Integrated disaster risk reduction in flood-affected areas by local communities [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Stefan Michel
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Umed Vahobov
Интегрированный подход к снижению риска стихийных бедствий местными сообществами, в местностях подверженным селевым потокам
approaches_4319 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของแนวทาง
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Muhidinov Nodir
nodir.sfl@gmail.com
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)
ทาจิกิสถาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Strengthening of Livelihoods through Climate Change Adaptation in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistanชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินแนวทาง (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
GIZ Tajikistan (GIZ Tajikistan) - ทาจิกิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกไว้ผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การอ้างอิงถึงแบบสอบถามเรื่องเทคโนโลยี SLM

Prevention of riverbank erosion by combination of green … [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Flashfloods in riverbeds cause intensive riverbank erosion, which threatens villages, infrastructure and productive lands. Preventive measures combining "grey" (physical structures) and "green" (living trees) elements are more effective, sustainable and cost efficient than constructive measures only.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Stefan Michel
2. คำอธิบายของแนวทาง SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของแนวทาง
Climate change and land degradation in upper catchment areas cause an increasing frequency and intensity of flash flood and debris flows affecting settlements and productive areas. GIZ in collaboration with the Committee on Emergency Situations assisted local communities in the implementation of integrated preventive measures.
2.2 การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง
การอธิบายอย่างละเอียดของแนวทาง:
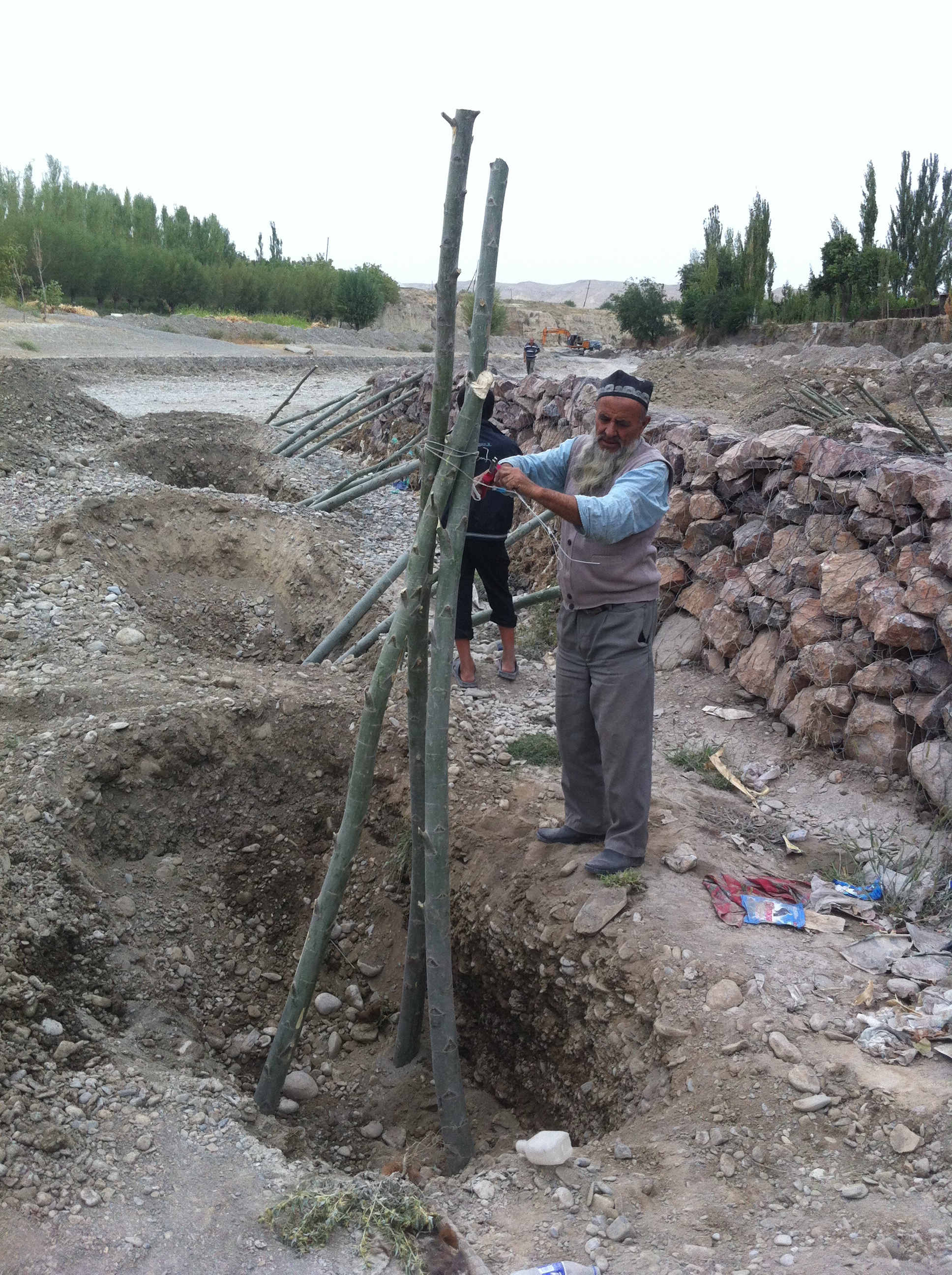
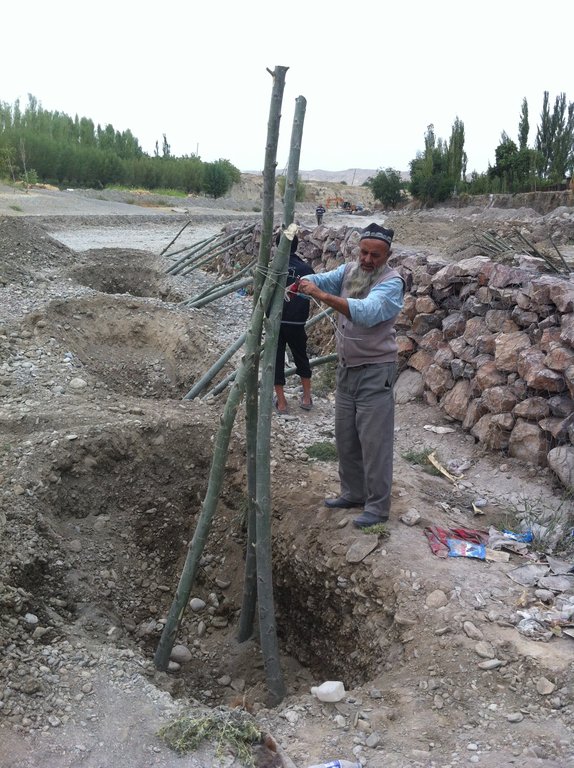
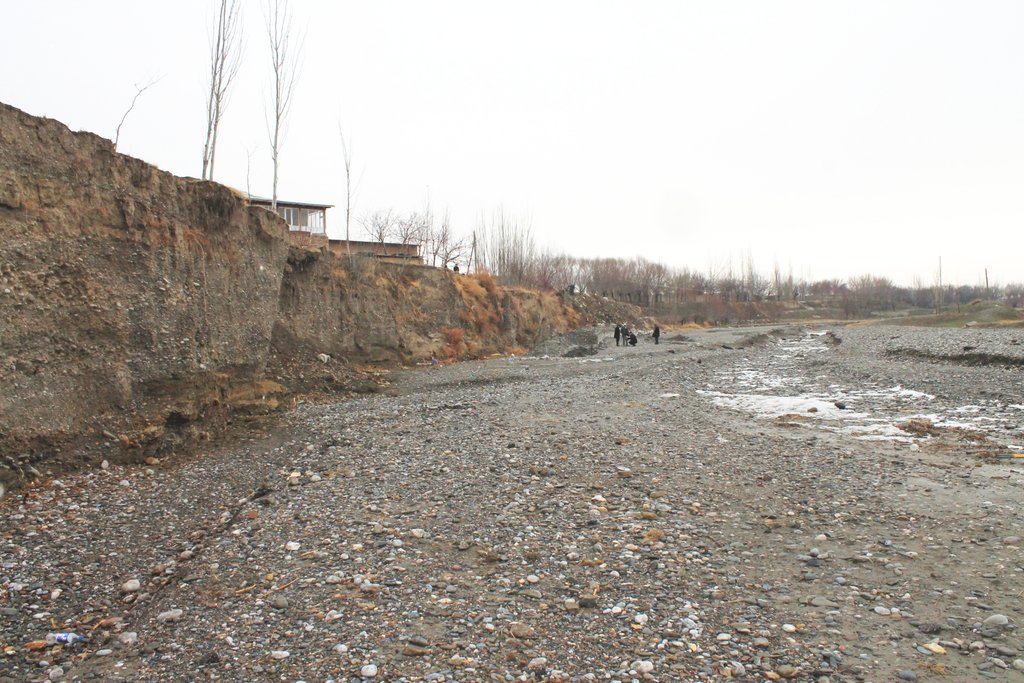
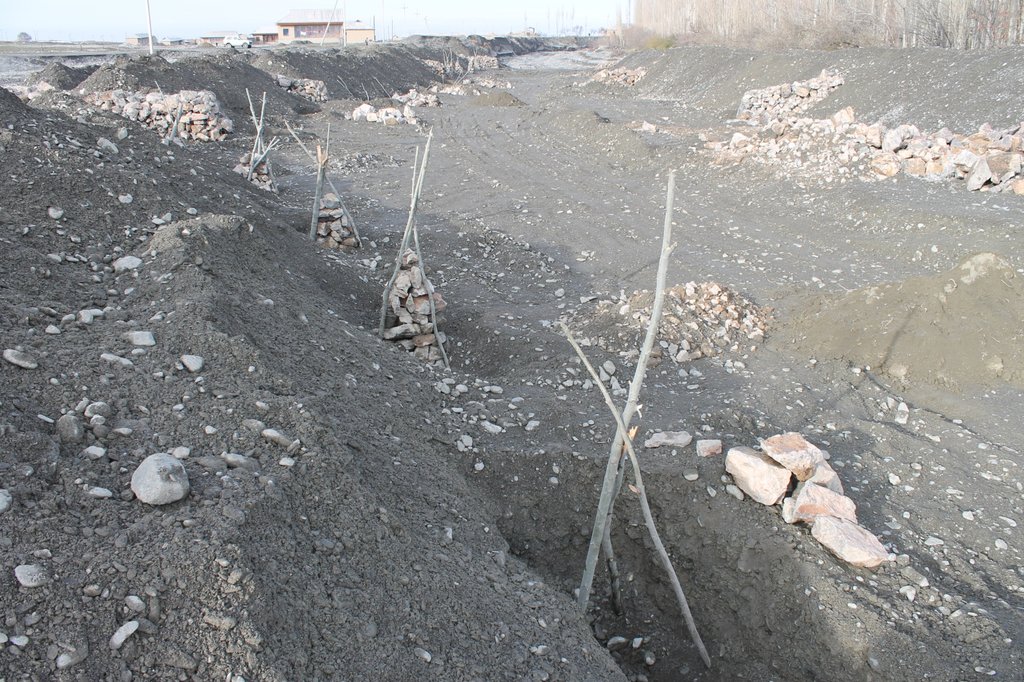
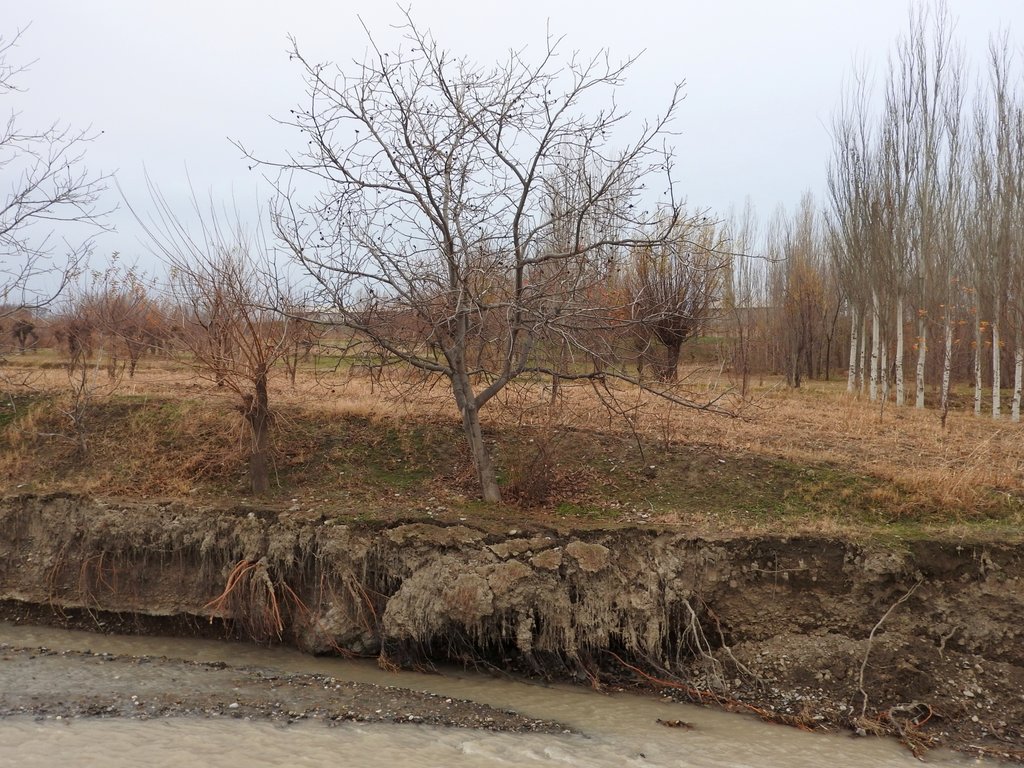
Villages and associated productive lands like orchards, gardens and arable fields in the lower parts of the northern main slope of the Turkestan mountain range are typically located in the valleys of rivers and streams. Water discharge in these rivers and streams is seasonally highly variable. During the wet season water flow is very high, while during the dry summer and fall months almost no water is visible at the surface and the limited discharge takes place in the gravel of the riverbed. After rainfall and during snowmelt extreme flow events happen with discharges several times exceeding the average of the wet season. Flashfloods with high speed and energy typically cause the transportation of large amounts of debris. These debris flows can be much more destructive than ordinary high water events. The resulting riverbank erosion is in some extent a natural element of the morphological dynamic of rivers and streams.
Land-use related factors have increased the vulnerability of communities to these flashfloods and debris flows as well as their destructiveness. Population growth, the expansion of settlements and the reclamation of more lands for irrigated orchards, gardens and arable fields have brought more people and values into potentially risky areas. The degradation of the vegetation in upper catchments has contributed to reduced infiltration of water and high and fast surface runoff. The riparian forests and woodlands which in some extent slow down flashfloods and keep sediment have been largely destroyed by clearing, livestock grazing and by the increasing intensity of flashflood events.
These problems are increasingly exacerbated by the impact of climate change. The already visible trends and predictions show higher levels of aridity, higher temperatures during the vegetation season, reduced overall precipitation in catchment areas – all affecting the retention potential of upper catchment areas – and more irregular rainfall patterns, reduced snow packs and accelerated snow melt as well as the loss of glaciers as buffers of water flow. These factors all contribute to a higher frequency and intensity of flashflood and debris flows.
These events threaten settlements, infrastructure and human lives, but they also pose substantial risks to the stability and functioning of irrigation canals, cause irreversibly losses of productive lands and thus threaten livelihoods of farmers and food security.
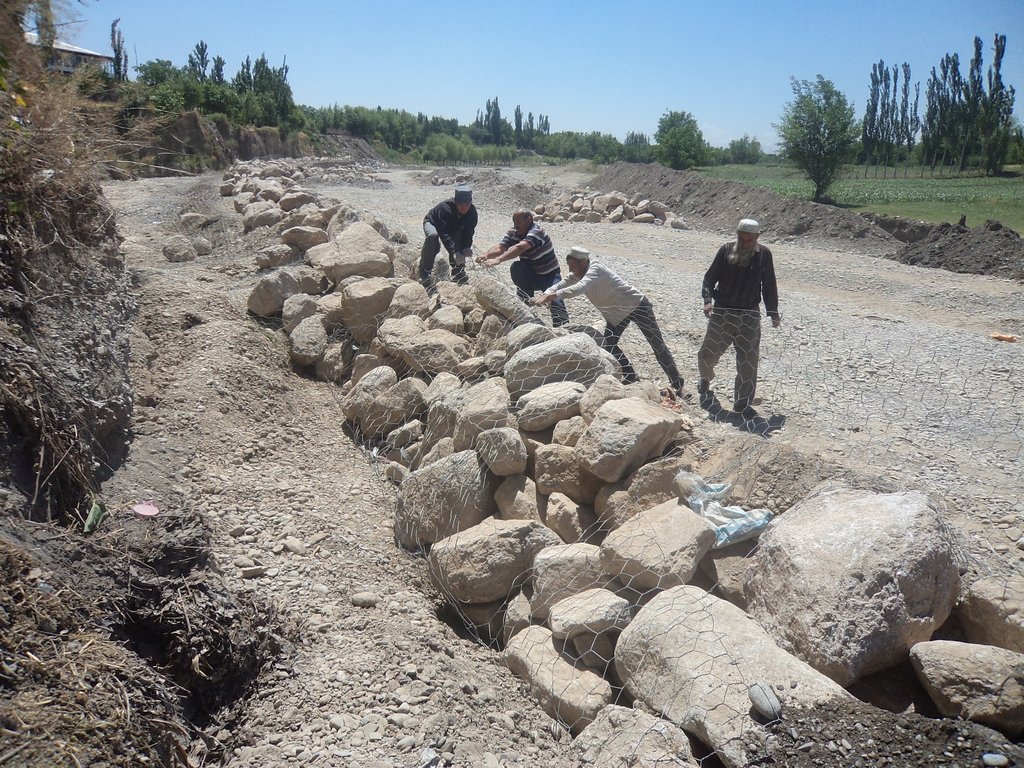
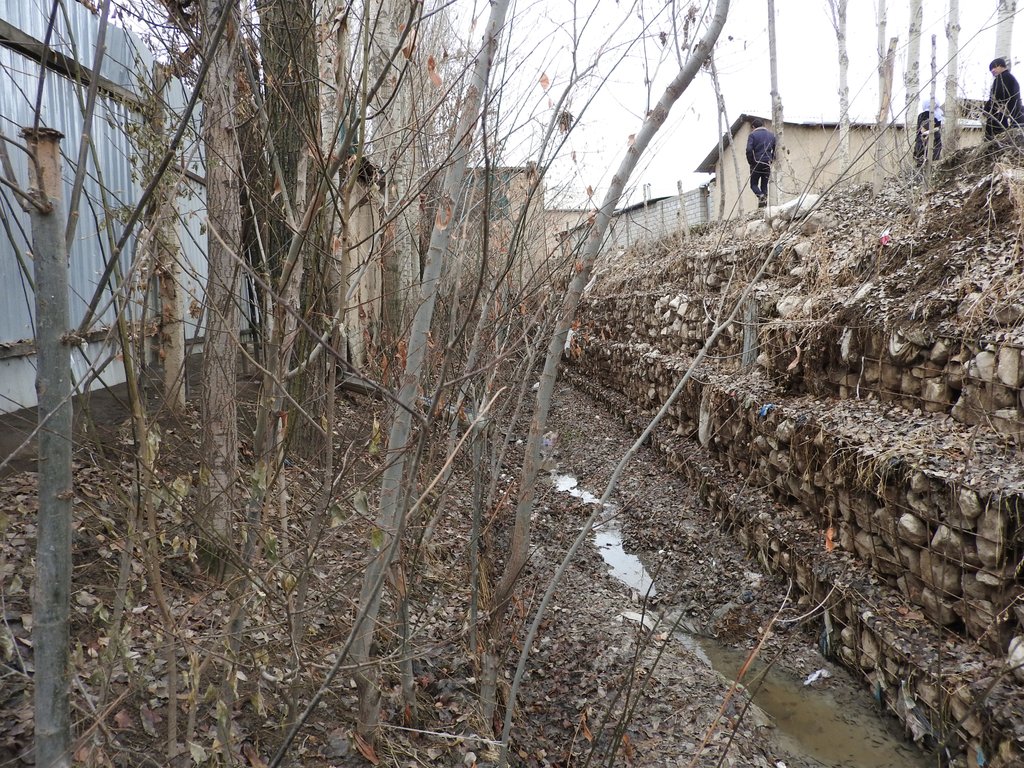
The approach brought together the Committee of Emergency Situations, affected local people and the administrative communities, the mahalla committees, which represent the inhabitants of one village or a section of a larger village. These institutions are called communal self-governance structures, but are subordinated to the government as they are reporting to the sub-district or jamoat. Assisted by experts provided by the project, the situation was jointly analyzed; risks identified and integrated intervention planned. Typically the interventions consisted of a combination of “grey” (i.e. constructive structures) and “green” (i.e. protective vegetation) measures. Most of the upper catchment areas belong to different communities, often to different districts and substantial parts are located in neighboring Kyrgyzstan. Therefore addressing the degradation of these areas and a reduction of disaster risk through integrated watershed management in the entire catchments was rarely possible.
The project assisted with technical planning, construction supervision, purchase and transportation of construction materials. The communities would contribute about 30% of the overall costs, mainly in form of voluntary communal work, the so called hashar, as well as in form of locally available construction materials. The community is also in charge of future operation and maintenance of the riverbank protection structures.
2.3 รูปภาพของแนวทาง
2.5 ประเทศ ภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่ได้นำแนวทางไปใช้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด: :
Sughd region
ข้อมูลเฉพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง:
Spitamen district, Devashtich district
Map
×2.6 วันที่เริ่มต้นและสิ้นสุดของแนวทาง
ระบุปีที่เริ่ม:
2014
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอนให้ประมาณวันที่ที่ริเริ่มใช้แนวทางนี้ :
น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (เร็วๆนี้)
2.7 ประเภทของแนวทาง
- ใช้โครงงานหรือแผนงานเป็นฐาน
2.8 เป้าหมายหรือวัตถุประสงค์หลักของแนวทาง
Prevention of disasters caused by flashfloods and debris flows
2.9 เงื่อนไขที่เอื้ออำนวยหรือเป็นอุปสรรคต่อการนำเทคโนโลยีภายใต้แนวทางนี้ไปปฏิบัติใช้
การมีไว้ให้หรือการเข้าถึงแหล่งการเงินและบริการ
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Communities and Committee of Emergency Situations without external assistance not able to implement effective integrated measures.
การจัดตั้งระดับองค์กร
- เอื้ออำนวย
Good collaboration between communities and Committee of Emergency Situations.
การร่วมมือหรือการทำงานประสานกันของผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติ
- เอื้ออำนวย
Good collaboration between communities and Committee of Emergency Situations.
ความรู้เกี่ยวกับ SLM การเข้าถึงการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
- เป็นอุปสรรค
Insufficient knowledge in communities about effective technololgy.
ปริมาณงานที่ทำได้ กำลังคนที่มีให้
- เอื้ออำนวย
Traditional joint volunteer work in communities for addressing common problems (hashar).
