Contour Trench cum Bund [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Niranjan Sahu
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Samapatana nali o huda ( Oriya)
technologies_1480 - Índia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Patel Anita
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [Índia]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- Compilador/a: Niranjan Sahu
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
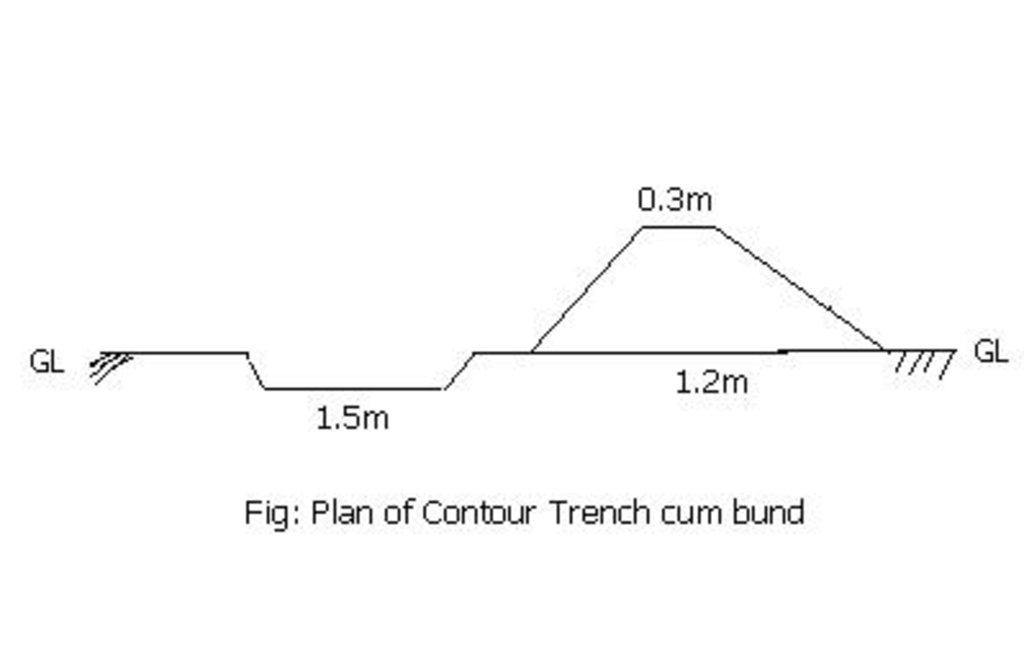
Contour trench cum bund is a bund laid out on contour along with trench either staggered or continuous to check the velocity of run off, conserve in situ moisture, increse ground water recharge and there by establish a sustainable land use system.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
It is a structural measure. The bund is constructed taking the excavated earth from a trench of 1.5m X 0.3m cross section and leaving a berm of 0.3m and put along the contour. Loose boulder water way are constructed on the bund for safe disposal of excess run off.
Purpose: To break the slope of land. To reduce the velocity of runoff. To increase the in situ soil moisture and increase ground water table. To reduce down stream sand casting.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The process adopted for implementation of the intervention followed participatory planning through resource mapping, transect, well being ranking, problem identification, prioritisation and negotiation; thus benefit sharing, contribution and future maintenance of the stucture is ensured before establishment of the structure. The poor land and poor people get the opportunity first.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
Orissa
Especificação adicional de localização:
Nangalbod-Tankamal Watershed,Mahanadi Basin
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
0,32
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.32 km2.
The technology area comprises of 0.3 2km2 within the watershed of 6 km2. The technology is an improvement of the age old practice of field bunding by the farmers.This has been promoted by the Soil Conservation department and watershed mission through watershed development programme.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Indegeneous but improved by Soil Conservation department, Watershed Mission, UNDP.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrossilvipecuária

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - painço
- rice
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Nomadismo
- cattle

Floresta/bosques
- Florestas/bosques (semi)naturais
Florestas (semi)naturais/ bosques: Especificar o tipo de manejo:
- Derrubada seletiva
Produtos e serviços:
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
- Pastagem/Alimentação de folhas e brotos
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The fertile top soil is gradually washed away.Productivity of the soil is also reduced. Thus, farmer is only taking minor millet in kharif.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of production. Soil is unable to retain moisture, so we suffer crop loss during long dry spell.Due to sand casting crop is also partially damaged in the down stream.
Nomadism: People allow the cattle to graze freely in the field after the crop is harvested
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: People have started managing forest through VSS and Forest protection committee.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: minor millets and up land paddy are the major crop under rain fed condition
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Desvio e drenagem de água
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services (Absence of institutional arrangements to disseminate the knowledge from lab to land and involve the users in implementation)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Subsistence economy, dependance on forests for fuelwood and fodder, livestock were low quality, free grazing type. And these were no regulatory mechanisms to share usufruct from forests with people.), poverty / wealth (Lack of capital at the grassroot to take the initiative by the farmers themselves)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60
Construction material (earth): earth is dug from the trench in the up stream
Construction material (stone): picked up boulders available locally
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Indian Rupee
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
50,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and alignment of trench, bund | dry season |
| 2. | Digging of trenches and construction of bunds | dry season |
| 3. | Construction of water way | dry season |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | 30,0 |
| Material de construção | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | |
| Material de construção | Earth | ha | 1,0 | 98,0 | 98,0 | 30,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 200,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 4,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grass turfing on bunds | during rainy season/annual |
| 2. | Maintaining shape and size of bund | after rainy season/annual |
| 3. | rearranging dispersed stone in water way | after rainy season/annual |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Cross-section and length of the structure per hectare
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
labour
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1382,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
80-100 days of rainfall occurs in most part of the state
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. ( the technology area is located at 196m.a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, the surrounding area is coverd with hillocks with forest) and footslopes (ranked 2, the technology area has undulating slopes with forest in betweem and mild slope)
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil texture: Also medium (ranked 2) and fine/havey (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter: Also medium (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
- Muito rico
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The livelihoods is less diversified. They also depends on NTFP marketing, off farm activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked ) and manual work (ranked 2)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1ha (ranked 1, marginal farmers)
1-2 ha (ranked 2, small farmers)
2-5 ha (ranked 3, big farmers)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Due to construction of bund
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Formal credit
Input constraints
Comentários/especificar:
Timely availability of inputs
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
22 SHGs has been formed and strengthened
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
NRM volunteers has been developed
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
During identification of land ownership and location of waterways
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Water table in wells
Water availability in WHS
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
24
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
12 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The farmers have realised the benefits from farmers' group meeting and visiting to the technology area.The farmers have started maintaining the bunds. They have also started taking crops both on bunds and field.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Our crop can with stand dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting of glaricidia and use of compost |
|
Value of land will increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? By maintaining bunds |
|
We can take crop in bunds How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting of bengal grams, tils, cow pea and sima |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Reduce runoff and velocity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Reduce sand casting in the down stream How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Crop diversification and promotion of improved agricultural practices How can they be sustained / enhanced? Through capacity building of volunteers and land users |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| loss of land | Productive use of trench and bunds |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Regular maintenance of the stone surplus | promote and strengthen user group |
| Open grazing | Promote community farming for collective actions |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Micro plan of Nangalbod-tankamal watershed. 12/30/2004.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
district Statistical hand book. 12/30/2004.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [Índia]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- Compilador/a: Niranjan Sahu
Módulos
Não há módulos