Top down approach [Руанда]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Desire Kagabo
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: David Streiff, Joana Eichenberger
Amabwiriza aturutse ibukuru
approaches_2465 - Руанда
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Rwanda Agriculture Board (Rwanda Agriculture Board) - РуандаНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - Италия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
01/01/2011
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП

Radical Terraces [Руанда]
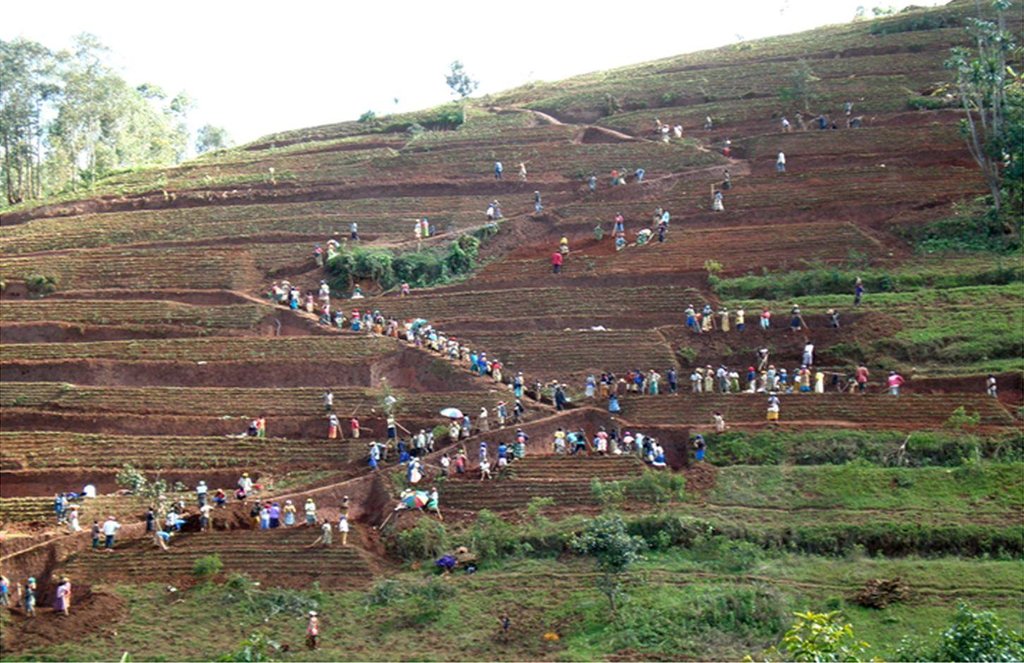
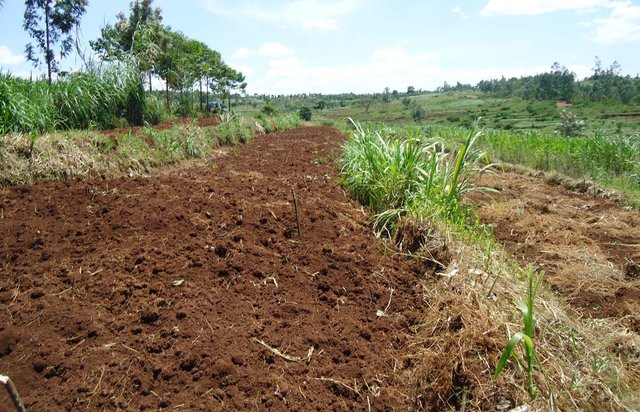
Locally referred to as ‘radical terracing’, the method involves earth moving operations that create reverse-slope bench terraces which have properly shaped risers stabilized with grass or trees on embankment to avoid collapse.
- Составитель: Desire Kagabo
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
This is a top down approach to technology development and dissemination with limited involvement of intended beneficiaries.
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
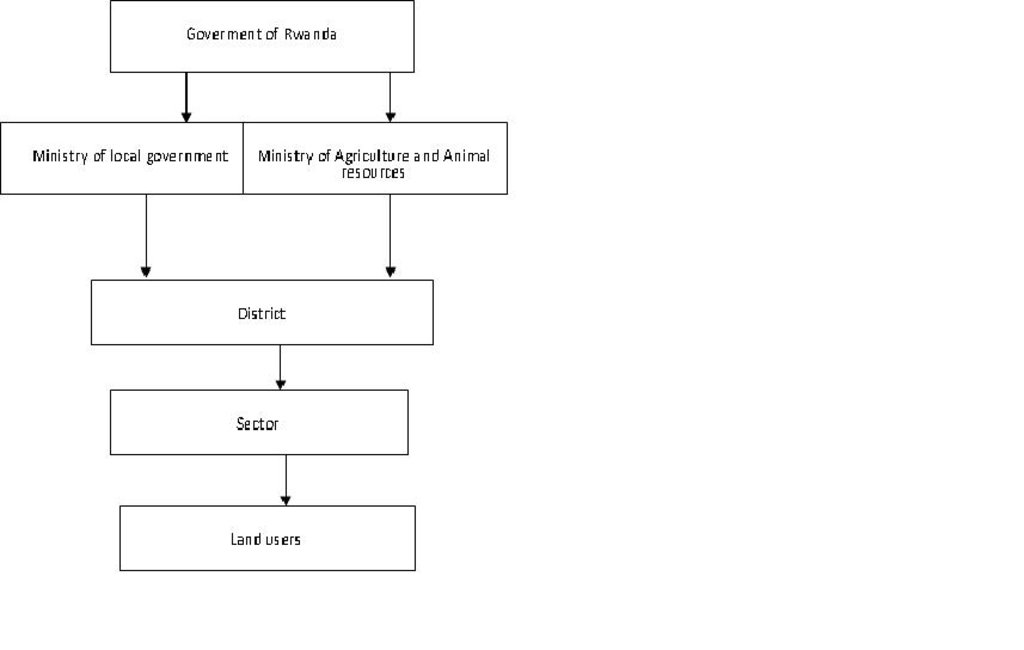
Aims / objectives: The objective of the top down approach is to assign the state a crucial role to drive a designed rural development and land management master plan that needs people to implement it.
To bring farmers together to address an identified problem such as to improve the socio economic situation of rural areas, to prevent , to conserve and to rehabilitate on-site damages caused by land degradation and erosion.
Methods: The top down approach here refers to the level of farmer participation in relation to shared decision making when establishing bench terraces/soil conservation practices in Rwanda. The focus being particularly on the role of farmers in the decision making process during two major phases of the process of terrace construction including: (1) when and where to construct bench terraces in communities and the criteria for site and beneficiary selection. The level of farmer participation and decision sharing have the potential of in increasing the ownership of the of the existing or future bench terraces, hence to ensure its sustainability. Recent studies assert that most of the terraces that are constructed are supply driven and that farmers do not participate in the decisions regarding where and when to construct them. When farmers do participate, it is mostly only through some consultation and their own efforts to mobilize collective labor for the construction of the terraces.
Stages of implementation: Stage one comprises the analysis of current or initial adoption decisions of soil conservation practices, while stage two assesses farmers’ ability to continue the use of these practices. Stage three analyses future adoption proxied by farmers’ willingness to uptake more soil conservation practices.
Role of stakeholders: The state plays a prime role in bench terraces development and the role of other stakeholders (e.g. extension agents, farmer associations) is marginal. Farmer associations involvement is is limited to mobilizing labor and, sometimes, to identifying land for terracing. Extension agencies/services are involved in providing advice to individual farmers or farmers grouped in cooperatives. Community representatives, whom are members of the farmers’ cooperatives themselves, are trained to provide additional support and advice to farmers.
Other important information: This SLM approach argues for a role of the state with top-down and coercive measures in the development of soil conservation practices, particularly bench terraces. Currently there is a two pronged approach based on the realization that bench terraces are ready made constructions which require substantial financial and institutional investments. Mustering labor and resources for the construction and maintenance of bench terraces remains a key aspect of the state’s conservation drive. State-farmer relationships, therefore, continue to be essential to soil conservation efforts in Rwanda and to bench terrace construction in particular.
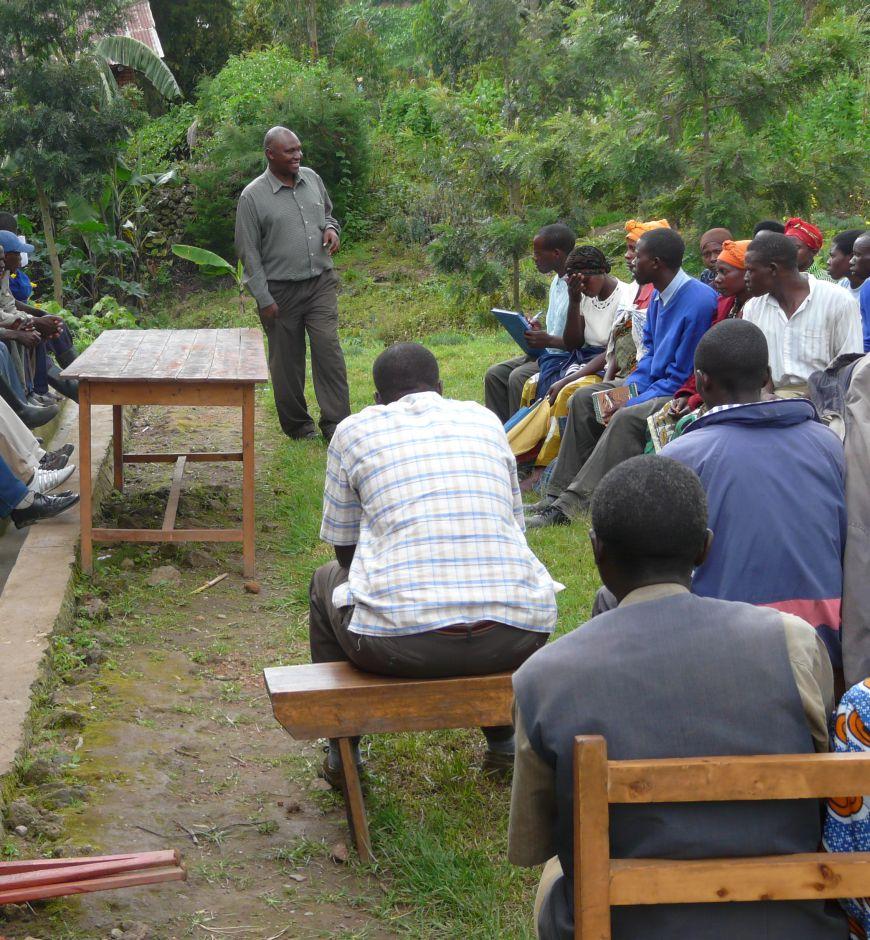
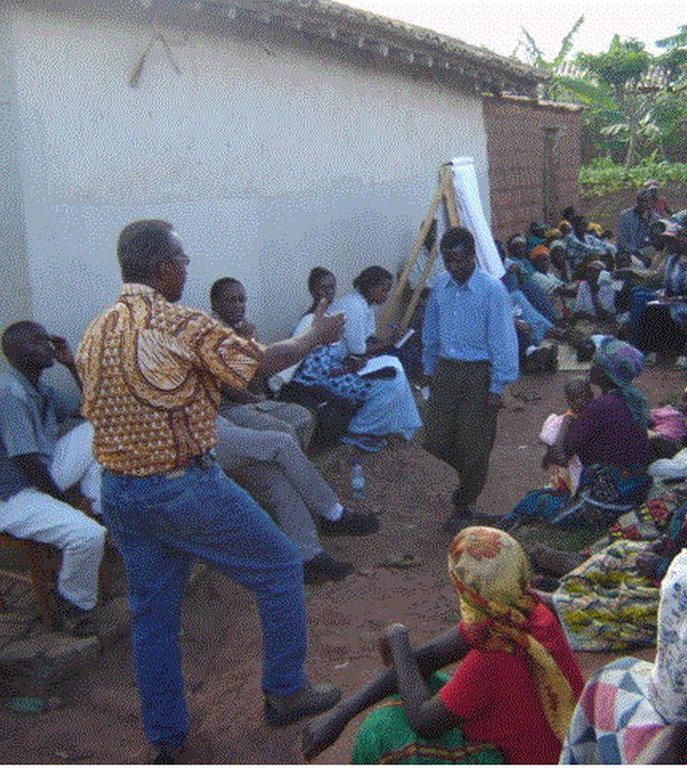
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Руанда
Административная единица (Район/Область):
East
Более точная привязка места:
Kayonza
Комментарии:
The area is not well known, it is approximately estimated
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
1950
2.7 Тип Подхода
- government based
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Increase soil fertility, good practices of land management in general)
To raise awareness to land users for a particular problem and involve them to get to the right solution
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: low agricultural production due to a poor agriculture practice and lack of technical knowledge by farmers
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Наличие/ доступность финансовых ресурсов и услуг
- затрудняют
terraces and trenches require high investment for establishment and maintenance.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: the government support and other local and Internationale NGOs is highly required
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- содействуют
- затрудняют
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки
- затрудняют
lack of technical knowledge and cohesion between farmers to address the main problem regarding agriculture in their location.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: implementation of agricultural cooperative
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Farmers
There were no limitation all farmers were involved
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
- ученые-исследователи
- местные власти
Local leaders
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
Parliament
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | нет | |
| планирование | нет | |
| выполнение | интерактивное | Land users and local authorities work together to get to greater result. |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | Land users are in daily interaction with Sector Agronomist who is in charge of all agricultural activities in the sector. |
| Research | нет |
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- исключительно специалисты по УЗП
Поясните:
Decisions were made in the ministry of agriculture after consultation of researchers.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by politicians / leaders. Politicians have decided the way of implementation through community work known as UMUGANDA
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Нет
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Описание/ комментарий:
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, умеренно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Укажите тип поддержки:
- финансовая
- повышение компетенций/ обучение
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: local leadres
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, government through measurements; indicators: local agronomist
technical aspects were regular monitored by government through observations; indicators: local agronomist
technical aspects were regular monitored by government through measurements; indicators: local agronomist
socio-cultural aspects were None monitored by government through observations; indicators: local leaders
area treated aspects were None monitored by government through observations; indicators: local agronomist
area treated aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: all person of 18 years and above are involved
no. of land users involved aspects were None monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
no. of land users involved aspects were None monitored by government through measurements; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were None monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Нет
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- 100 000-1 000 000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (planing): 20.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (sensitization and follow up): 25.0%; local community / land user(s) (implimentation): 55.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
Если да, укажите тип(-ы) поддержки, кто ее предоставил и условия предоставления:
inputs (seeds, fertilizers, etc..) provided by the Government
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- сельскохозяйственные
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| семена | профинансированы полностью | |
- строительные материалы
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| material | профинансированы частично | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
After the sensitization by local leaders, activities are done voluntarily or with food-for-work by farmers.
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
the approach helped in the implementation of technologies which improved crop production and soil conservation.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
some project introduced new technology (e.g. one cow per family) with the help of local leaders
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
as the production increase, it increases as well the well being of farmers
6.2 Основные причины, побуждающие землепользователей внедрять УЗП
- рост продуктивности
improve soil quality and crop production
- рост прибыли (доходности) и рентабельности
as production increases this allows farmers to take a part of the production on market
- материальное стимулирование/ субсидии
low cost of inputs as they are provided by the government
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
as production and income increases, its facilitates farmers to access to all sanitary services, etc.
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- нет уверенности
Если нет или нет уверенности, объясните почему:
It require a strong follow up
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| It help farmers to work together for a common issue. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continuous sensitization ) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Improvement of livelihoods (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continuous sensitization) |
| farmers are getting benefits, as it has a direct impact in increasing the soil productivity and improve workability of the land (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continuous sensitization ) |
| the approach helped to establish SLM measures which reduced soil erosion and improve soil quality (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: continuous sensitization) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| lack of strong link in the farmers association and cooperatives | continuous sensitization |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| High costs: farmers depend on external support from the government, they are not willing to invest their labour without payments. | To make the working time as short as possible for the community work so that farmer can plan other income activities after this. |
| lack of land users participation in the design and planing | involve all stakeholders |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Radical Terraces [Руанда]
Locally referred to as ‘radical terracing’, the method involves earth moving operations that create reverse-slope bench terraces which have properly shaped risers stabilized with grass or trees on embankment to avoid collapse.
- Составитель: Desire Kagabo
Модули
Нет модулей