Pond Sand Filter (PSF) with Raised Embankment [บังกลาเทศ]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: John Brogan
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Shahid Kamal, Md. Rahmatullah Faruque
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Alexandra Gavilano, Hanspeter Liniger, Nicole Harari, Deborah Niggli
FILTER
technologies_550 - บังกลาเทศ
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
16/08/2016
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The combination of pond sand filters (PSF) and raised pond embankments protect drinking water sources and increase the resilience to flood and tidal surge events in low-lying coastal areas.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
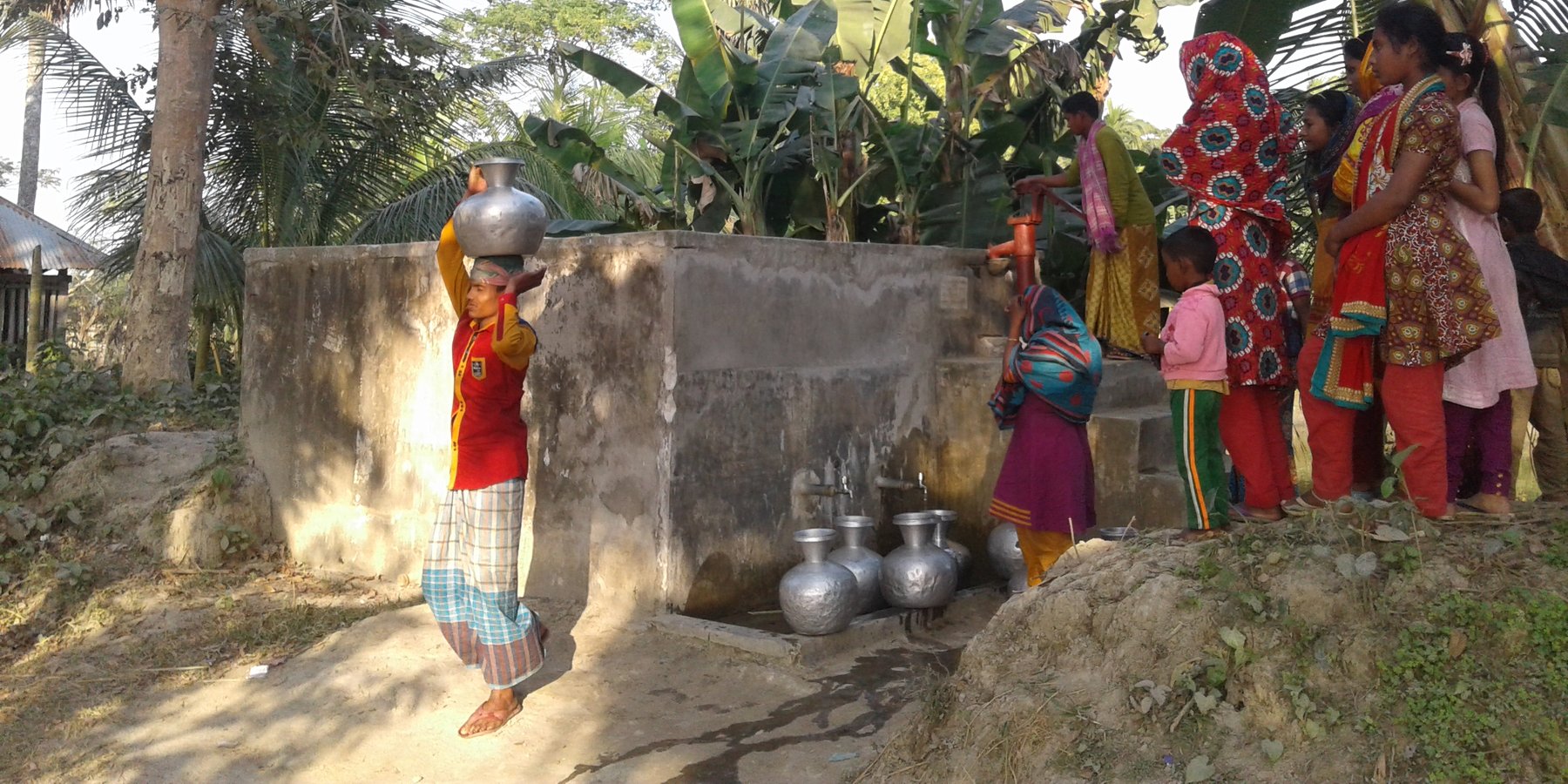
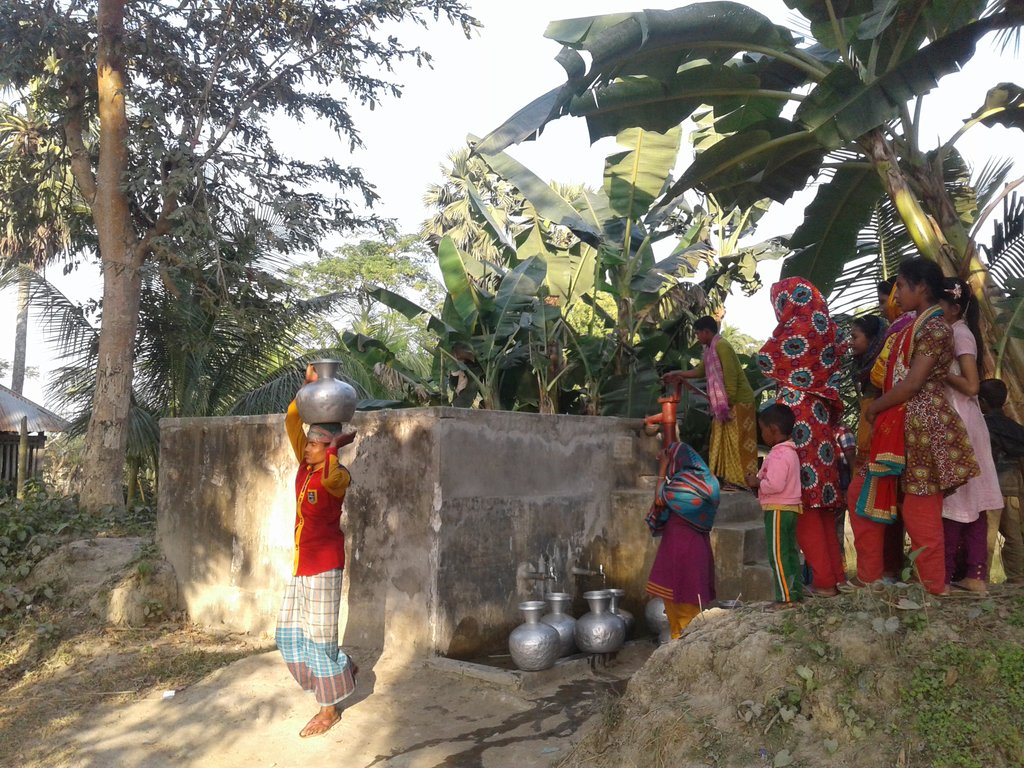
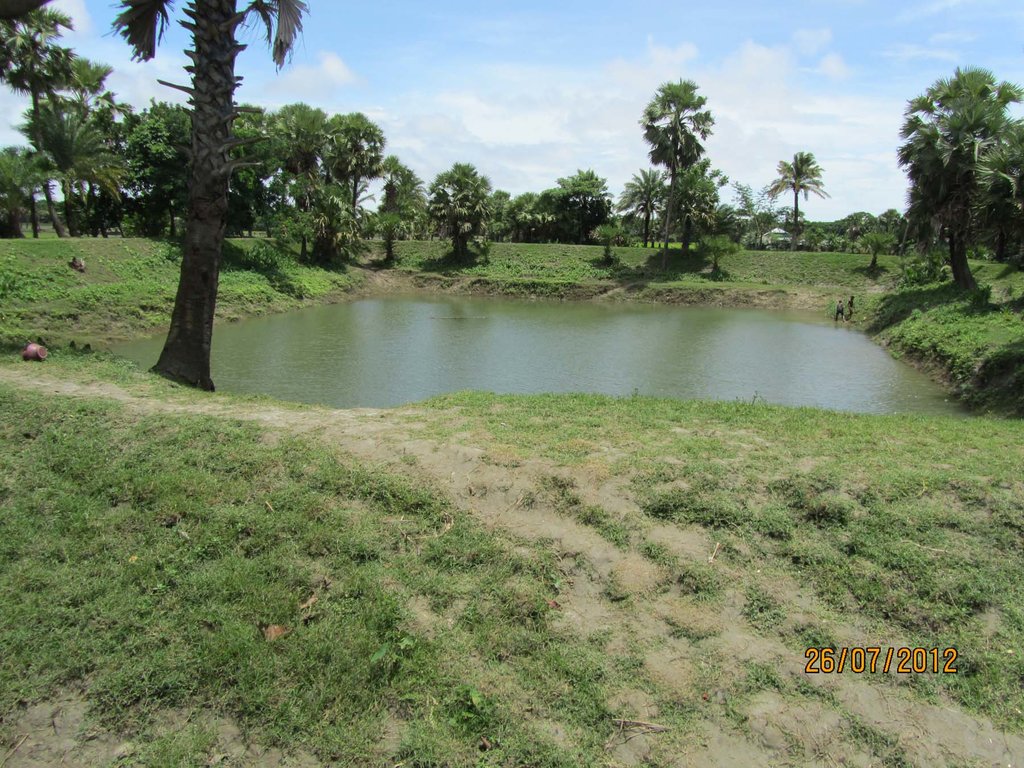
Coastal areas along the Bay of Bengal experience extreme seasonal variance in the presence of surface water including flooding, tidal surge, and drought. Many families living in these rural communities construct small ponds to ensure water availability for a variety of uses, such as washing, bathing, fish farming and animal watering as well as domestic use. Some families build larger ponds that are open to the use of all community members; whereby water is carried by women and children to households. Use of pond surface water may last up to several months during the year depending on the location, seasonal weather patterns, geologic conditions, capacity of the pond and user habits. Residents rely on ponds as a source of drinking water during the dry season when household rainwater harvesting techniques are no longer viable, making treatment essential.
Pond sand filters (PSF) is acentralised or semi-centralised water treatment technology often employed in many coastal areas where surface water is the only option due to saline aquifers and lack of resources for more robust, safely managed community water supply systems. The technology uses slow-sand filtration to remove turbidity (sediments) and pathogenic organisms whereby freshwater flows through layers of sand and gravel populated by a thin layer of microorganisms and treatment happens through physical and biological processes. Due to resource constraints, the number of PSF serving as water sources is usually limited. The technology considerably reduces the risk of infection with enteric pathogens. In conjunction with PSF, safe water transport (covered and cleaned containers) and household water treatment systems (chemical or additional filtration devices) are essential.
As stated in the Sustainable Sanitation and Water Management Toolbox (SSWM) slow sand filtration systems are characterised by a high reliability and rather low lifecycle costs. Moreover, neither construction nor operation and maintenance require more than basic skills. Hence, slow sand filtration is a promising filtration method for small to medium-sized, rural communities with a fairly good quality of the initial surface water source. As stated by the the World Health Organisation, slow sand filtration provides a simple but highly effective and considerably cheap tool that can contribute to a sustainable water management system.
Once a SSF facility is built, only clean sand is required for occasional replacement. The sand layers are put in gradually according to their grain sizes: rather coarse grains at the bottom and fine grains at the top. The sand-bed is usually covered with one meter of supernatant water (LOGSDON 2003). As the process of biological filtration requires a fair amount of time in order to improve effectiveness of water treatment, SSFs usually operate at slow flow rates between 0.1 – 0.3 m3/h per square metre of surface (WHO n.y.). The water thus remains in the space above the medium for several hours and larger particles are allowed to separate and settle. It then passes through the sand-bed where it goes through a number of purification processes (HUISMAN 1974).
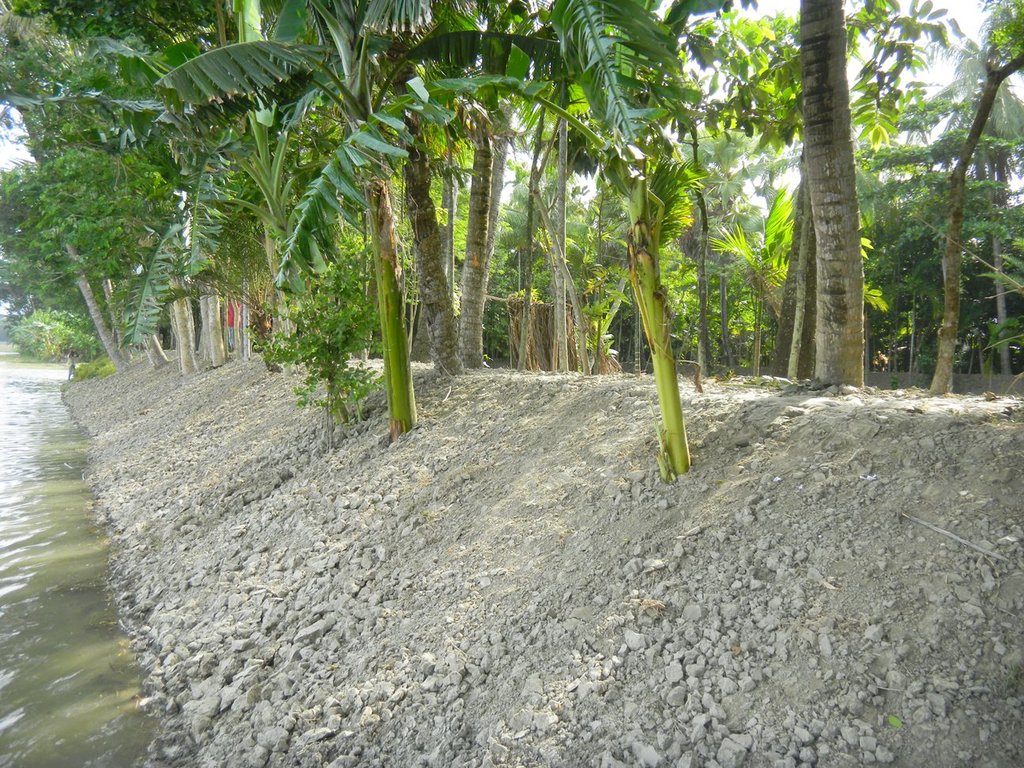
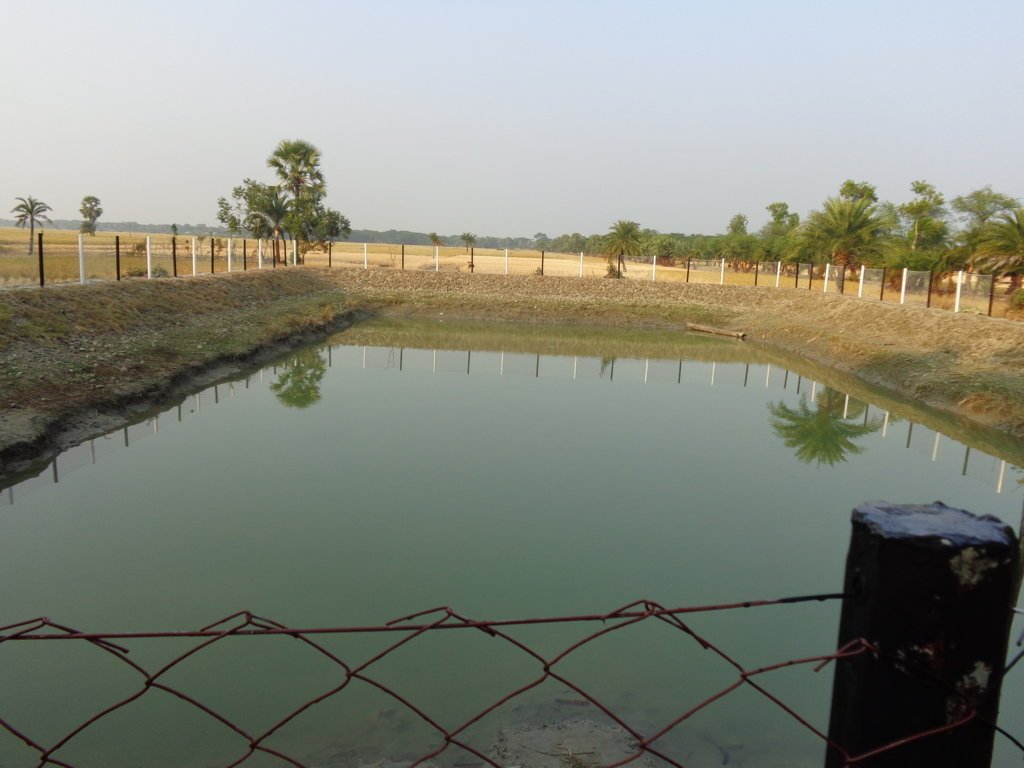
Due to the risk of inland flooding and (seawater) tidal surges from offshore storms, communities build earthen embankments around the ponds to prevent contamination. Local authorities and community members must be involved in the design height of the embankment—which should be equivalent to the highest pre-recorded flood level. In the geo-referenced area (Patharghata) this is equivalent to the tidal surge of Cyclone Sidr (2007). Constructed roadways are often a good reference point. In southern Bangladesh , rural roadways are built to at a ten-year flood return period, so exceeding this height according to the means of the community and/or project is recommended.
Pond embankments are best raised with soil preferably of a clayey nature. The final covering layer must be rich in clay. Embankments should be planted with native grasses and flora that have strong root systems to stabilize slopes and prevent erosion during the rainy season and in cases of tidal surge due to storms. In Bangladesh, the native kolmi (Ipomoea) has proven effective. Community members have also planted crops on the embankments, such as banana trees, medicinal plants and even small garden trenches in the middle of the slope. Beyond structural support, the horticulture helps diversify nutrition and can provide a source of income for maintaining the pond sand filter.
Fences should be installed to prevent animals from entering ponds reserved for drinking water. Community members must guarantee that the ponds selected for PSF construction shall not be used for purposes such as: washing, bathing, fish farming (natural fish however can be allowed), direct cattle access washing and watering. Furthermore:
• Fertilizers and other chemicals shall never be allowed to go into the pond.
• The flow of any polluting materials in the vicinity of the pond shall always be directed away from the pond.
• Latrines, cowsheds, garbage dumps, graveyards, fuel outlets and similar polluting structures shall not be constructed within a distance of 30 meters from the pond.
• Duck or poultry rearing hanging sheds shall never be constructed over the pond.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
บังกลาเทศ
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Patharghata, Barguna district in coastal region
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Baratangra, Ward:4, Union: Patharghata Union Parishad
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม

การใช้ที่ดินแบบผสมผสาน (รวมถึงวนเกษตร)
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology may be applied to selected ponds within a community.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S2: ทำนบ เขื่อนดิน
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Preventing salt water intrusion, the surface water quality and quantity is protected. Turfing and planting the embankment prevents erosion.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ไม่สามารถใช้ได้
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
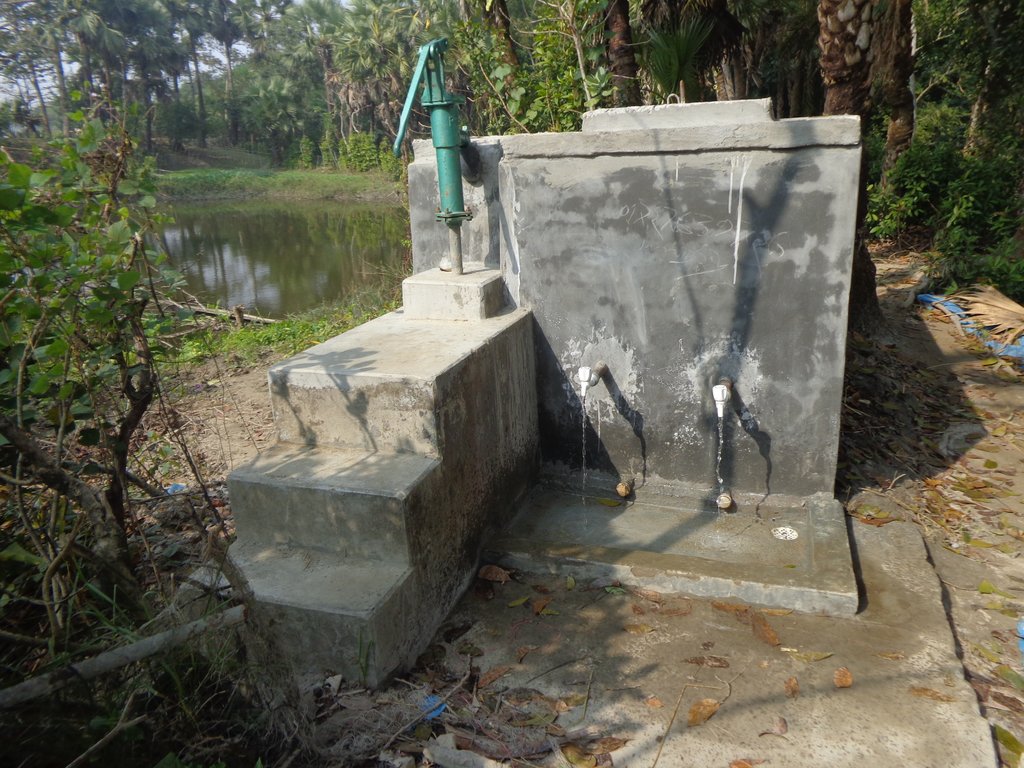
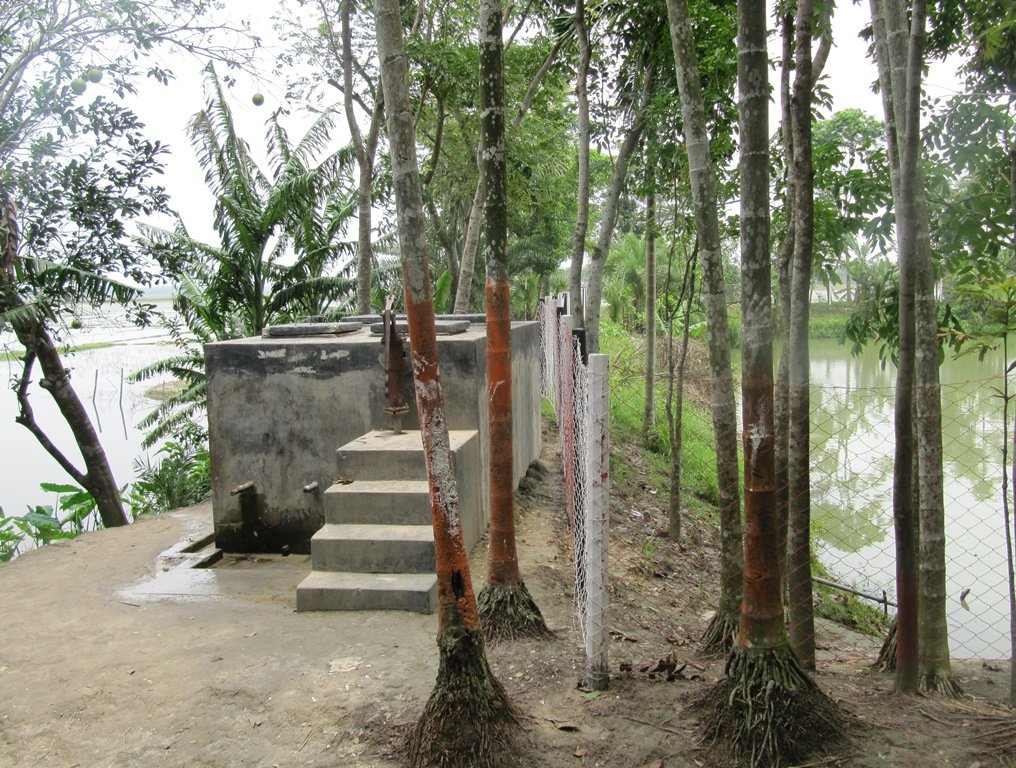
PSF is built on top of the raised embankment as a reinforced concretes structure consisting of a sand filter chamber, filtered water chamber and the sedimentation tank. The height is 4 feet 2 inches; Length-14 feet 5 inches; Width-7 feet. The capacity of PSF is 2500 liters. The construction materials used include include brick, sand, brick chips, cement, galvanized iron pipe, water tap and rebar.
The medium in the filter chamber shall comprise of three layers: 1) filter sand of 2 feet (60 cm) depth placed above 2) a 3” layer of fine gravel and 3) a 3" layer of coarse gravel.
1) The filter sand shall have the following size and grade: (a) Sand grains in the range 0.1 to 1 mm, with (b) effective size ( d10) in the range 0.15 to 0.20; and (c) Uniformity Coefficient ( d60/d10) in the range 1.5 to 2.5. Sieves are used to test sand size and grade.
The "under drainage" bottom gravel layers:
2) Fine gravel: 3” layer ¼” to 1 mm grains (gravel that passes through the ¼” sieve and are retained on 1 mm sieve)
3) Coarse gravel: 3" layer of ½” to ¼” grains (gravel that passes through ½” sieve and are retained on ¼” sieve)
Use different sized sieves made of wire mesh in wooden frame to prepare the media to prepare the two layers of gravel.
Every 5-6 weeks (or when flow rate is limited) cleaning the filter should be performed. Remove the filter aggregate layers, clean the PSF by removing any remaining objects in the three chambers (sand filter chamber, filtered water chamber and the sedimentation tank). Clean these chambers thoroughly using hard brush in necessary. Sequentially clean and replace t the coarse gravel media, then the fine gravel media, and finally the filter sand. For cleaning the gravel and sand place about 1/4th bucket of grave or the sand in plastic bucket (8, 10 or 12 liters, whichever may be convenient), pour about ½ bucket of water and then wash lifting the gravel or the sand from the bottom with hand several times, then decant the water by tilting the bucket. (Only fine particles less than 0.1 mm should be poured out while washing the sand.)
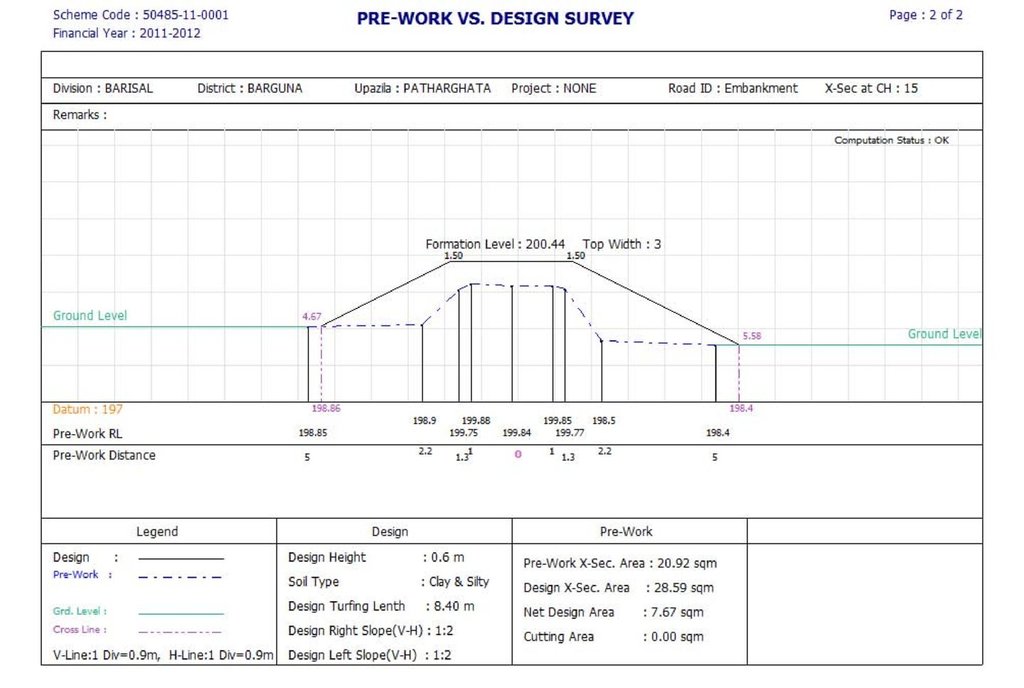
Raised Pond embankments are built with earthworks of clayey soils designed per the maximum flood height. The design depicted in this section is an indication, however the services of a qualified structural/civil engineer will be required. In general building the embankment is raised 0.6m above the maximum flood level is recommended, at a slope of 1:2. From the ground level, the average height of an embankment is two meters, and the average excavation depth is also two meters. All plans for both embankment works and PSF construction were reviewed and approved by the Bangladesh Government Department of Public Health and Engineering.
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อหน่วยเทคโนโลยี
โปรดระบุหน่วย:
Pond Sand Filter with raised earthen embankment
ระบุปริมาตร ความยาว เป็นต้น (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง):
2,500 Litres capacity of filter; embankment average of 100 meter perimeter.
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- ดอลลาร์สหรัฐ
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5 $ per day for labor
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Community consultation for Committee Formation | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rain |
| 2. | Create PSF Users' Committee, agre on user contributions | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rain |
| 3. | Committee / pond selection approved by local Government | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rain |
| 4. | Technical orientation to PSF Committee, input on designs | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rain |
| 5. | Excavation of Pond | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Before onset of rain |
| 6. | Embankment Construction | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rain |
| 7. | PSF Construction | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 8. | Fencing | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | |
| 9. | Turfing and hortiuclutre on the embankment | จัดการพืช | Before onset of rain |
| 10. | PSF Training on Media Selection and maintenance | ด้วยการจัดการ | Regular intervals throughout the year (every 1-2 months) |
| 11. | Pond embankment maintenance | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | Before onset of rain |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In general, the community approach begins with several consultation meetings in the community (inclusive: gender balanced and representative of the diversity makeup of the community) and with municipal authorities. An Outcome Mapping process is initiated to observe signs that a village is prepared and mobilized to receive support for PSF and pond embankment construction. Families must be willing to participate and contribute in the construction and take complete responsibility for operation and routine maintenance.
During the initial phase, a PSF Users’ Committee is formed and approved by the municipal government. Its members make time to participate in trainings on the design, use, maintenance and community organization for managing a PSF. Importantly, the PSF User’s committee must seek public commitments toward the construction costs in cash and/or in kind (labor, construction materials, embankments plants, etc). In Bangladesh this was 10% and usually in kind. Roles and responsibilities of the PSF Users’ Committee:
1) Be responsible for regular operation, maintenance and cleanliness of the pond sand filter;
2) Ensure that the maintenance points for pond water quality is respected per the manual;
3) Advocate for local authorities to conduct regular water quality testing; and to promote household water treatment systems
4) Establish a system of collecting money from users for the regular maintenance;
5) Organize Committee meetings before the start of each season and whenever needed. Similarly if required organize a wider meeting with users in connection with resolving any O&M issues.
6) Care for the tools and other materials that may be purchased for the pond sand filter.
Selection of ponds for PSF construction should be participative with criteria agreed and communicated with the community members and local authorities. The following criteria are suggested based on Terre des hommes’ experience in Bangladesh:
• Ponds that are large enough to retain water throughout the dry season.
• The salinity of the pond water must not exceed 600 ppm at any time of the year.
• While the location of the PSF should be close to a family to ensure its security, it must be as centrally located as possible for ease of access
• Freely accessible to the public; ideally donated for public use.
• Ponds located on higher ground and thus more resistant to flooding / sea water intrusion.
• Space available for raising the embankments around the ponds
• Ponds most accessible to a largest segment of the population during disaster.
• Each PSF should have an effective drainage space and system.
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Pond Excavation and Embankment Raising | Person-days | 180.0 | 5.0 | 900.0 | 10.0 |
| แรงงาน | Pond Fencing Works | Person-days | 20.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Masonry | Person-days | 36.0 | 6.25 | 225.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Repairing tools | Set | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tubewell/handpump | Pieces | 1.0 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 10.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sanitary Fittings | Set | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Bleaching powder for disinfection | kg | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Lime for cleaning | kg | 50.0 | 0.5 | 25.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | ||||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | ||||||
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | bricks | pieces | 6000.0 | 0.075 | 450.0 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | cement | 50 Kilo Bags | 50.0 | 5.75 | 287.5 | 10.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | sand | cubic feet | 52.0 | 0.375 | 19.5 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | mild steel round bar | kg | 210.0 | 0.75 | 157.5 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Materials Transport Cost | Lump Sum | 1.0 | 185.0 | 185.0 | 10.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 2501.5 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
The project requested 10% contribution in kind (materials, transport, labor) from each community. The remaining costs were covered by the project.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The budget is for raising a 100m perimeter length of embankment.
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing | มาตรการอื่น ๆ | Before onset of rains |
| 2. | Cleaning | ด้วยการจัดการ | Before onset of rains |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | two-monthly cleaning of filter materials | Person days | 12.0 | 5.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Seasonal erosion control | Person days | 12.0 | 5.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | bleeching powder | bag | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 130.0 | |||||
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Comparatively, construction materials costs was reflected as the most expensive consideration.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
www.discoverybangladesh.com
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ใช่
ระบุ:
groundwater table is salty along the Bay of Bengal, salt water intrusion. Tidal surge following cyclones also creates soil salinity.
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
บ่อยครั้ง
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ผสม (การเลี้ยงชีพ/ทำการค้า)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- ผู้เยาว์
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Embankments provide a modest space for small scale gardening and fruit/medicinal tree cultivation. Such agriculture activities would be protected from tidal surge waters that destroy agriculture in low-lying areas.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Terre des hommes had raised embankments on ten community ponds prior to cyclone Mahasen (2013). Nine of the ten ponds embankments remained intact, preserving valuable fresh water from sea water contamination for drinking after treatment with PSF.
คุณภาพน้ำดื่ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
>1000 fecal coliform units
หลังจาก SLM:
<10 fecal coliform units
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The PSF water source considerably reduces the risk of infection with enteric pathogens from the pond water. In Terre des hommes’ field experience, although a reduction in presence of fecal coliform (FC) by over 99% is possible, the PSF technology rarely eliminates all FC. A level of 1-10 fecal coliform units (FCU: colonies of E. coli per 100 mL of water) has been achieved, which is equivalent to an intermediate risk, or “probably safe” as defined by WHO. In conjunction with PSF, safe water transport (covered and cleaned containers) and household water treatment systems (chemical or additional filtration devices) are essential.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความเหลื่อมล้ำทางเศรษฐกิจ
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Users reported a decrease in water borne diseases through use of PSF water compared to surface water.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During disaster, the use of the PSF increased, with people walking from further distances to take water from the PSF to their homes.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำขึ้นจากพายุหรือน้ำท่วมชายฝั่ง | ดีมาก |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
PSF serves as disaster resilient Technology that helps residents in coastal villages along the Bay of Bengal to cope with the effects of climate change; such as increased incidence and intensity of storms and salt water intrusion.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 0-10%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| The Technology is useful for supplying drinking water at household level and supports cultivation of fruit trees, medicinal plants and vegetables at the pond embankment, above the flood line. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| The Technology is conducive for ensuring supply of water for drinking, cooking and irrigation purposes if the community is motivated and understands the impact of PSF when faced with water shortage during dry season and other disaster events. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Every five to six weaks, the PSF filter media needs to be maintained, requiring some training, as well organising labor and collecting petty funds for bleaching powder. | The PSF User's Manual has been translated into local language with images and tips for maintenance. This is distributed following the training. The PSF User's Committee must regularly collect user fees for smooth operations. A bank account promotes transparency. Sale of crops harvested on the embankments can help defray costs of maintenance. |
| Although not laborious, the hand pump requires some degree of force, and the taps are often a target of children's play. | Children should be supervised and small children must not be allowed to operate or play near the pump. Investing in sturdy tap systems is essential. |
|
The bio-film will form after seven days of operating the pump. |
Users must boil or treat water very carefully in this period. |
| Private owners could lose interest availing their asset for the communty. For example, they may start using the pond for fish farming in order to sustain their livelihoods. | Formal agreements with the municipality about the usage rules for the pond, and public commitments taken by the pond owners are important. Posting signboards that identify the pond as "Drinking Water Only" and specify forbidden activities is also helpful. Owners can take a higher share of crops cultivated on the embankment. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
Interviews with six informants
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
Compilation from five documents from past projects.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
SSWM University Course Module 6: Disaster Situations: Planning and Preparedness Further Resources: Water Purification Slow Sand Filtration, Marco A. Bruni, Dorothee Spuhler (seecon international gmbh), 2012.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
https://www.sswm.info/sswm-university-course/module-6-disaster-situations-planning-and-preparedness/further-resources-0/slow-sand-filtration
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Pond Sand Filter (PSF) Manual – community operation and maintenance, Laxman Kharal (Terre des hommes), 2012
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Contact: info@tdh.ch
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th Edition, WHO, 2011
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/2011/dwq_guidelines/en/
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล