Alfalfa intercropping in terraced fruit orchard [Afeganistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Aqila Haidery
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Baghe Tabaqabandi
technologies_1198 - Afeganistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Sthapit Keshar
HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
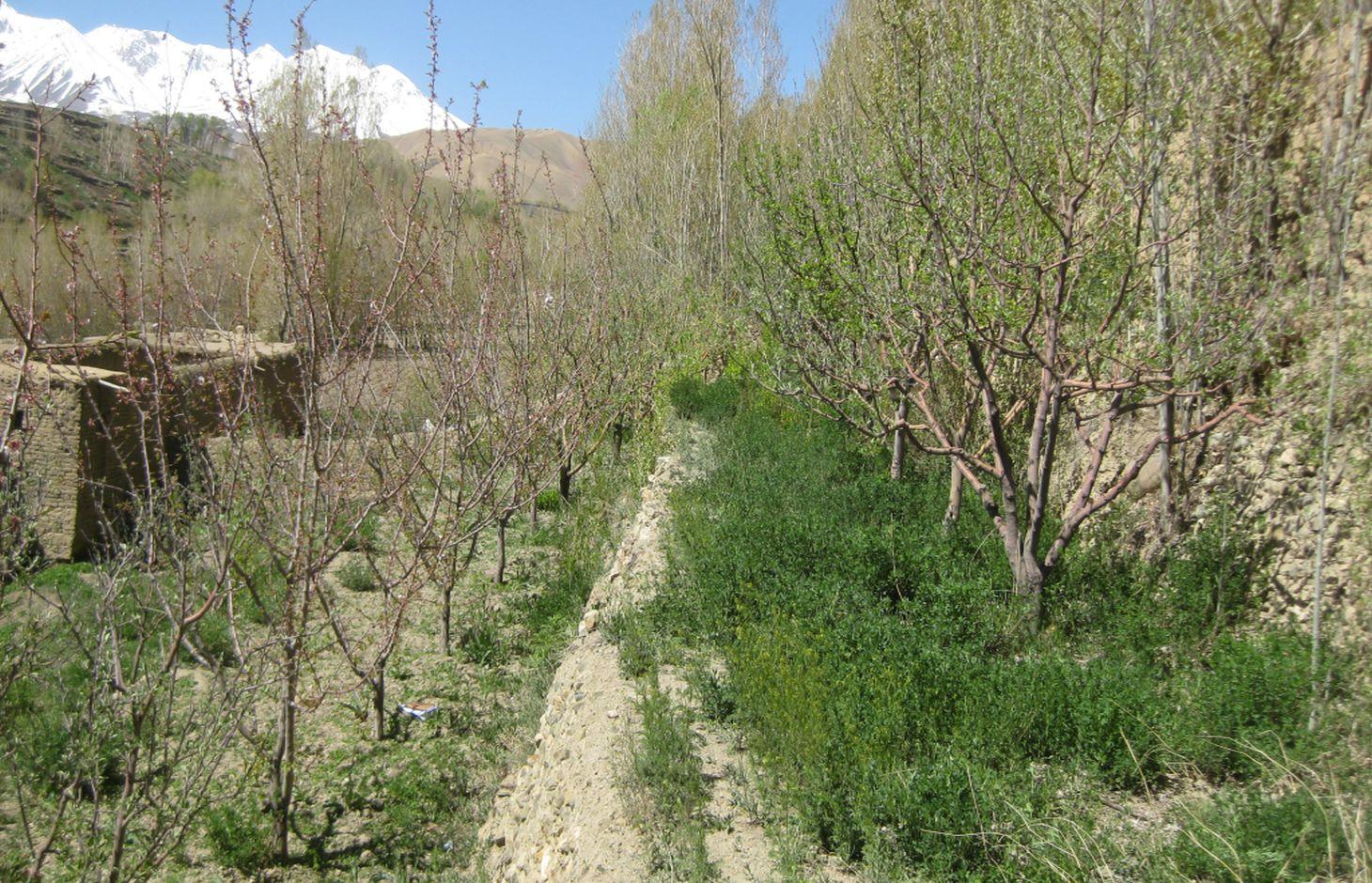
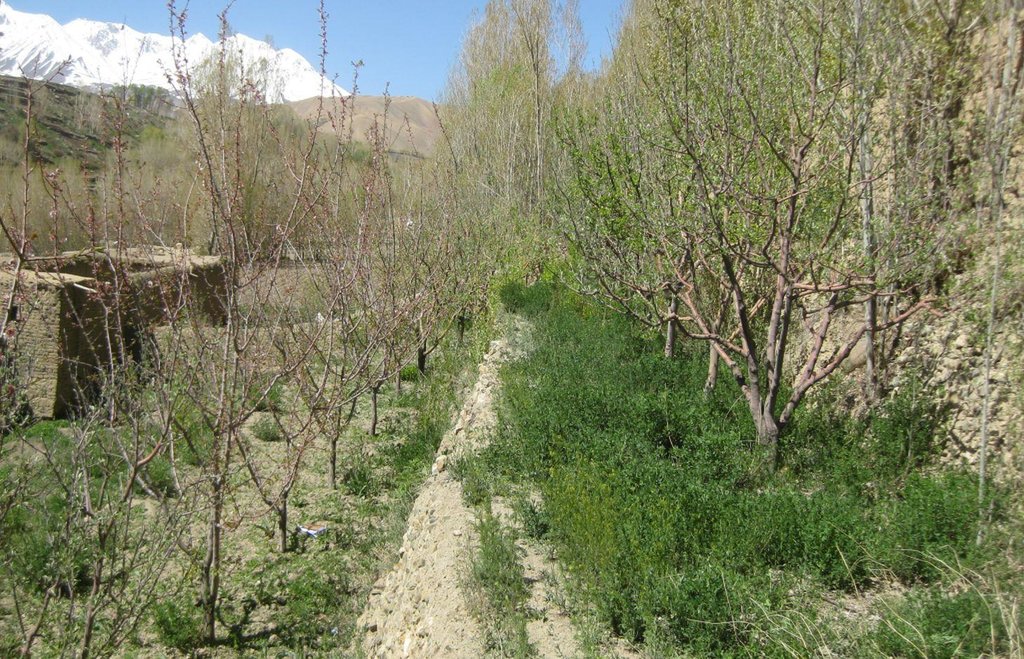
Terraced orchard with alfalfa cultivation for fruit and fodder production and soil and water conservation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Alfalfa inter-cropping in terraced fruit orchard technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation with financial support of Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
In the semi-arid regions of the Central Highlands in Afghanistan, land is intensively used for the
cultivation of subsistence (wheat) and cash crops. The technology presented here provides an economically sound solution for soil and water conservation. In this example, Alfalfa is grown in the spaces between the young trees to make use of the soil, light and water. The soil and water conservation quality of the technology is further enhanced with terracing to capture water.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of establishing the fruit orchard with Alfalfa was to produce fruits for both
consumption and income, as well as for animal fodder. Terraces are important for retaining soil moisture, reducing soil erosion and preventing nutrient leaching. Alfalfa increases soil fertility as it fixes
nitrogen.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area under this specific technology is less than 0.03 ha. The technology was established by the land user five years ago without external support. In the past, the site was sloping agriculture land used for potato and wheat cultivation, the two major staple crops in Bamyan. Animal manure, with small quantities of chemical fertilizers, were used to maintain the soil fertility. The farmer, Haji Hussain, learning from similar examples from Kabul, applied this technology on his private land
with sight modifications by including terraces for soil and water conservation. For the construction of one terrace, 14 person days are needed. The size of one terrace was about 43 m in length and 4 m in width.Initially the terraces were used for vegetable cultivation. Later on, he planted mainly apple and apricot trees and a few saplings of pear and plum. Two varieties of apple (red and yellow) were planted in the orchard and the distance between two trees in a row was about 3 m (for more details, please see the technical drawing). The saplings were prepared by the farmer himself using grafting. The trees vary in age, from 3-5 years. Alfalfa was planted 1-3 years ago. The farmer applies 1 kg urea and DAP per tree every spring in addition to a small quantities of manure. The orchard requires irrigation almost every week from mid-spring to autumn from a nearby canal. The water distribution and operation and maintenance of the irrigation infrastructure is regulated by a Mirab, or “Water Master”, elected by the water users and farmers.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan Center has temperate and semi-arid climate with an average annual rainfall of about 230 mm. The area receives snow during the winter season and the temperature can drop below -20 degree centigrade.There is one growing season from April to September. The soil in the orchard is sandy loam with moderate soil fertility. Orchards are considered to be more profitable by the land user than growing crops like wheat and potato. Before applying this technology, the average annual income of the owner from 0.3 ha land was 9,000 Afghani, equivalent to approx 180 USD. While after the application of terraced orchard with Alfalfa cultivation technology, his average annual income from 0.3 ha increased to 45000 Afghani or 900 USD.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Afeganistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Bamyan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Bamyan Centre / Shinya Fuladi
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
0,0003
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0003 km2.
Alfalfa is cultivated in apple and apricot mixed terraced orchard for multiple benefits.
2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The farmers learnt this technology by seeing others apply it.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agrossilvipecuária

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
- Wheat, Alfalfa
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
- frutas com caroço (pêssego, damasco, cereja, ameixa, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: April-September
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
- Pastos melhorados
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): In the past, the orchard site was a sloping land and used for cultivating wheat and potato without soil and water conservation measures. This resulted in soil erosion, soil fertility decline and low crop production.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Due to sloping land, most of the animal manure applied to the crops used to get leached affecting crop production.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V5: Outros

Medidas estruturais
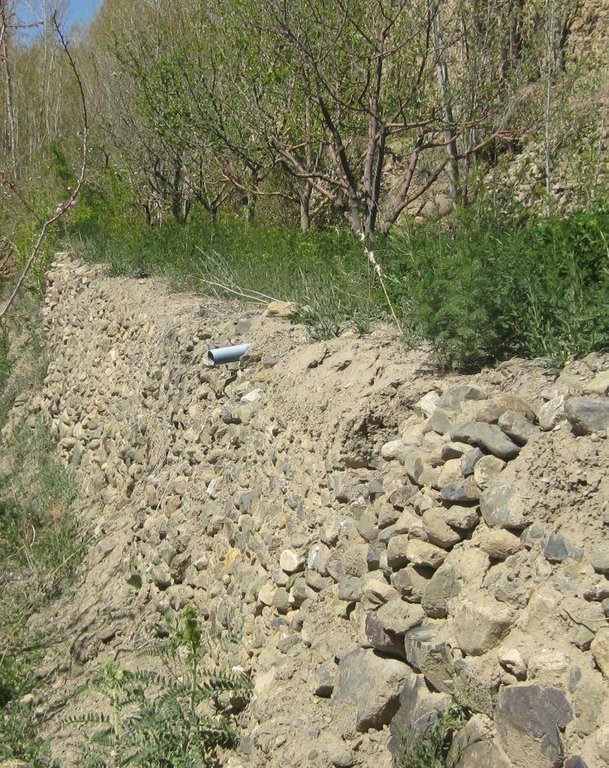
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Specification of other vegetative measures: fruit trees and alfalfa
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Agriculure on sloping land without conservation measures), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Due to sloping land), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge about sloping agriculture land soil and water conservation technologies)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
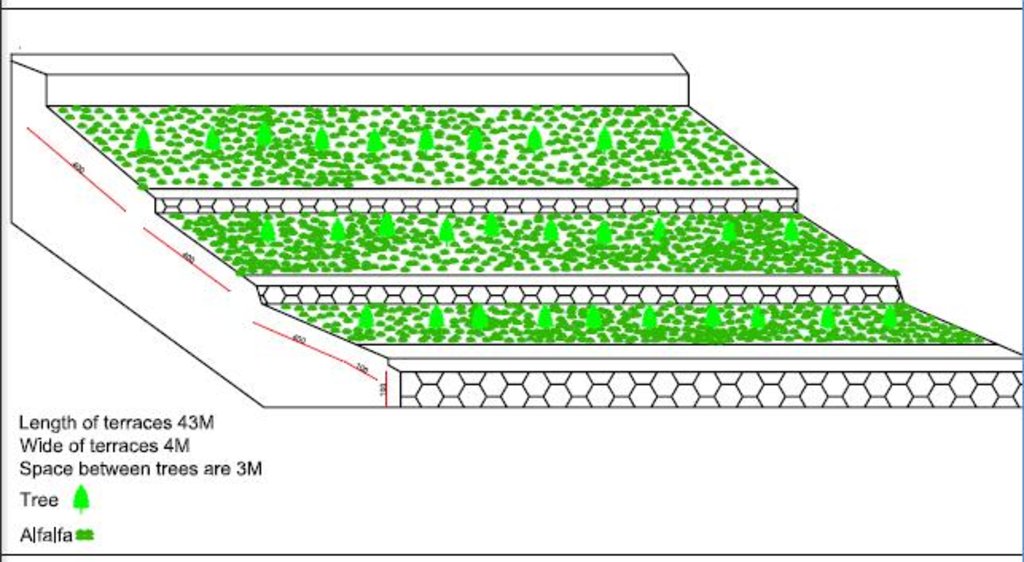
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Layout of the terraced fruit orchard with alfalfa crop.
Location: Shenya, Foladi valley. Bamyan
Date: 14.06.2016
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 800
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Apple and Apricot
Perennial crops species: Alfalfa
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2%
Terrace: bench level
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 43
Bund/ bank: graded
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 1.3
Construction material (earth): for making terraces
Construction material (stone): for making risers
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Change of land use type: Conversion of annual cropland into perennial fruit orchard with perennial fodder crop
Autor:
Rohullah Zahedi, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, Afghanistan
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Afghani
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
57,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
400
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantation of saplings | Late Autumn or early spring |
| 2. | Plantation of alfalfa | early spring |
| 3. | Construction of terraces | Dry season |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of terraces | persons/day/ha | 400,0 | 400,0 | 160000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Plantation of saplings | pieces/ha | 800,0 | 150,0 | 120000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Plantation of alfalfa | kg/ha | 100,0 | 250,0 | 25000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 305000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 5350,88 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilizer application only | Spring |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer application only | kg/ha | 800,0 | 16,0 | 12800,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 12800,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 224,56 | |||||
Comentários:
The costs are extrapolated for 1 ha. Current (2014) labour and currency exchange rates were used for calculations.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour for construction work is the most determinate factor affection costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
230,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Most rainfall is recorded in the months of April and May. Rainy season begins in April and ends in June.
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. Temperatures can drop to below -22 degree centigrade
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Level terraces
Altitudinal zone: About 2600 m above mean sea level
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium due to use of manure, fertilizer and also alfalfa
Soil drainage / infiltration is good due to vegetation
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Access to irrigation water canal
Water quality (untreated): From the canal.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Many works concerning orchard maintenance and harvesting are done by women as well.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: Mainly land users with large irrigated agriculture land holdings. The majority of the population has less than 1 ha land thus off-farm income seems to be very important.
Level of mechanization: He performed with his son and family
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
2-5 ha: This applies to a very small extent of the population like this land user
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Water use rights are common and organised. The village has access to sufficient irrigation water throughout the year.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
420 kg
Comentários/especificar:
Fruit production
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Alfalfa
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Alfalfa
Produção animal
Comentários/especificar:
Due to alfalfa consumption
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Pruned twigs can be used for firewood
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10,000 Afghani
Quantidade posterior à GST:
45,000 Afghani
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Due to more income and production
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
Due to greenery and sound of birds.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Farmer to farmer knowledge exchange
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The technology help in increased income which can be used for buying food. Families consume more and a greater variety of foods which is beneficial for health.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
More species, cultivated and natural
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
E.g. Birds
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Fruit tress are sensitive to frost | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
1 household
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There are other 20 land user families in the region who has applied this technology.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a small but growing trend towards spontaneous adoption of the technology among farmers with access to irrigated lands.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The technology has multiple benefits and needs less labour inputs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology system can be enhanced by including honeybee keeping. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Reduced soil erosion and improved water management compared to sloping agricultural land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Efficient use of water by the application of mulching and pitcher irrigation. Use of well decomposed compost for increasing production and reinforcement of soil quality. Reduced usage of chemical fertilizer. |
|
The technology can be easily applied. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Exposure visit of farmers to improved orchard cultivation practices. |
|
Including perennial fodder crop like alfalfa has multiple benefits. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Alalfa is a water demanding crop. Other nitrogen perennial high quality perennial crops like sainfoin could be tried by the farmer. |
|
The demand for fruits is high, therefore, it contributes to the increased income of the farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Production could be increased through better orchard management. Farmers may need training and information on improved methods through agriculture extension departments and concerned non-governmental organisations. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Fruit trees are sensitive to frost. | Relevant research organisations need to develop tolerant varieties through participatory technology approach. Sharing better practices from other countries may be useful. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The technology depends on a constant supply of irrigation water. | Demonstration of improved orchards with a focus on water conservation and soil nutrient management (use of compost, mulch, pitcher irrigation, etc.) |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos