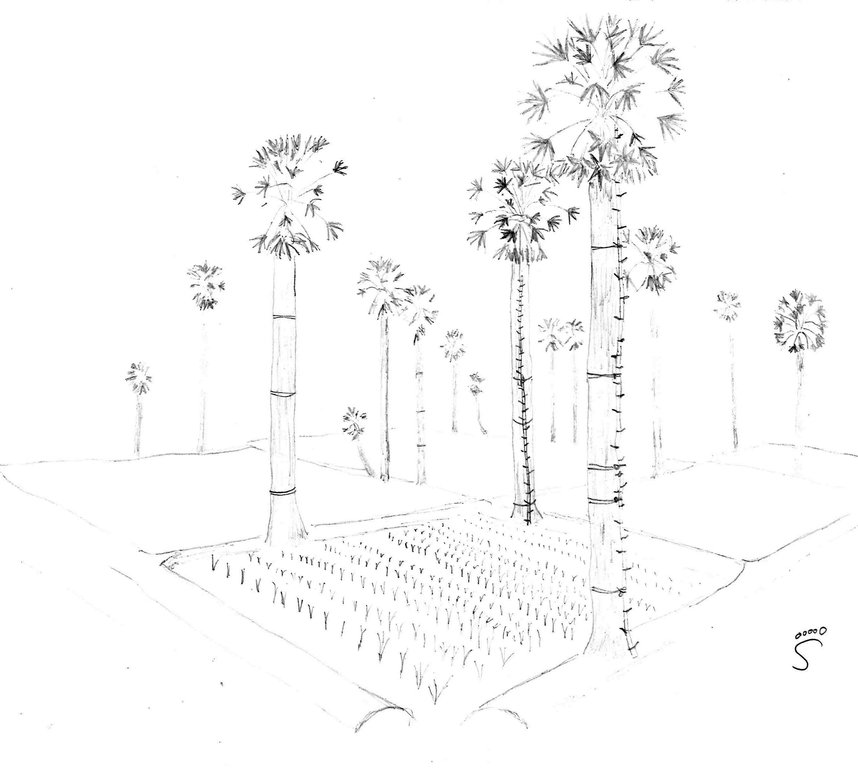
Multipurpose use of sugar palm grown on rice field dykes. [กัมพูชา]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Stefan Graf
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
ការប្រើប្រាស់ដើមតោ្នតដែលដំានៅតាមភ្លឺស្រែ (Khmer)
technologies_1629 - กัมพูชา
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Khun Lean Hak
SOFDEC/LAREC, www.sofdec.com
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
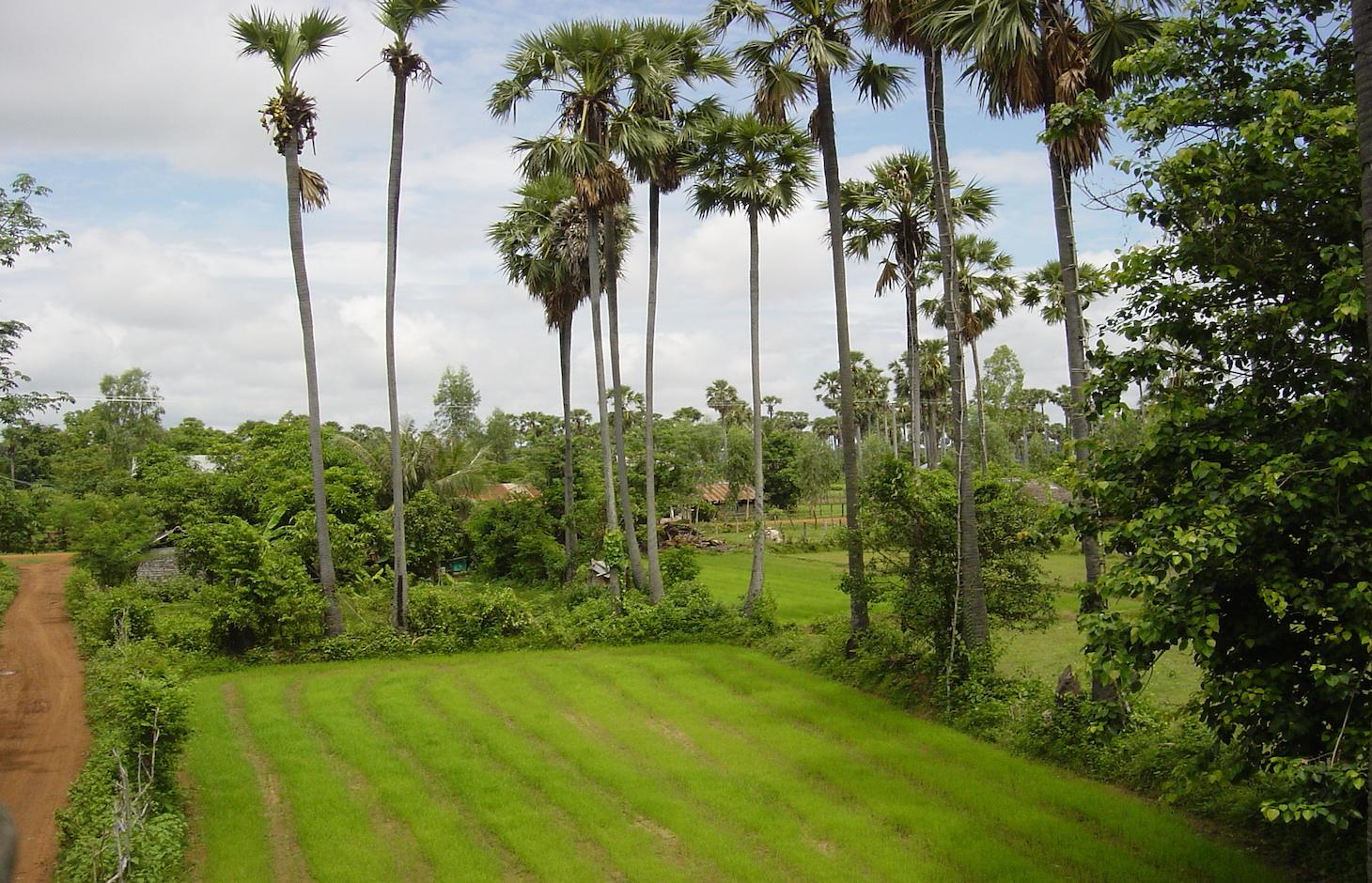
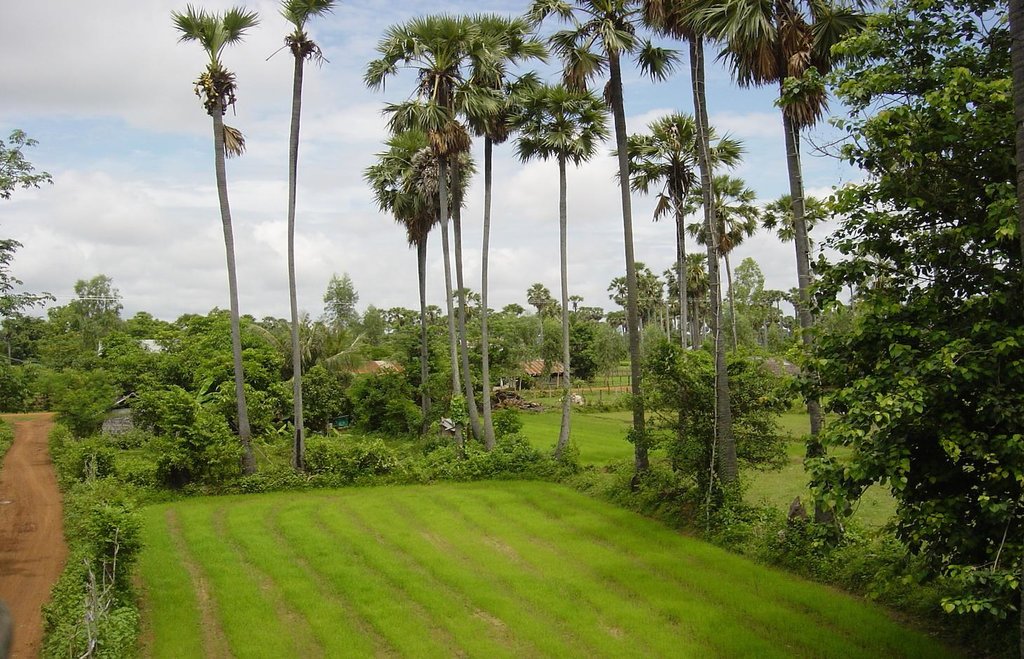
Sugar palms growing on the dykes along the rice fields are used as source of income and have different effects on the growing of the rice, like reducing the wind speed and thus the evaporation and wind erosion.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
The sugar palm (Borassus flabellifer ) is the national tree of Cambodia, it is well adapted to the local natural environment and there is a long tradition to grow sugar palms. Therefore, only a negligible workload is required for both the establishment (fruits falling down from the already existing trees will grow) and the maintenance of the trees. As the sugar palm is resistant to waterlogging and floods (even in flooded areas in the floodplains), and it grows well at low pH, it is planted/grown on the rice field dykes and around the houses. The trees which are growing around the paddy fields have some positive effects on both soil and rice, as they slow down the wind and thus reduce evaporation and wind erosion. They also attract wildlife, and thus allow the establishment of other vegetation. The trees also have a purifying effect on the groundwater, and cycle the nutrients which are otherwise lost in the groundwater. The sugar palms and their products can be used in manifold ways: the leaves for wickerwork and roofs; the stems as fences, for ropes and strings; the fruits as food, fodder and to make straw palatable for cattle; the sap as fodder, to make wine, sugar, and vinegar; and the trunk as construction wood – these are only some of its uses. They reduce the risk of a complete crop failure, as their products are not subject to weather fluctuations.
After the collectivization of land during the civil war (1975-1979), the land and the trees were newly distributed to the people according to the size of the household. The ownership of the land and of the trees was not related. Until today, the trees can be growing on someone’s land, but can be sold or rented to somebody else who harvests its products.
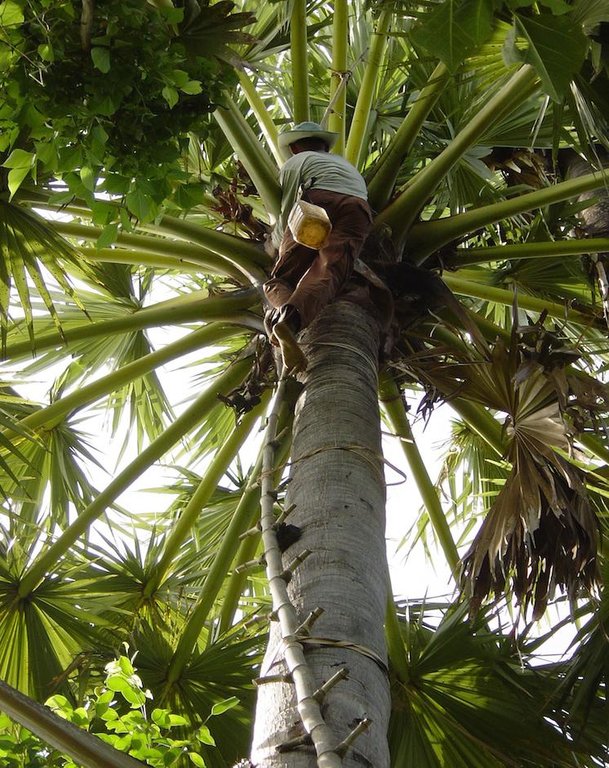
The main reason to plant sugar palms in this area is the sap collection. In order to collect the sap, firstly bamboo ladders are tied to the sugar palm trees. In the dry season, the tapper climbs up the trees to collect the sap. The male or female inflorescence is crushed with a special tool and a piece of it sliced off. Bottles are hanged beneath the cut part, and the sap will flow into these bottles. The crushing and slicing is repeated twice a day, so the amount of collected sap can be optimized. Most of the sap is cooked on a fire and made into syrup, and if there is too much sap, it is fermented and sold as palm wine.
The fruits that fall down on the rice fields are thrown on the dykes, where they grow. The seedlings tolerate some cattle grazing, as long as only the leaves and not the bud are eaten.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate (dry season from November to May and wet season from June to October), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soil has a low fertility, contains little organic matter, and acidifies. The area has been deforested a long time ago, and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season). Due to climate change, farmers notice more erratic rainfalls, temperature rises and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities).
The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge which different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
กัมพูชา
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Kampong Chhnang
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Rolear Bier / Thnorng Kombot
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 10-100 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
This technology is applied in most parts of Cambodia. Almost everywhere there are some sugar palms growing along the rice fields, but not in this density. The area mentioned is the area in the district where the technology is applied.
2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It is a traditional tree in Cambodia, with historical use. Its introduction on the rice field dykes is unknown.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
- rice
- sugar palm
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June-December
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of organic matter, lack of water retention in soil, irregularity of rainfall, low soil fertility (sandy soil), monocultures, bare soil during dry season, ploughing, wind erosion and dust storms.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil fertility is low, rainfall is not secured in the beginning of the rainy season.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปลูกป่าร่วมกับพืช
- แนวกันลมหรือแนวต้านลม
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing of the soil. Depending on the rainfall, sometimes the land is left bare for several days or weeks.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Mainly rice is grown in monocultures.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Straw is usually removed from the fields.), labour availability (Labour availability is low due to high migration rates (garment industry, drift to the cities, working abroad).)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (More hot days, the soil dries out faster.), droughts, education, access to knowledge and support services (Little knowledge about soil conservation.), war and conflicts (During the Khmer Rouge regime, a lot of agricultural knowledge got lost.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Sugar palms (Borassus flabellifer) with bamboo ladders growing on the dikes around the rice fields.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (They grow almost by themselves, as the fallen fruits are just thrown on the dykes as only management.)
Main technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 63
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mostly naturally regenerated, but seeds are thrown on the dykes when they fall into the rice fields.
ผู้เขียน:
Stefan Graf, Switzerland
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Build a stove and buy pans to cook the sap into sugar. |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 35.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 35.0 | |||||
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tie the bamboo ladders to the tree | |
| 2. | Collect the sap by pressing the inflorescence, cutting a slice off and putting a bottle underneath. | December-April, twice a day |
| 3. | Cook the sap to make sugar | Once or twice a day |
| 4. | Ferment the juice to make palm wine | If there's too much juice. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 3221.0 | 3221.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Firewood | ha | 1.0 | 357.0 | 357.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Bamboo and rattan | ha | 1.0 | 471.0 | 471.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4049.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 4049.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: Self-made crusher to induce a higher sap flow.
The costs were calculated with 44 trees (one unit), transformed into 62 trees per ha. The assessed farmer owns 0.35 ha of rice fields, with 22 trees on the dykes, but he bought additional trees on nearby dykes. The whole family is involved in the process.
The maintenance costs indicated above are that high because labour was calculated for each step. However, a big part of the work is done voluntarly by local land users and are not payed.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The factors affecting the costs are mainly the inputs (firewood, work to cook the sap to sugar) used to transform the sap into saleable products. They are not necessary to benefit from the positive effects of sugar palms on the microclimate and soil. To implement sugar palms on the rice field dikes the costs are negligible.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27-35°C
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
<5 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ไม่ดีหรือไม่มีเลย
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: during dry season
Availability of surface water: during dry season
Drinking water: People use it for drinking after filtering or boiling.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Handicraft, remittances, and factory work.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
- รายบุคคล ไม่ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Land users have a title that is not recognized by the state. The trees sold by farmers to neighbours have a paper signed by the village chief to certify the ownership.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Leaves fall on the fields, but if they are removed the adverse effect is negligible.
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Old trees are logged and used as firewood or construction material.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sugar palms can grow in adverse conditions.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trees on the dykes might hinder the use of machines on the fields.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Trees have a purifying effect on the water.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The products of the sugar palms are sold on the market, whereas rice is only grown for sustenance.
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The products of the sugar palms are sold on the market, whereas rice is only grown for sustenance.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Harvesting and processing of sap is strenuous and time consuming, especially during dry season.
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ด้านสุขภาพ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Cheap alcohol, diabetes
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Aesthetic value.
contribution to human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The products of the sugar palms generate income to the land user and his family (rice is only used for home consumption), and they are more resilient to erratic rainfall patterns.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The roots reach the ground water table, and have a difficult to quantify effect on it.
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Evaporation is tackled due to the decrease of wind speed.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Evaporation is tackled due to the decrease of wind speed.
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Nutrients below the root level of annuals are picked up and reintroduced in the nutrient cycle.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The region is prone to monocultures (rice), however in this region there are a lot of sugar palms and other tree species. Sugar palms protect the other plants, attract birds (dissemination of seeds) and have therefore a positive impact on biodiversity.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Sugar palms as habitat for different animals (bats, birds, etc.)
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ความเร็วของลม
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Purifying effects of trees.
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Reduction of wind velocity.
Deforestation
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Firewood is used as the main source of energy. The land user buys the wood.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Since it is a traditional technology, the initial costs cannot be estimated.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
100% or 7 land user families
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The growing of sugar palms and its use for economic activities is a traditional technology.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
7 farmers produce sugar, however sugar palms are widely spread in this area. This is the reason why estimations are difficult to make.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Many different uses of sugar palms, both for selling on the market and for home consumption (leaves, construction wood, fibre, sugar, wine, fruits, and vinegar). |
| Sugar palms protect the rice from the wind. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| They slow down the wind, thus reduce evaporation, crop destruction and wind erosion. |
| Sugar palms are tolerant plants growing in adverse conditions like water logging, floods and droughts; they don’t need any care like fertilizer or pesticides. They produce anyway their useful products (Sap, leaves, stems) which can be transformed in many different ways (Sugar, wine, vinegar, house coverings, handicraft…) |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Fallen palm leaves can hinder the rice growth on the fields. | Check the fields regularly and remove the fallen leaves. |
| Old trees can fall in storms and destroy a part of the crop. | Remove the oldest trees. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Collecting sap is dangerous, especially when there is wind. | Use safety devices. |
| To make sugar, firewood is used, which induces deforestation. | As energy is needed in the dry season, solar energy could be used to boil the sap, with parabolic mirror cookers for example. |
| Plants producing a lot of sap are tapped more, thus produce no fruit, so no offspring. Only plants producing less sap will reproduce. | Select good producing trees and plant the selected seeds. |
| Because of the trees, mechanized farm operations on the rice fields are hindered. | Plant the trees in rows perpendicular to main wind, or long curved rice fields. |
| Only syrup can be made on farm, which is sold at a low price. | Organize in cooperatives to make sugar, which could get a better price. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
10/07/2014
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Borin, K. 1998. Sugar Palm (Borassus flabellifer): Potential feed source for livestock in small-scale farming systems. WAR 91
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/docrep/w9980t/w9980T04.htm#TopOfPage (free)
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Feedipedia Sugar Palm (Borassus flabellifer)
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.feedipedia.org/node/178
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Johnson, D.V. 2010. Tropical Palms. FAO.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
http://www.fao.org/docrep/012/i1590e/i1590e.pdf
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล