Chagga Homegardens [แทนซาเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Julie Zähringer
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
technologies_1337 - แทนซาเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Hemp Andreas
andreas.hemp@uni-bayreuth.de
University of Bayreuth
เยอรมนี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Hemp Claudia
claudia.hemp@uni-wuerzburg.de
University of Würzburg
เยอรมนี
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Universität Bayreuth (UBT) - เยอรมนีชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
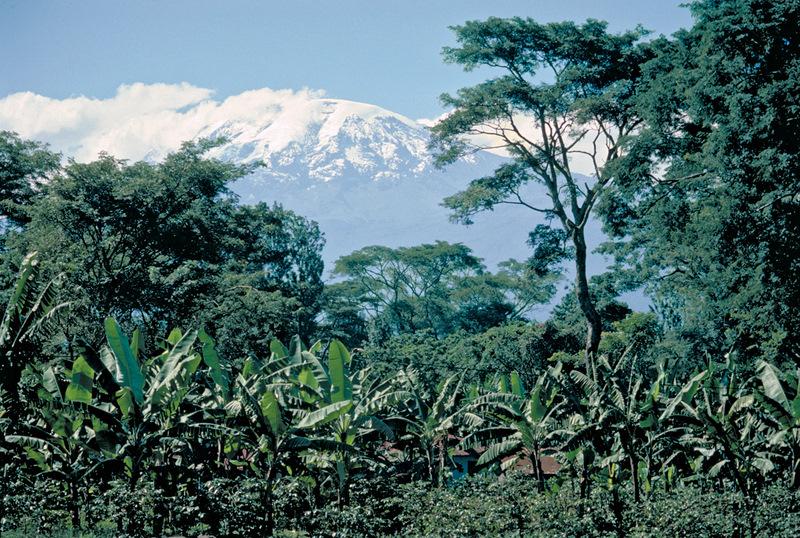
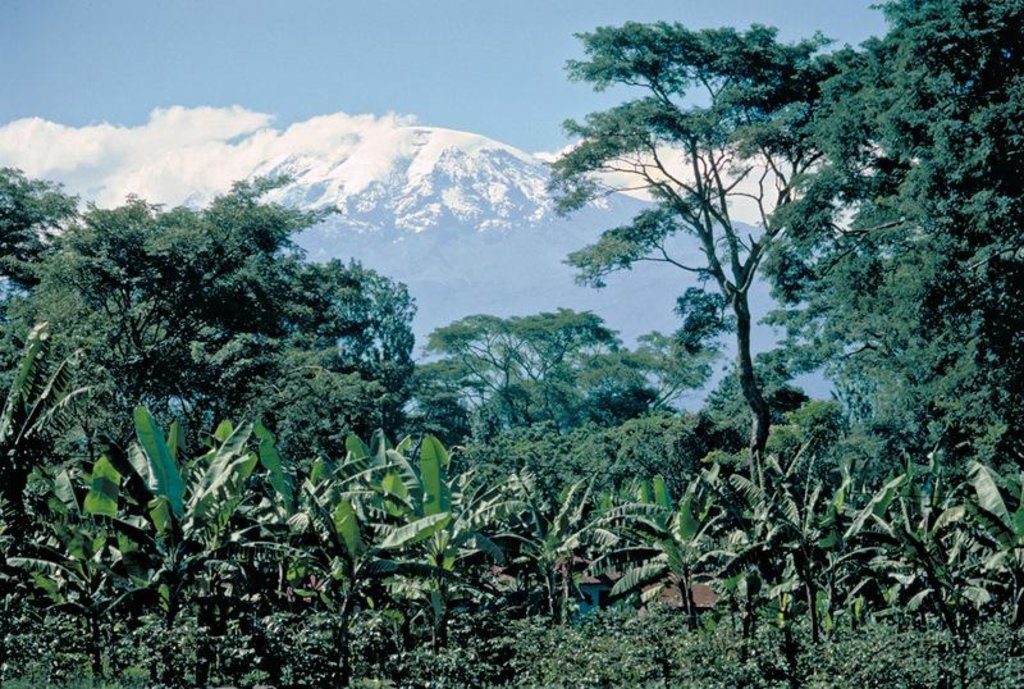
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The Chagga homegardens are traditional, densely planted ‘banana forests’ with a scattered upper tree layer.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The complex multicropping system evolved over several centuries through a gradual transformation of the natural forest on the footslopes of Kilimanjaro. A Chagga homegarden has an average size of 0.68 ha and integrates numerous multipurpose trees and shrubs with food crops, and stall-fed animals, without a specific spatial arrangement. However, vertically, the following 4 stories/canopies can be distinguished: (1) food crops: taro, beans, vegetables and fodder herbs / grasses; (2) coffee: 500-1,400 plants/ha; (3) banana: primary crop; 50% cover; 330-1,200 clumps/ha; and (4) Trees, such as Cordia abyssinica, Albizia schimperiana and Grevillea robusta. The trees provide shade for coffee, act as live fences, provide medicines, firewood, fodder, mulching material, bee forage; and some have pesticidal properties (e.g. Rauwolfia caffra). This multilayer system maximizes the use of limited land in a highly populated area, making sustained production possible with a minimum of external inputs, minimizes risk (less production failure, increased resistance against droughts and pests) and ensures at the same time environmental protection. The large species diversity provides both subsistence and cash crops. Parts of the homegarden area are irrigated and drained by a network of over 1000 canals and furrows tapping runoff from the montane forest. However, many systems are now in disrepair.
Natural / human environment: Starting in the 1930s when coffee took more space from the food production, it became necessary to expand food production to the lowlands. Today, the Chagga highland homegarden works only in combination with a lowland field where maize, millet, beans, sunflower and groundnuts are grown to ensure food security.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
แทนซาเนีย
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Mt. Kilimanjaro Region
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
major cash crop: Coffee, banana, avocado, mango
major food crop: Taro, beans, vegetables and fodder herbs / grasses
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Chagga homegardens are traditional, densely planted ‘banana forests’ with a scattered upper tree layer
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- สวนครัว
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1200 m2.
individual homegardens are 0.68 ha on average
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M5: การควบคุมหรือการเปลี่ยนแปลงขององค์ประกอบของชนิดพันธุ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
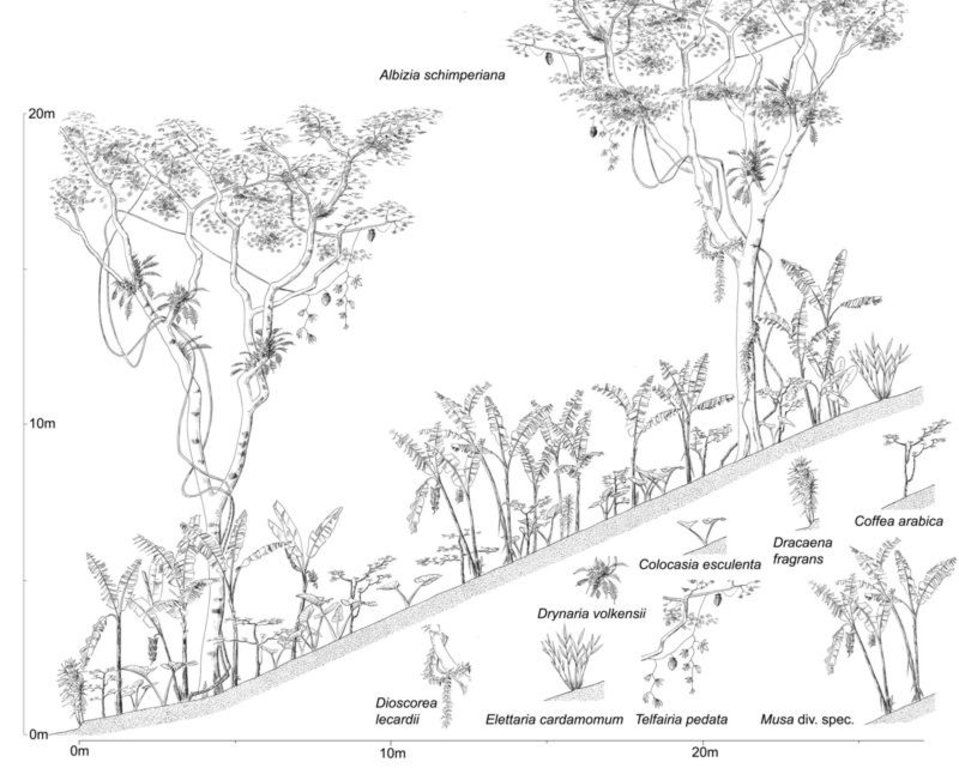
Typical chagga homegarden on a 45% slope at 1400 m a.s.l. with 4 vegetation layers: open light upper canopy with Albizia schimperiana (up to 20 m high); upper shrub layer with banana (4-6 m); a lower shrub layer with coffee (1.5-2 m) and food crops such as taro (< 1.5 m) -2.5 m; 3-6 m; 5-30 m
Mt. Kilimanjaro Region
Date: 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia abyssinica, Albizia schimperiana, Grevillea robusta, Rauwolfia caffra, Persea americana
Fruit trees / shrubs species: banana, avocado, mango
Perennial crops species: taro, coffee
Grass species: fodder herbs / grasses
Change of land use type: from natural forests to agroforest
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
homegarden
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transforming the native forest: trees that provided fodder, fuel, fruits, medicines, shade, timber, bee forage, anti-pest properties are retained while the less useful species are eliminated | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | Introduction of new fruit and timber tree species, such as avocado, mango, Grevillea robusta, Persea americana | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Planting crops species (banana, coffee, taro, beans, vegetables) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 4. | Establishment of irrigation/drainage channels | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 5. | Terracing or building of bunds in steep places | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting, tending and harvesting of bananas, taro, yams / Opening up the canopy to ensure better fruiting of the coffee | ด้วยวิธีพืช | all year round |
| 2. | Spacing out the banana stools; Manuring crops (using dung from the stall-fed livestock and compost) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Lopping fodder trees/shrubs; Pruning and spraying against coffee berry disease and leaf rust | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 4. | Maintaining irrigation furrows; Coffee harvest | ด้วยวิธีพืช | August to January |
| 5. | Tending and milking the stall-fed cows (typically only one cow) / Mulching, terrace maintenance (soil erosion prevention in general) | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Planting, tending and harvesting | unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | unit | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Compost / manure | unit | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 445.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: axes, hoes, pangas (machetes)
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
depending on slope orientation and altitude
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
Tropical montane; bimodal: long rains in March-May, short rains in Nov-Dec
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Also steep (31-60%)
Altitudinal zone: 1000-1800 m.a.s.l.
Landforms: Orientation south / south-east
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is high
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
traditional clan regulations (land cannot be sold to outsiders)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Fuelwood production 1.5-3 m3/ha/year
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
185 kg beans/ha; 410 kg coffee/ha; 400 bunches of banana /ha; ca. 30 kg honey/ha
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased labour efficiency
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
value of gene pool
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
for breeding programmes to improve crop varieties for multistorey cropping systems
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
preservation of traditional knowledge
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
over 500 plant species including 400 non-cultivated plants
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
การจัดการศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
micro-climate
biodiversity / crop diversity
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
? land use change from natural forest to agroforest
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
the system has a high buffer capacity (micro-climate, biodiversity, irrigation)
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on adoption trend: Locally well adopted traditional land use system, covering an area of approximately 1200 km2; further spread at local level is not possible due to land shortage.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| this system allows for maintaining high biodiversity at the same time with diversified production of fruits, vegetables, timber, medicinal products etc. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| High demand of wood, low coffee prices and the introduction of sun-tolerant coffee varieties endanger the homegardens | incentive-based tree planting in the gardens to reduce the pressure on the forest |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Productivity of Chagga homegardens is not optimal | (1) Replace the less productive trees / shrubs with fast growing nitrogen fixing species; (2) improve animal husbandry (e.g. to increase lactation period), (3) improve apiculture, |
| Productivity of Chagga homegardens is not optimal | (4) introduce new crop varieties using the gene pool developed by natural and farmer selection, (5) use fertilizers, |
| Productivity of Chagga homegardens is not optimal | (6) improve coffee production: certified production (organic, fair trade) to fetch higher prices, (7) replace old coffee plants with new ones, (8) integrated pest management, (9) facilitate access to capital for farm investments |
| Productivity of Chagga homegardens is not optimal | (10) improve erosion control (terraces and bunds), (11) include productive fruit trees, (12) improve advisory services |
| Water management causes nutrient loss in the gardens and water shortages on the lower slopes | improve efficiency of furrows: Install pipes and surfacing by cement, protect river banks from cultivation |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hemp, A. (1999): An ethnobotanical study on Mt. Kilimanjaro. Ecotropica 5: 147-165
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hemp, A. (2006): The banana forests of Kilimanjaro. Biodiversity and conservation of the agroforestry system of the Chagga Homegardens. Biodiversity and Conservation 15(4): 1193-1217.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hemp, C. (2005): The Chagga Home Gardens – relict areas for endemic Saltatoria Species (Insecta: Orthoptera) on Mt. Kilimanjaro. Biological Conservatrion 125: 203-210.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hemp, A., C. Lambrechts, and C. Hemp. (in press). Global trends and Africa. The case of Mt. Kilimanjaro. (UNEP, Nairobi)
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Hemp, A., Hemp, C., Winter, C. (2009) Environment and worldview: The Chagga homegardens. In: Clack, T.A.R. (ed.) Culture, history and identity: Landscapes of inhabitation in the Mount Kilimanjar area, Tanzania. BAR International Series 1966, Archaeopress Oxford, pp. 235-303
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Fernandes E.C.M., Oktingati A., Maghembe J. 1985. The Chagga homegardens: a multistoried agroforestry cropping system on Mt. Kilimanjaro (Northern Tanzania) in Agroforestry Systems 2: 73-86
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล