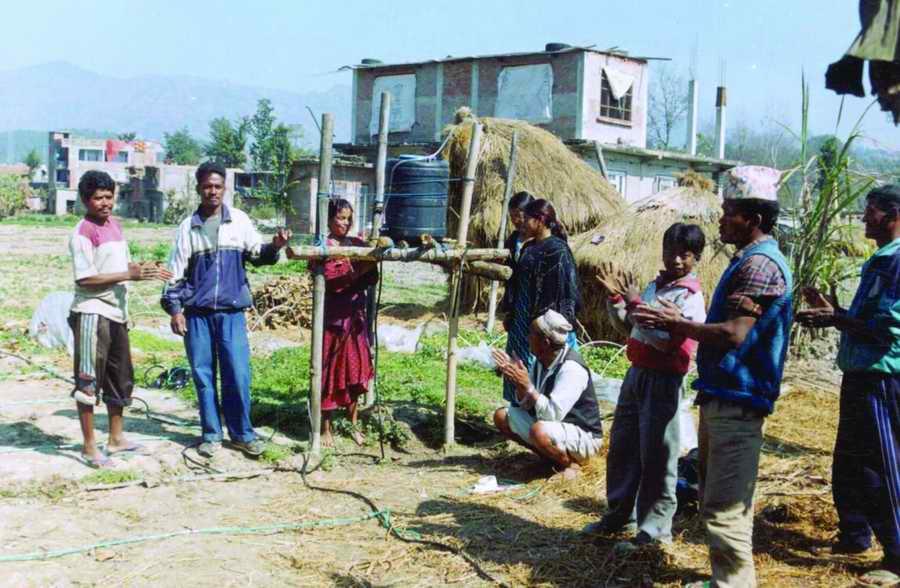
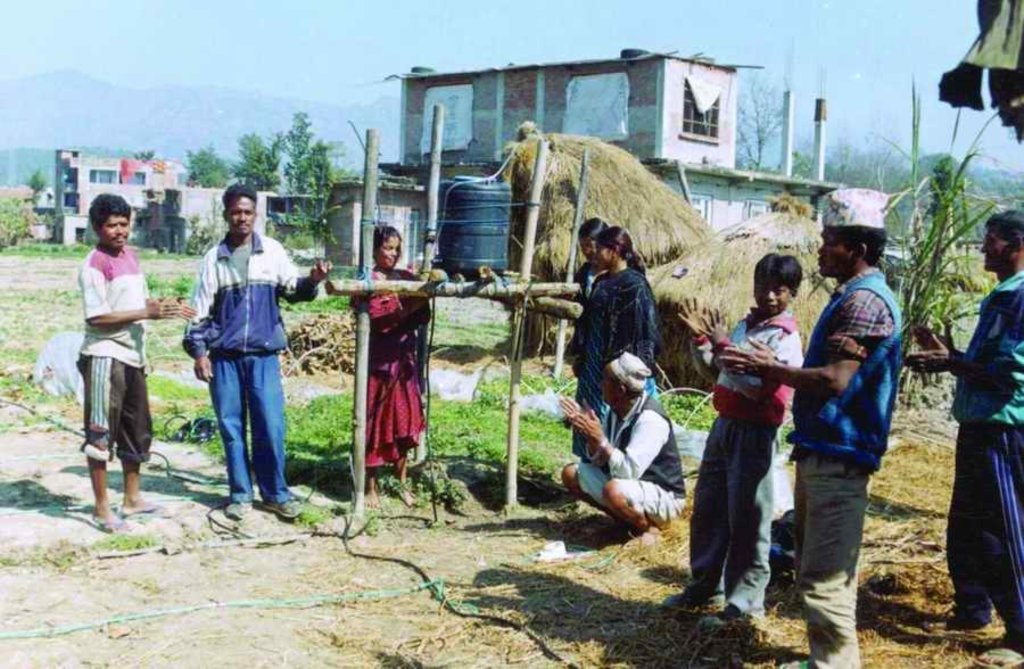
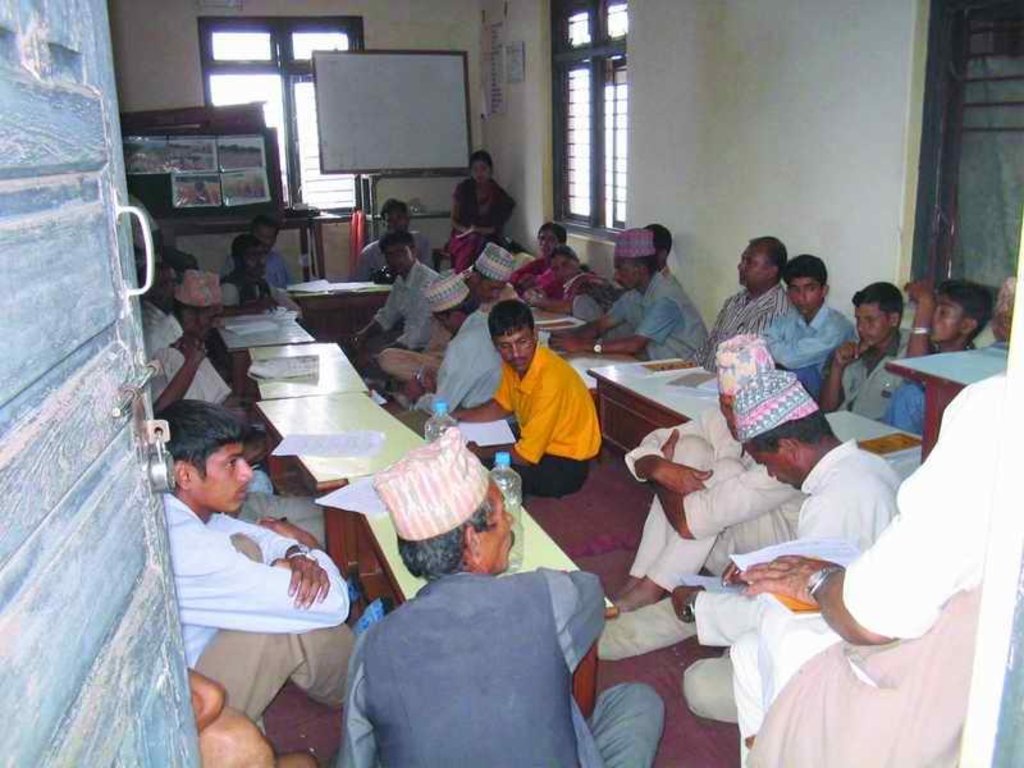
PARDYP started research on drip irrigation at an agricultural research station (the Spices Crop Development Centre at Tamaghat, Kabhrepalanchok) and brought different stakeholders, principally farmers, to the station to learn. After seeing the trials some farmers, especially those living near the research station, started testing drip irrigation on their farms. From 2001 to 2004, PARDYP subsidised 50% of the cost of the drip sets to most adopting farmers. PARDYP organised several farm visits for stakeholders to the research station and farmers’ fi elds. The number of interested farmers increased and many started testing and demonstrating the technology on their farms. PARDYP provided technical support during installation, advice about water application, and trouble shooting training to user farmers. Soon, many farmers started using drip irrigation with little or no technical support from PARDYP. Some collected quantitative and qualitative information on the performance of their systems. Results and experiences were shared regularly after cropping seasons through interaction meetings. Users’ experiences convinced many others to adopt the technology.
Interaction meetings were organised to communicate farmers’ feedback to the organisation and businesses involved in making the drip sets. Farmers from the watershed were taken to the drip set manufacturers to establish a direct link between them and to allow the project to phase out its support.
This approach emphasised on-station to on-farm research and demonstration to facilitate ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the performance of locally made drip sets.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Непал
Более точная привязка места:
Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год окончания (Если Подход больше не применяется):
2005
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (income generating activities, vegetable farming with micro irrigation system)
To test, demonstrate, and evaluate drip irrigation systems under local conditions with multiple stakeholders. To share results and experiences with communities to scale up the technology
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of systematic on-farm research on drip irrigation. - Weak institutional collaboration for developing, disseminating and scaling up drip technology. - Inadequate water available for agriculture alongside strong seasonality and poor irrigation facilities
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
Insufficient government incentives
Treatment through the SLM Approach: A Cost-effective technology and implementing approach
Институциональные условия
- затрудняют
Weak institutional collaboration among line agencies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Participatory action research with several institutions - universities, local research centres, and farmers
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- содействуют
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Because of private land owners there were no conflicts on land to implement the technology and for it's dissemination. and scaling up.
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки
- затрудняют
Promotion of micro irrigation was not a priority of line agencies in the study area
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Technology implemented with multiple stakeholders' participation
другие
- затрудняют
Lack of awareness on potential water-saving options
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Community-based training, discussions and field visits
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
On farm research and demonstration
men and women worked equally
- организации местных сообществ
existing groups of land users; community forest user group and terrace improvement committee
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
Field technicians
- общественные организации
On station research
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
On station research
- международные организации
On station research
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | интерактивное | A water demand and supply survey identified problem of lack of water in the dry season for irrigating crops. The concept of drip irrigation was shared at public meetings and a demonstration plot established at a local agricultural research centre. Several farmer visits organised to the research cent |
| планирование | интерактивное | Public meetings; farmers showed interest in drip irrigation. The project supported them by transporting drip sets to the nearest roadhead and subsidising the purchase costs |
| выполнение | самоорганизация | Farmers implemented the technology and the project provided technical support |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | Mainly: measurements/observations, public meetings; partly: reporting; Farmers monitored the technology with project support. Evaluation was usually done at meetings and exchange visits. |
| Research | самоорганизация | On-farm; The technology was tested at the local research centre during the first few years followed by on-farm research with farmers. Farmers collected and analysed quantitative and qualitative information themselves. |
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
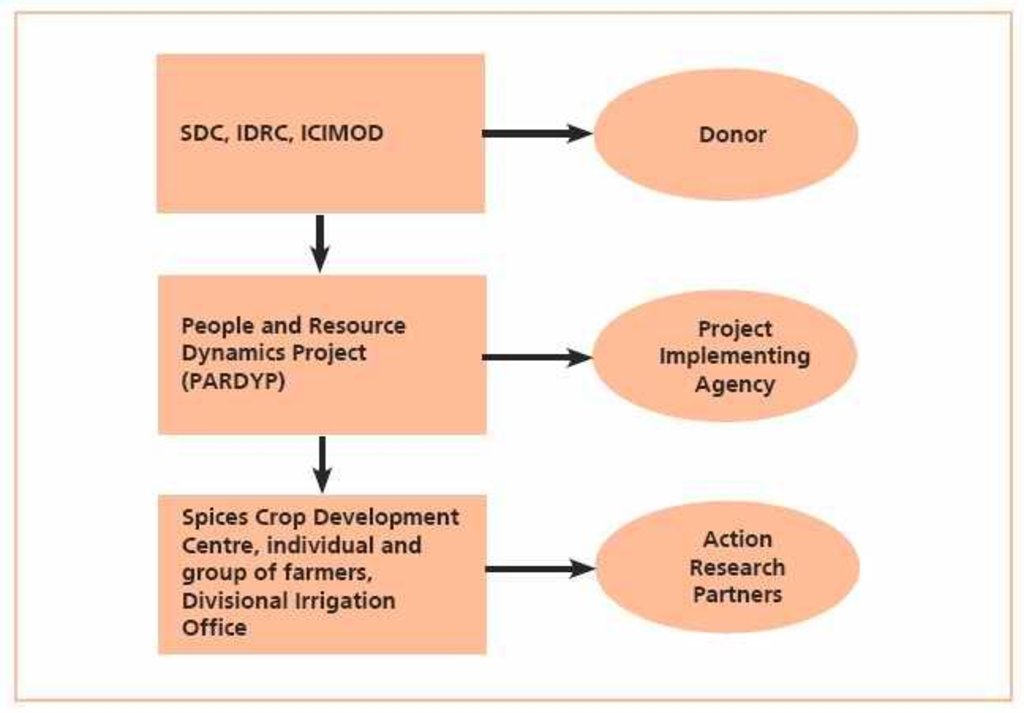
Описание:
PARDYP project donors and implementing partners: SDC (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation); IDRC (International Development Research Centre); ICIMOD
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
The project tested drip irrigation as a promising water-efficient technology.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. It was tested first in the research station to build confidence of the project staff and surrounding villagers, and was then taken to interested farmers' fields.
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Укажите, кто проходил обучение:
- землепользователи
- extensionists/trainers
Тип обучения:
- обмен опытом между фермерами
- опытные участки
- общие собрания
Рассматриваемые темы:
Training programmes were organised on how to install and maintain the drip systems. Likewise farmers were trained on record keeping for water application, production, and cost-benefit analysis.
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Описание/ комментарий:
Name of method used for advisory service: Farmer to farmer dissemination; Key elements: Interactive meeting, on-station and on-farm visits, workshops; 1) Mainly: projects own extension structure and agents, Partly: non-governmental agency; Extension staff: specifically hired project employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users, technicians/SLM specialists; Activities: interactive meeting, farm visits , workshops
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Government , NGOs and CBOs still continuing the activities.
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, существенно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Укажите тип поддержки:
- повышение компетенций/ обучение
Подробнее:
On-site training during drip installation provided to a local NGO (Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra) with vegetable seedling support.
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land use change, crop rotation, soil surveys
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: water requirements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: socioeconomic surveys
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: cost-benefit production
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: area under drip irrigation
land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations; indicators: number of drip users
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The subsidy system was withdrawn and work with groups rather than single households was started. In addition, interaction programmes were organised at different locations in the watershed.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation.
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
Action research was carried out to compare the water requirements, the cost-benefit, and the advantages and disadvantages of traditional and drip irrigation.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 2000-10000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (labour): 50.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- оборудование
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| техника | ||
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
Fifty percent subsidy on drip was provided by the project during initial stages (first two years) to a limited farmers.
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
Land users started cropping land that was previously left fallow in the dry season and increased the area under cash crops - especially vegetables. Drip irrigation used only 60% of water compared to bucket irrigation.
Na Na
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
A few institutions and district level line agencies like Ranipani Gram Sewa Kendra, a local NGO, and the Divisional Irrigation Office Kabhrepalanchok started organising interactive meetings to discuss drip irrigation.
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост продуктивности
increased vegetable production
- снижение объёма работ
less time required for irrgation, fertigation
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- да
Если да, опишите как:
Most of the land users continue to use drip irrigation and are maintaining the sets. A few farmers, including women, abandoned drip after using it for some time. The women who abandoned it said they did so because of 'lack of technical knowledge', 'not enough labour' and 'too far to get water'
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Regular interaction meetings provided land users with a platform to share ideas and for non-adopters to learn about drip from users. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| Farmer-to-farmer visits were helpful to build confi dence of farmers by seeing on-site results (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| On-site training on drip installation and maintenance helped build confi dence in using drip sets (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue such meetings and involve more potential adopters) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| This approach emphasises the participation of multiple stakeholders in researching, disseminating, and scaling up the use of the technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Identify and involve new interested stakeholders.) |
| On-station and on-farm research was important to get results from different locations and under different conditions. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue research to acquire in-depth knowledge on performance of drip irrigation under different conditions.) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Women drip farmers' constraints were not sufficiently addressed. | Women's priorities and constraints must be better understood and addressed by programmes and projects on drip irrigation. |
| Many local land users remain unaware about the potential of drip irrigation technology. | Make more funds available to further promote the technology. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Shrestha-Malla, S. (2004). Adoption of Drip Technology and its Impact on Gender: a Case Study from Jhikhu Khola Watershed, Nepal. PARDYP/ICIMOD (unpublished)
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
ICIMOD
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
ICIMOD
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Low cost drip irrigation [Непал]
An irrigation system which allows the slow and precise delivery of water to crops
- Составитель: Madhav Dhakal
Модули
Нет модулей