3. การมีส่วนร่วมและบทบาทของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้อง
3.1 ผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียที่เกี่ยวข้องในแนวทางนี้และบทบาท
- ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น
Inhabitants of village
Participation in identification of risk sites;
Volunteer work
- ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM หรือที่ปรึกษาการเกษตร
Engineers provided by GIZ
Identification of risk sites;
Design, planning and supervision of interventions.
- รัฐบาลระดับท้องถิ่น
District branches of Committee for Emergency Situations
Participation in identification of risk sites;
Agreement of plans for interventions
3.2 การเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่นในช่วงต่างๆของแนวทาง
| ความเกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นหรือชุมชนระดับท้องถิ่น | ระบุผู้ที่มีส่วนเกี่ยวข้องและอธิบายกิจกรรม | |
|---|---|---|
| การริเริ่มหรือการจูงใจ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Participation in identification of risk sites; |
| การวางแผน | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Participation in discussion of interventions; |
| การดำเนินการ | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Volunteer work |
| การติดตามตรวจสอบหรือการประเมินผล | ปฏิสัมพันธ์ | Control of conditions and functioning of protective structures |
3.4 การตัดสินใจเลือกใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM
ระบุผู้ที่ทำการตัดสินใจเลือกเทคโนโลยีมากกว่าหนึ่งวิธีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
- ผู้ลงมือปฏิบัติที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดในฐานะที่เป็นส่วนรวมของแนวทาง
4. การสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค การสร้างขีดความสามารถ และการจัดการด้านความรู้
4.1 การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
ได้มีการจัดอบรมให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดินหรือผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.2 การบริการให้คำแนะนำ
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินมีการเข้าถึงการรับบริการให้คำปรึกษาหรือไม่:
ใช่
การอธิบาย/แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Not involved in this approach
4.3 การเสริมความแข็งแกร่งให้กับสถาบัน (การพัฒนาองค์กร)
สถาบันได้รับการจัดตั้งขึ้นมาหรือเสริมความแข็งแกร่งโดยแนวทางนี้หรือไม่:
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
ระบุระดับของสถาบันที่ได้รับการเสริมความแข็งแกร่งหรือจัดตั้งขึ้นมา:
- ท้องถิ่น
อธิบายถึงสถาบัน บทบาทและความรับผิดชอบ สมาชิก เป็นต้น:
Strengthening of community institutions in addressing issues of common concern.
ระบุประเภทของการให้ความช่วยเหลือสนับสนุน:
- การสร้างขีดความสามารถ / การอบรม
4.4 การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผล
การติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าตอบว่าใช่ แสดงว่าการจัดเตรียมเอกสารนี้มุ่งหวังที่จะเอาไปใช้สำหรับการติดตามตรวจสอบและประเมินผลใช่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
4.5 การวิจัย
การวิจัยเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแนวทางหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5. การสนับสนุนด้านการเงินและวัสดุอุปกรณ์
5.1 ระบุงบประมาณประจำปีสำหรับแนวทาง SLM นี้
ถ้าหากว่างบประมาณประจำปีไม่เป็นที่ทราบแน่นอน ให้ระบุช่วงลงไป:
- 10,000-100,000
แสดงความคิดเห็น (แหล่งของการระดมทุน ผู้บริจาคคนสำคัญ):
Government of Germany, implemented via Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). The approach has been implemented in the frame of a much larger program and the specific budget for the SLM component of the Approach cannot be determined.
5.2 การสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ให้แก่ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินได้รับการสนับสนุนด้านการเงิน / วัสดุอุปกรณ์ไปปฏิบัติใช้เทคโนโลยีหรือไม่:
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ให้ระบุประเภทของการสนับสนุน เงื่อนไขและผู้จัดหามาให้:
Costs of planning, design and supervision, costs of materials, transportation and machinery covered by GIZ.
5.3 เงินสนับสนุนสำหรับปัจจัยนำเข้า (รวมถึงแรงงาน)
- อุปกรณ์
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| เครื่องจักร | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
- วัสดุสำหรับการก่อสร้าง
| ระบุปัจจัยนำเข้าที่ได้รับการสนับสนุน | เห็นด้วยระดับไหน | ระบุเงินสนับสนุน |
|---|---|---|
| หิน | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินบางส่วน | |
| Gabion nets | ได้รับการช่วยเหลือทางการเงินแบบเต็ม | |
ถ้าแรงงานโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินเป็นปัจจัยนำเข้าที่มีอยู่มากมาย ระบุด้วยว่าเนื่องจาก:
- สมัครใจ
5.4 เครดิต
มีการจัดหาเครดิตมาให้ภายใต้แนวทาง SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ
แรงจูงใจหรือเครื่องมืออื่น ๆ ได้ถูกนำไปใช้ส่งเสริมการใช้เทคโนโลยี SLM หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6. การวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบและการสรุป
6.1 ผลกระทบของแนวทาง
ทำให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินระดับท้องถิ่นมีอำนาจขึ้น ปรับปรุงการเข้าร่วมของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
People mobilized to address common issues.
ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ที่ดินนำเอาเทคโนโลยี SLMไปใช้และบำรุงรักษาสภาพไว้ได้หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Grey and geeen measures for prevention of riverbank erosion
ปรับปรุงความร่วมมือกันและการดำเนิน งานของ SLM ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
ระดมกำลังหรือปรับปรุงการเข้าถึงแหล่ง เงินทุนสำหรับการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Combination of financial and technical support by GIZ and contributions in form of work and locally available materials by community members.
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการดำเนินการ SLM หรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Community members capable of replicating the technologies.
ปรับปรุงความรู้และความสามารถของผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียคนอื่น ๆ ให้ดีขึ้นหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Committee of Emergency Situations capable of replicating the technologies.
Improved collaboration between Committe of Emergency Situations, communal self-governance and community members.
ส่งเสริมให้เยาวชนหรือบุตรหลานของผู้ใช้ที่ดินให้เข้าร่วมใน SLM:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Involvement of young people in joint work
นำไปสู่ความมั่นคงด้านอาหารหรือปรับปรุงโภชนาการให้ดีขึ้น:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Reduced risk of destruction of irrigation infrastructure and of loss of productive lands.
ปรับปรุงความสามารถของผู้ใช้ที่ดินในการปรับตัวให้เข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงของสภาพภูมิอากาศหรือสภาพที่รุนแรงและภัยพิบัติหรือไม่:
- ไม่ใช่
- ใช่ เล็กน้อย
- ใช่ ปานกลาง
- ใช่ อย่างมาก
Reduced risk of destructive impacts of flashfloods and debris flows, which due to climate change are increasing in frequency and intensity.
6.2 แรงจูงใจหลักของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเพื่อที่จะนำ SLM ไปปฏิบัติใช้
- ความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติลดลง
6.3 ความยั่งยืนของกิจกรรมของแนวทาง
ผู้ใช้ที่ดินสามารถทำให้สิ่งต่างๆ ที่ได้ปฏิบัติใช้โดยแนวทางนี้ยั่งยืนได้หรือไม่ (โดยไม่มีการสนับสนุนจากภายนอก):
- ใช่
6.4 จุดแข็งและข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทาง
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Reduced disaster risk |
| Availability of wood from green measures |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบของแนวทางในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Same as land-users |
| Improved collaboration at local level and strengthened institutions |
| Ownership feeling among community members |
6.5 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบของแนวทางและวิธีในการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| None |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| None |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการหรือแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Prevention of riverbank erosion by combination of green … [ทาจิกิสถาน]
Flashfloods in riverbeds cause intensive riverbank erosion, which threatens villages, infrastructure and productive lands. Preventive measures combining "grey" (physical structures) and "green" (living trees) elements are more effective, sustainable and cost efficient than constructive measures only.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Stefan Michel
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล