Cultivation of blueberries on infertile/degraded soils using plant pots [Bósnia e Herzegovina]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Melisa Ljusa
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Donia Mühlematter, THEODORA FETSI, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Kontejnerski uzgoj borovnice na neplodnim ili degradiranim tlima
technologies_4126 - Bósnia e Herzegovina
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Čustović Hamid
Universiyt of Sarajevo, Faculty of Agriculture and Food Sciences
Bósnia e Herzegovina
co-compilador/a:
Agronomist of the Živinice Municipality:
Butković Mirsad
Municipality of Živinice - Department of Local Economic Development, Finance and Treasury
Bósnia e Herzegovina
usuário de terra:
Đogić Alija
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
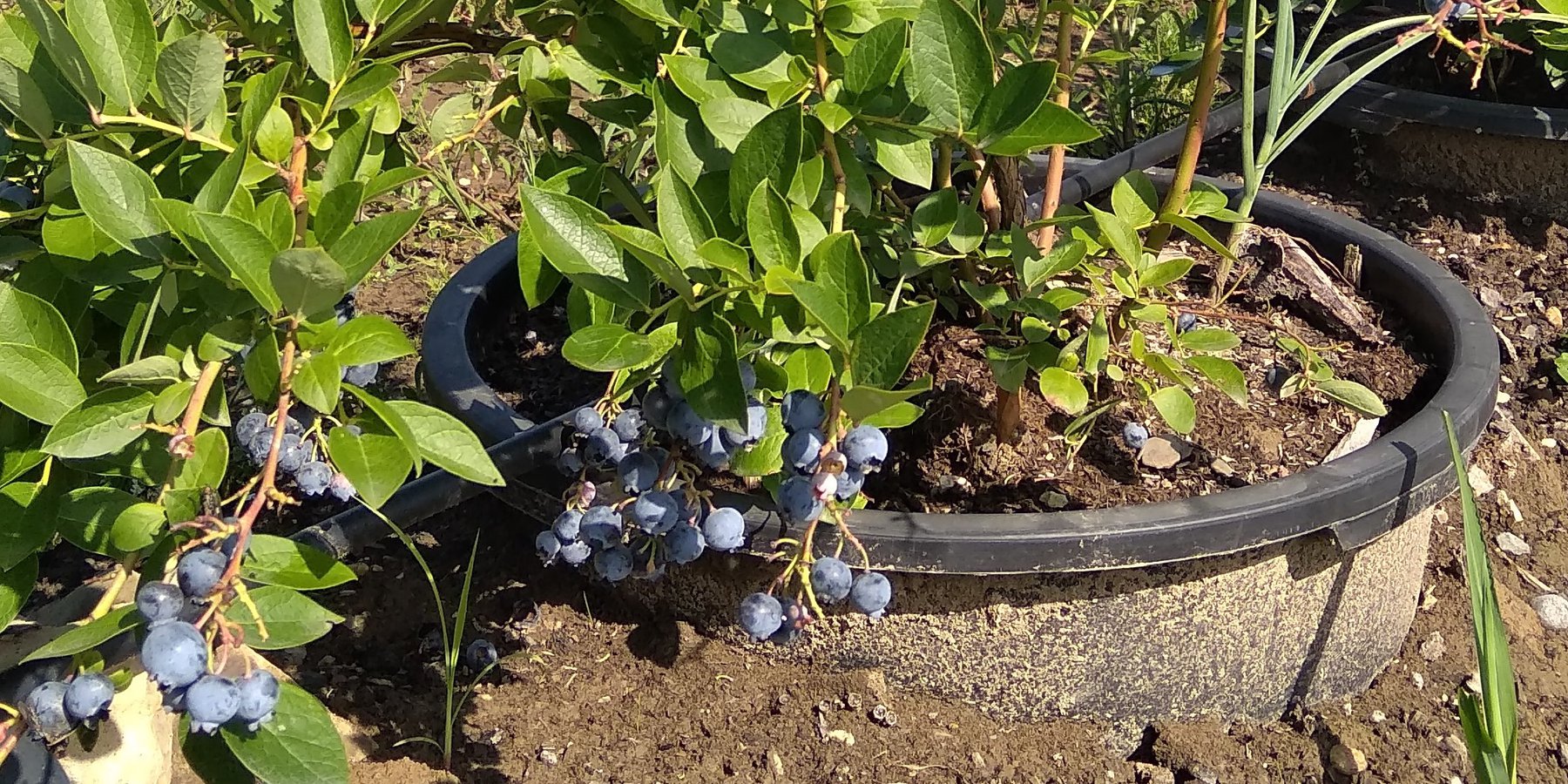
Establishment of blueberries cultivation in plant pots on soils with bad physical or chemical properties. The technology improves productivity and generates income for the farmers. The implementation requires drip irrigation system.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
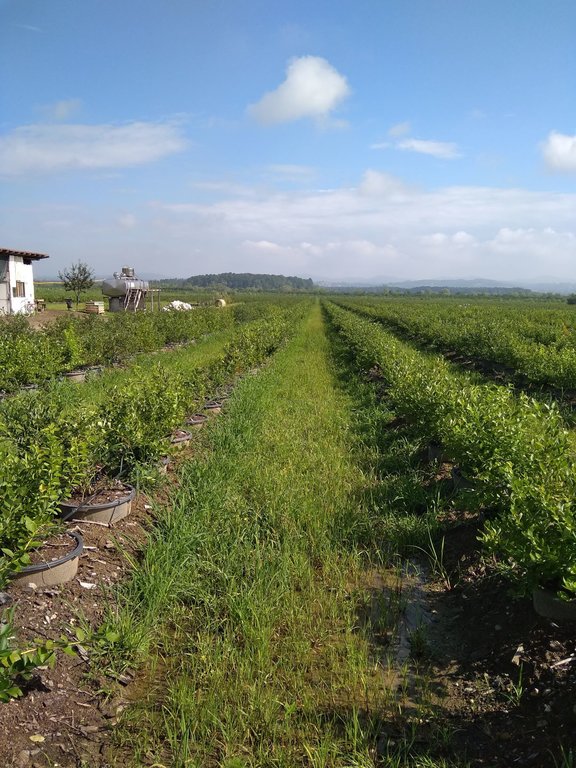
The cultivation of blueberries in plant pots has been successfully implemented in the area of Živinice municipality - on soils of poor composition, physical properties and low fertility. Many efforts have been made to introduce a conventional production of blueberries but did not bring the expected results due to the bad soil quality.
The soil (Stagnogley) is poorly permeable to water, so even moderate rainfalls cause water remain on the surface, making it difficult or completely impossible to cultivate the land. In addition, soils of high acidity are required for the successful cultivation of blueberries. Planting blueberries in a conventional way is often carried out on soils where the acidity is increased by various additives (often with wood sawdust or similar wooden materials). Practical experience has showed that in the course of time the acidic properties of the soil in the zone of the development of the blueberry root change, i.e. soil/substrate acidity decreases due to resorption processes on the primary soil. Todays' market offers multi-component substrates for the cultivation of blueberries, which, in addition to their adequate acidity, have other properties necessary for a good development of the blueberry's root system. These substrates were also used in some localities of the municipality of Živinice in conventional or modified conventional planting of blueberries (on embankments using soil and commercial substrates). This technique did not yield satisfactory results, probably because of the loss of substrate properties (decrease of soil acidity) due to resorption to the nearby original soil. The substrate keeps its desirable properties much longer if it is put into the planting where blueberries are being planted.
The basic advantage of this technology is its ability to be applied on practically all soils of poor agricultural-productive properties, including heavily degraded and low water permeable soils. Even if the cost for introducing the technology is relatively high, its maintenance is reduced to standard agro-technology (fertigation, plant protection, weed control, harvesting, etc.) due to the type of crop. In the Živinica municipality, technology is currently being applied only in the cultivation of blueberries. The results have shown that the cultivation of blueberries in plant pots provides a yield of about 15 t/ha, which is about 5 t/ha (50%) higher than in the conventional cultivation of the blueberries. The farm on which the technology is described cultivated blueberries of the Duke variety on 8 ha whose fruits are sold at prices between 3.50 and 4.50 USD/kg. The estimated life span of the blueberries grown in plant pots under full yield is 15 years.
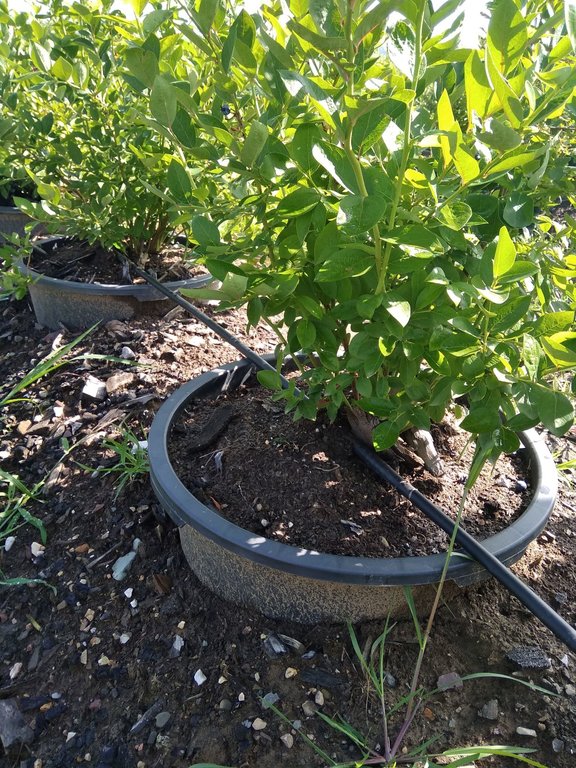
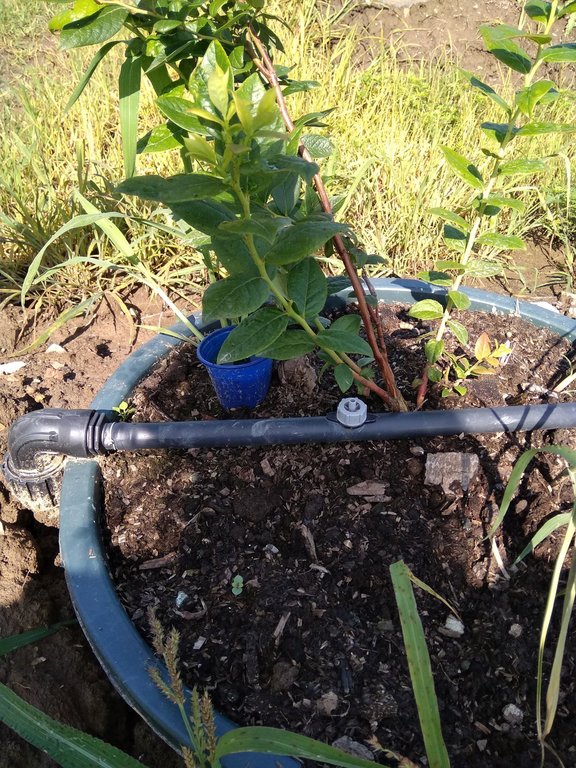
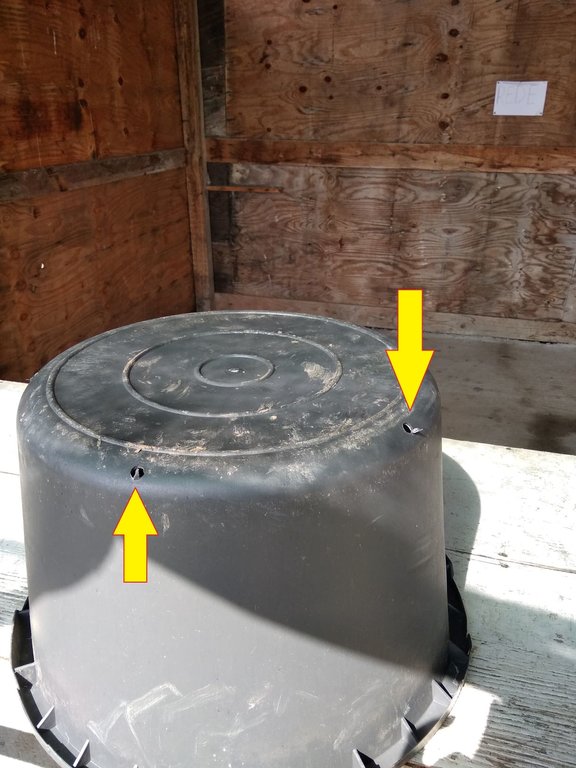
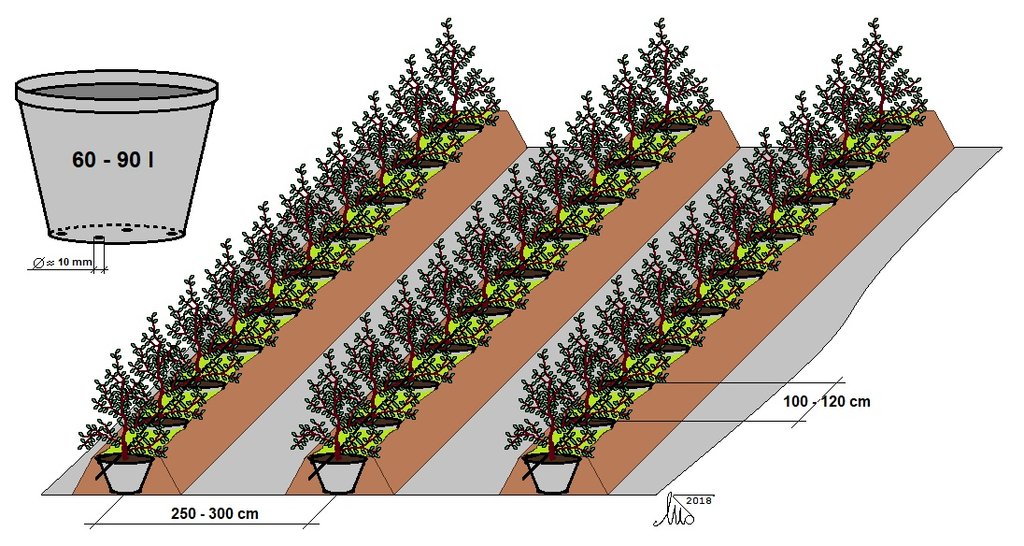
Regarding the technical characteristics of the SLM technology, the plant pots with blueberry plantings are placed in rows of low trenches with a distance of 100-120 cm between the plant pots (from center to center); and 250-300 cm between rows. The plant pots (60 to 90 liters) are placed in later formed embankments (trussing with the original soil), thus ensuring the stability of the plant pots (e.g. from wind) and more favorable temperature and humidity conditions of the substrate in the plant pots. The technology implies possession and use of the drip irrigation system, using the water collected in accumulations and distributed from tanks situated on the farm.
The technology offers relatively innovative use of infertile or degraded soils for the intensive and profitable production of blueberries or other crops, primarily berry fruits. Positive experiences from the implementation of the technology on about 8 ha, on the observed farm resulted in the replacement of the earlier conventionally planted and grown blueberries in the wider area of Živinice. By expanding blueberries cultivation in wider areas, the municipality is considered among the leading blueberry producers in the Balkans.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bósnia e Herzegovina
Região/Estado/Província:
Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Tuzla Canton
Especificação adicional de localização:
Živinice municipality
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2014
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was introduced by the endorsement of the Municipality.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Comentários:
The land, where the described technology is applied, is characterized by bad soil physical properties (heavy soils, poorly permeable to water, even moderate rainfalls do not allow movement of workers and mechanization).
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Crop management
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
- Pu: perda da função bioprodutiva devido a outras atividades

Outro
Comentários:
The technology could be applied on practically all kinds of degraded lands if there is a possibility to provide (preferably) drip irrigation.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Adaptar à degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1 ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
29.25 USD
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchasing of plantings | Any time |
| 2. | Purchase of substrate | Any time |
| 3. | Ground leveling (if necessary) | Any time |
| 4. | Filling the containers with substrate and planting blueberries in containers | Any time |
| 5. | Formation of rows of containers | Any time |
| 6. | Trussing of rows of containers by original soil | Any time |
| 7. | Installation of drip irrigation system | Any time |
Comentários:
Preferably blueberry plantings are 3 or 2 years old, in plant pots (containers) not smaller than 2 liters.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Filling the containers with substrate and planting of blueberries | Person day | 28,0 | 29,25 | 819,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Forming and trussing the rows of containers (embankments) | Person day | 30,0 | 29,25 | 877,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | (Mecahnization for ground leveling - optional) | Hour | 4,0 | 70,2 | 280,8 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Blueberry plantings in containers (2 or 3 L plant pots) | Piece | 2800,0 | 5,26 | 14728,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Plastic containers (65 l) | Piece | 2800,0 | 5,47 | 15316,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Drip irrigation system (including water tank and pump) | ha | 1,0 | 13460,0 | 13460,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Multi-functional substrate for blueberries | L | 182000,0 | 0,07 | 12740,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 58221,3 | |||||
Comentários:
Ground leveling with use of mechanization is not necessary on plain or relatively plain terrains.
The cost of 2 or 3 years old blueberry planting in small (2 l) container include delivery (on farm) costs.
The costs of plastic plant pots (65 l) and substrate for blueberries include delivery (on farm) costs.
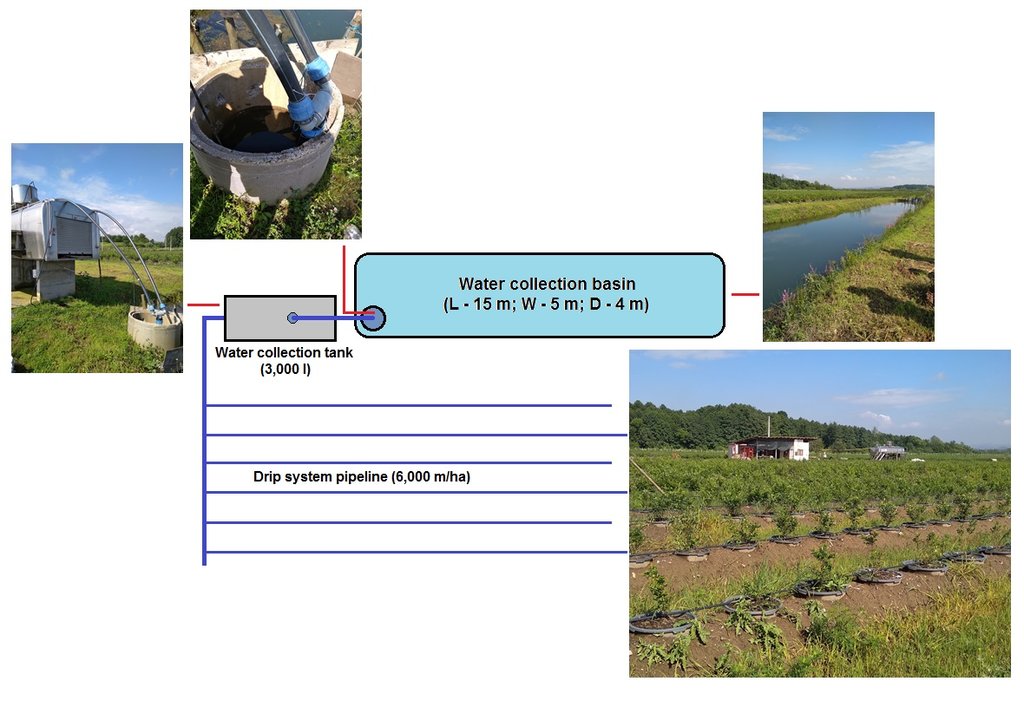
The price of drip irrigation system include delivery (on farm) and installation costs. It includes water reservoir (3,000 l), pump for water transfer from the basin to the reservoir and construction of well for pump in the basin. The costs of the irrigation system does not include construction of the basin for collection of water (it was constructed earlier, by previous land user), but one can calculate the costs of such structure (basin: L - 15 m, W - 5 m, D - 4 m) under local conditions. Current estimate of costs for such construction in Živinice municipality is around 4,000 USD. The total length of drip system pipeline per ha for the presented technology is 6,000 m.
Under the concrete conditions, the land user handles land leased from the municipality. The land rental charges are not included in the costs of establishing or maintaining the technology since they are, in this case, favorable (103 USD/ha/year) and can vary considerably under other conditions.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking and maintenance of embankments (rows of containers) | Once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of drip irrigation system | During the growing season |
| 3. | Maintenance of blueberry orchard | During the growing season |
Comentários:
During the exploitation of the technology ordinary agro-technical measures (plant protection, applied in growing of blueberries) are applied and they are not listed here as the technology maintenance activities.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Checking and maintenance of embankments (rows of containers) | Person day | 10,0 | 29,25 | 292,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Maintenance of drip irrigation system | ha | 1,0 | 344,08 | 344,08 | |
| Outros | Maintenance of blueberry orchard (lump sum) | ha | 1,0 | 20644,57 | 20644,57 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 21281,15 | |||||
Comentários:
The costs of maintenance of the blueberry orchard include all agro-technical measures and works (fertigation, plant protection, weed control, harvest) applied in growing of blueberry (Duke variety) in plant pots. The farm provide water free of charge, from its own drip irrigation system.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The prices of blueberry plantings, containers, and multi functional substrate for blueberries on the market.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
894,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The highest precipitations appear during spring and early summer, (June 111 L/m2; February 55 L/m2). Heavy downpours during the summer are one of the climatic features of this area.
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Tuzla
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Qualidade da safra
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Compactação do solo
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | muito bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | muito bem |
Comentários:
The technology also copes very well with annual rainfalls which, due to gradual climate change, are characterized with extreme fluctuations (long dry periods, mostly during the growing season, and with intense short time rainfalls, mostly during early spring and late autumn).
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Much more profitable agricultural production compared to previous use of the land characterized by heavy, less fertile soils unfovorable for most of agricultural crops growing. |
| Decreased workload compared to conventional cultivation of blueberries. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Possibility to organize profitable agricultural production on less fertile, non fertile or degraded lands. |
| Possibilities to apply the technology at the landfill sites of many coal mines in the region. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Relatively high costs of the technology introduction due to high prices of the inputs for blueberry cultivation in plant pots. | Cultivation in plant pots could be applied with other crops whose plantings are cheaper and which does not need specific, multi component, expensive substrate. |
| Necessity of drip irrigation system. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Relatively short period of the exploitation of the technology (an expert estimate: 15 years). | Producing of the goods (fruits in this case) with high market prices. |
| Due to the high introduction costs the technology could be reasonably applied in growing of highly priced crops. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
In total, three field visits and surveys were conducted from May to October 2018 during which blueberry production plots (fully conventional, modified conventional - embankments, and plant pot growing) were examined.
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
The most valuable information regarding the technology were provided by agronomist/technician Mr. Alija Đogić who manage blueberry growing plots on the spot where the technology was described.
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
Valuable information, especially about the possibility of spreading the technology to the degraded lands in the area of coal mining, were provided by the engineer Mr. Mirsad Butković from the Živinice municipality administration.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
10/07/2018
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos