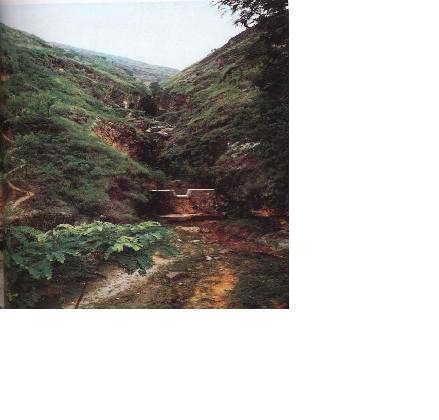
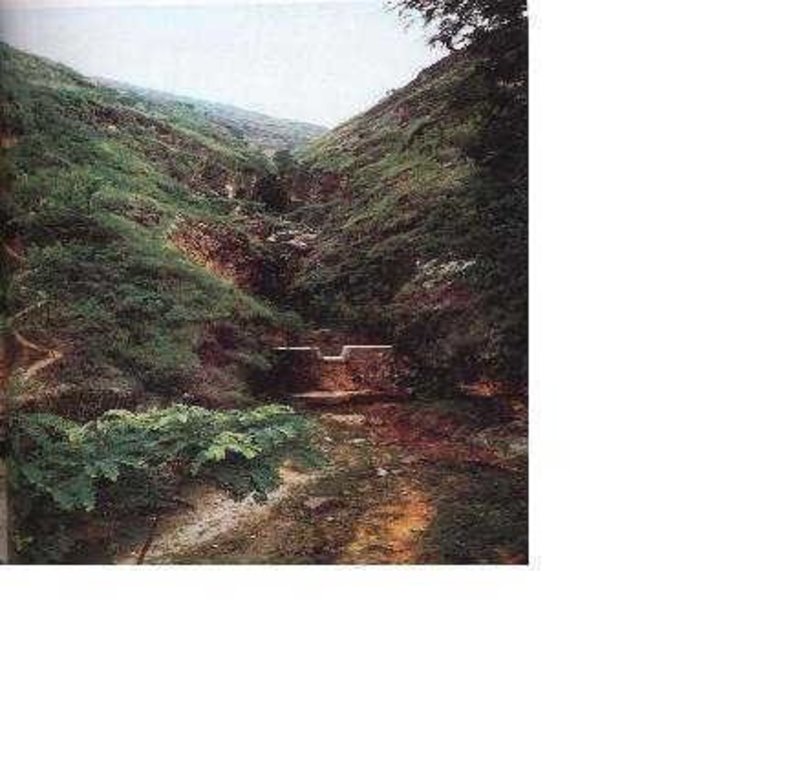
Check Dam [จีน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Haiyan WEI
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Lan Sha Ba
technologies_1365 - จีน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)
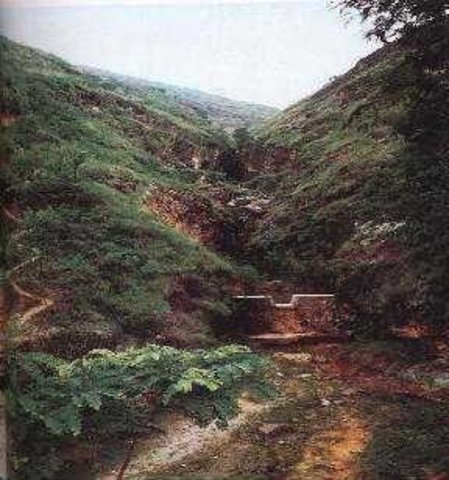

Check Dam [จีน]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Haiyan WEI
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
Check dams are built in the gully systems to harvest water and sediment. Usually many check dams are built in a gully or waterway to control the gully erosion. Check dams can be classified into "masonry dam", "check dam of earth", "check dam with willow" according to materials. Some strong masonry can last more than 10 years. As willow pegs in the "check dam with willow" can grow into timber after years.
Maintenance work should be done before rainy seasons every year so as to prevent the dam from destruction.
Following are the building procedures:
Masonry dam & check dam using earth:
1. Preparation---Removing grass, roots and surface soil; Digging a channel along an axis of a check dam in order to combine the dam and the bed firmly.
2. Construction---If a dam is planned to be made of earth, do scarification first, then adding earth (about 0.3m thick) and ramming it into 0.2m layer by layer. Building the dam with stones and/or rocks.
3. Base---If a bed of a gully consists of earth or sand, "base" should be built at the downstream feet of the dam. Length of the base should be twice as that of the dam and thickness should be 50-70cm.
4. Building a spillway at the top of the dam.
Check dam with willow:
1. Removing grass, roots and surface soil.
2. Cutting branches from willow; chopping the branches into pegs with the thick ends wedge.
3. Inserting the pegs into the ground.
4. Entwining wattles from willows around the pegs compactly.
5. Filling the space between two rows of pegs with stones, bricks, treetops etc. Making the stuff surface 10cm lower than the pegtop.
6. Combining the dam into a whole with iron chains.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
จีน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Shanxi, Beijing
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, specify area covered (in km2):
145.0
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 100-1,000 ตร.กม.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 145 km2.
As a traditional SWC technology, check dams have been used widely in China.
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Experiences from the local people's many SWC practice.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- cereals - wheat (winter)
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์

ทางน้ำ แหล่งน้ำ พื้นที่ชุ่มน้ำ
- บ่อน้ำ เขื่อน
ผลิตภัณฑ์หลักหรือบริการ:
Check Dam
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious gully erosion by water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies were widened and deepened greatly in the rainy season and crop land area is decreasing above the gully edges.
Constraints of urban land use
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการน้ำผิวดิน (น้ำพุ แม่น้ำทะเลสาบ ทะเล)
- reduce loss of cropland
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wg (Gully erosion): การกัดกร่อนแบบร่องธารหรือการทำให้เกิดร่องน้ำเซาะ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Description of Building Check Dam Procedures
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shanxi, Beijing
Date: 2000
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (earth): Loessial earth
Construction material (stone): if available
Construction material (wood): willow pegs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 16%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 90%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:30
ผู้เขียน:
LIU Baoyuan, Beijing China
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
RMB Yuan
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.27
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
2.00
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | |
| 2. | Construction | Before rainy season |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | reparing after rainstorm. |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Length, width and height of check dams.
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Sizes and materials of the check dams.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
580.00
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณแอ่งบนที่ราบ (concave situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Slopes on average also gentle, moderate and rolling
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (No difference).
Off-farm income specification: The land users who made the check dams can own more "deposited land". Generally these deposited land is fertile and produces high yield.
Level of mechanization: animal traction: on steep slope
Level of mechanization: mechanized/motorized: plateau or gully flat.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
48
หลังจาก SLM:
30
ดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
180
หลังจาก SLM:
110
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- > 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
180 household are using the technology and represent 65 percent of the poeple living in the stated area
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 11-50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In the past (planning economy)SWC activities are administrative action to call local land users to carry out, but nowadays in the market economic conditions, if no or little benefits obtained, land users would not like to do any more.
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing.. 2000.3.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1990.6.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region, Shanxi Province. 1986-2000.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1986.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Check Dam [จีน]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Haiyan WEI
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล