Irrigated agro-biodiversity system in arid high mountain area [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1034 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - Tajiquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
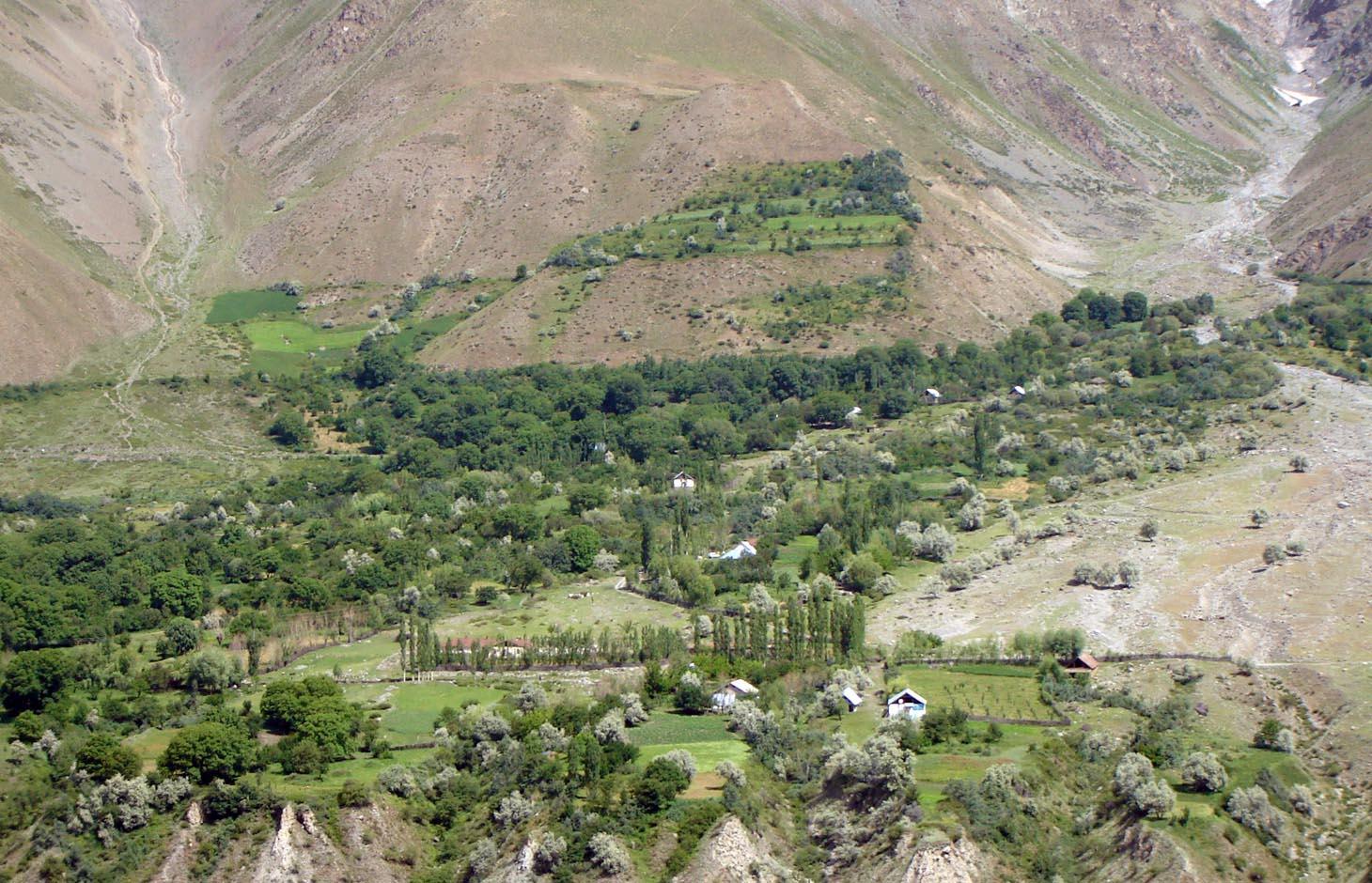
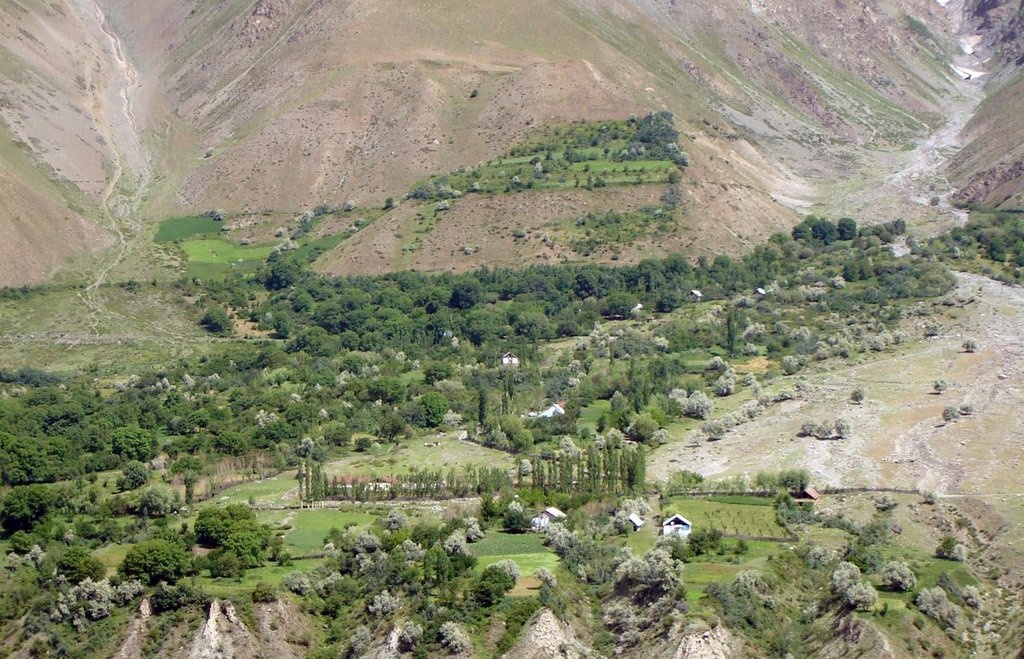
An individual farmer family, has changed an overgrazed pasture area on a steep slope in the upper part of the village into an irrigated agro-biodiversity system, by constructing an irrigation canal, by tilling and removing stones from the terraces for crop production and afforesting the surrounding area with fruit trees and bushes.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The site was established in 1989, with the construction of an irrigation canal. The canal brings water from a small watershed and the slowly melting snow fields within. In years with limited snowfall, the water is insufficient for irrigation throughout the summer months.It is a open, mud canal, 730 m long. When establishing new cropland, removal of stones from the plots is the most laborious part of the work. After an initial removal of stones, the land is tilled and appearing stones are again removed. This process is repeated several times.
Year round maintenance work is required to keep the canal functioning. Maintenance work on the cropland includes stone removal, manuring of potatoes fields, weeding and tilling.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
GBAO
Especificação adicional de localização:
Vanj / Udob / Trit
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
This technology can be found all along Vanj valley.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
A traditional agroforestry system is implemented on a steep slope above the village, as there is a lack of flatter cropland. This requires improved and carefully adapted land practices.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Preserva ecossistema
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrofloresta

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- cereais - trigo (inverno)
- culturas forrageiras - alfalfa
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- vegetables, sea-buckthorn
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
- frutos secos (castanhas do Brasil, pistache, nozes, amêndoas, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: May - September

Floresta/bosques
- willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)"; withthorn, dog rose
Produtos e serviços:
- Frutas e nozes
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water scarcity is the major factor limiting vegetation growth and agricultural production in this arid areas. The soils are stony and slopes are steep (20-30 degrees).
The area is irrigated from streams fed by snow and glacier melting, and therefore water availability is strongly depending on yearly snow precipitation. If due to climate change snowfalls are decreasing in the future, this is a threat for agriculture in the region.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As the area is on steep slopes there is a high risk of small land slides triggered by irrigation. Fast snow melting in spring time may also cause land slides.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Pastagem
Comentários:
Extensive grazing land
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M3: Disposição de acordo com o ambiente natural e humano
Comentários:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking crust / sealed surface, breaking compacted topsoil, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bh: loss of habitats, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts (in years with droughts part of the perennial vegetation may dry up), land tenure (common grazing land), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to irrigation water, access to markets)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (early grazing, overgrazing), labour availability (mostly manual work and thus labour intensiv), governance / institutional (limited access to market, no water association)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Vast practical knowledge is required, through practical experiments, the practices were improved over time.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Agronomic measure: crop rotation on wheat fields
Material/ species: perennial fodder plants (alfa-alfa)
Remarks: high density of alfa-alfa plants
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cow manure
Quantity/ density: 15
Remarks: for patatoe fields
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: "super phosphat" or "silitra"
Quantity/ density: 0.025
Remarks: for wheat fields
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Contour tillage
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)";
Fruit trees / shrubs species: sea-buckthorn, walnut, plum, appel, pear, apricot, mirabelle, whitethorn, cherry, dog rose
Grass species: graminoids and legumes
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2500
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 750
Construction material (earth): The waterways are all dug into the ground, and are mostly fortified with bushes and trees.
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: extensive grazing to agroforestry
Layout change according to natural and human environment: carefully designed layout taking advantage of flatter areas for cultivation of annual crops, and protecting steep slopes with perennial tree and bush cover
Control / change of species composition: mix of cultivated and wild plants (trees, bushes and grasses)
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tajik Somoni
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4,4
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
30.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | spring |
| 2. | Construction of irrigation canal | autumn |
| 3. | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | spring |
| 4. | Alfa-alfa seeds (12kg/ha) | for 4 years, then can produce own seeds |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | Persons/day | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Mão-de-obra | Construction irrigation canal | Persons/day | 100,0 | 30,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | Persons/day | 30,0 | 30,0 | 900,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Alfa-alfa seeds | kg/ha | 6,0 | 20,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 4020,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 913,64 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wheat (barley) sowing | anually |
| 2. | Wheat (barley) sowing | |
| 3. | Tilling potato fields | 3 times per growing season |
| 4. | Irrigating wheat (barley, alfa-alfa) | times per growing season |
| 5. | Planting potato | during planting |
| 6. | Planting potato | |
| 7. | Applying fertilizer to wheat fields | 3 times per growing period |
| 8. | Maintenance of canal and on-farm water distribution network | spring and after rains |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing wheat with ochses | Persons/day | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Tilling with ochses | Persons/day | 6,0 | 40,0 | 240,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Irrigating wheat, barley alfalfa | Persons/day | 6,0 | 30,0 | 180,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting potatoe | Persons/day | 8,0 | 30,0 | 240,0 | |
| Equipamento | Ochses for wheat sowing | Ochses/ha | 2,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Ochses for potatoe tilling | Ochses/ha | 6,0 | 30,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Donkey for carrying dung to the fields | loads | 120,0 | 0,66666 | 80,0 | |
| Equipamento | Labour: Going with donkeys | Persons/day | 8,0 | 40,0 | 320,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Wheat seeds | kg | 200,0 | 1,2 | 240,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | tons | 12,0 | 50,0 | 600,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Poatoe seedling | kg | 800,0 | 1,0 | 800,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer for wheats | kg | 140,0 | 0,58571 | 82,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 3102,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 705,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs were calculated fro an area of 5 ha. The length of the irrigation channel from the creek to the plot is 730 m.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
With regard to the establishment costs, the most determining factors are: the distance to the creek from where water is channeled away and the steepness of the slope and amount of stones when preparing the land for annual cropping. With regard to the maintenance costs it is the exposure of the water channel to rock fall and small land slides.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Most of the precipitation consits of snow, the main rainfall period is March / April
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Thermal climate class: temperate. high mountain area
A2240 m asl
gricultural areas need irrigation, which is supplied by snow and glacier melt
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 2240 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich.
10% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The here described farmers family has very limited off-farm income. The farm provides sufficient fuel, fodder, fruits and potatoes for subsistence farming.
In general, seasonal migration to Russia is widespread in the area, which provides additional income in form of remittances. Only households with only young children, elderly and sick persons have no family member working in Russian.
Level of mechanization: One uses ochses for plowing, motorized is really rare.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
The land use right for the individual farmer is documented with an official land user certificate.
Water use right has been agreed on with the village council.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
1 Household
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos