Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China [จีน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Christian Rumbaur
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
膜下滴灌 (Chinese)
technologies_1305 - จีน
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 4 เมษายน 2018 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 13 มีนาคม 2019 (public)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Müller Joachim
University of Hohenheim
เยอรมนี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Zia-Kahn Shamaila
University of Hohenheim
เยอรมนี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Universität Hohenheim - เยอรมนี1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Drip irrigation under plastic mulch, associated with drainage, to reduce water demand and improve cotton yields in Xinjiang Province, China.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
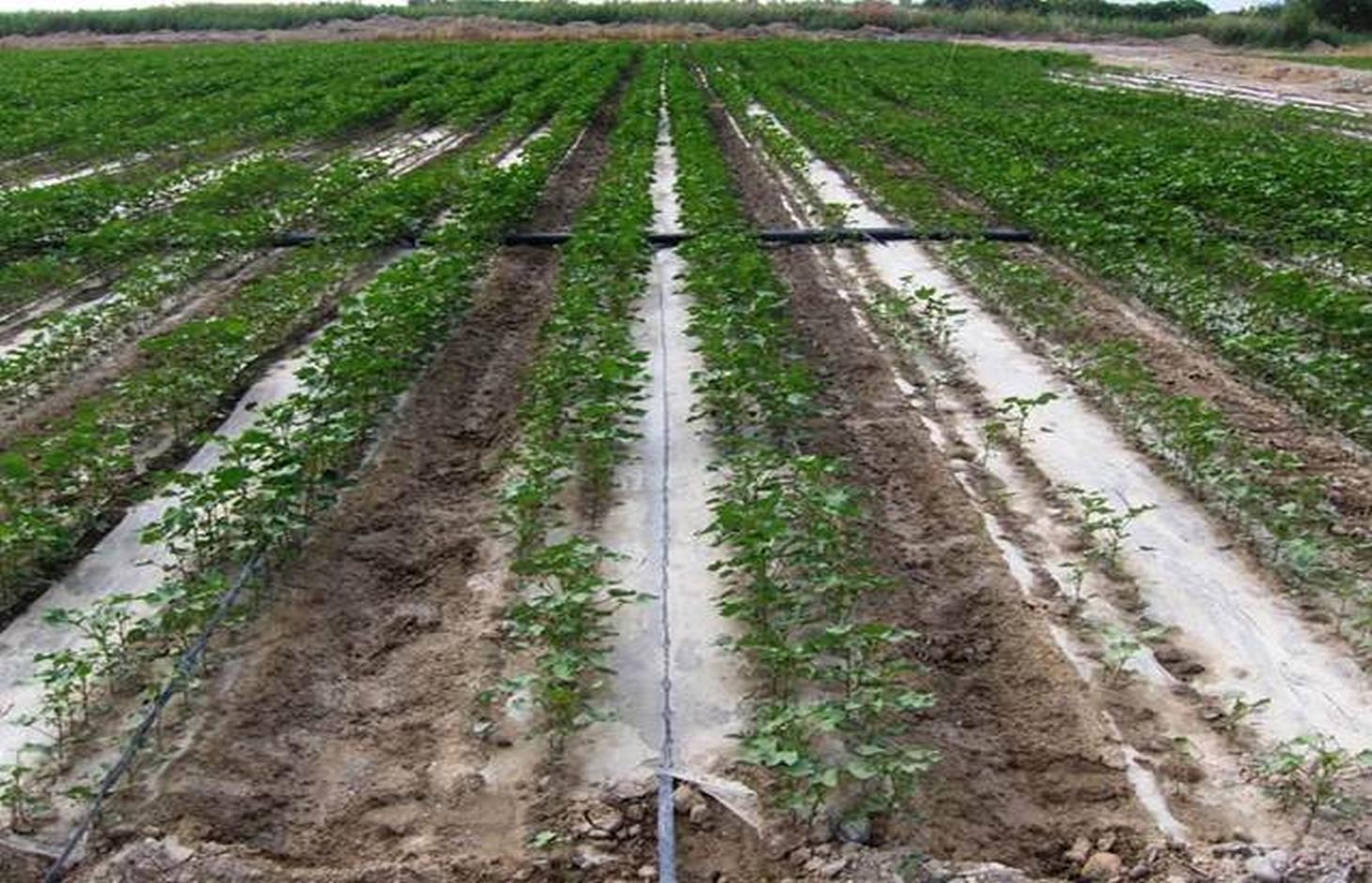
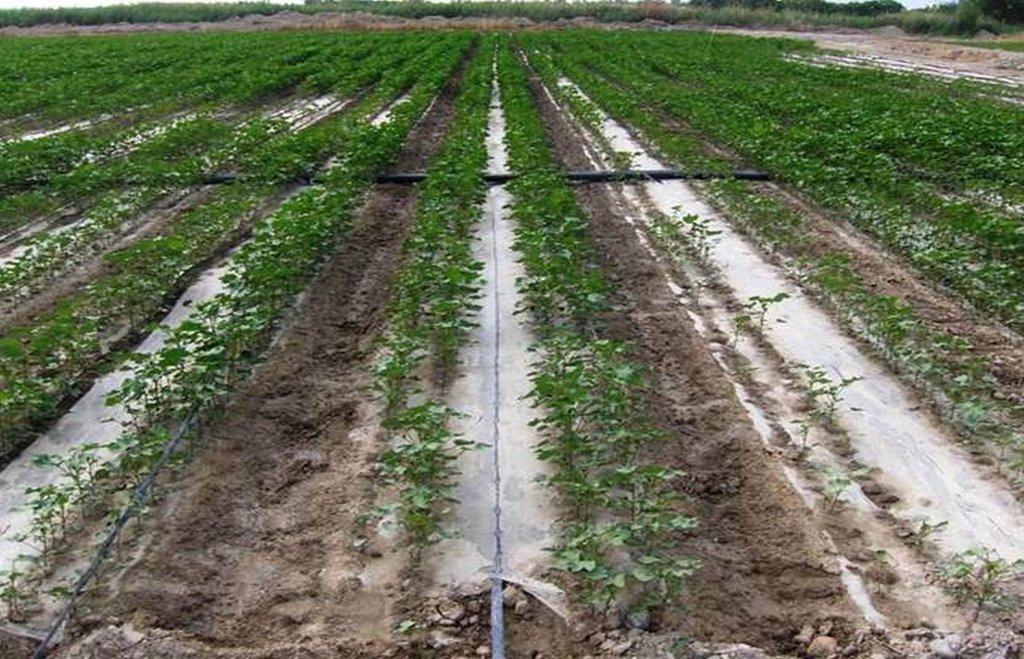
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
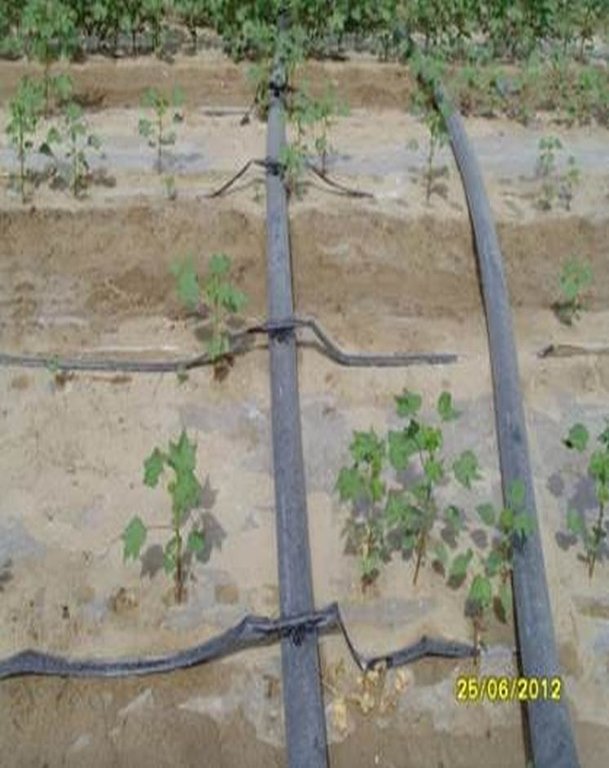
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
จีน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
China / Xinjiang Province
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Tarim River Basin
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- > 10,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
It might be used also in other provinces. But this not known to the author.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
It is not clear how the technology was invented.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fibre crops - cotton
- wheat
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- fruits, other
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
major cash crop: cotton
major food crop: wheat
other: fruit trees
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water use conflicts between agriculture and natural vegetation, soil salinization, desertification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization and water shortage.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: water availability, evaporation
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- การชลประทานแบบเต็มรูปแบบ
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การผันน้ำและการระบายน้ำ
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M4: การเปลี่ยนแปลงช่วงเวลาให้เหมาะแก่การทำกิจกรรม
- M6: การจัดการของเสีย (การทำ รีไซเคิล การเอากลับมาใช้ใหม่หรือการลดปริมาณ)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pw (Waterlogging): ภาวะชุ่มน้ำ

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pw: waterlogging
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage - Increase of groundwater - salinization of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (cotton monoculture), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation to gain new arable land), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), wind storms / dust storms (Dust storms, blow out of top soil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (Doubling of population during the last thirty years.), land tenure (Land belongs to the state), poverty / wealth (Family farmers are poorer than city dwellers), education, access to knowledge and support services (Poorer farmers have less access to extension services.)
Secondary causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining (There is oil production in the region, but it was not studied), discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (use of surface and ground water for large scale irrigation), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests))
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
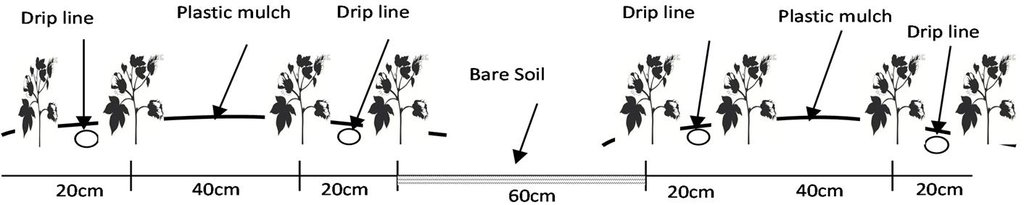
There are double rows of cotton 20 cm apart, with a drip line between. 40 cm then separates each double row. Two double rows are covered by one length of plastic mulch. There is a small strip of bare soil between each length of plastic mulch. Mulch covers around 80% of the soil surface.
Location: Korla City. Xinjiang Province / China
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For the easy and fast installation a tractor is needed)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), increase of water use efficiency
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: transparent plastic (Polyethylene), thickness: 0.08 mm
Quantity/ density: 7100 m/ha
Remarks: 1.4 m width in lines with spacing of 20 cm between lines
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Change from flood irrigation to drip irrigation
Major change in timing of activities: Plastic mulch enables early sowing of cotton
ผู้เขียน:
Shamaila Zia-Khan
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
1
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor | |
| 2. | Drip line installation, plastic mulch and seeding tool | At sowing |
| 3. | Making holes for the (cotton) plants in the plastic mulch.Maintaining hoses | After emerging |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Drip line installation | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tractor | Piece | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | seeds | kg | 30.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Plastic mulch | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 50.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Black dripe lines | Set | 1.0 | 380.0 | 380.0 | 50.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 5510.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 5510.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.33 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing and leveling of field. | Before sowing |
| 2. | Irrigation | |
| 3. | Removal of the drip lines and the plastic mulch |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Collecting mulch | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 98.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Irrigation and flooding water | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 13.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 13.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with installation tool for the drip irrigation under plastic mulch, other tools: hoe
The costs for the machine, the plastic hoses and the plastic mulch are calculated above are for 1 ha and were calculated on the basis of 2013 (subsequently costs have risen). Water price: 0.019 CNY/m3. Farmers need 3000 m3 per ha.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
90 mm per year. Jan, Feb, Apr and May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5 mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- แห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone: altitudes of 800 to 1300 meters
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium high
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: also < 5 m and the installation of drip irrigation under plastic mulch should be installed with a drainage system. If the groundwater table is too high salinisation of the soil will be the result
Availability of surface water: For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch mostly surface water is used. It is diverted by channels to the agricultural fields. There must be a good water availability at the fields.
Water quality (untreated): For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch the water quality must be quite high, otherwise the small holes of the drip lines will be blocked soon.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- รวย
- รวยมาก
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the earth works in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land (income from large fields of cash crops).
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have not implemented the drip irrigation under plastic mulch also generate off-farm income.
Manual labour: harvesting
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
5-15 ha: state farms
< 0.5 ha: family farmers
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
15% of more cotton yield
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ความต้องการน้ำจากการชลประทาน
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
สถานการณ์ของกลุ่มด้อยโอกาส ทางด้านสังคมและเศรษฐกิจ
Livelihoods and human well-being
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
การระเหย
ดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความเค็ม
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
salinization below root zone
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| พายุลมประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมตามปกติ (แม่น้ำ) | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
No number on households
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The government gives subsidies to the farmers who are installing the drip irrigation under plastic mulch.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government want to spread the technology in the whole region by giving subsidies to the farmers.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
|
helps to save water thus saves costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is subsidies by the government. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
It helps to save water during the vegetation period and thus helps to reduce the conflicts between the upstream and downstream farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology (drip + mulch) needs to be supplemented by installing a drainage system in the fields otherwise there will be a build-up of salinity and farmers will abandon land and move on. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Salinization of the soils is increasing The consequence is that the fields are flooded after harvest in November/December to leach out the salt. The water used for drip irrigation plus the water to flush the salts to lower soil layers add up to almost the same amount as if farmers were using the original flood irrigation technology. | drainage system in the fields required. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Zia-Khan,S., Spreer, W., et al. Effect of dust deposition on stomatal conductance and leaf temperature of cotton in Northwest China.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Water 2015, 7, 116-131; doi: 10.3390/w7010116. www.mdpi.com/journal/water open access.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล