Environmentally-Friendly Community Practices [มอลโดวา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Valentin Ciubotaru
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Valentin Ciubotaru, UNCCD PRAIS
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Practicile comunitare prietenoase mediului
technologies_1816 - มอลโดวา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ciubotaru Valentin
+37322 545733 / +37322 69134294
ngobios@yahoo.com / valentin.ciubotaru@yahoo.com
NGO BIOS
72/3 Columna str., office nr. 3. Chisinau- MD-2012
มอลโดวา
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NGO BIOS (.) - มอลโดวา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
02/06/2014
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Community area development plans were developed taking into consideration the main problems, opportunities, necessities and wishes of the local population. All communities included afforestation of severely eroded land, re-establishing degraded forest belts and planting new forest lines, creating protection shields for aquatic areas, and an ecological education community program.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Community area development plans were developed for six communities for the period of 2008-2028, taking into consideration the main problems, opportunities, requirements and wishes of the local population. Special attention was paid to environmental impact assessment to harmonize economic and social development with environmental protection. All communities included afforestation of severely eroded land, re-establishing degraded forest belts and planting new forest lines, creating protection shields for aquatic areas, and elaborating and implementing a ecological education community program.
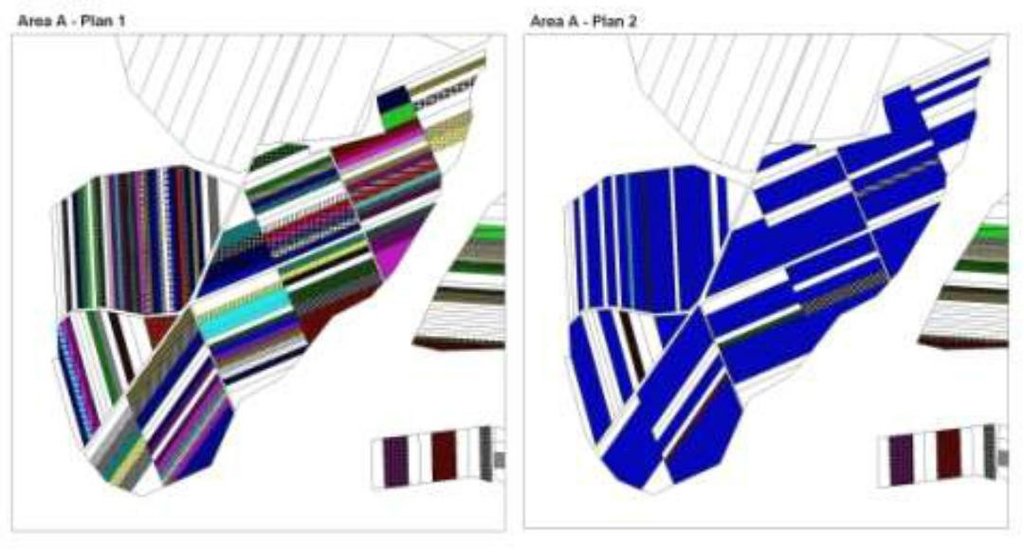
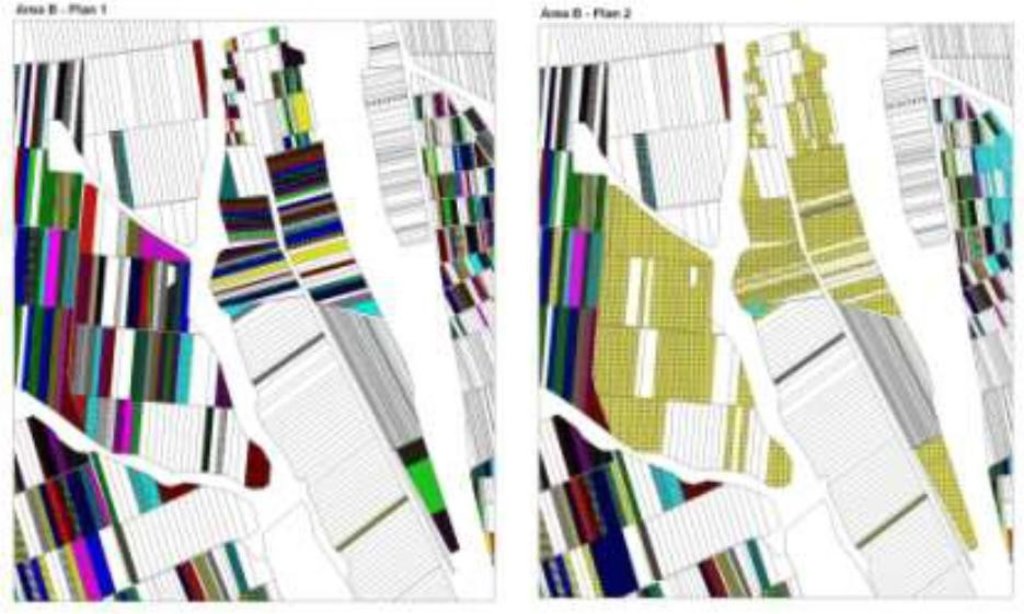
The first action implemented was agricultural land re-parcelling, based on FAO guidelines. Training programs were conducted for project staff and beneficiaries. Following land planning, discussions and individual negotiations with each land owner, the project promoted the application of the following land parcels operations: sale, exchange and long term lease. The costs incurred during land transactions were fully covered by the project. The Land Use Scheme implies changes in some categories of use and especially expanding the area of vineyards and orchards as well as using agricultural land for community development according to the needs and wishes of the population. Land re-parcelling offers farmers the possibility of rearranging agricultural land according to ecological principles and potential.
The overall goal of land re-parcelling component was to respond to the concerns of the Government and others about the fragmentation of agricultural land: it focussed on small peasant farms as its primary target group. The specific objectives of the pilot action were:
- to test the demand for and feasibility of land re-parcelling with small landowners as the primary target group;
- to facilitate development of 6 community area development plans, taking into account environmental impact assessment.
- to use the pilot experience as the basis for designing a potential national-level approach, including techniques, resource requirements and legislative framework;
- to assess the impact of re-parcelling at the local level, including on land markets, agricultural production, and equity.
The re-parcelling activities were extended to 40 villages on the proviso that the concept and the experience of the implemented re-parcelling pilots would be precisely followed. Based on this experience, the Ministry of Agriculture is in active partnership with National Agency for Rural Development and NGO BIOS, supported by the FAO-developed National Strategy for Land Consolidation.
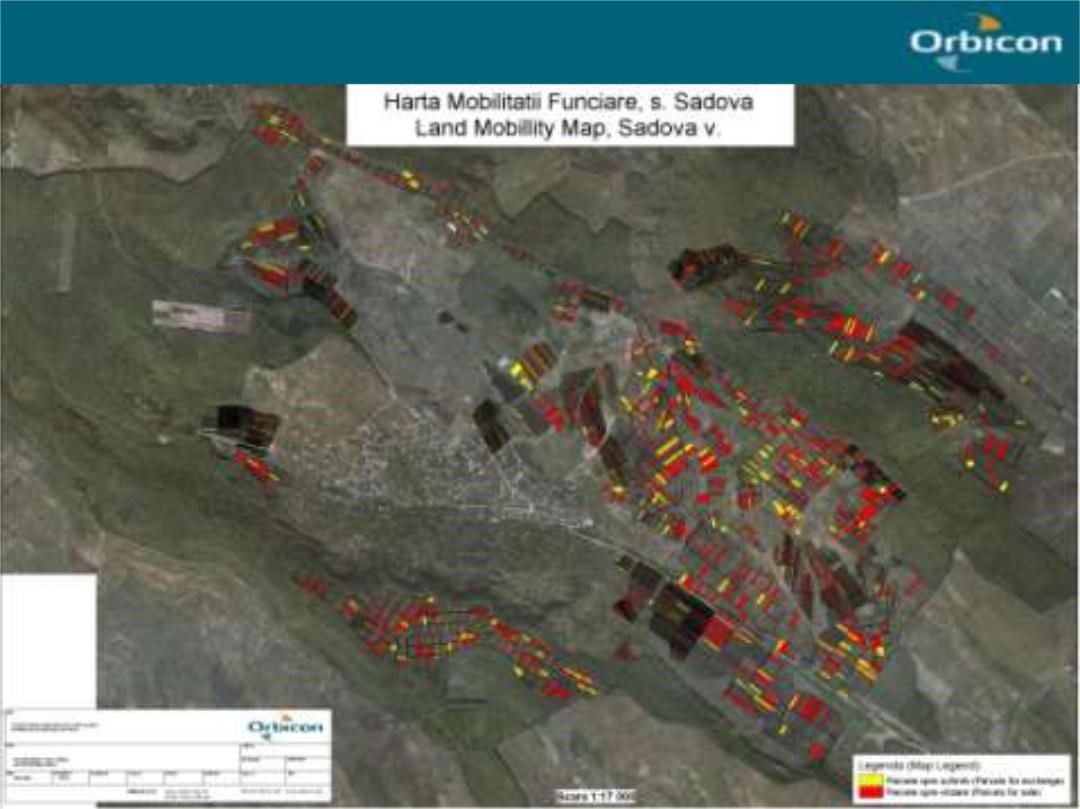
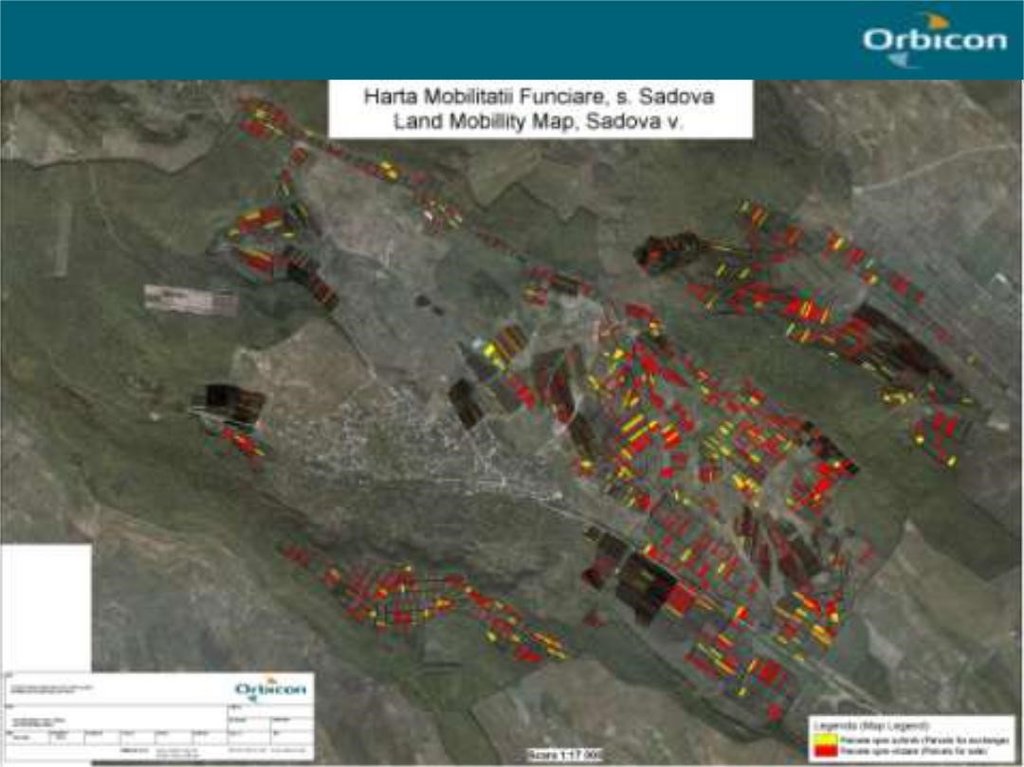
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มอลโดวา
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
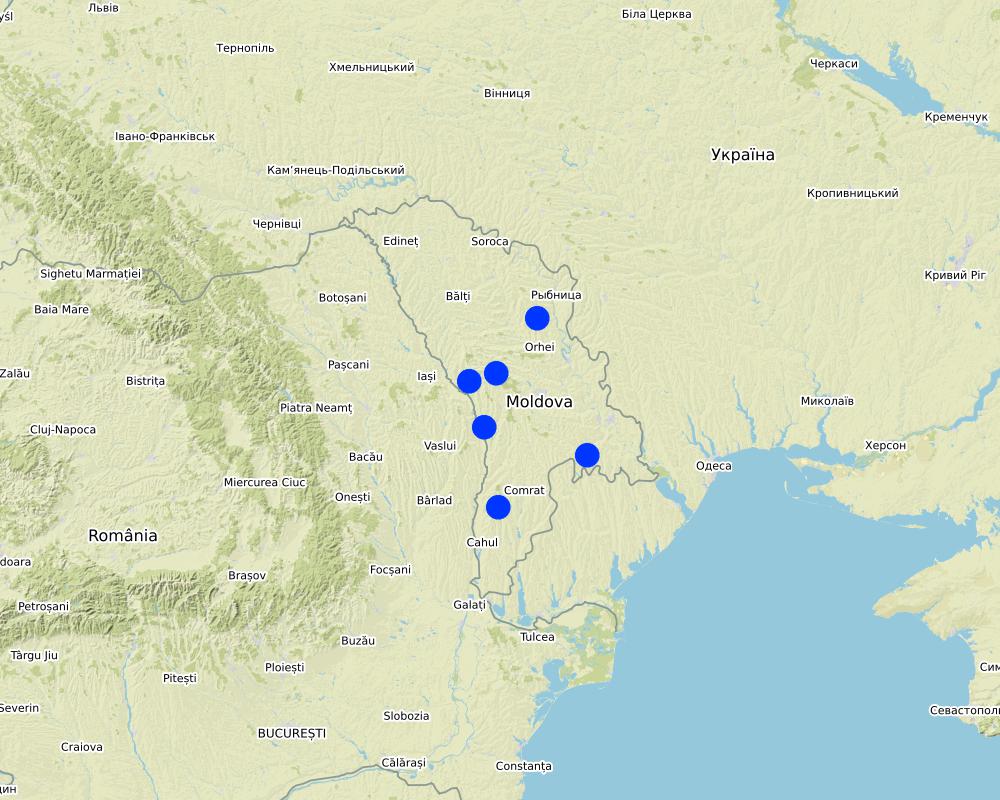
The six communes which form the pilot area, namely Basauca village Rezina district, Sadova village Calarasi district, Calmatui village Hincesti district, Bolduresti community of Cantemir district, Baimaclia community Cantemir district, Opaci village Causeni district, Republic of Moldova. The experience was replicated in 40 villages.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The six communes which form the pilot area, namely Basauca village Rezina district, Sadova village Calarasi district, Calmatui village Hincesti district, Bolduresti community of Cantemir district, Baimaclia community Cantemir district, Opaci village Causeni district, Republic of Moldova.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้

อื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
- Land fragmentation; - Environmentally unsustainable land management practices; - Illegal cutting of forests, leading to the destruction of forest belts and buffer strips; - Point and non-point sources of pollution, - Over-grazing..
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
- มาตรการปลูกพืชขวางความลาดชัน (cross-slope measure)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- > 10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The Technology was replicated to 40 villages in South, Center and North regions of Moldova
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
- S9: ที่พักพิงสำหรับพืชและสัตว์

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M1: การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบของการใช้ประโยชน์ที่ดิน
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
- Implementing activities of protection, maintenance and improving of degraded soil fertility;
- Agroforestry consisted of planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts.
- Improving the quality of pastures and implementing controlled pasturing.|
- Regeneration of degraded commune forest as well as existing forest protective belts.
- Planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts. |
Facilitate the development of farms by reducing the fragmentation and expanding the area of agricultural lands. The project provides assistance to land owners and farmers to undertake voluntarily land transactions based on market economy principles, elaborating the land ownership maps (GIS MapInfo|
The elaboration of the Community Area Development Plans was effected together with the local public administration, professors, legal persons, non-governmental organizations, and the population of communities with active involvement of Zonal Ecologic Agencies, Preventive Medicine Centers, |Agriculture and Economy Departments of district Executive Committees.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
- Ed (Deflation and deposition): การกัดกร่อนโดยลมและการทับถม

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pu (Loss of bio-productive function): การสูญเสียหน้าที่การผลิตทางชีวภาพอันเนื่องมาจากกิจกรรม อื่นๆ

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Implementing activities of protection, maintenance and improving of degraded soil fertility | ||
| 2. | Agroforestry consisting of planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts. | ||
| 3. | Improving the quality of pastures and implementing controlled pasturing| | ||
| 4. | Regeneration of degraded commune forest as well as existing forest protective belts | ||
| 5. | Planting of tree rows on cultivated lands, primarily of windbreaks and anti-erosion protective belts |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The Project
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Chisinau, Nisporeni, Calarasi, Cahul, Leova, Hincesti, Rezina
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Moldova's climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging 20 °C, and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging −4 °C. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 600 millimeters in the north to 400 millimeters in the south, can vary greatly. The heaviest rainfall occurs in summer; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common. Because of the irregular terrain, heavy summer rains often cause erosion and river silting.|
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Most of Moldova's territory is a moderate hilly plateau cut deeply by many streams and rivers. Geologically, Moldova lies primarily on deep sedimentary rock that gives way to harder crystalline outcroppings only in the north. Moldova's hills are part of the Moldavian Plateau, which geologically originate from the Carpathian Mountains. |
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
About 75% of Moldova is covered by black earth or chernozem. In the northern hills, more clay textured soils are found; in the south, red-earth soil is predominant. The soil becomes less fertile toward the south but can still support grape and sunflower production. The hills have forest soils, while a small portion in southern Moldova is in the steppe zone, although most steppe areas today are cultivated. The lower reaches of the Prut and Dniester rivers and the southern river valleys are saline
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
high water mineralisation
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
- ผู้สูงอายุ
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
After independence (1991), land was privatized. The average family was entitled to plots of between 1.5 and 2.5 ha. Four categories of farms emerged: (i) small individual farmers; (ii) individual commercial farmers; (iii) farmers in associations with close relatives; and (iv) farmers in groups (from less than 10 farmers to large, joint-stock companies). The small size of many farms precludes the use of agricultural machinery and advanced technology. |
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The principal activity of local farmers is crop farming; main arable crops are maize and wheat. The cultivation of grapes and fruits is another traditional element of agriculture in this area. Vineyards and orchards take a significant share of cropped land. Income is derived from sale of agricultural produce, including milk and eggs, from forest products, but also from seasonal work at the small workshops in their own and surrounding communities.|
Income depends much on weather conditions and agricultural policies. Estimated average income per person is 50 US dollars per month for the last three years (no including this year).
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตสัตว์
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำท่วมพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Expected changes include utilization of local resources, change in existing land use management, change in landscape, changes in erosion rates, etc. These in their turn are expected to lead to social and economic impacts on people.
• The main environmental indicators are largely the same. • The expected environmental impact of re-parcelling and initiated actions are significant, especially in the long run. |
People learn to live with the new approach, new land structure, alternative solutions of solving their own problems, etc. |
Implementation of the land re-parcelling project contributes to improving the structure of the agricultural land, efficient use of technology, increase the possibility of arranging the community territory with a consolidated network of roads; |
The economic levels stayed practically unchanged, while social cohesion and culture has somewhat improved from exposure to new things, common work. The expected social impact of re-parcelling and initiated actions are significant, especially in the long run.|
Expected changes include increased jobs for people, there will be favourable conditions for the young population to stay in the rural area and those who left abroad could return back and start various businesses in their village.|
Improving the community infrastructure by water and natural gas supply, etc. It offers farmers a possibility to start processing enterprises so that they can sell the final product at a higher price than the raw products.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 10-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Business opportunities related to community development, etc. | Highly motivated local governments Highly motivated farmers |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
6000
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Assessment Study on Land Re-parceling Pilot Project in 6 Villages in Moldova
URL:
http://www.capmu.md/wp-content/uploads/images/docs/Impact_Assessment/Final%20report%20IA%20land%20rep.pdf
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Experiences with land reform and land consolidation in Moldova
URL:
file:///C:/Users/USER/Downloads/59-357-1-PB.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล