The 'Triple bottom line' [ออสเตรเลีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Anthony J. Webster
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
approaches_2668 - ออสเตรเลีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CSIRO (CSIRO) - ออสเตรเลีย1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
A new expression used by agriculturalists in Australia to explain why farmers change practices: the 'triple bottom line' implies economic, environmental and social concerns.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
Aims / objectives: A fundamental change has occurred in farming practice amongst sugar cane growers in the tropics of far north Queensland. Where it was once standard practice to burn cane before harvest (defoliating green canes for easier harvest), tradition has been turned on its head and now almost no-one burns. Instead a 'green cane trash blanket' system has developed, with multiple benefits and few or no drawbacks. There has been no official campaign or punitive sanctions imposed, no enticing financial incentives offered or charismatic environmental leadership - just a quiet technological revolution, based on the principles of the 'triple bottom line' (TBL).
Methods: TBL has recently emerged into common usage amongst agriculturalists in Australia. Rather than attributing farmers' actions as simple responses to economic stimuli ('the bottom line') TBL is a framework that helps explain the complexity of factors that influence farmers to modify their practices. TBL suggests that farmers do indeed respond to money, but also to environmental concerns, and furthermore to social considerations as well. This gives credit to farmers for being responsible stewards of the land. In this particular case, the transition in technology started in 1974, when sugar cane growers in the far north of Queensland were simply unable to burn their cane prior to harvest because of the exceptionally heavy rains. Instead, they had to harvest wet - and green. The technical implications were first, a slower harvest speed because machinery had to cope with a greater load of biomass, and second, a thick residual blanket of trash that covered the soil. The multiple benefits of mulching were recognised by a few growers, who then continued to harvest green cane. Non-burning spread - a technology now described as the 'green cane trash blanket'- until almost every grower adopted it within one generation. While the extension service has supported the transition, growers themselves tookthe initiative to change. There are indeed small financial benefits, chiefly in terms of reduced overall input costs, but growers have simultaneously been motivated by social and environmental considerations. Burning has come to be considered anti-social: a dirty practice, carrying the danger of fire spreading outside the targeted fields. Neither is it a pleasant task, requiring help of family and friends, often at inconvenient times.
Other important information: From an environmental perspective, the benefits of trash mulch are tangible in terms of improved soil quality, and reduced erosion rates. And, equally important, the end result is reduced damage to the close-by Great Barrier Reef with its sediment-sensitive living coral.
The triple bottom line(TBL) is an expression which has evolved in Australia to help explain why farmers act as they do. Its three components of economics, the environment and social aspects cover the considerations that cause farmers to modify technologies. TBL implicitly gives credit to farmer for being sensitive to multiple external signals. In this case the change in practice is from burning sugar cane to harvesting it green in Far North Queensland. This is a case where emerging conservation-friendly farmer practice and the goals of the environmental lobby have neatly coincided.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ออสเตรเลีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Queensland
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
1974
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- แบบดั้งเดิม/ แบบพื้นเมิอง
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
The Approach focused on SLM only
(1) Demonstration and dissemination. (2) The spread of non-burning practices, specifically the 'green cane trash blanket' technology to promote sustainable and environmentally friendly sugar cane production. (3) Indirectly: to satisfy social concerns associated with burning of sugar cane.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: (1) Anti-social farming practice of burning sugar cane which also has negative environmental impacts, both in situ, and offsite in the coral reef. (2) Resistance to change in traditional farming practice.
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
บรรทัดฐานและค่านิยมทางสังคม วัฒนธรรม ศาสนา
- เป็นอุปสรรค
traditional way of doing things/social resistance
Treatment through the SLM Approach: demonstration and dissemination of benefits
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Higher costs of harvesting (a small premium charged by contractors per tonne of green cane harvested).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: These costs are offset by lower tillage input, no costs associated with burning, and lower inputs of agrochemicals also.
กรอบแนวทางในการดำเนินการด้านกฎหมาย (การถือครองที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและน้ำ)
- เอื้ออำนวย
- เป็นอุปสรรค
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Harvesting machines at first were not so well able to cope with the greater biomass to be harvested.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Manufacturers developed higher capacity harvesters.
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
There is no difference between men and women in principle, though de facto most growers are male.
- รัฐบาลแห่งชาติ (ผู้วางแผน ผู้ทำการตัดสินใจ)
politicians (govt. agencies)
- environmentalists
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ระดมกำลังด้วยตนเอง | starting up the practice; starting up the practice of green cane trash blanket (GCTB) |
| การวางแผน | ไม่มี | |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | spreading the word; growers spreading the word, support by extension services |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | growers joining hands with research; formal and informal disseminations of observations |
| Research | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | growers joining hands with research. Quantifying benefits short, long term and downstream |
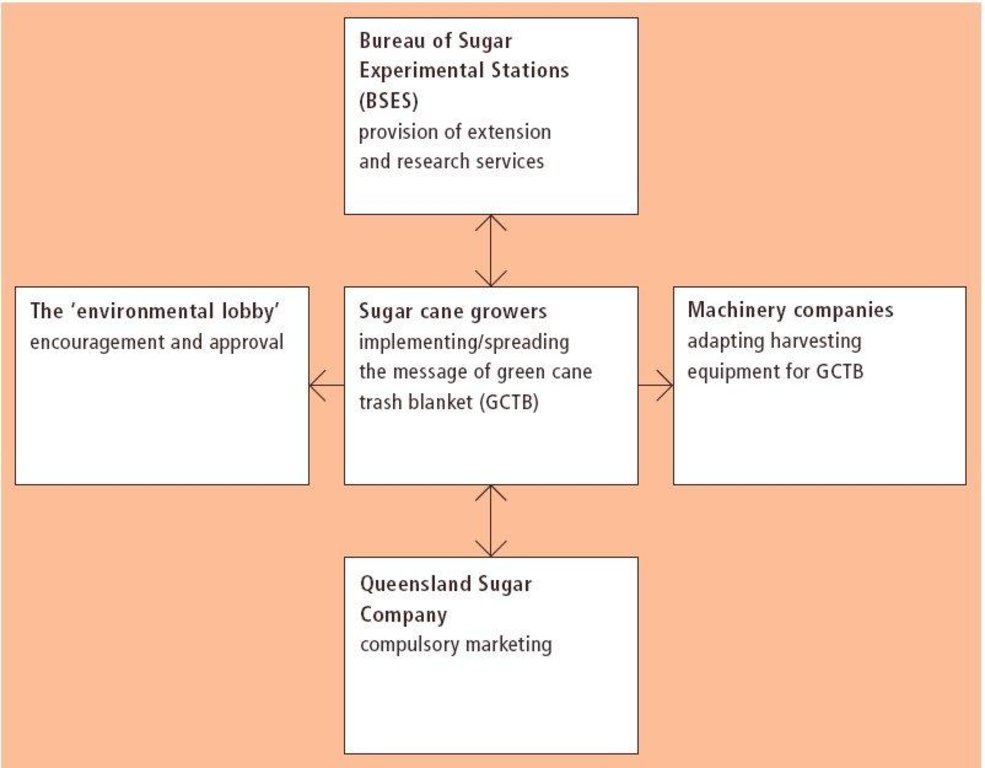
3.3 แผนผังแสดงขั้นตอนการทำงาน (ถ้ามี)
คำอธิบาย:
Institutional framework Inter-relationships between sugar cane growers and other stakeholders.
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพียงผู้เดียว ( ริเริ่มด้วยตัวเอง)
การอธิบาย:
sugar cane growers
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by land users* alone (self-initiative / bottom-up)
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุว่ามีบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
- ไปเยี่ยมชมสถานที่
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Name of method used for advisory service: green cane trash blanket (GCTB) system; Key elements: visits, Field days, publications; (1) Advisory service was carried out through: Bureau of Sugar Experimental Stations (BSES).(2) Advisory service was carried out through: Bureau of Sugar Experimental Stations (BSES).
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ไม่
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ความคิดเห็น:
Technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations
There were None changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Not applicable.
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุหัวข้อเรื่อง:
- เศรษฐศาสตร์หรือการตลาด
- นิเวศวิทยา
- เทคโนโลยี
ให้ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและให้ระบุผู้ทำการวิจัย:
There has been some ad hoc research carried out on technical parameters by both the BSES as well as CSIRO.
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national government, Bureau of Sugar Experiment Stations): 20.0%; other (growers themselves): 80.0%
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
By government (national government, Bureau of Sugar Experiment Stations)
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- ไม่มี
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
ความคิดเห็น:
Farmers themselves provide labour
There are no subsidies connected to GCTB. Australia does not subsidise its sugar cane growers and sugar is sold at the world price.
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Considerable: nutrient losses reduced, erosion reduced, organic matter built up, etc.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
The 'triple bottom line' is probably active throughout Australia in influencing farmers??? decisions.
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ ให้อธิบายว่าอย่างไร :
By definition this is sustainable: it is an internal mechanism amongst farmers.
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Farmers take the responsibility of choosing a land management practice that has a positive 'triple bottom line': environmental, economic and social benefits. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Support awareness raising and give appreciation to the on-site and off-site benefits; acknowledge sugar produced under this system an environmentally friendly and economic product.) |
| Has successfully stimulated the spread of the green cane trash blanket system. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Outsiders should continue to support farmers' multiple concerns.) |
| Sugar cane growing has previously had a bad environmental and social reputation, especially here, close to the Great Barrier Reef, which is a World Heritage Site. This change in practice, resulting from the 'triple bottom line' has changed the reputation of sugar cane growers. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Make this public.) |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The fact that farmers are responsive to environmental and social as well as economic stimuli is covered up by conventional thinking that 'only money matters to them'. | Investigation and documentation of the 'triple bottom line' is required. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล