Participatory Negotiated Territorial Development [กานา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Philippe Zahner
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2570 - กานา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Groppo Paolo
paolo.groppo@fao.org
FAO
Rome
อิตาลี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Cenerini Carolina
carolina.cenerini@fao.org
FAO
Rome
อิตาลี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - อิตาลี1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Participatory Negotiated Territorial Development (PNTD) is a rural development approach developed by FAO.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: It offers a structure to build consensus among individual communities and development partners on natural resources/territorial management and development issues. PNTD facilitates consensus based planning within a team that represents different actors at different levels, including sector offices / technical services (agriculture, environment, etc.) and NGOs (involved in community-based rural development) at district/ department/ municipality level; and traditional authorities, user groups and associations at community/ village level.
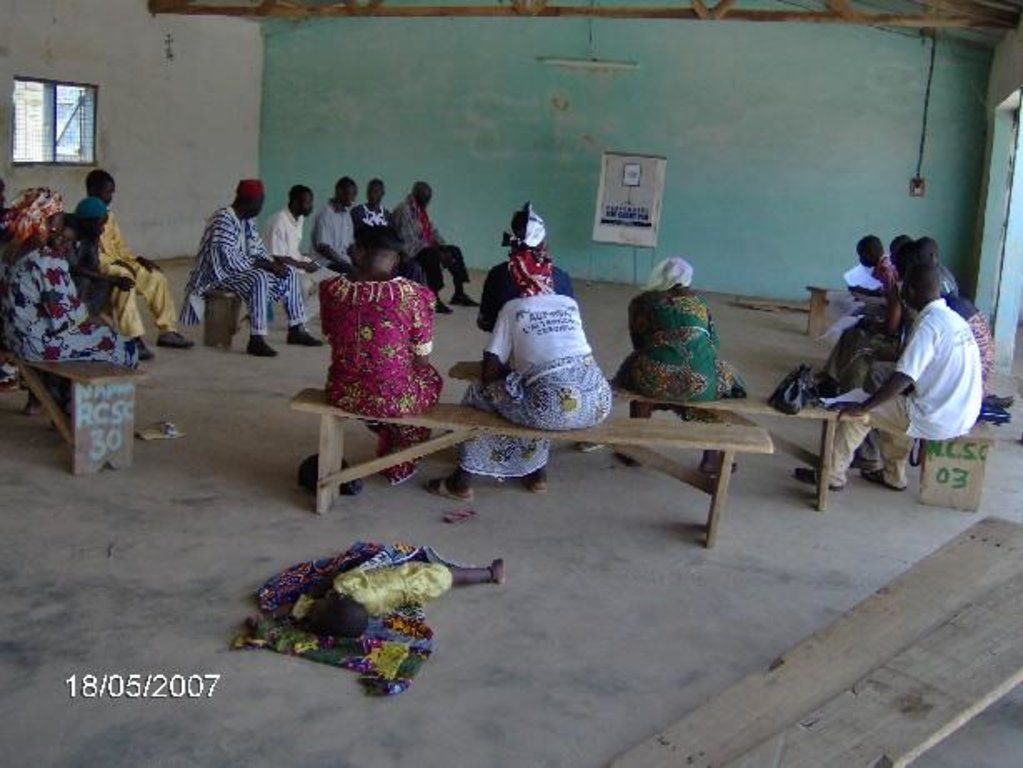
Methods: During the diagnostic phase of the PNTD process, local territorial issues are analysed based on the viewpoints of the different actors and on a historical analysis. This step contributes to a coherent, shared understanding of the territorial system, thus providing the basis for collective agreements on development. These are referred to as Social Territorial Agreements. They are based on negotiation within the PNTD team. Main activities of PNTD include: (1) Facilitation of the planning process; (2) Provision of technical expertise; (3) Linkages to relevant institutions; (4) Technical advisory to assess viability and costs of joint development proposals; (5) Reporting back to communities and provision with final plans and resource maps; (6) Signing of ‘Social Territorial Agreements’ and endorsement by local government; (7) Establishment of a joint monitoring and evaluation system; and (8) Follow-up meetings between government institutions and NGOs.
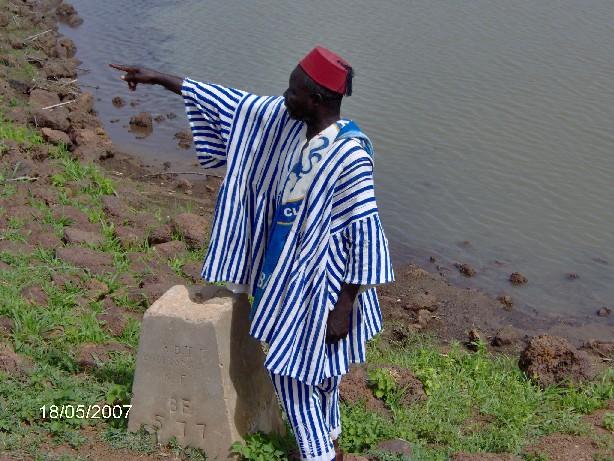
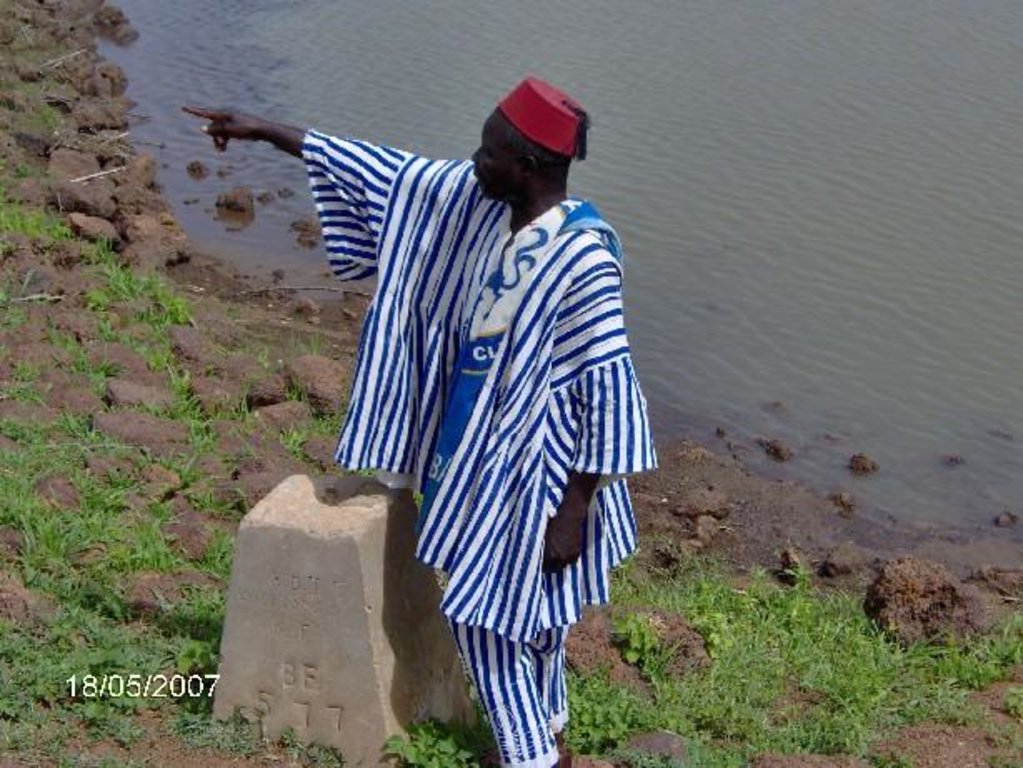
Other important information: Independent external support by territorial facilitators is essential to assist in various aspects of the process. A PNTD approach was piloted within a project in the Onchocerciasis (riverblindess) Freed Zone along the Burkina Faso-Ghana border. This newly opened zone lacked a well defined, accepted management structure to support the development process, while cross-border aspects further complicated development, requiring cooperation among the communities and development partners from both countries. The PNTD team was supported by facilitators from the Netherlands Development Organisation (SNV). The team’s capacity to carry out inclusive planning processes has improved significantly, in terms of proposal development, negotiation and consensus building, and in placing the findings of the diagnostic phase in the larger geographical context. Joint development plans were elaborated and agreed upon from the perspective of the communities. FAO has been supporting the exercise through technical backstopping.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
กานา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Ghana and Burkina Faso
Map
×2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (a road to link two communities directly)
Testing a PNTD approach for local (transboundary) territorial planning; Refining the methodological process; Preparing a joint development plan for the two areas in Ghana and Burkina Faso
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Limited commitment from central governments; Cross-border planning proved to be considerably more expensive than regular planning activities
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Community leaders
- องค์กรพัฒนาเอกชน
SNV
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
- องค์การระหว่างประเทศ
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ไม่มี | |
| การวางแผน | ไม่มี | |
| การดำเนินการ | ไม่มี | |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ไม่มี | |
| Research | ไม่มี |
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ใช่
ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้ได้รับการอบรม:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- เจ้าหน้าที่ภาคสนาม / ที่ปรึกษา
รูปแบบการอบรม:
- กำลังดำเนินการ
หัวข้อที่พูด:
Training focused on: (1) the PNTD process and its application in the context of cross-border natural resource management; (2) PRA tools relevant to the diagnostic phase; (3) participatory resource mapping (a tool to support the negotiation on development proposals)
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This approach focuses on establishing and maintaining social dialogue within the territory and restructuring and/or strengthening territorial institutions.
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- ไม่มี
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
No subsidies were given. Labour was not rewarded and inputs were not financed by the project.
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
improved soil conservation and livestock rearing
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Invoked a high level of interest within the targeted communities; increased active participation, planning and consensus building capacity at community level
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- เกียรติภูมิ แรงกดดันทางสังคม ความเชื่อมแน่นทางสังคม
avoiding potential transboundary conflicts
- จิตสำนึกด้านสิ่งแวดล้อม
improving natural resources and land management
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
The PNTD-approach has shown applicability. Yet, there are some aspects which need to be considered: (Local) governments need to take ownership of the cross-border planning and development processes. This could be realized by structuring external support differently: (1) Local government (districts, municipalities) supported by NGO’s are responsible to carry out all activities; (2) External (project) support focuses on overall coordination, the provision of technical advice, the provision of op
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Provides a suitable framework for cross-border planning in the West African context |
| PNTD process raised the level of participation of local government institutions and NGO’s in a negotiated territorial development process through the PNTD team which comprised technical staff of these organizations. |
| PNTD enabled (and stimulated) the communities on both sides of the border to interact and joint development plans were elaborated and agreed upon from the perspective of the communities. |
| Looking beyond community boundaries, and consensus building between communities and stakeholders were new aspects of planning to the team members |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| It took time for team members to grasp the conceptual approach of PNTD. They were used to working within individual communities, and if they were involved in planning then mostly at a diagnostic level. | |
| Language problems required almost continuous translation, and thus effectively doubling the time required | recruitment of linguistic mediator(s) need to be considered in the project budget |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
FAO. 2005. An approach to rural development: Participatory and Negotiated Territorial Development (PNTD). Rural Development Division, FAO. OFZ Project (Socio Economic Development Programme for the Transborder Onchocerciasis Freed Zone of Burkina Faso and Ghana)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
SNV Burkina Faso - SNV Ghana. 2007. X-border Participatory, Negotiated, Territorial Development (PNTD) – pilot phase report.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล