Cut-off drain [ไทย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Fabian Ottiger
Rong rabai nam (Thai)
technologies_1405 - ไทย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Tiparat Sutep
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
ไทย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Outarasak Vorachai
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
ไทย
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Suksom Prasong
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project
P.O. Box 36, P.O. Huay Khrai, Chiang Rai 57220
ไทย
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center - ไทยชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project - ไทย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
30/11/1997
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 อ้างอิงไปที่แบบสอบถามเรื่องแนวทาง SLM

Cut-off drain [ไทย]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Samran Sombatpanit
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
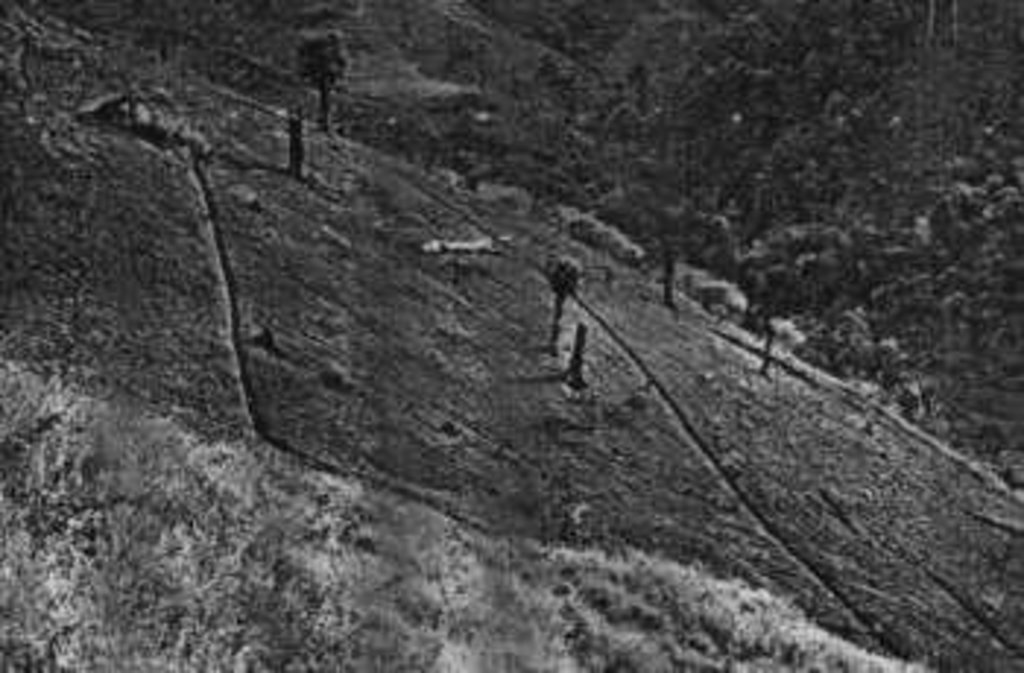
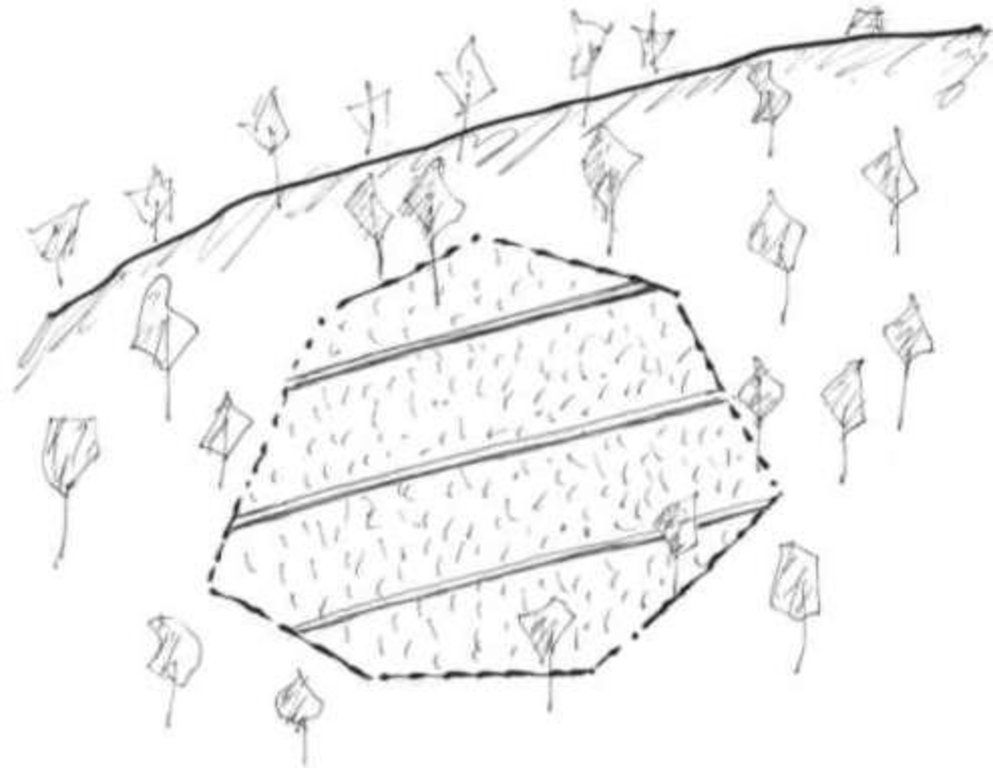
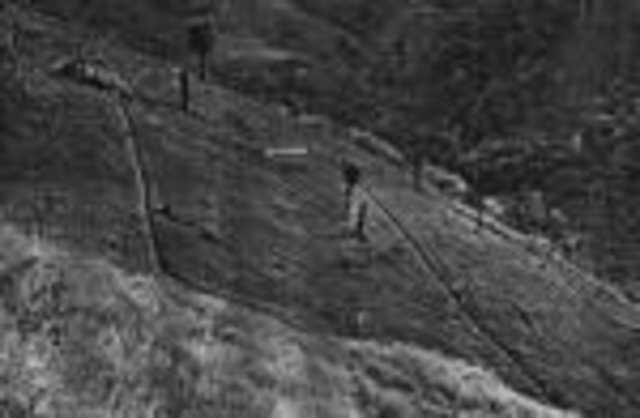
Cut-off drain is a drainage ditch dug to quickly drain water out of sloping agricultural land.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The cut-off drain is the same thing described as 'diversion' or 'diversion ditch'. It is dug by hand-hoe, only one hoe wide in the first year and may expand wider in the second and third year. It is dug with gradient from 15-50% to facilitate drainaing of runoff, not to scour the soil. Note: 1. The width of one hoe is approx. 21 cm , 2. The dimension of the ditch may become 30-40 cm wide and deep after 3 years.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ไทย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Chiang Rai
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Amphur Mae Fa Luang
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It is an original idea. No one knows how/when it was originated.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major cash crop annual cropping: Maize
Major food crop annual cropping: Upland rice
Major cash crop mixed system: Maize
Major food crop mixed system: Upland rice
Major other crop mixed system: Fruit trees

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ใช้พื้นที่กว้าง:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
- กึ่งเร่ร่อน / อาจมีการทำทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ร่วมด้วย (Semi-nomadism/ pastoralism)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. There is soil erosion problem because of high terrain, 2. Lacking of land ownership (The whole land area is reserved forest), 3. Low price of agricultural produce,
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Lacking of land ownership, 2. Land users do not have Thai citizenship; less than 20 % have ID cards (not citizenship).
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Aug Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Nov
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15 m2.
E-kaw, Lahu, Lisu, Mien, Khin, Thai Yai, Haw Chinese, H'mong. They have been doing this practice for a long time. The technology transfers from generation to generation.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Lack of enforcement of legislation or authority
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural activities), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
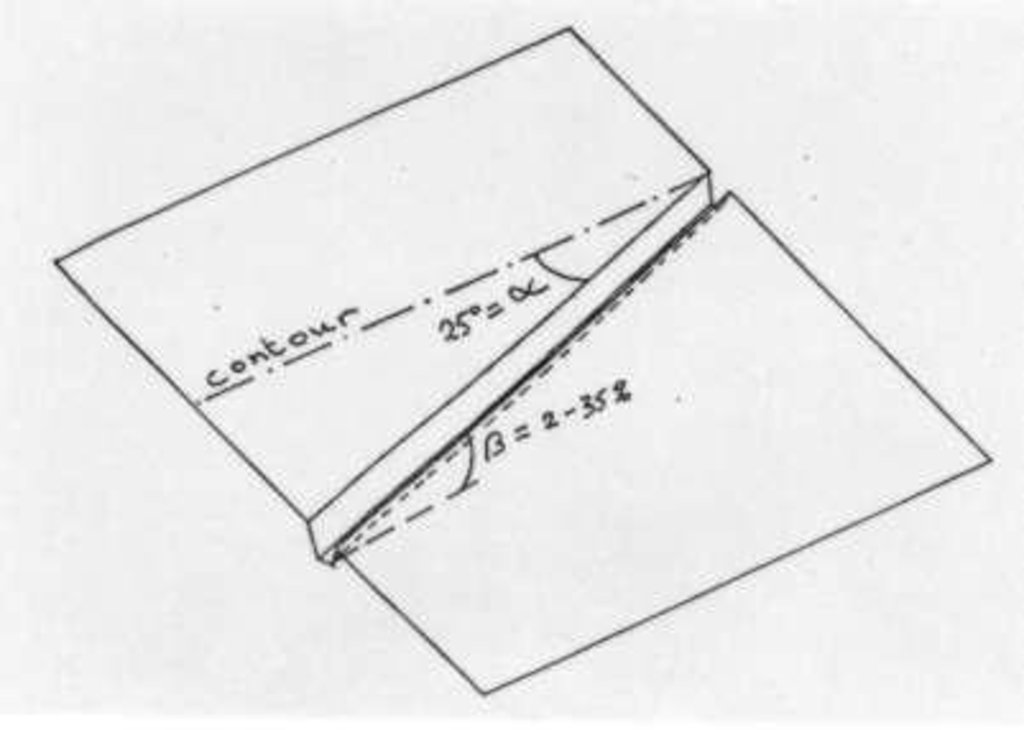
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.
The cut-off drain is the same as 'diversion'. It is dug by hand hoe, only one hoe wide in the firs yer and may expand wider in the second year and third year. It is dug with gradient in order to facilitate draining of runoff, not to scour the soil. The gradient may vary from 3:20 (15%) to 1:2 (50%).
Note: The land may be cropped for 3 years and left for shrubs to grow for some years. Then farmers return to clear the land to grow crop again.
Location: Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.. Chiang Rai Province
Date: 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Structural measure: Cut-off drain
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40
Construction material (earth): It is the earth dug in situ.
Lateral gradient along the structure: 20%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Baht
ระบุอัตราแลกเปลี่ยนจากดอลลาร์สหรัฐเป็นสกุลเงินท้องถิ่น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง) คือ 1 เหรียญสหรัฐ =:
37.0
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.16
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the ditch after land preparation | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Before rainy season |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 4.32 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dredging up the earth that fell down when preparing for next crop | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Before rainy season/Annually |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4.32 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Cost per ha of land protected
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Steep slope will require larger number of the cut-off drains, thus affecting the cost.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Average = 1600-1800 mm
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- ชื้น
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil depth on average: Also shallow (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: High (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (good drainage though being clayey soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low (both ranked 1)
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
6% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
24% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (Large proportion are poor).
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers spend much time doing wage earning labour jobs.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Ranked 1: 1-2 ha. Farmers may farm at 2-4 plots far apart from each other
Ranked 2: 2-5 ha
Ranked 3: 0.5-1 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Production is not decreased.
คุณภาพพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Farmers don't mind
การจัดการที่ดิน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Drainage can function as a farm path
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Input constraints
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20
หลังจาก SLM:
15
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50
หลังจาก SLM:
10
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การไหลของน้ำคงที่และสม่ำเสมอในช่วงฤดูแล้ง
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
800. 13% of the area covered
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 50-90%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
800 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: When farmers understand the use of it they will do it.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. |
| This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When farmers get the idea, this T will be sustained/enhanced. |
|
This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cheapness and simplicity will make it sustained. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Land users do not see any disadvantages |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| This T may cause erosion of its own structure at the beginning. | Government agencies should help design the size and gradient of this T toi be properly used. |
| This T may cause erosion off-site especially when the drained water is allowed to flow directly to open land | Design and build waterway to receive the disposed water. |
| This T does not enhance soil fertility improvement | Try to use it along with other measures which improve soil fertility or change it to something else. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Pongsapich, A. Indigenous Technical Knowledge for Land Management in Asia. 152 pp.. 1998.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
IBSRAM, Bangkok
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Turkelboom, F. On-farm diagnosis of steepland erosion in Northern Thailand, PhD thesis. 309 pp.. 1999.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Laboratorium Voor Bodemvrucktbaarheid en Bodembiologie, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven,Kardinal Mercierlaan 92, B-3001 Heverlee,Belgium
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Cut-off drain [ไทย]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Samran Sombatpanit
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล