Delegating the management of facilities to users [มาลี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Dieter Nill
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Laura Ebneter
Délégation de gestion des équipements aux exploitants (French)
approaches_2503 - มาลี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Tamini Jacques
jacques.tamini@helvetas.org
HELVETAS - Swiss Intercooperation
มาลี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Doumbia Moussa
douballa03@yahoo.fr / bulonbasecom@yahoo.fr
Intercommunalité de Bougouni "Bulonba"
มาลี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - เยอรมนีชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล (ภาคสนาม):
01/07/2012
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Promote the sustainability and cost effectiveness of schemes by setting up management delegation systems that enable local authorities to entrust infrastructure owned by the territorial community to groups of local farmers.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
The basic economic infrastructure is usually provided through state or decentralised-authority funding. The building phase of the project is entirely managed by the territorial community (TC). A delegation process ensures that responsibility for managing this infrastructure is transferred to beneficiary actors organised in user associations. Agreements are concluded between the TCs and communities with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities. This agreement makes it possible to extend the ownership of schemes beyond that of the traditional management committee model. It can also increase local tax revenues and prolong the lifespan of facilities when they are well run.
The commune is the owner of the scheme but delegates its management to a user group (an interprofessional farming committee for lowland development projects) by means of a management delegation contract. Member subscription fees and upkeep fees are paid into a bank account opened by the community. The commune has the right to oversee the administrative and financial management of the delegatee and ensures the application of access and farming rules in the scheme. Group managers regularly report on activities to other members and the commune.
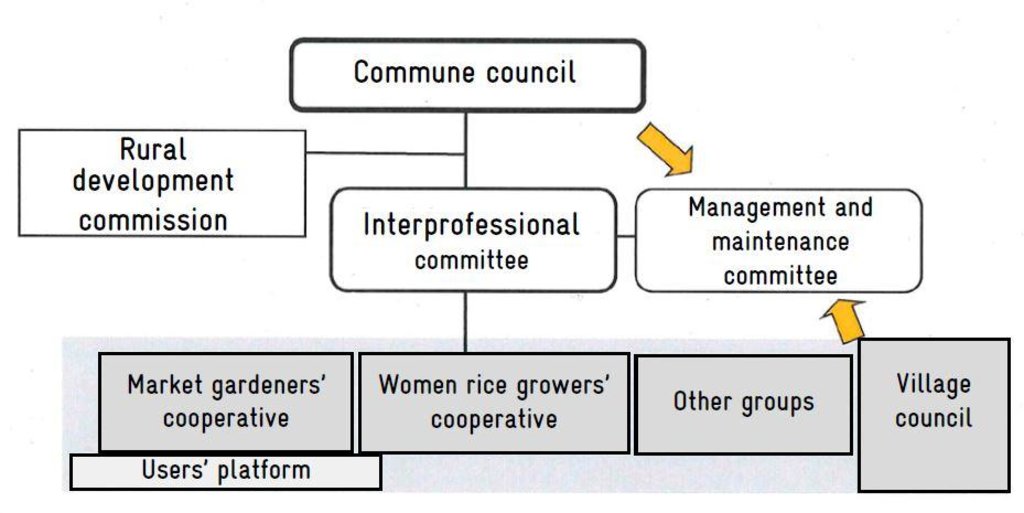
The commune council undertakes the overall project management of the installation works, contributes to funding the developments, provides key guidance on farming matters, delegates the management of the infrastructure to the interprofessional committee (IPC), supports the IPC in recovering fees, and ensures the monitoring and development of the project. The rural development commission of the commune council exists within each council. Its role is to catalogue the issues actors face and propose solutions to the commune council, support cooperatives in their search for partners together with the IPC, research the land titles for schemes on behalf of the council (registration), validate the development plan, support IPC in managing conflicts between cooperatives, and carry out any other tasks that are required of it by the commune council. The interprofessional committee brings together representatives from different cooperatives, associations and groups and takes on the delegated management role. Its role is to: maintain communications between users, the town hall and partners; coordinate activities that affect several local-level cooperatives; ensure the rational use of lowland resources; secure the agreement of the different user groups on the rules for accessing and dividing up the scheme site; assess and validate the cooperatives’ farming plans (individual needs analysis in terms of production capacity); monitor the use of inputs, seed and equipment obtained by the cooperatives; receive the fees collected by each cooperative from its members; manage renovation and maintenance funds; prevent conflicts of interest arising among the cooperatives. The management committee is a sub-committee within IPC and is tasked with managing water supply (opening and closing the distribution gates), carrying out small-scale maintenance and alerting the IPC to any failures to respect the farming code. Consultancies facilitate the process, support the institutional and organisational strengthening of actors and provide training on management tools. Technical services ensure the application of technical and environmental standards and ensure sound financial management (fee collection, financial controls, delegated public procurement). The project team provides advisory support, organises users structurally and delivers training, tools, coordination and monitoring.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
มาลี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Mali
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Sikasso region, circles of Bougouni, Kolondiéba and Yanfolila
2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2008
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities
The objective of the practice is to promote the sustainability and cost effectiveness of schemes by setting up management delegation systems that enable local authorities to entrust infrastructure owned by the territorial community to groups of local farmers.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: lack of infrastructure for local farmers, low sustainability and cost-effectiveness of schemes
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
The basic economic infrastructure is usually provided through state or decentralised-authority funding.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: A delegation process ensures that responsibility for managing this infrastructure is transferred to beneficiary actors organised in user associations with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
- รัฐบาลระดับท้องถิ่น
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | |
| Research | ไม่ลงมือ |
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
The measure relies on the direct actors shown in the diagram, who are supported by other stakeholders. From the start of installation works, the commune supports the project in setting up a management system. Installation works are co-funded by the technical and financial partners (TFP), communes and beneficiary villages. It must nevertheless be highlighted that the infrastructure remains the property of the commune and beneficiaries must pay a fee for its upkeep. The commune selects the consultancy (project manager) and chooses the contractor. The commune also Monitors scheme installation and accepts works. A second consultancy is tasked with giving producers guidance on farming and management techniques. The different user groups (market gardeners/planters, women rice growers, livestock farmers, etc.) are formed into interprofessional committees or farming committees. The commune draws up the draft delegated management contract with the interprofessional committee or the cooperative. To this end, it evaluates the potential of the resources that can be mobilised and discusses with its partners the rules for farming the scheme and the methods for its maintenance and repair. Following this, the contract is signed.
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นผู้ตัดสินใจหลัก โดยการสนับสนุนจากผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM
การอธิบาย:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ที่ศูนย์ถาวร
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Setting up this system requires ongoing support for two to five years to allow beneficiaries to take ownership of the scheme.
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- ด้านการเงิน
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through measurements
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- สังคมวิทยา
- เศรษฐศาสตร์หรือการตลาด
- นิเวศวิทยา
- เทคโนโลยี
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: private sector (technical and financial partners (TFP)): 85.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (commune): 10.0%; local community / land user(s) ( village): 5.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
Installation works are co-funded by the technical and financial partners (TFP), communes and beneficiary villages. In small-scale irrigation projects, for example, the project provides up to 85% of the funds; the village 5% and the commune 10%. The beneficiaries contribute either in-kind or financially.
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Consensually agreed farming codes and rules are instituted and monitored. Agreements are concluded between the TCs and communities with the aim of guaranteeing the sustainability and economic viability of facilities.
ทำให้กลุ่มด้อยโอกาสมีอำนาจทางสังคมและเศรษฐกิจหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The system was first initiated and developed at 34 commercial infrastructure trade fairs. Today, it involves 15 farming sites. The practice has been applied since 2008.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
In the Bougouni area, 552 hectares are being farmed by 1,671 rice growers, 80% of whom are women. Production has increased for 70% of growers. The principle of a maintenance fund has been accepted and is now operational, with deposits ranging from 75,000 to 300,000 CFA francs per year
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- การผลิตที่เพิ่มขึ้น
- กำไร (ความสามารถ) อัตราส่วนค่าใช้จ่ายต่อผลประโยชน์ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ไม่แน่ใจ
ถ้าตอบว่าไม่หรือไม่แน่ใจ ให้ระบุและแสดงความคิดเห็น :
Setting up this system requires ongoing support for two to five years to allow beneficiaries to take ownership of the scheme.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Many repairs are already being handled by the delegated management structures. These structures ensure that the consensually agreed rules are appropriately applied. A new kind of partnership has been created between the local authorities and village communities. |
|
It can increase local tax revenues and prolong the lifespan of facilities when they are well run. How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The commune authorities must be willing to promote transparency in communications on works procurement and accept requests for clarification (public audits). The community must have leaders in place who are prepared to lead frank public discussions among key players that are also courteous and respectful. This also applies to the management committee. Monitoring and evaluation of the delegation contract is essential between the commune and platform. It is important to undertake an annual review, the conclusions of which will also be shared with the wider community. To do this, the management committee must be in a position to draw up a balance sheet. The village must be prepared to contribute (with their labour or funds) towards installing the scheme, prior to registering it in the PDESC. It is essential to remove any ambiguity from bylaws for the scheme belonging to the commune. If it is true that actors rarely challenge the old, established rules for accessing rice growing sites, the same cannot be said for market gardens, where the plot allocation rules fall easily into place. Growers must pay the amounts/fees agreed with the commune.) |
| Subscription fees are collected more easily: 84% of members pay their subscription fees for the area in question. Consensually agreed farming codes and rules are instituted and monitored. In the Bougouni area, 552 hectares are being farmed by 1,671 rice growers, 80% of whom are women. Production has increased for 70% of growers. The principle of a maintenance fund has been accepted and is now operational, with deposits ranging from 75,000 to 300,000 CFA francs per year. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
ช่องทางในการสืบค้น และราคา:
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Rapport appui à la valorisation des ouvrages hydroagricoles [Report on supporting the development of small-scale irrigation schemes], GSAD, June 2012
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Annual report: Monitoring lowland areas, BEACIL, June 2012
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล