Integrated Land and Water Management [มอลโดวา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Valentin Ciubotaru
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Valentin Ciubotaru, UNCCD PRAIS
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Managementul integrat al solului și al apei
technologies_1817 - มอลโดวา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Ciubotaru Valentin
+37322723372 / +37369134294
valentin.ciubotaru@yahoo.com / valentin.chiubotaru@gmail.com
NGO BIOS
11/1 Gheorghe Asachi str., ap. nr. 87
มอลโดวา
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NGO BIOS (.) - มอลโดวา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
01/07/2010
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
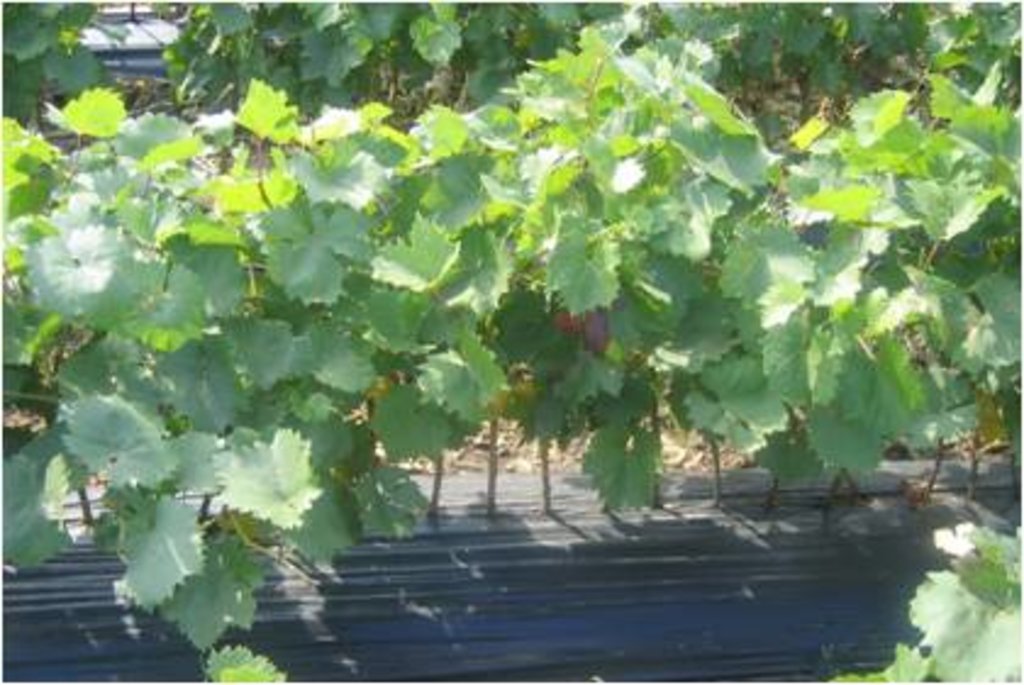
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Integrated land and water management was promoted in order to improve agricultural production while reducing soil loss and nutrient discharge into water bodies. Technical assistance and financial support was provided for sustainable agricultural practices, including: nutrient management, conservation agriculture, integrated cropping management, agroforestry and wetland management.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Integrated land and water management was promoted in order to improve agricultural production while reducing soil loss and nutrient discharge into water bodies. Technical assistance and financial support was provided for sustainable agricultural practices, including:
1. Manure Management Practices:
Organic manure was substituted for inorganic fertilizer, and eight commune/village stores were constructed together with 1200 household stores and equipment provided for manure handling and field application. A monitoring database was made available.
2. Promotion of Environment-Friendly Agricultural Practices:
A well-documented pilot was completed and evaluated for replication, and 300 farmers then trained in the application of environment-friendly agricultural practices. The capacity of extension staff significantly improved. A monitoring system to determine the impact of practices on soil quality was installed and data collected.
3. Shrub and Tree Planting:
• 132 hectares of shelterbelts for water protection established; 112 hectares of improved anti-erosion forest belts set up; 50 hectares of improved pasture established; 484 hectares of the existing forests rehabilitated and properly managed; forest monitoring was incorporated into the general monitoring scheme.
4.Wetland Restoration and Promotion of Sustainable Management Practices:
The existing ecosystems were rehabilitated and ecologically well balanced. In this context two dams were built with a sluice gate system for the stabilization of water levels; three concrete bridges with adequate culvert capacity were installed for accessibility to different portions of the wetland; and 10 small wood bridges with culverts were built for access.
5 .Monitoring Soil and Water Quality and Environmental Impacts
Availability of water for downstream users and fisheries was increased, drinking water supplies was improved, there was increased quality and availability of groundwater for human and animal consumption, and simultaneously better productive lands with increased organic matter and carbon sequestration, as well as increased biodiversity.
Key Elements of the Manure Management System:
a. Segregation of inert and recyclable materials from livestock waste through the provision of a separate household waste container.
b. Improved manure stores for storage of waste at a single impermeable store at the household with enough storage for up to one month's production.
c. Transfer of waste from the farm store to a central site, using transport units then unloading it at the commune platform, to aerate the waste, promoting continued bacterial activity.
d. At the commune/village store level, the segregated inert materials deposited in designated bunkers.
e. At the commune/village store level, management of the household manure at the main bunker involving stacking in shaped windrow heaps three metres high.
f. Store the waste deep so that the areas getting wet from rainfall is minimised. Provide impermeable walls and floor to eliminate leaching.
g. Provide storage capacity for over the winter so that matured manure will be available for use on the land.
Key Elements of facilities at the Village Platform are:
a. Concrete area for the management of the manure.
b. Bunkers for the segregated household manure.
c. Collecting channel for runoff from the platform.
d. Storage pits and tanks with impermeable base and walls.
e. Security fencing.
f. Office / Staff facilities and Landscaping. Monitoring wells to check for leakages.
Overall results show that 8,250 farmers from both the project pilot area and other regions of Moldova had adopted at least one environmentally-friendly agricultural practice promoted by the project, and had implemented these on 14,028 ha of land.
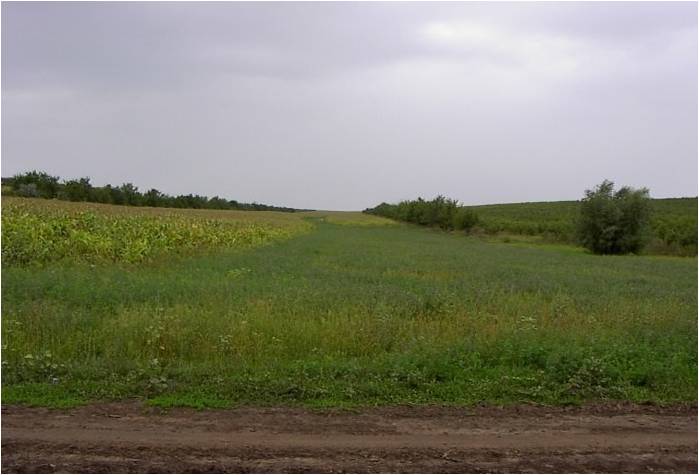
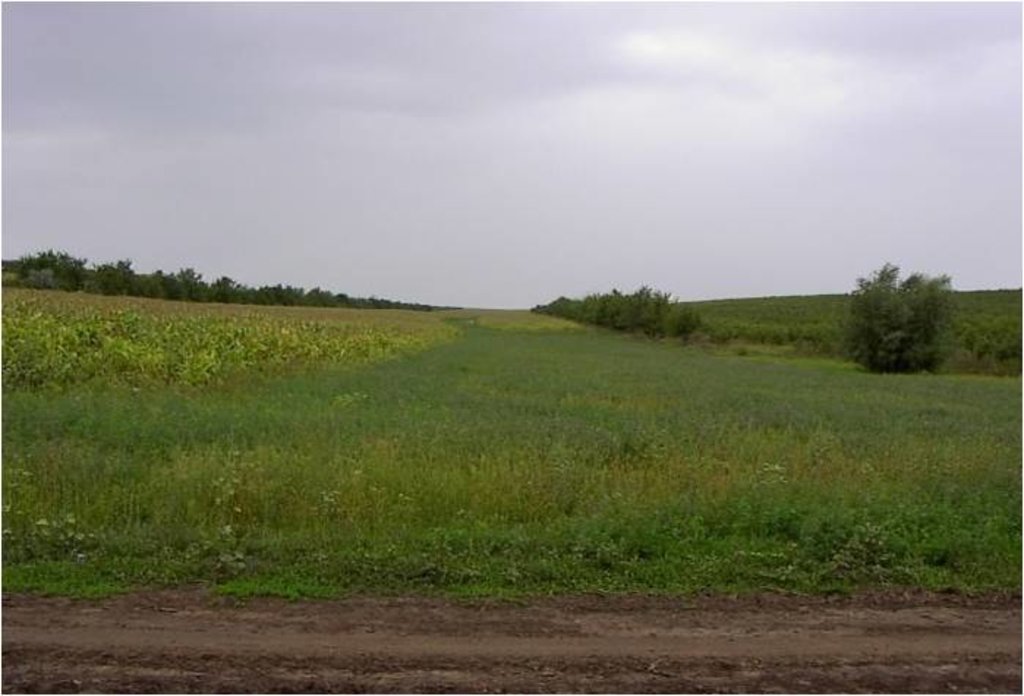
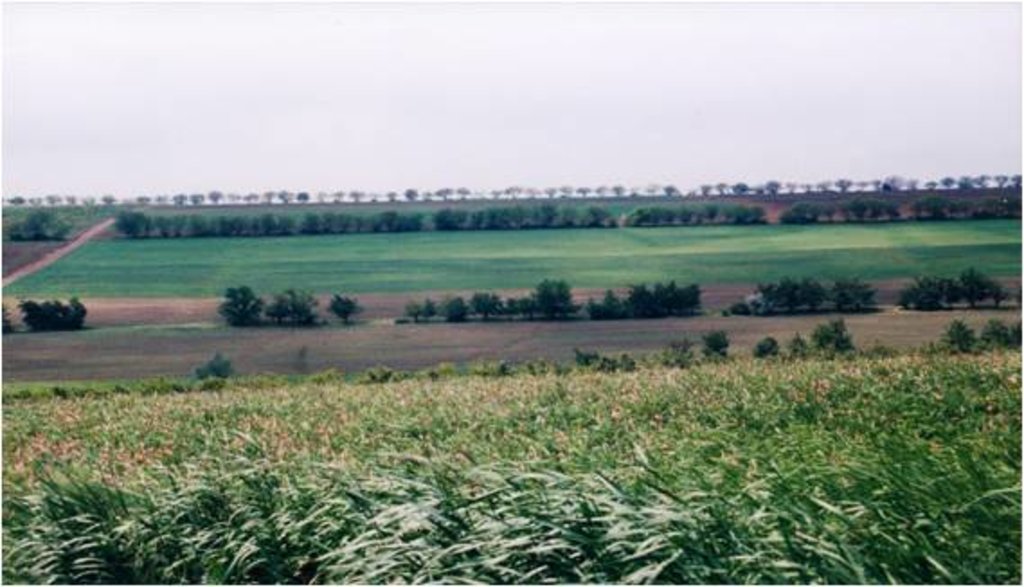
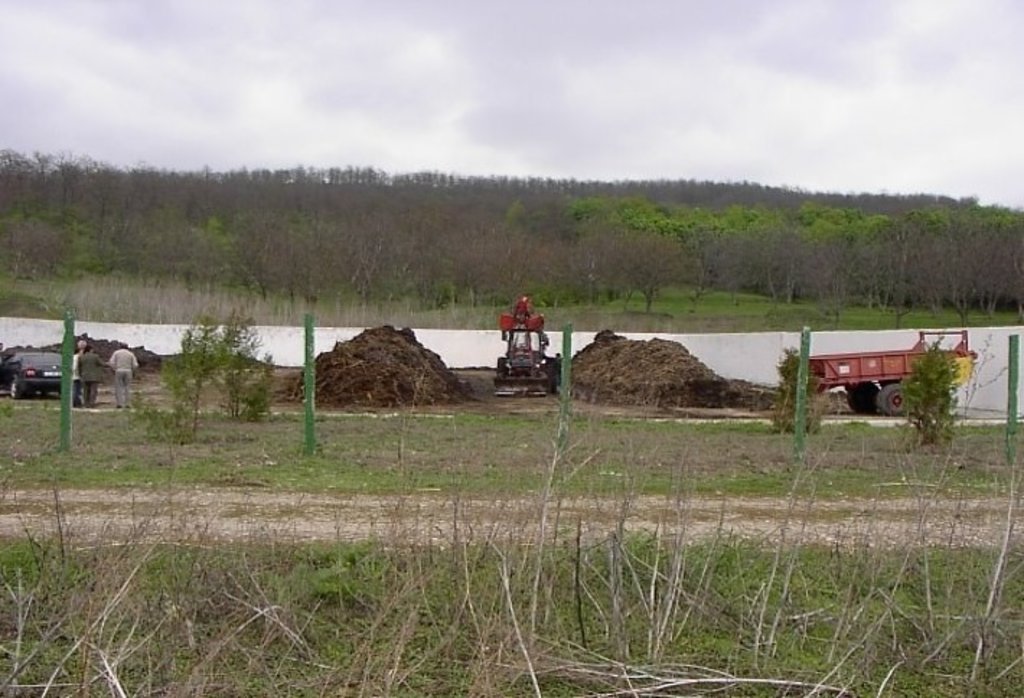
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
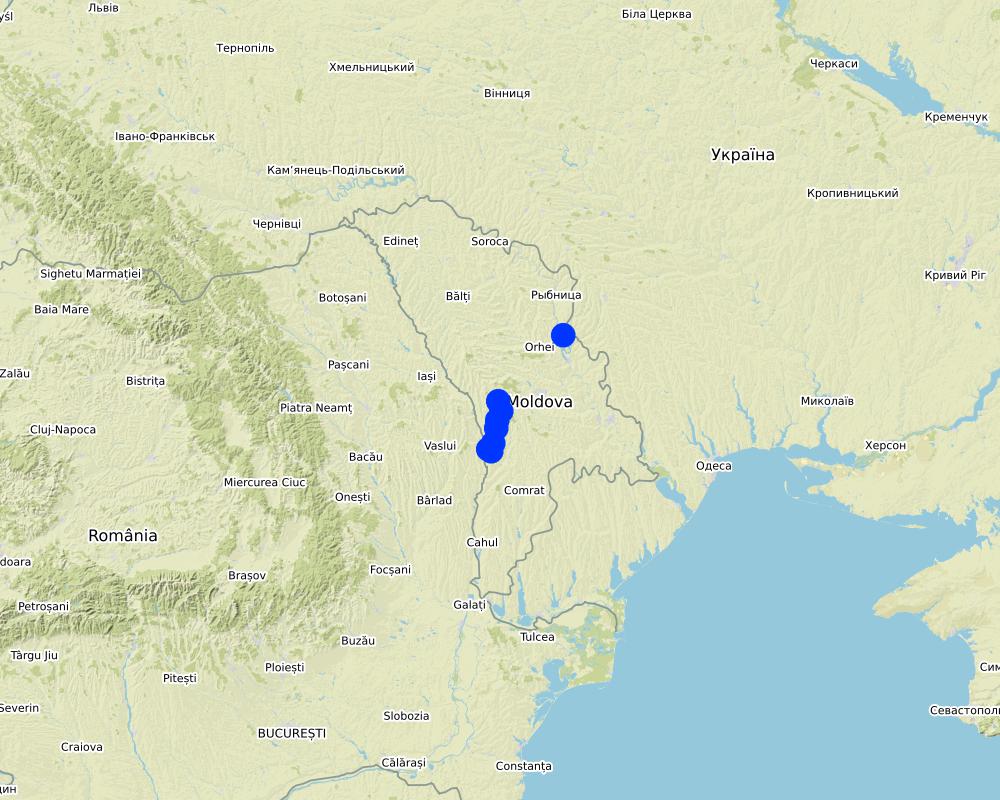
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
มอลโดวา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Hincesti and Orhei districts
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Negrea, Lapusna, Carpineni, Minjir communes, Hincesti district; Sarata Razesti commune, Leova district, and Jora de Mijloc, Orhei district
Map
×3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- ป้องกันพื้นที่ลุ่มน้ำ/บริเวณท้ายน้ำ โดยร่วมกับเทคโนโลยีอื่นๆ
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Wheat, corn, sunflower, alfalfa (lucerne), vineyards, orchards, vegetables

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- ทางระบายน้ำ ทางน้ำ
- หนองบึง พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
The existing ecosystems rehabilitated and ecologically well balanced; dams with a sluice gate system for the stabilization of water levels; concrete bridges with adequate culvert capacity for access to different portions of the wetland; and wooden bridges with culvert capacity for access through the zone constructed
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
1 growing season per year for rainfed and 2 growing seasons per year for irrigated areas
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- ระบบหมุนเวียน (การปลูกพืชหมุนเวียน การพักดิน การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อนลอย)
- การจัดการปลูกพืชร่วมกับปศุสัตว์
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
ถ้าหากว่าเทคโนโลยีได้มีการกระจายออกไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ ให้ระบุปริมาณพื้นที่ที่ได้รับการครอบคลุมถึง:
- > 10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
8,250 farmers from both project pilot area and other regions of Moldova that adopted at least one environmentally friendly agricultural practice promoted by the project implemented on as much as 14,028 ha of land in total.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
- V4: การแทนที่หรือการนำพันธุ์ต่างถิ่น/ที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา ออกไปจากพื้นที่

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
- M6: การจัดการของเสีย (การทำ รีไซเคิล การเอากลับมาใช้ใหม่หรือการลดปริมาณ)
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
- Wm (Mass movement): การเคลื่อนตัวของมวลดินหรือดินถล่ม
- Wr (Riverbank erosion): การกัดกร่อนริมฝั่งแม่น้ำ
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Cp (Soil pollution): มลพิษในดิน
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Ps (Subsidence of organic soils): การยุบตัวของดินอินทรีย์ การทรุดตัวของดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
- Hw (Reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland): การลดลงของความทนทานต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลง ของพื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
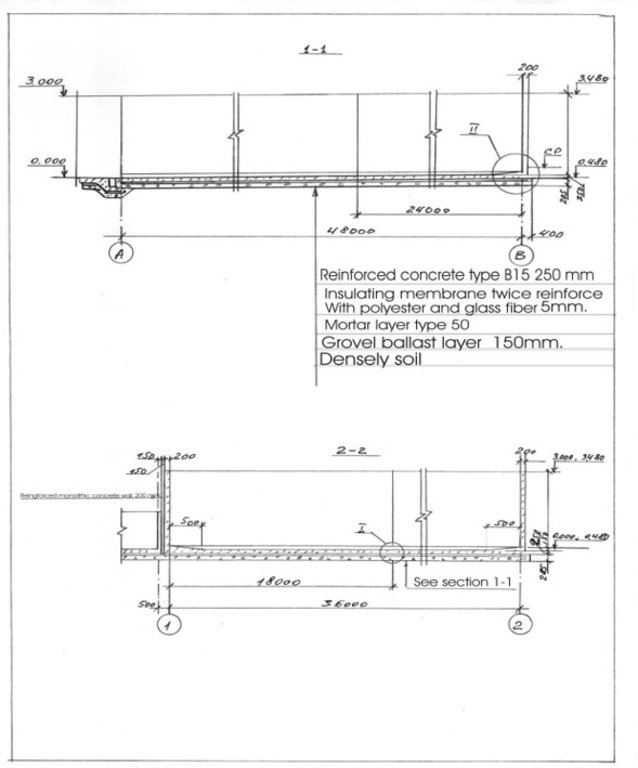
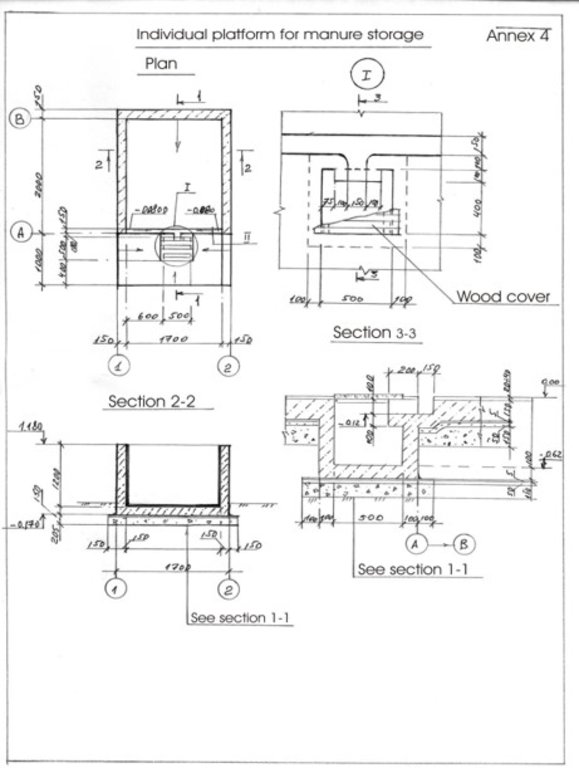
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
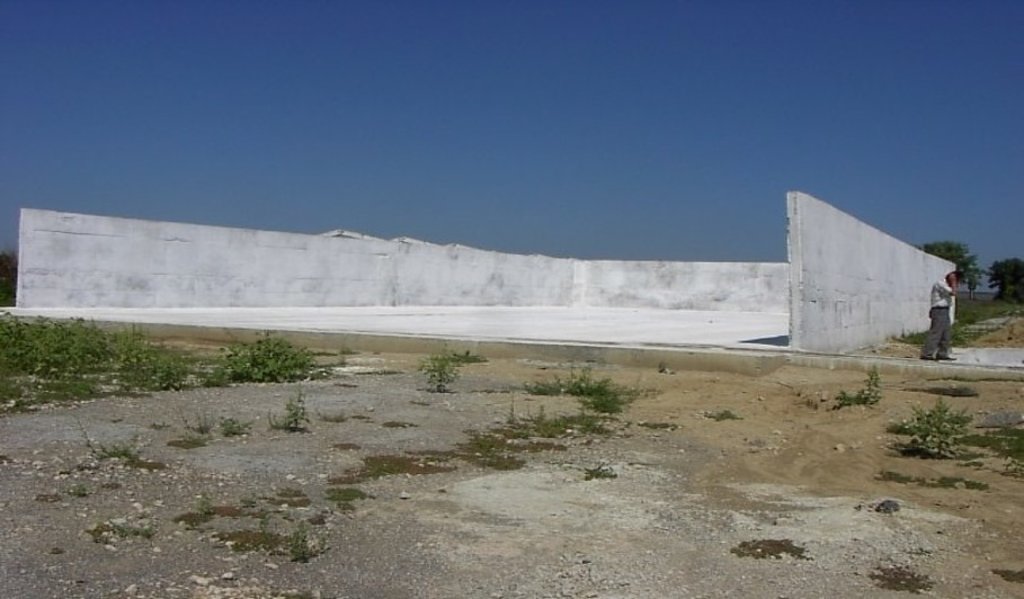
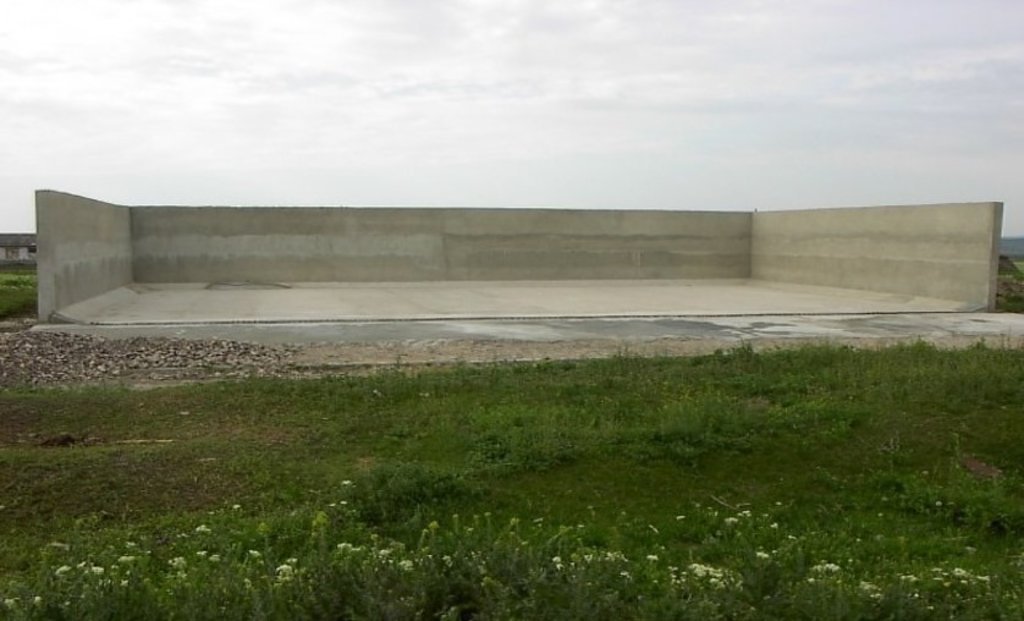
Schematic structure of village platform: Length - 48 m, Width - 36 m, Height - 3 m, Capacity - 3400 tons, Storage period - 5 months
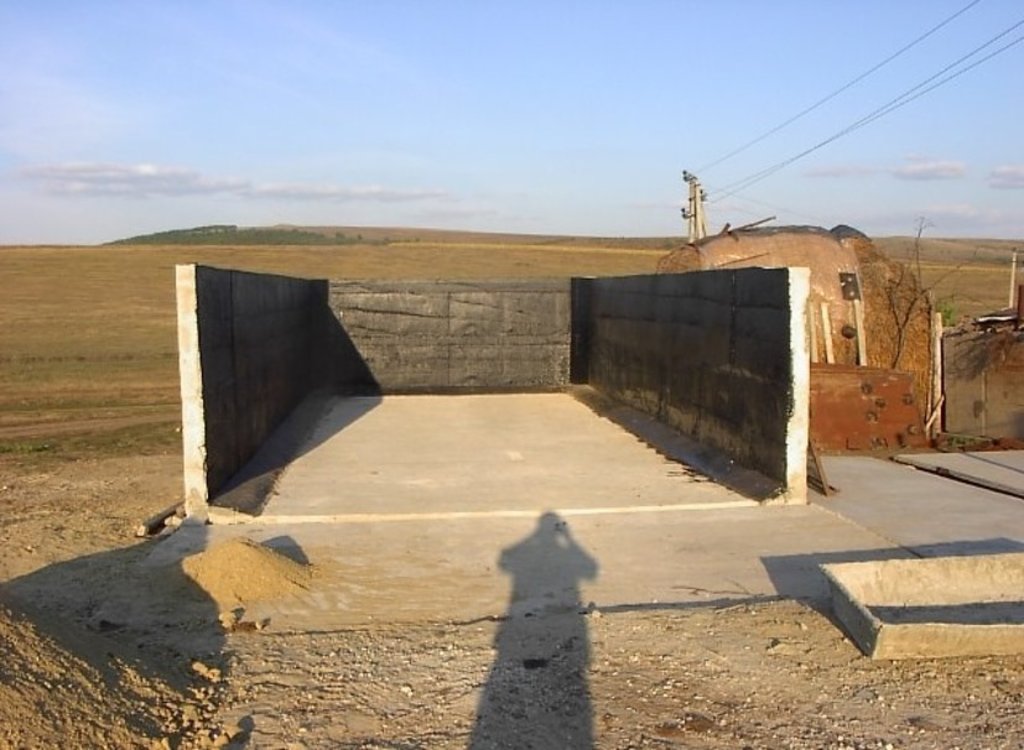
Schematic structure of household platform: Length - 2.2 m, Height - 1.2 m, Capacity - 4.8 c.m., Storage period - 1 month.
At village level, the project supported the construction of waste storage platforms of 3400 tonnes capacity and a storage period of 5 months. The platform has 48 m length and 36 m width. It is surrounded by a concrete 3 m high wall and bedded by a concrete floor with an impermeable insolating membrane. The platform is equipped with a bunker for inert material and a basin for collection of liquid fraction. The platform is built on the commune land (administrated by the Mayoralty) in full compliance with the environmental protection requirements.
At the household-level 150 platforms were built. The platforms have 2.55 m3 and a storage period of one month. The platform capacity was calculated based on estimated quantity of manure for an average household with at least two cattle, two-three pigs and a certain number of poultry. The designed platform consists of a simple open fronted store with a concrete floor and 1.5 m height walls. In front of the platform, a concrete below ground tank (125 dcm3 volume) covered by a wood lid with a plastic basket inside of 50 liters capacity for collection of liquid fraction would be equipped. A separate small capacity container (about 90 liters) for the collection of recyclable and non-recyclable household wastes was also provided.
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Packages developed for manure management at village and household level and evaluated for replication | ||
| 2. | Public awareness & education | ||
| 3. | Use of good agricultural practices by farmer associations, family farms and individual farmers on cropland. | ||
| 4. | Monitoring & evaluation. |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The Project
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
500.00
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Hincesti
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about 20°C, and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging -4°C. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 500 millimeters; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in summer; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
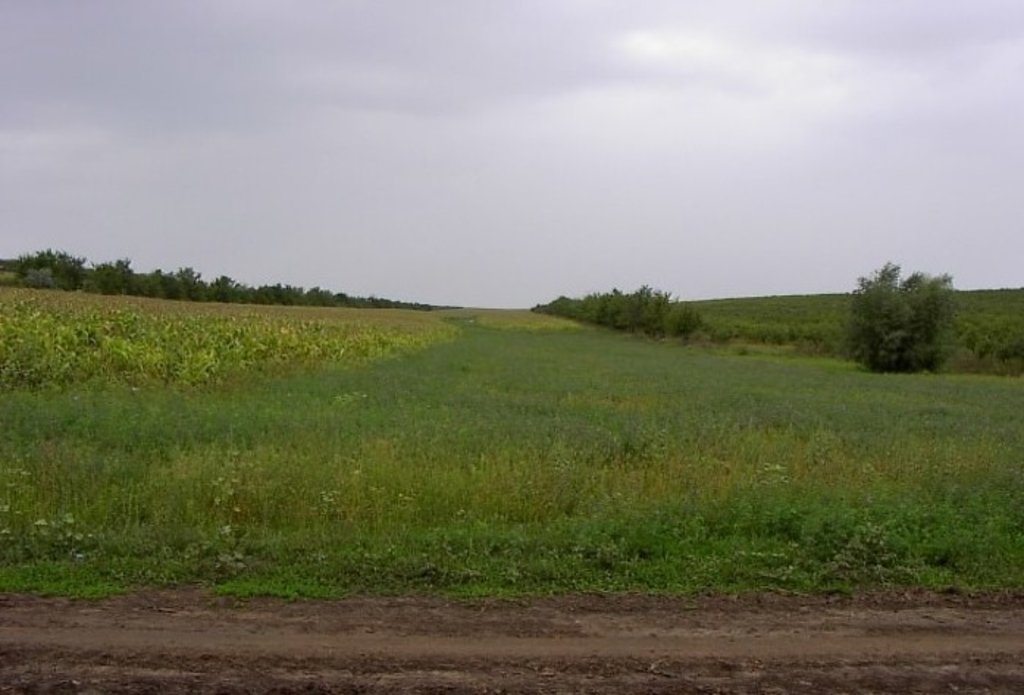
The territory belongs to the Central Moldova Height and the Plain of Upper Prut. The landscape is hilly, very fragmented with a dense network of valleys, hollows and plains. Almost 75% of the land is situated on slopes. Water erosion processes are widespread and quite intense. The predominant length of the hillsides in Negrea pilot area is 800-900 m.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Chernozems (black soils) prevail in the soil composition (65% of the area) divided into argilo-illuvial and carbonate subtypes. These soils are perfectly suited for agriculture. They are friable, permeable, have good water and air saturation and are easy to till. Chernozems are rich in organic matter (3-4% humus content), however they are degraded. Alluvial soils are spread in the floodplain of the Lapusna river and its tributaries. alluvial soils are often subject to salinization and water logging.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
high water mineralisation
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้สูงอายุ
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
The principal activity in the commune is agriculture. The farmers cultivate arable crops, grapes and fruits. From vegetables, pea and bean plantations, cabbage, cucumber, tomatoes, beats and carrots are most usual. Potatoes are predominantly cultivated on the households’ plots. There are two small economic units dealing with wood processing and meat production activating under the umbrella of the local farmer’s association, “SRL Negrea-Pomvit”. |
The income of the people depends much on the harvest and climatic conditions, but also on imbalances of the market, import policies, governmental purchases, etc. The estimated average income per capita in the community over the last 3 years was 45 US dollars per month.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
- ขนาดใหญ่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The total number of land shares in the commune is 772. Each land share has on average 1.20 ha, including 0.70 ha of arable land, 0.15 ha of orchards and 0.35 ha of vineyards. The number of individual farms is 190. The principal landowner in the region is the association of shareholders “SRL Negrea-Pomvit”. The association manages collectively 664 ha. |
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
According to elevator (NGO BIOS), •The SROI (Social Return on Investment) ratio for the period of 2004-2009 was 3,34, or, every $US1 invested by the Project $US 3,34 worth of value (economic, social and/or environmental) was delivered to society.
การผลิตสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
การผลิตของจากป่าทุกชนิดยกเว้นไม้
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
การจัดการที่ดิน
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับปศุสัตว์
คุณภาพน้ำสำหรับการชลประทาน
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การอัดแน่นของดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
พืชพันธุ์ต่างถิ่นที่รุกล้ำเข้ามา
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การทับถมของดินตะกอนพื้นที่ท้ายน้ำ
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ความคิดเห็นเกี่ยวกับการประเมินผลกระทบ:
he Social Survey indicated an improved environmental situation in LPA in comparison to other rural localities. Some problems in LPA are not so acute as there were in 2002, especially soil erosion, aquatic reservoirs pollution and quality of potable water, which demonstrates the efficiency of APCP P|
The fact that over 50 % of the respondents from Lapusnita Pilot Area consider APCP implementation has a positive impact on life, health and environment, shows that APCP contributed substantially to the improving the economic, social and ecological conditions, especially in LPA. The acknowledged impa|
It is expected that the project will be scaled up at the national level and facilities for waste management will be improved in all communities; the value of manure will be appreciated and used as fertiliser, wetlands will be restored; environment-friendly practices, including reintroducing trees wi|
The level of applied good agricultural practices in LPA is higher than in other communities of the country and has increased as compared to 2003. Farmers apply more organic fertilizers (by 13%), forest belts (10%), strip cropping (9%) and less mineral fertilizers (17%).
ACSA organized 90 seminars. People from all districts attended the training seminars. Survey data show that 90 % of the participants in seminars intended to apply GAP.
Over 3,000 farmers adopted at least 1 of GAP in Lapusnita Pilot Area and over 12,000 outside LPA. The total area, where environmentally-friendly practices were applied was 28,275 ha.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Healthy organisms are adapted easily to various conditions. In this way agro-ecosystems having soils and water with improved properties (due to application of good agricultural practices) with adequate management practices will have also positively impact on climate change adaptation.
Due to the fact that Good Agricultural practices improve soil and water qualities, they create very good conditions for the development of soil biodiversity and wild biodiversity in farming landscapes. Due to the reduction of pollution landscapes become more healthy and also is very beneficial for the agricultural biodiversity.
Permanent vegetated strips established at field and stream riparian boundaries and in water courses will create conditions for the development of biodiversity.|
Conventional agriculture is the major contributor to increasing of methane and nitrous oxide concentrations in earth's atmosphere. Aforestation and soil conservation technologies are one of the main sink of carbon dioxide. In this way good agricultural practices have a positively impact on climate change mitigation.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 10-50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
8,250 farmers from both project pilot area and other regions of Moldova
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 10-50%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Farmers did not calculate properly expenses and benefits. | They should be provided simple instruments to calculate their inputs and to plan for future activity. |
| Agricultural literature is too difficult for rural people to understand. | Knowledge should be provided in an accessible manner. Small guides should exist for separate crops with drawings and schemes. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
300
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Guidelines for Good Agricultural Practices (Practici agricole prietenoase mediului). Îndrumar: /Ungureanu V., Cerbari V., Magdîl A., Gherman E.- Chişinău: Tipografia Centrală, 2006. – 96 p.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.acsa.md/album.php?l=ro&idc=152&t=/GALERIE-FOTO/Practici-agricole-prietenoase-mediului
7.3 เชื่อมโยงกับข้อมูลที่มีอยู่บนออนไลน์
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Moldova - Agricultural Pollution Control Project (English)
URL:
http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/117701468287732017/Moldova-Agricultural-Pollution-Control-Project
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล