Chat Ridge bund [เอธิโอเปีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Chat Katara
technologies_1066 - เอธิโอเปีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
20/10/2005
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
It is a mechanical conservation measure where a basin and a ridge are formed for planting chat along a contour
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
A contour line is maked and a pit (trench) is dug and the soil embanked on about 75x50 cm. Chat cuttings are planted on the trench. The purpose of the technology is to collect as much water as possible. The embankment protects soil from erosion. Water is collected in the trench. Households using family labour make the ridge bund. During cultivation the ridge is strengthend. Maintenance is done in case of breaks on the ridge.The technology is suitable to semi-arid with rainfall 500-700 mm/annum. Farmers grow chat as the main means of finance/capital generation. Cultivation is done twice or three times.
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เอธิโอเปีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Harari
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Hamaressa/Bisidimo/Errer
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
locally originated
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop: Chat
Major food crop: Sorghum

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- การปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์และการทำป่าไม้ (Agro-silvopastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): land shortage, continuous cropping, land degradation, open grazing.
Other grazingland: Tethered/stall feed: grazing land shortage forced to tethered feeding and stall keeping.
Other grazingland: free grazing
Grazingland comments: Livestock (cows, goat) are mostly stallfed. In lower parts of the technology area livestock are let to graze openly. This part is a very dry area and there is large area for grazing. Goats browseon open woodlands that have acacia trees.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The woodlands are getting extremely denuded as a result of heavy exploitation such as charchoal making, cutting trees for fuel wood and overbrowsing.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: sorghum, ground nut
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 210
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
60% of the total cultivated area in the region is under this technology
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
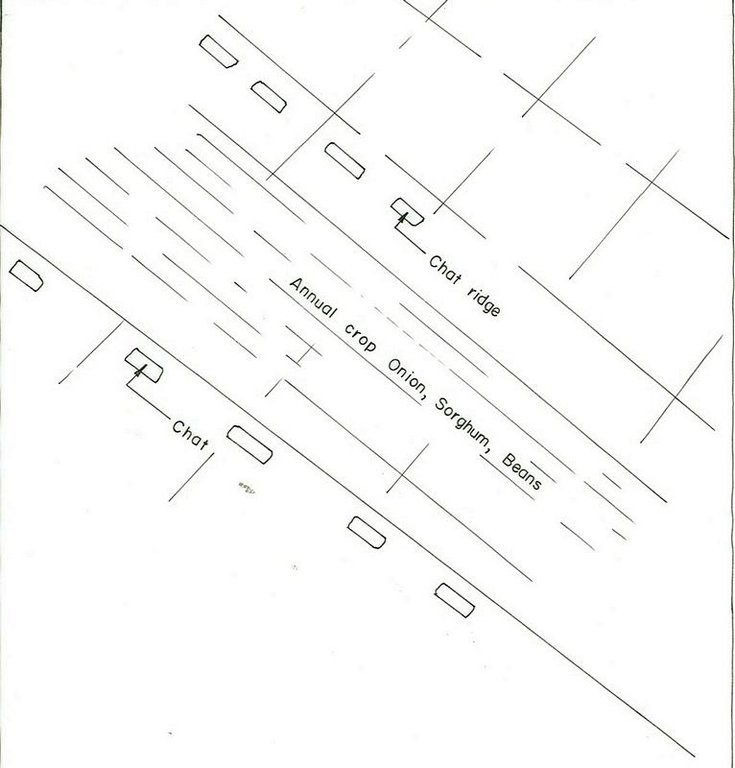
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Harari
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope length
Early planting
Material/ species: sorghum
Relay cropping
Material/ species: legume/sorghum
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: beans sorghum
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Chat, sorghum, onion
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia, Acacia, Mango
Perennial crops species: Chat
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Bund/ bank: level
Spacing between structures (m): 1-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2-3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3-4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 70-80
Construction material (earth): earth bunds
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 4%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1%
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Birr
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
8.6
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
0.85
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | seed bed preparation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | Dry season |
| 2. | preparing cutting | ด้วยวิธีพืช | rainy season |
| 3. | cutting plantation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | rainy season |
| 4. | cultivation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after rain |
| 5. | Protect from free grazing animals | ด้วยการจัดการ | especially after crop harvest. |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging | จัดการพืช | before rains / each cropping season |
| 2. | Cultivation and weeding | จัดการพืช | mid of rains / twice a year |
| 3. | replanting of dead cuttings | ด้วยวิธีพืช | May, June /during rain |
| 4. | cultivation | ด้วยวิธีพืช | July /during rain |
| 5. | reridging of breaks | ด้วยวิธีพืช | September /after rain |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: hand tools
Volume of earth excavated and moved.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Landforms: Also hill slopes (ranked 2) and ridges (ranked 3)
Slopes on average: Also hilly (ranked 2) and steep and gentle (both ranked 3)
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is low (ranked 1), medium (ranked 2), very low (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
- รวย
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy.
25% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users who have SWC measures on their land have lower off-farm income compared to those who have no SWC measures on their land.
Market orientation of production system: mixed (Sorghum: mostly used at home and partly sold) and commercial/ market ( Livestock (cows, goat) are mostly stallfed. In lower parts of the technology area livestock are let to graze openly. This part is a very dry area and there is large area for grazing. Goats browsing open)
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land holding is extremely low
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: more and more land users are getting engaged with the technology.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Efficient in rainwater harvesting |
| Laid out by farmers with little technical support |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Highly flexible How can they be sustained / enhanced? change of structures (size, position) possible |
|
Material needed is locally available How can they be sustained / enhanced? soil and stone are found everywhere |
|
Low cost How can they be sustained / enhanced? tools available at local markets |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล