Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Firdavs Faizulloev
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Tajikistan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_1458 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields: 4 de Janeiro de 2017 (inactive)
- Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields: 20 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields: 21 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Shelterbelts with Russian Silverberry for the protection of irrigated fields: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Ibragimov Firuz
(+992 44) 600 55 19
firuz.ibragimov@undp.org
National Capacity Building Coordinator, Energy and Environment Programme, UNDP Tajikistan
Tajiquistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Shelterbelts are used to protect irrigated land from deposition of sand and to reduce wind speed
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
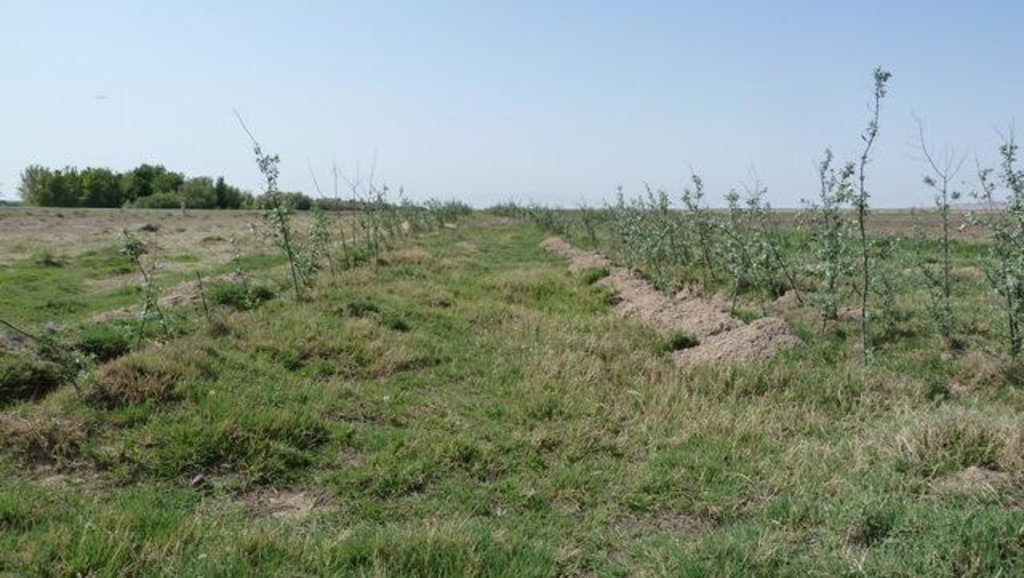
This technology consists of shelterbelts made of Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) to protect irrigated wheat and rice fields from strong winds.
In the Shaartuz area wind erosion poses huge problems to crop cultivation as topsoil is being removed and deposited as sediments on neighbouring fields. Dusty storms not only damage the crops but they also cause damage to the main surface, the fertile layer of soil. Sand also damages the irrigation canals, roads, gardens and streets in urban areas which forces people to leave such areas. Good yields cannot be achieved if fields are not properly protected.
A solution to this problem is the planting of shelterbelts around fields to slow wind speed and to prevent erosion of the arable soil layer. During Soviet times shelterbelts were planted on collective farms by the state forestry committee under contracts. After the collapse of the USSR and before the formation of Dehkan farms land users were not interested in investing in shelterbelts due to unprotected land use rights and unclear legal procedures. One farmer however tested the planting of a shelterbelt in 1992 when his son came back from his studies at the Agricultural University where he had learnt about the technology. They planted the first shelterbelt using a mixture of different tree species to protect newly irrigated fields. Due to financial constraints they could not invest in any other shelterbelts but in 2010 UNDP provided them with financial support to buy seedlings to increase the shelterbelt area. For this new shelterbelt the native Russian Silverberry (Elaeagnus angustifolia) was considered the most appropriate species as soils were highly saline and only this species proved tolerant.
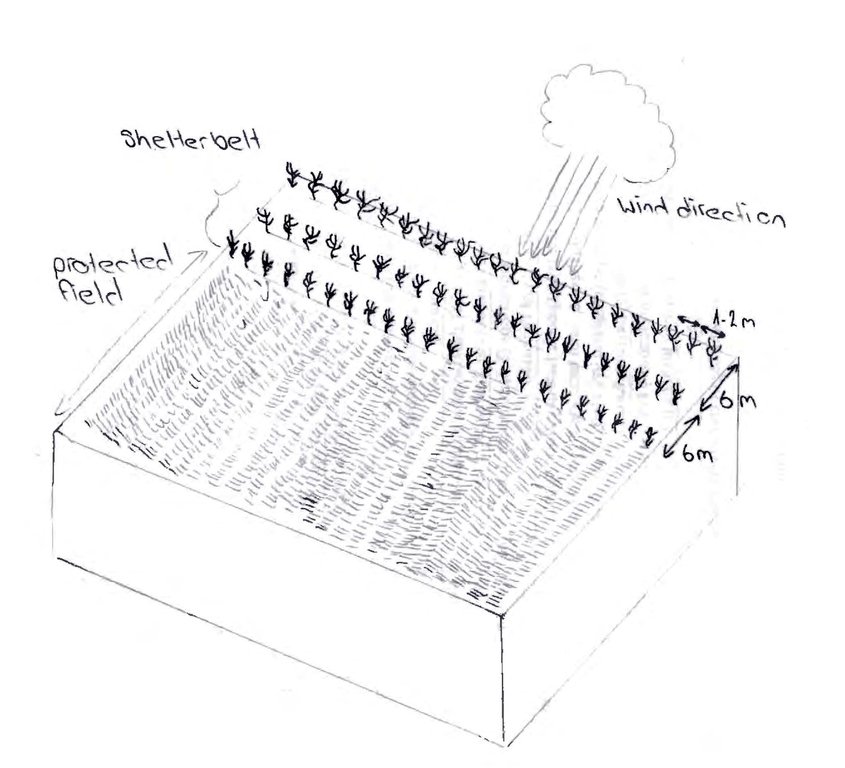
Trees were planted in three rows, along field boundaries and also along irrigation channels. Within rows trees were spaced at a 1m interval with a 6 m distance between rows. The plantations were established through “haschar” (voluntary neighbourhood help) with 30 people planting about 10,000 trees within one month. During the first three years after planting the saplings need regular irrigation and sanitary cleaning to help establish themselves. After 6-7 years the trees start drawing a lot of water from the soil which prevents the irrigated soils from damage through water logging. Russian silverberry can grow up to 12 m in 10-12 years.
Benefits of these shelterbelts are increased crop yields (wheat and rice) due to the protection from strong winds and decreased evapotranspiration. Thanks to the species association with nitrogen fixing root bacteria soil fertility is improved. The trees further produce edible fruits and provide valuable firewood that is consumed by the households. Russian Silverberry is resistant to pests and diseases and drought-tolerant once established; however, it requires a lot of water during the first few years. One constraint to the establishment of the shelterbelt is local people who often cut down branches for firewood. The farmer therefore has to guard his field whenever possible with the help of his family and staff he has employed to work on his field. Implementation of forestry initiatives began in 2009 and a total of 11 ha land was covered between 2009-2010. 11 farmers were involved in the project and establishment of the shelterbelts was initiated stage by stage during these two years. The project initiatives have also continued into 2011 as well. As other farmers do observe and understand the importance of shelterbelts, there has been a trend towards adoption of the technology by other farmers.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khatlon
Especificação adicional de localização:
Shaartuz
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The land users son learnt about the technology while he studied at the agricultural university and the first shelterbelt was implemented through the land users own initiative
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Preserva ecossistema
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Dusty storms not only damage the crops but they also cause damage to the main surface, the fertile layer of soil. Sand also damages the irrigation canals, roads, gardens, streets in urban areas which can force people to leave such areas.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Wind erosion leading to deflation of sandy soils, low soil fertility, reduction of vegetation cover, and increasing impacts of climate change.
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Other: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.09 m2.
The technology has been applied by 11 different farmers on 9 ha of land
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
- Ed: deflação e deposição
- Eo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação biológica
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, wind storms / dust storms, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (breakdown of soviet irrigation systems and therefore abandonment of land)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Shelterbelts consist of three rows of trees (Russian Silverberry). The rows are spaced 6 meters apart from each other and the interval between trees within the rows is 1-2 m.
Location: Shaartuz. Khatlon
Date: 27.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1500
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-2
Trees/ shrubs species: Elaeagnus angustifolius (planted)
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.50
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of grafting material or tree seedlings | Vegetativo | December |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 720,0 | 720,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 1350,0 | 1350,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2070,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation of seedlings | Vegetativo | regularly during first three years |
| 2. | Sanitary cleaning of trees | Vegetativo |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 85,0 | 85,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 85,0 | |||||
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour was provided for free through the so-called "haschar" or neighborhood help.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Risco de falha de produção
Impactos socioculturais
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
through increased crop yield
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
reduced deflation
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
shelterbelts can provide habitat to birds, insects etc.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
from prevention of deposition
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
the trees take time to establish during which the benefits are not yet tangible
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
11 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
It is impossible to get good yield in these areas which are prone to strong winds without shelterbelts. Farmers do realise and understand the importance of shelterbelts and there is a trend towards growing spontaneous adoption of the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Reduced deflation and deposition of sand on fields and therefore improved crop growth |
| Increased crop yield as before the establishment of shelterbelts no crops could grow on this land |
| Reduced wind speed |
| Russian Silverberry produces edible fruits rich in vitamins |
| Increased production area |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Russian silverberry is a native tree species with high drought-tolerance and the ability to grow on nutrient-poor soils thanks to its root association with nitrogen fixing bacteria |
| Once established the shelterbelts do not need a lot of maintenance |
| Rehabilitation of unproductive, denuded land into productive cropland |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The shelterbelts have to be protected from being damaged by local people who want to cut them for firewood | Awareness raising; increase of firewood supply through tree planting |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos