Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management [เคนยา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Unknown User
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Julie Zähringer
technologies_958 - เคนยา
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: 22 ธันวาคม 2016 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: 28 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: 12 พฤษภาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Push-Pull Integrated Pest and Soil Fertility Management: 25 เมษายน 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Khan Zeyaur
zkhan@mbita.mimcom.net
International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE)
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Pittchar Jimmy
jpittchar@icipe.org
International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE)
เคนยา
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Wartmann Flurina
f.wartmann@biovision.ch
Biovision Foundation for ecological development
สวิตเซอร์แลนด์
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Biovision Foundation (Biovision Foundation) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE) - เคนยา1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
“Push-Pull” is a technology to efficiently control pests and progressively improves soil fertility.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
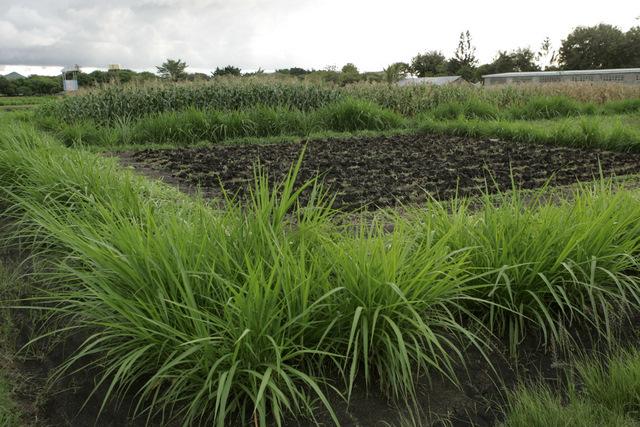
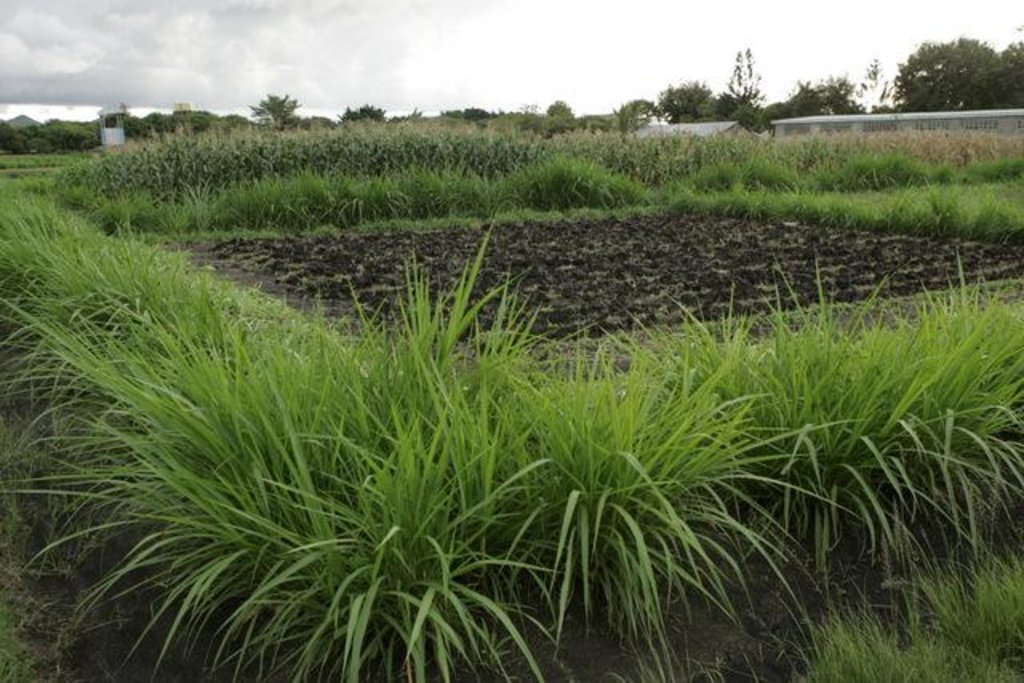
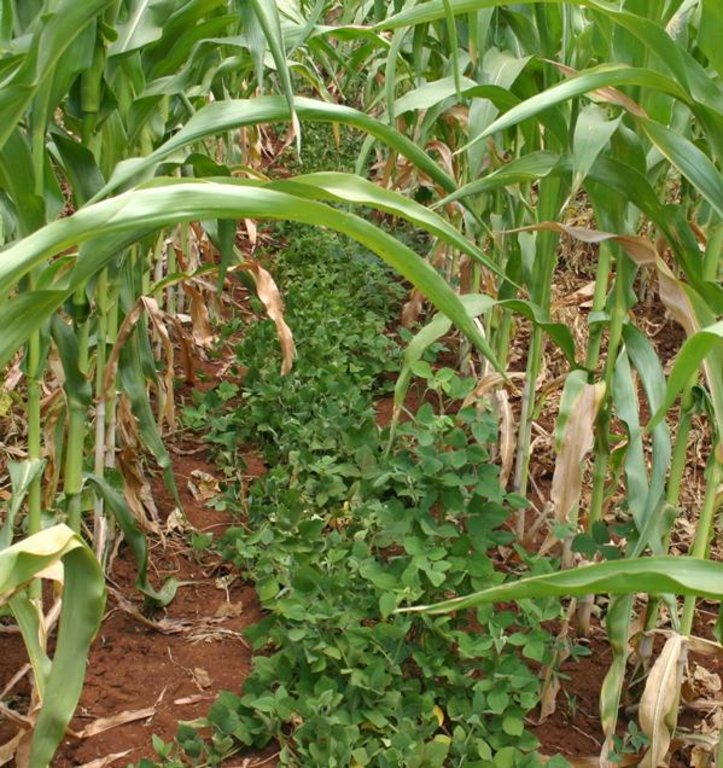
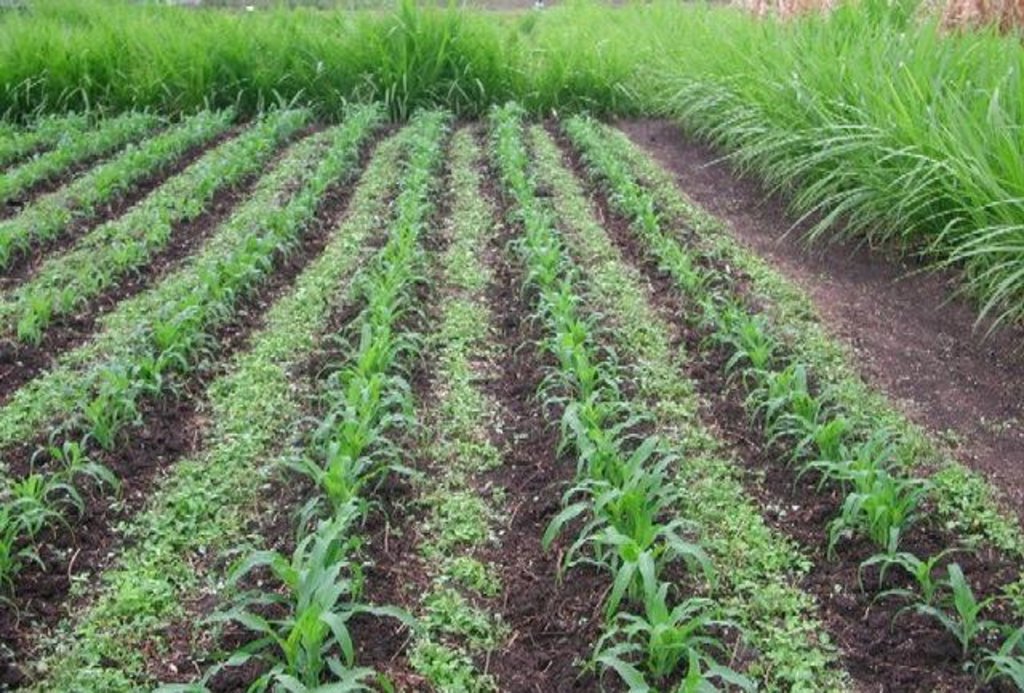
In the Lake Victoria region - like in many other parts of sub-Saharan Africa – stemborer pests, striga weeds and poor soil fertility are the main constraints to efficient production of cereals. In combination they often lead to complete crop failure. The “Push-Pull” technology efficiently controls the pests and progressively improves soil fertility. It involves intercropping maize with a repellent plant, such as desmodium (“push”); an attractant trap plant, such as napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) is planted as a border crop around this intercrop (“pull”). The stemborer moths are attracted to volatile compounds emitted by the napier grass which at the same time serves as a haven for the borers' natural enemies. When moths lay eggs on napier grass a sticky substance secreted by the grass physically traps the moths’ larvae. Napier is also an important carbohydrate-rich fodder grass. Desmodium, a perennial cover crop, produces repellent volatile chemicals that push away the moths, and the plant effectively suppresses striga weeds through its root exudates. Furthermore, desmodium fixes nitrogen, conserves soil moisture, enhances arthropod abundance and diversity and improves soil organic matter, thereby making cereal cropping systems more resilient and adaptable to climate change. Being a low-growing plant it does not interfere with the crops' growth. Push-pull simultaneously improves cereal productivity; enables production of year-round quality fodder - thereby allowing for integration with livestock husbandry; diversifies income streams and enables smallholders to enter into the cash economy. It also improves soil fertility; protects fragile soils from erosion and enables a minimum tillage system. The technology is appropriate to resource-poor smallholder farmers as it is based on locally available plants, affordable external inputs, and fits well with traditional mixed cropping systems practiced in SSA.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เคนยา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Lake Victoria region
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Main cash crop (CA): Maiz
Others (CP): Desmodium (fodder)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cereal pests and diseases, decline of soil organic matter and fertility
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การปรับปรุงพันธุ์พืชหรือพันธุ์สัตว์ต่าง ๆ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 76000 m2.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, retaining more vegetation cover
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, aligned: -linear
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bp (Increase of pests/diseases): การเพิ่มขึ้นของศัตรูพืชและโรคพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bh: loss of habitats, Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
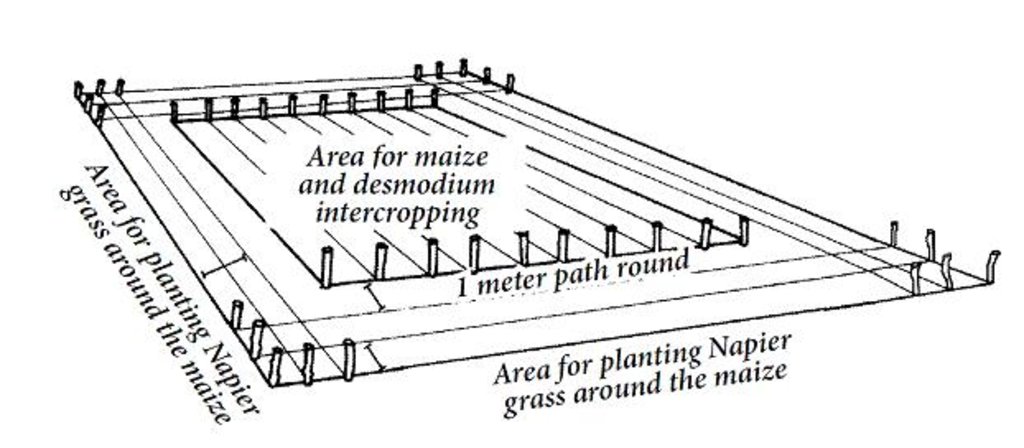
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
Layout of push-pull plot with1 m spacing between napier border and maize field
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), pest control
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Desmodium as a perennial intercrop
Remarks: Desmodium is drilled in between maize rows at 75 cm row to row distance
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum)
Remarks: Spacing of napier plants should be 75 cm between rows and 50 cm between plants within a row
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 75.00
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 50.00
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 75.00
Perennial crops species: Desmodium
Grass species: Napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum)
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1.2
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant 3 consecutive rows of napier grass (Bana variety) around the plot: make planting holes, apply fertilizer (or manure), place 3-node canes or root splits, cover with soil (before rains) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | Land preparation for desmodium: plough and harrow the land (to get fine soil), make furrows between the rows where the maize will be planted (using strong pointed stick; before rains) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Mix desmodium seed with super phosphate fertilizer (ratio 1:2), or alternatively with fine soil. Sow into the furrows and cover with soil (onset of rains) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 4. | Plant maize./ Weeding of maize, desmodium and Napier grass | ด้วยวิธีพืช | 3 and 5-6 weeks after planting maize |
| 5. | Manage napier grass: 1st harvest after 3 months (plants are 1-1,5 m high), leave stem height of 10 cm for quick regrow, start with inner row | ด้วยวิธีพืช | 1st harvest after 3 months |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Plant 3 consecutive rows of napier grass | Persons/day | 8.0 | 1.25 | 10.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Napier | pieces | 1200.0 | 0.1666666 | 200.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Desmodium seeds | kg | 0.5 | 18.9 | 9.45 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | kg | 47.0 | 0.6808 | 32.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 251.45 | |||||
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for maize: carefully dig/plough between desmodium lines not to disturb / uproot the desmodium (it is a perennial crop!) | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 2. | Plant maize | ด้วยวิธีพืช | |
| 3. | Trim the desmodium so that it does not overgrow in between the maize plants | ด้วยวิธีพืช | after 3 and 6 weeks |
| 4. | Repeat activities 5.-7. listed under establishment | ด้วยวิธีพืช |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Land preparation for maize | Persons/day | 6.0 | 1.166666 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer for maiz | kg | 47.0 | 0.6808 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 39.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: planting stick / hoe
Size of push-pull plot for the cost calculations above = 0.25 ha.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Input prices (in US$):
1 Person-day = 1.2 US$.
1 napier root split / cane = 0.14 US$.;
1 kg desmodium seeds = 18.9 US$.;
1 kg superphosphate fertilizer = 0.68US$
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics
Mainly sub-humid; bi-modal rainfall pattern, with main rainy season March-May; short rainy season Oct.-Nov.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average: Also flat (0-2%)
Landforms: Also plateau / plains
Altitudinal zone: 1200-1250 m.a.s.l.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: Also coasre/light but texture is mostly loamy clay, partly sandy
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- ยากจนมาก
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: some organized in informal groups
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Market orientation of production system: commercialization is just starting
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
2ha, production area 0.9 ha
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land ownership: state, communal / village, individual, not titled, individual, titled
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Maize yields increase by 25-50% where stemborer is the only problem and by 300% in areas affected by stemborer and striga weed
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
All-year round quality fodder for cattle (napier grass and desmodium)
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced fertilizer inputs thanks to nitrogen-fixing by desmodium
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Selling cereal grains, desmodium seed, napier grass (if not fed to own livestock), and milk
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Weeding is minimized
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
Social capital generated through common learning and implementing agricultural “best practices”
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crop, live mulch
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cover crop, live mulch
การสูญเสียดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Soil protected from erosion through desmodium (cover crop) and napier grass (barrier)
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduced wind impacts due to napier barriers
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Technology is tolerant to climatic extremes.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: To date it has been adopted by over 29,000 smallholder farmers in East Africa, mostly without incentives. Where the technology is being introduced for the first time, farmers only need demonstration and technology information
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Improves cereal productivity |
| Enables production of year-round quality fodder - thereby allowing for integration with livestock husbandry |
| Diversifies income streams and enables smallholders to enter into the cash economy |
| Improves soil fertility; protects fragile soils from erosion and enables a minimum tillage system |
| The technology is appropriate to resource-poor smallholder farmers as it is based on locally available plants, affordable external inputs, and fits well with traditional mixed cropping systems practiced in SSA. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Napier grass is an aggressive plant that spreads through rhizomes under the ground | regular control and weeding. |
| The older napier stems and leaves are less palatable for livestock | regularly cut young, tender leaves and stems. |
| Minor adjustment of the smallholder farming system to introduce desmodium in traditional maize-bean intercrops | desmodium (fodder crop) and beans (food crop, important protein source) can both be intercropped with maize. In areas where striga weed is not a problem, farmers can plant desmodium after every 3 or 5 rows of maize, and use the other rows for beans. Stemborers will still be repelled |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan (Principal Scientist and Programme Leader) and Jimmy Pittchar, Push-pull Programme, International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE), Mbita Point, Kenya; zkhan@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@icipe.org
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Prof. Zeyaur R. Khan (Principal Scientist and Programme Leader) and Jimmy Pittchar, Push-pull Programme, International Centre of Insect Physiology & Ecology (ICIPE), Mbita Point, Kenya; zkhan@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@mbita.mimcom.net; jpittchar@icipe.org
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล