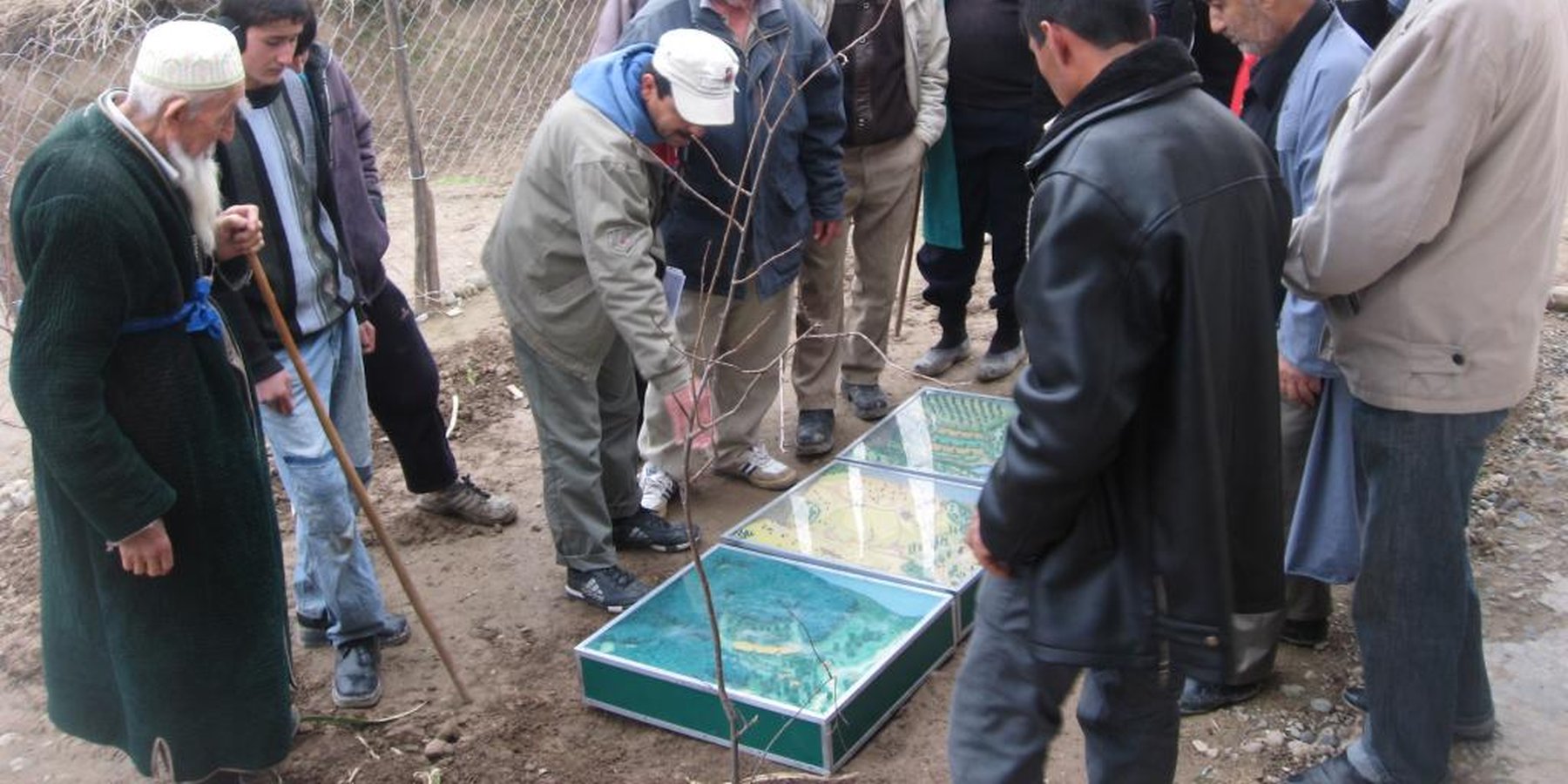
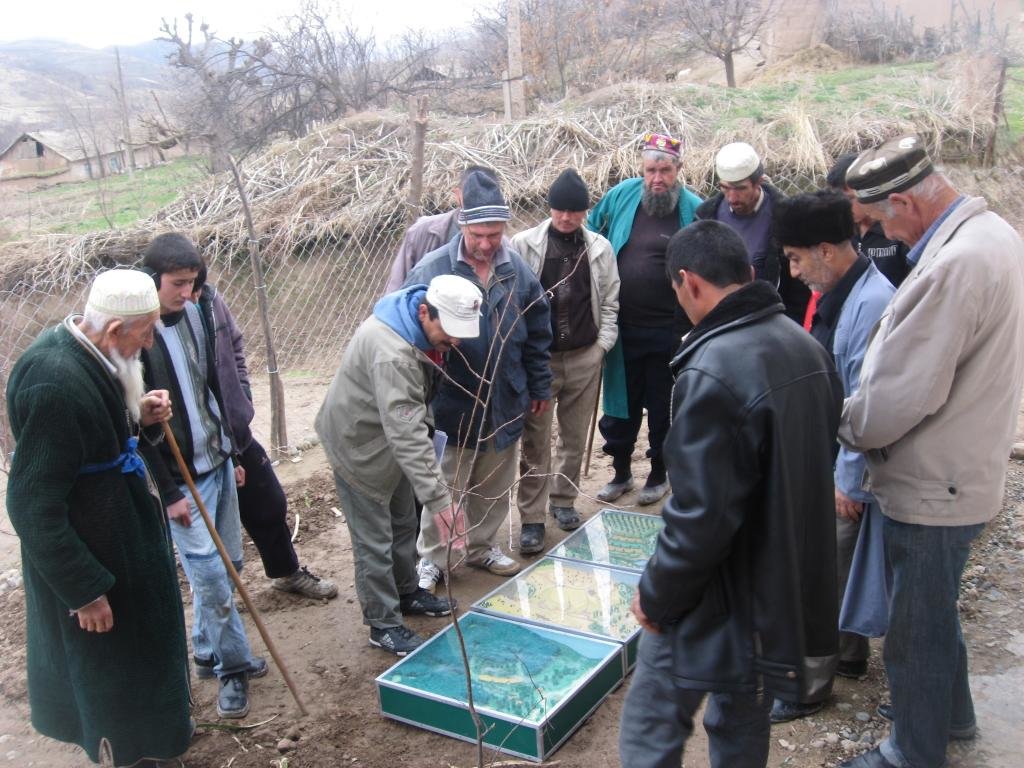
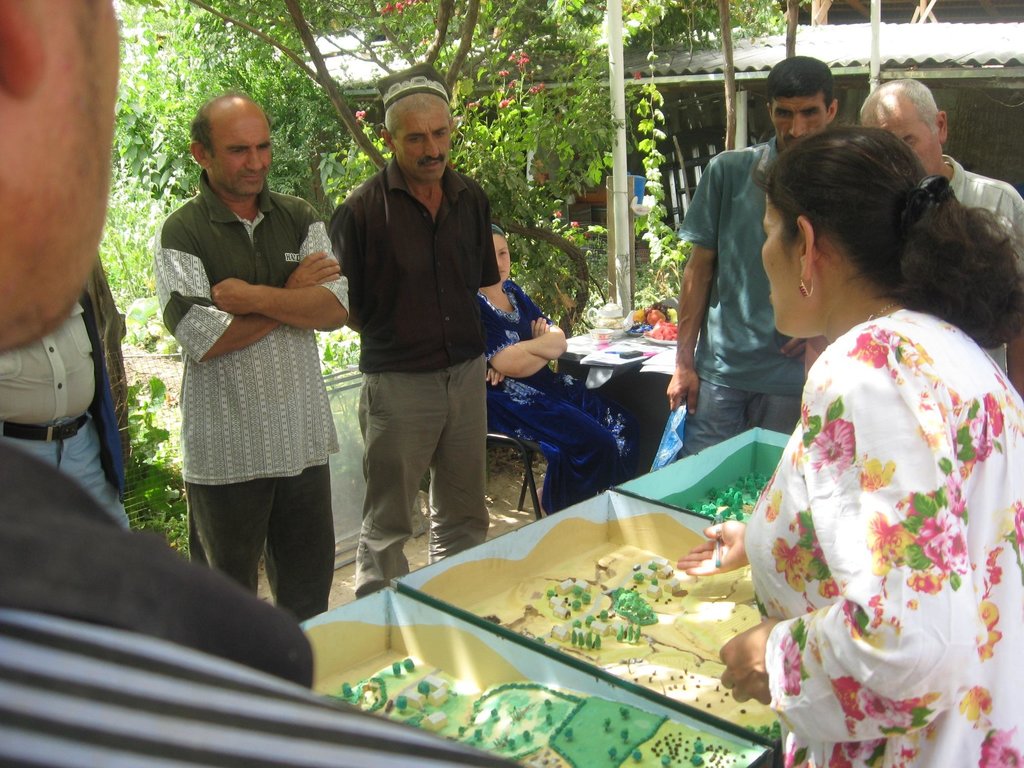
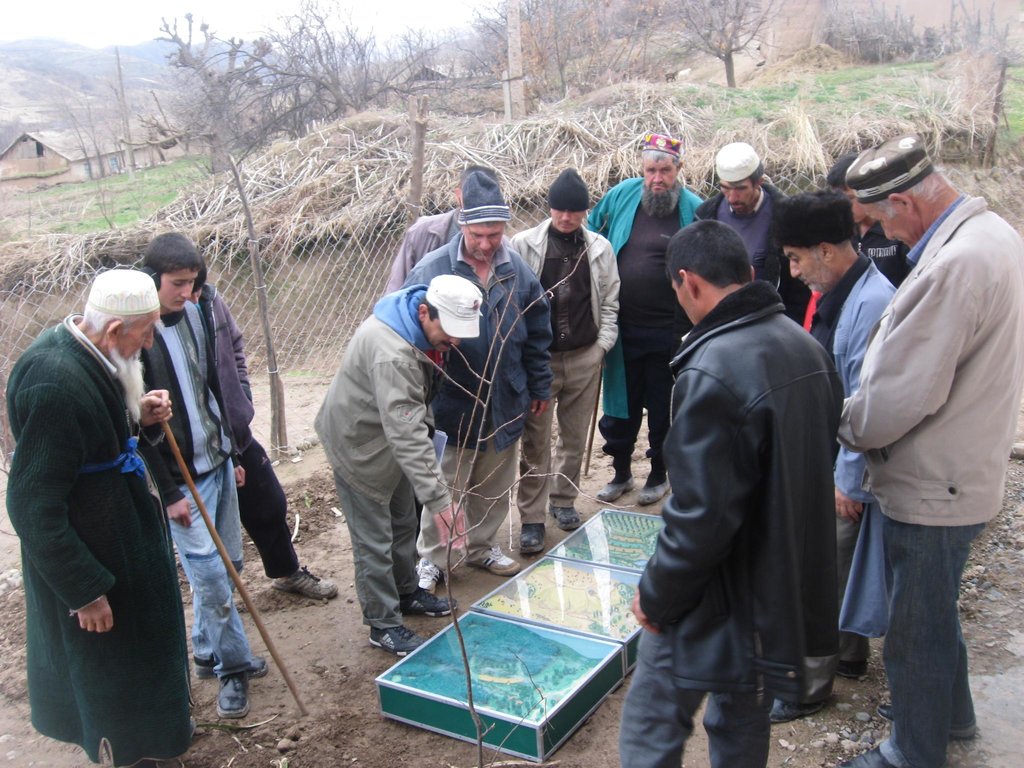
Facilitation of micro-watershed management for farmers [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Фасилитасияи амалиётхои дехкон барои идораи микрохавза
approaches_2443 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Bronkal Daniel
daniel.bronkal@welthungerhilfe.de
เยอรมนี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe (Welthungerhilfe) - ทาจิกิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
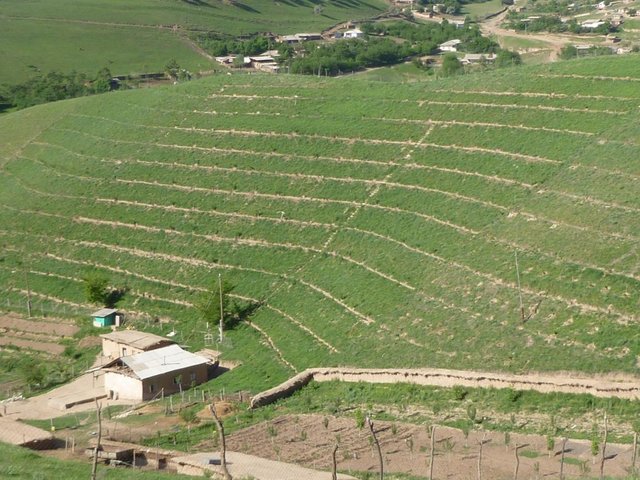

Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Relying on integrated watershed management principles, farmers were assisted by the project to implement soil and water conservation measures in a microwatershed.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: To strengthen the capacity of the community to plan and implement integrated natural resource management approaches, at micro watershed level in sustainable ways. These include; conserving soil by introducing actions to rehabilitate the eroded land, stop gully formation resulting from water run-off; enable water retention to secure soil moisture for a longer time period; mitigate effects of overstocking resulting in overgrazing; hoof erosion and soil compaction; reverse inappropriate agriculture practices towards more efficient and environmentally friendly management types; enable better employment and higher income generation to improve the livelihood standards and food security.
Methods: The project facilitated the following activities: Farmer participation, and using their initiative, community involvement in the planning, fundraising and implementation. Farmers increased their own contribution for material inputs, and a greater than 50% rate of adoption of the innovation was seen. The project also funded 'on the job' training, technical support, consultancy, and mediation of communication between parties.
Stages of implementation: 1. Awareness raising, 2. On the job training, 3. Watershed management activity planning, 4. Implementation, 5. Monitoring, 6. Evaluation, 7. Readjustment based on results, 8. Further replication in new area
Role of stakeholders: The DWHH Project had a leading role in initiation, orientation, awareness raising, mobilisation, training, consultancy, input provision and mediation of communication to land committee. Farmers have been actively participating, have provided labour input / financial contribution, provided indigenous knowledge and skills. Local authorities - providing land titles, participation in planning and decision making process Village Development Committee (VDC) - community mobilisation, information dissemination, input / finance documentation, fund raising.
Other important information: There are 5 households in the microwatershed. Almost 40 people live in all HH, all are Tajiks. Members of all households took part in discussion rounds and training. Non of HHs were strong enough to implement measures on own funds. One HH has rejected implementation of measures, due lack of capacity and lack of trust of the project's success. Women: farmers came to the discussions together with their wives, women took part in training, in implementing almost all of the adoption measures, and equally benefited from the project. However, they were not involved in decision making.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Tajikistan, Khatlon
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Baljuvon / Khirob
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2009
การสิ้นสุดลง (ถ้าแนวทางไม่ได้ใช้อีกต่อไป):
2011
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- เป็นนวัตกรรมท้องถิ่นล่าสุด/ นวัตกรรมใหม่
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities ( land use change, resource conservation, capacity building, focus on low cost local material, income generation, on the job training)
To assist farmers in the planning and implementation of activities for the conservation and improvement of the local land, to enable conditions for replication of the approach/technology, and to improve food production, and in the long run provide income generation.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of land tenure rights implementation. Nominal state farm reorganisation. Low agricultural production - lands depleted of nutrients, very low yields, no crop rotation, overgrazing. Soil degradation, progressing land mass transport, gully formation. Lack of technical knowledge and awareness of soil & water conservation measures. Lack of cash to invest in development of land - just limited capacity to invest but need external financial input. Conflict over land use - livestock owners are against land enclosures. Poverty - underlying cause of general lack of potential to invest in development.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Technology implementation has required a major investment for imported materials, like a metal net for fencing or fuel. Most farmers could not afford themselves to buy costly inputs. Moreover such inputs were rarely available on the local market.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The INGO covered the costs of 50% of each action, here mainly higher price inputs were paid off. The low-cost approach fits the financial capacity of the target group.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Capacities of communities and local authorities to jointly plan and implement SLM activities at micro-watershed level was weak.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Knowledge improved on the complex interrelations in natural ecosystems (farmers and staff of local authorities). Project cooperation was not limited to those interested, there was inclusion of gov. structures (agriculture, land committee, ecology) committ
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: On going legislative development in land tenure and farming provides good opportunities for implementation of the approach. But, ongoing nominal farm reorganisation and corruption at the local level, together with farmers reduced awareness of their land use rights requires more effort, time and funds in the application of SLM approaches. In this situation, DWHH has a good reputation in the district administration and with locals and so this helped overcome many barriers more easily.
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Implementing the land tenure law and the privatisation of state farms is still a difficult process with many inconsistencies for people claiming a land title in the area.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There are a few instances where the project was able to support farmers in getting land-titles to degraded land plots which they then had to rehabilitate using SLM technologies.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Treatment through the SLM Approach:
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Village Development Committee, farmers
Men have played bigger role in the organisation of activities, in the implementation of more manual work, whereas, women took part in the lighter work and in routine maintenance.
Most of the participating households live below the poverty line.
Farmers joined under one microwatershed approach, male (wife assisted), middle age, Tajiks, rural middle class.
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
Project TAJ1068 staff, and an international consultant
- องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe
- รัฐบาลระดับท้องถิ่น
Subdistrict, District Heads, Agriculture, Land committees, Forestry department
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | farmers meeting through VDC, orientation explaining goals, objectives, advertising in the local news paper, information boards in 6 watersheds |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | on site planning with farmers |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | training on the job, material input and labour provision, cross visits |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | data input, open to monitoring, communication on ongoing activities, collaboration while monitoring and evaluation |
| Research | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | collaboration in the test for Acacia seed germination on the plot |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
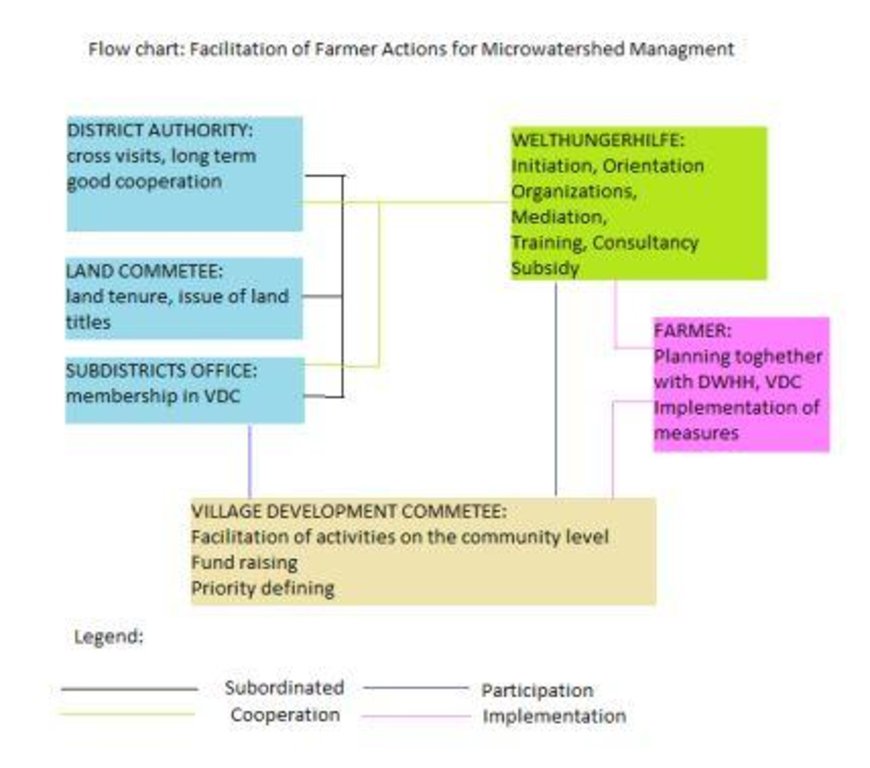
คำอธิบาย:
Flow chart depicts the major actors involved during implementation of the approach. The relationship between stakeholders and primary functions is described as well.
ผู้เขียน:
Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov (16, Firdavsi Street 734003, Dushanbe)
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM เป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก ที่ติดตามให้คำปรึกษากับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
การอธิบาย:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Focused on principles of farmer participation, self motivation and self help.
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
- local land and agriculture departments, village development committee
ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง ให้ระบุ เพศ อายุ สถานภาพ ชาติพันธุ์ เป็นต้น:
Land users: 5 men, 5 women, 30 to 50 years old, all Tajiks, all families.
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- กำลังดำเนินการ
- ใช้พื้นที่ทำการสาธิต
- จัดการประชุมสู่สาธารณชน
หัวข้อที่พูด:
Use of the A-frame, watershed model, tree planting in contour ditches, intercropping
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ไปเยี่ยมชมสถานที่
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A chain of meetings with international consultants from India and Nepal: Key elements: consultation on watershed concepts and watershed choice, capacity building in strategy design , draft development plan for watershed management
The consultants were : Yashvant Tkhakur, India; Jaganat Joschi, Nepal
Advisory service is inadequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; the govenment branches need more development and organisation to become able to manage land conservation activities; an independent advisory service is not in place, the only potential still exists within the DWHH Project
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติม :
Village development committee (VDC), use of locally available resources, focus on low cost
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: space used for technology
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: fodder produced cent/ha, vegetables
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: labour availability, health status
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: tree planting
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: soil degradation, gully formation
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: monthly trends, how hardworking they were, gender
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: technology adaptation based on own experience
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Change of the design - adjustment of the contour boundary based on experience on the plot; Adjusting of tree planting in contour ditches according to the topography
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
Tests were completed on the germination of Acacia seeds in two different setups: on the demo plot of the project and on the farmers plot.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 2,000-10,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government (material input: tools, fencing, planting material, diesel. etc.): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (the rest of material input, labour, time (mainly low cost inputs)): 50.0%; other
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
50% of activities were subsidised by the DWHH Project TAJ1068
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เครื่องมือ | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | hand tools |
- การเกษตร
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เมล็ด | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
| manure | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| metal net | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| โรงเรียน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | school, 2 rooms thermo insulated |
- อื่น ๆ
| อื่นๆ (ระบุ) | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel, diesel, oil | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | 1/4 of the need |
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
Rennovation of the chool for the children was a strong and vital argument demanding considerable investment. This was competed with the implementation of the SLM technology, where farmers had to make a choice; either spend the available funds for the school or continue with the SLM. The project has provided partial financial and technology support to farmers which made it easy to overcome the school situation and concentrate again on SLM activities.
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
Village development committee (VDC), use of locally available resources, focus on low cost
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Most of the previous types of damage caused by water runoff were prevented. Trees grew in a landscape where they didn't before, due to long dry periods and high livestock pressure from grazing. There was a change in the farmer's attitudes, who prior to witnessing the technology were highly sceptical
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Only four families out of five in the microwatershed were able to receive the opportunity to improve their socio-economic status in the long term as a result of the project.
ปรับปรุงประเด็นของการถือครองที่ดินหรือสิทธิในการใช้ ซึ่งขัดขวางการนำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The approach has added to the farmers self belief, ensured that they will effectively use existing land resources, and following the sustainable improvement of soil conditions, should add good potential for their own economic growth.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Farmers from the neighbouring watershed, came repeatedly to observe the plot. Three of these farmers adopted the technology themselves in the following year.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Vegetables could be grown to supply more food to the family, a good amount of hay could be prepared for winter time, more benefits could be seen in the long run with extra fruits and fire wood
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
This was a pilot project, and only looked at poverty alleviation on a small scale. This technology has the potential to reduce poverty in the long term on a bigger scale.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
- กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
- ภาระงานลดลง
- การจ่ายเงินหรือการช่วยเหลือ
- จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
Yes, but only those who would have enough funds to implement costliest part of technology: the perimeter fencing (metal net). Overall, most farmers will happily continue with the implementation of the technology, if the initial costs are subsidised. There are also a few new farmers who were able to replicate the technology completely by themselves.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The approach to share the implementation costs, consideration of general social needs, good project communication. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More donor funding would be required to support more local farmers in the future. ) |
| The approach has enabled a range of innovations that were never used before: contour lines, mulching etc. |
| The approach has helped to reveal the local problems related to technology implementation. It has helped participants to learn about the strength and potential of local land users in the implementation of the SLM approach and technology. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Lessons learned must be applied in the future implementation of SLM actions and replication. ) |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The approach enabled the use of both international and local knowledge. Attention was given to capacity building and sustaining the organisation, as well as the mobilisation structure (VDC) at the grass roots level. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: All the knowledge experience gained from the project has to be documented and disseminated for replication.) |
| The reputation of DWHH, and long term collaboration with the Baljuvon district administration played a very positive role in the successful implementation of the conservation approach. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Members of the local authority should be continuously involved in training, capacity building and planning measures. ) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Sometimes the approach enabled unproductive discussions during the planning and designing phases. | Project ambitions and objectives have to be adjusted to the local situation and farmer capacity and needs. |
| Farmers were facing situations where their other social and economic needs were strongly competing with the objectives of the project. | Some additional funds, may need to be provided and more awareness of the farmer's situations need to be taken into account. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The approach required a lot of funding until the majors actors were trained and had the capacity to implement the conservation measures. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Grant Application Form to EU Commission: 'Individual incomes & Improving Living Standarts in Khatlon and Sughd Regions', TajikistanSketch map of Khirob MicrowatershedInterim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
DWHH Regional Office, Dushanbe
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Sketch map of Khirob Microwatershed
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
DWHH, Baljuvon
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Interim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
DWHH, Baljuvon
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล