Irrigated agro-biodiversity system in arid high mountain area [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1034 - ทาจิกิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - ทาจิกิสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - ทาจิกิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
21/06/2010
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
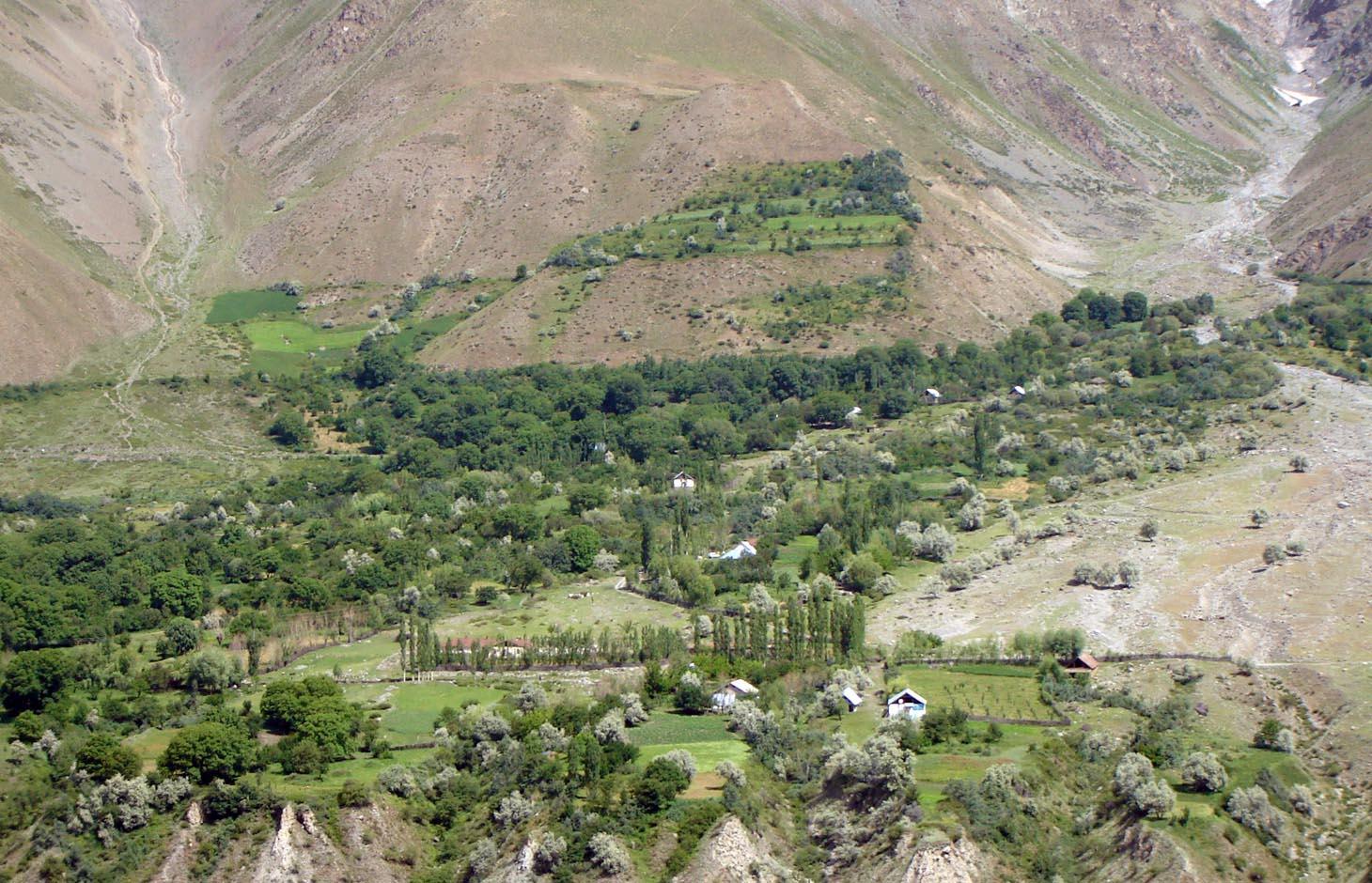
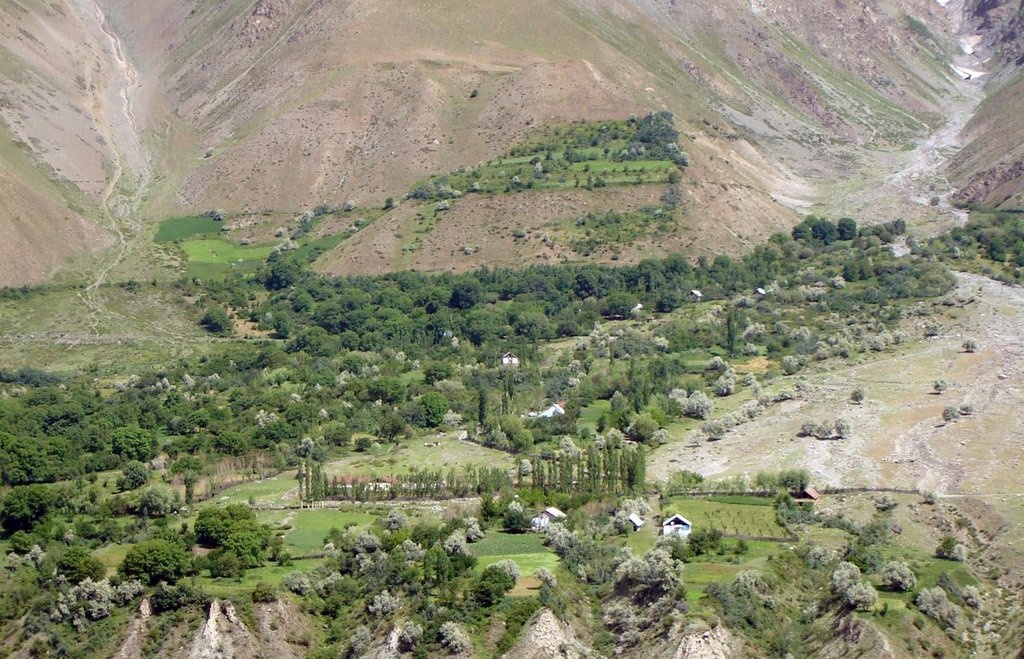
An individual farmer family, has changed an overgrazed pasture area on a steep slope in the upper part of the village into an irrigated agro-biodiversity system, by constructing an irrigation canal, by tilling and removing stones from the terraces for crop production and afforesting the surrounding area with fruit trees and bushes.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The site was established in 1989, with the construction of an irrigation canal. The canal brings water from a small watershed and the slowly melting snow fields within. In years with limited snowfall, the water is insufficient for irrigation throughout the summer months.It is a open, mud canal, 730 m long. When establishing new cropland, removal of stones from the plots is the most laborious part of the work. After an initial removal of stones, the land is tilled and appearing stones are again removed. This process is repeated several times.
Year round maintenance work is required to keep the canal functioning. Maintenance work on the cropland includes stone removal, manuring of potatoes fields, weeding and tilling.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
GBAO
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Vanj / Udob / Trit
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
A traditional agroforestry system is implemented on a steep slope above the village, as there is a lack of flatter cropland. This requires improved and carefully adapted land practices.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
major food crop: potato, wheat, barley, alfa-alfa

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water scarcity is the major factor limiting vegetation growth and agricultural production in this arid areas. The soils are stony and slopes are steep (20-30 degrees).
The area is irrigated from streams fed by snow and glacier melting, and therefore water availability is strongly depending on yearly snow precipitation. If due to climate change snowfalls are decreasing in the future, this is a threat for agriculture in the region.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As the area is on steep slopes there is a high risk of small land slides triggered by irrigation. Fast snow melting in spring time may also cause land slides.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: May - September
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology can be found all along Vanj valley.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S1: คันดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking crust / sealed surface, breaking compacted topsoil, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bh: loss of habitats, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts (in years with droughts part of the perennial vegetation may dry up), land tenure (common grazing land), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to irrigation water, access to markets)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (early grazing, overgrazing), labour availability (mostly manual work and thus labour intensiv), governance / institutional (limited access to market, no water association)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Vast practical knowledge is required, through practical experiments, the practices were improved over time.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Agronomic measure: crop rotation on wheat fields
Material/ species: perennial fodder plants (alfa-alfa)
Remarks: high density of alfa-alfa plants
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cow manure
Quantity/ density: 15
Remarks: for patatoe fields
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: "super phosphat" or "silitra"
Quantity/ density: 0.025
Remarks: for wheat fields
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Contour tillage
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)";
Fruit trees / shrubs species: sea-buckthorn, walnut, plum, appel, pear, apricot, mirabelle, whitethorn, cherry, dog rose
Grass species: graminoids and legumes
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2500
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 750
Construction material (earth): The waterways are all dug into the ground, and are mostly fortified with bushes and trees.
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: extensive grazing to agroforestry
Layout change according to natural and human environment: carefully designed layout taking advantage of flatter areas for cultivation of annual crops, and protecting steep slopes with perennial tree and bush cover
Control / change of species composition: mix of cultivated and wild plants (trees, bushes and grasses)
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Tajik Somoni
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
4.4
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
30.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | ด้วยวิธีพืช | spring |
| 2. | Construction of irrigation canal | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | autumn |
| 3. | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | spring |
| 4. | Alfa-alfa seeds (12kg/ha) | จัดการพืช | for 4 years, then can produce own seeds |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | Persons/day | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| แรงงาน | Construction irrigation canal | Persons/day | 100.0 | 30.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | Persons/day | 30.0 | 30.0 | 900.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Alfa-alfa seeds | kg/ha | 6.0 | 20.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4020.0 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wheat (barley) sowing | จัดการพืช | anually |
| 2. | Wheat (barley) sowing | จัดการพืช | |
| 3. | Tilling potato fields | จัดการพืช | 3 times per growing season |
| 4. | Irrigating wheat (barley, alfa-alfa) | จัดการพืช | times per growing season |
| 5. | Planting potato | จัดการพืช | during planting |
| 6. | Planting potato | จัดการพืช | |
| 7. | Applying fertilizer to wheat fields | จัดการพืช | 3 times per growing period |
| 8. | Maintenance of canal and on-farm water distribution network | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | spring and after rains |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Sowing wheat with ochses | Persons/day | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Tilling with ochses | Persons/day | 6.0 | 40.0 | 240.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Irrigating wheat, barley alfalfa | Persons/day | 6.0 | 30.0 | 180.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Planting potatoe | Persons/day | 8.0 | 30.0 | 240.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Ochses for wheat sowing | Ochses/ha | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Ochses for potatoe tilling | Ochses/ha | 6.0 | 30.0 | 180.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Donkey for carrying dung to the fields | loads | 120.0 | 0.66666 | 80.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Labour: Going with donkeys | Persons/day | 8.0 | 40.0 | 320.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Wheat seeds | kg | 200.0 | 1.2 | 240.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost/manure | tons | 12.0 | 50.0 | 600.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Poatoe seedling | kg | 800.0 | 1.0 | 800.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer for wheats | kg | 140.0 | 0.58571 | 82.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 3102.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Costs were calculated fro an area of 5 ha. The length of the irrigation channel from the creek to the plot is 730 m.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
With regard to the establishment costs, the most determining factors are: the distance to the creek from where water is channeled away and the steepness of the slope and amount of stones when preparing the land for annual cropping. With regard to the maintenance costs it is the exposure of the water channel to rock fall and small land slides.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Most of the precipitation consits of snow, the main rainfall period is March / April
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate. high mountain area
A2240 m asl
gricultural areas need irrigation, which is supplied by snow and glacier melt
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: 2240 m a.s.l.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
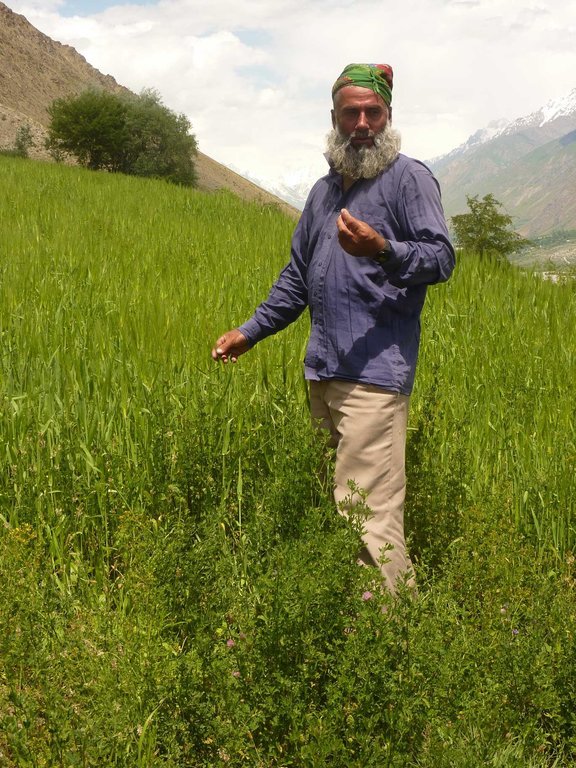
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich.
10% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The here described farmers family has very limited off-farm income. The farm provides sufficient fuel, fodder, fruits and potatoes for subsistence farming.
In general, seasonal migration to Russia is widespread in the area, which provides additional income in form of remittances. Only households with only young children, elderly and sick persons have no family member working in Russian.
Level of mechanization: One uses ochses for plowing, motorized is really rare.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land use right for the individual farmer is documented with an official land user certificate.
Water use right has been agreed on with the village council.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- ครั้งเดียวหรือเป็นการทดลอง
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
1 Household
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล